What kind of pathology is this
It is known that the brain is covered with dura, arachnoid (arachnoid) and soft membranes.
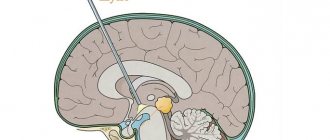
The septum pellucidum separates the anterior part of the brain from the corpus callosum. It includes 2 plates consisting of brain tissue. Between them there is a slit-like cavity. Its shape is comparable to a square filled with liquor. The formation of the septum occurs in the initial stages of intrauterine development. The distance between the plates determines the gestational age. Therefore, signs of congenital abnormalities can be noticed already during this period.
Due to excessive concentration of cerebrospinal fluid, a cystic neoplasm can form between the plates. Doctors assure that the appearance of such growths does not affect human health. But the whole point is the size of the cyst: the rapidly growing formation begins to put pressure on adjacent tissues and vessels, which contributes to a rapid increase in intracranial pressure.
Primary (or congenital) Verge's cyst can be combined with other pathological conditions:
- Malformations. The cause of this type of disorder is the choroid plexus of veins and arteries in the nervous system.
- Arnold-Chiari malformation, in which the cerebellar tonsils descend and compress the medulla oblongata.
- Neuronal heterotopia, characterized by impaired movement of nerve cells.
- Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. There is a decrease in the content of axons in the structure of the affected nerve fibers.
The following pathologies are most often detected by ultrasound of the brain:
- an enlarged ventricular cavity indicates the presence of rickets and hydrocephalus. With hydrocephalus, the baby has an unusually large head and swelling of the fontanel;
- dilation of the lateral ventricles occurs as a result of a large amount of fluid. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in premature babies;
- septal cyst, represented by a cavity with fluid. It usually disappears after some time. If pathology is detected in a newborn, then this condition does not require treatment. If the disease occurs after an injury, then it is necessary to begin prompt therapy.
Why does it happen?
The following factors can provoke the development of a Verge cyst:
- head injuries;
- inflamed meninges;
- infectious diseases, especially meningococcal damage;
- head injuries with brain damage and short-term acute impairment of its functions;
- cerebral hemorrhages.
If we talk about the congenital form of pathology, then doctors tend to classify it as developmental abnormalities that are not life-threatening and are provoked in most cases by intrauterine infections, at the same time they can be combined with other pathologies:
- disruption of the mechanism of movement or absorption of cerebrospinal fluid;
- reduction in the number of axons in the optic nerve;
- pathological connections between veins and arteries;
- arachnoid cyst formation;
- Chiari malformation, in which the lymphoid tissues of the cerebellum compress the medulla oblongata;
- atypical localization of neurons, in which the migration of nerve cells in the cerebral cortex occurs with disturbances.
The cause of the congenital form of pathology is considered not only to be abnormal development of the embryo and infection, but also to injuries received by the fetus during development inside the mother's womb, as well as premature birth.
Anomaly of the septum pellucidum of the brain
The human brain is the most complex organ, not fully studied, consisting of a large number of neurons and sections interconnected with each other. Pathological features and disruptions in the functioning of one part lead to procedural changes in other parts.
The slit-like cavity is localized between two thin plates of brain tissue. The fissure cavity serves as the space between the plexus of nerve fibers and the forebrain. A healthy person has a square-shaped cavity containing cerebrospinal fluid.
The wall is formed in the first trimester of pregnancy. Ultrasound diagnostics monitors the gap parameters between the sheets in proportion to the weeks of pregnancy.
Causes and mechanism of formation
A capsule with liquid inside can be congenital or acquired.
Congenital form of Verga's cyst:
- diagnosed in young children in 60% of cases, and in cases of prematurity in almost all;
- in this case, it is almost always asymptomatic and is often diagnosed accidentally;
- usually does not require treatment and is eliminated in 75% on its own;
- The cause of the cavity is pathology of fetal development, intrauterine infection and injury.
Acquired form of cyst:
- occurs during life due to head injuries, concussions, cerebral hemorrhages, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the central nervous system;
- this form can develop to large sizes, thereby causing health complications;
- To avoid worsening the situation, the acquired form must be systematically observed and treated.
Clinical picture
If it grows uncontrollably, a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain can cause the following unpleasant symptoms:
- Attacks of aching cephalgia that are not relieved by analgesics.
- Feeling of squeezing, bursting, squeezing of the head.
- Deterioration of visual acuity, hearing problems.
- Ear noise on one or both sides.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Trembling and numbness of the limbs.
Symptoms caused by the growth of a cyst depend on its location and size. Compression of neighboring organs can lead to their destruction and serious consequences. If the victim has the above symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Timely and adequate treatment will help to avoid complications associated with the growth of the cyst and prevent the development of a cancerous tumor.
Changing parameters, the growing Verge's cavity puts pressure on the vascular part of the brain, epithelial tissue - the patient feels pathological symptoms:
- periodic feelings of squeezing headache;
- deterioration in the functioning of the organs of touch and hearing;
- the ability to perceive sounds without an external auditory stimulus - noise, ringing in the ears;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- rhythmic, rapid contractions of the muscles of the trunk and limbs;
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
Having identified an acquired anomaly, constant medical examinations, timely appropriate therapy, and surgery are important.
Symptoms
A small neoplasm in most cases does not show itself at all; the symptoms of the pathology become more noticeable as the cyst increases in size. In this case, the following symptoms may occur:
- there is severe pain in the head, which is not eliminated with the help of conventional analgesics;
- visual acuity decreases, the patient hears poorly;
- dizziness and noise in the ears;
- pressure inside the head increases;
- limbs go numb and tremors appear;
- there is a feeling of constriction in the head in the area where the formation is located;
- arterial hypertension develops;
- Memorization ability deteriorates.
These symptoms are characteristic of acquired formations, and congenital cysts in 75% of cases are asymptomatic and resolve on their own.
What are Verge's cysts?
The consequences of growth in the transparent septum of the brain largely depend on its nature and size. If a cyst appears and grows very quickly, the patient develops chronic increased intracranial pressure. He often loses consciousness, due to a lack of oxygen supply to the brain, many body functions are disrupted, convulsive seizures occur, vision deteriorates greatly, hearing deteriorates, and motor functions suffer.
The acquired anomaly leads to circulatory disorders and dropsy of the brain. A malignant tumor can be fatal.
The most dangerous consequences of the disease include:
- Atrophy of brain tissue caused by compression of the meninges and the formation of adhesions that interfere with normal blood circulation. In advanced cases, the pathological process leads to loss of performance.
- Dropsy of the brain. As the cyst grows, it impedes the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to impaired drainage of fluid from the brain cavity. The disease negatively affects the activity of all vital organs and systems.
- Stroke. The Verge cyst itself does not cause pathological processes in the vessels, but often provokes a violation of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid and blood. And its constant growth threatens rupture of arteries and massive internal bleeding.
The normal size of a Verge cyst is calculated individually in each case. Experts believe that if the pathology does not grow and does not in any way affect the functioning of parts of the brain, then there is no need for specific treatment of the patient.
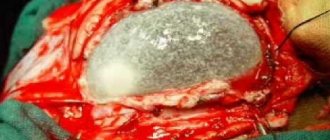
Verge's cavity is a benign neoplasm, similar to a capsule, with dense walls. The cavity formation is filled with liquid exudate, reminiscent of the composition and properties of cerebrospinal fluid. The walls of a Verge cyst are based on cells of the arachnoid meninges. The anomaly is not considered a pathology; in the early stages of the disease, the disease does not threaten the life, health, or brain functions of a person.
The location of the cyst plays an important role:
- the cystoma is localized in the anterior part of the IVS;
- the cyst is located between the plexus of nerve fibers in the brain and the “small brain”
Cystic anomaly refers to arachnoid pathologies in the area of the main organ of the central nervous system. Men suffer from the disease more often than women.
The factors that provoke the appearance of Verge's cavity are different.
A septum pellucida cyst is formed by a lack of circulation. Liquor accumulates due to lack of circulation, some areas are isolated, one area grows under the pressure of accumulated liquorrhea.
Abnormal etiological varieties:
- Primary - benign asymptomatic formations that appear in the early stages of fetal development, resolve on their own, are diagnosed in 60% of newborns. If a woman did not carry the baby to term, the probability of an anomaly is 100%. Magnetic resonance imaging “sees” a neoplasm with clear edges and uniform contents;
- Secondary - acquired as a result of traumatic brain injuries, inflammation, infections, bleeding. Negative consequences of acquired cystic formations: lack of monitoring of the tumor, compression of the brain region
At an early stage of the disease, the cyst does not cause discomfort to a person. The disease is diagnosed by chance, after a complete examination of the brain. In the absence of symptoms, doctors do not consider the anomaly a disease. A progressing cyst must be monitored by regularly visiting a neurologist to clarify the development and growth of the tumor.
Content
Hello! I am 29 years old, my first pregnancy proceeded without complications, now I am 35 weeks 5 days pregnant. 1). At 32 weeks 5 days, a fetal ultrasound (hitachi avius) was performed: no late-onset malformations were detected. 2). At 35 weeks, an ultrasound of the fetus (Toshiba aplio 500) was performed: according to fetometry, uterine pregnancy was 34 4, more evidence for an enlarged Verge's cavity, a consultation at a genetic center was recommended to exclude congenital malformation of the central nervous system.
— Bipariental head size — 87 mm — Fronto-occipital head size — 109 mm — Head circumference — 315 mm — The lateral ventricles of the brain are not expanded, the cerebellum is without features. — The cistern magna is not dilated, the PPP is 6.3 mm, the PPP is connected to an echo-negative formation 11*14 mm with thin walls. 3).
Doctors claim that the formation found in the child’s brain is a normal variant, but they still send him for an MRI examination. Considering the queue for appointments, I will only get an MRI at the 38th week of pregnancy. There is claustrophobia. How necessary is it to perform an MRI of the brain of a fetus with our diagnosis, given the long gestational age? Will it be enough to have a scheduled follow-up with a neurologist and undergo neurosonography after the birth of the child?
Definition
An arachnoid cyst is a cerebrospinal fluid cyst, the walls of which are formed by the arachnoid membrane. Arachnoid cysts are located between the surface of the brain and the arachnoid (arachnoid) membrane.
Goals and methods of therapy
The goal of treatment is:
- normalization of cerebrospinal fluid circulation;
- monitoring the state of education;
- restoration of cerebral circulation.
When a cyst of the septum pellucidum of the brain is diagnosed, treatment usually involves the use of the following techniques:
- Observation - if the formation does not cause discomfort and does not worsen the patient’s well-being, the specialist recommends monitoring the condition of the cavity twice a year using MRI or CT, and if the course is favorable, treatment is not required.
- Conservative treatment - if the Verge's cavity begins to enlarge, drug treatment is used: osmotic diuretics, nootropic drugs, drugs to improve blood circulation and fluid outflow are used to reduce intracranial pressure. Also, during therapy, drugs are used to eliminate the cause of the formation, and an active fight is carried out against the disease that caused the problem.
- Surgery is practiced when conservative therapy does not help. The essence of the operation is to drain the walls of the cyst using a special probe, which is inserted into the ventricle. Through the holes made, the fluid flows into the cavity of the ventricles of the brain and the size of the formation decreases. This operation is 80% effective, but sometimes fluid accumulates again due to the closure of the walls and closing of the gaps. A relapse leads to a repeat operation - bypass surgery; a hole is made in the skull bone to insert a special drainage tube into the formed body; it will no longer allow substance to accumulate and close the lumen. The disadvantage of this operation is the possibility of infection.
Surgical intervention gives results only with a single-chamber formation; if the Vergi cyst has several sections or very dense walls, then relapse is inevitable.
Operation
This technique is used when conservative medicine has failed. During the operation, the cystic walls are drained using a special probe, which is inserted into the ventricle. Through the punctures made by the probe, fluid flows into the space of the cerebral ventricles, and the volume of the cystic capsule decreases.
During a repeat operation, a bypass is performed, during which a hole is made in the skull, a drainage tube is inserted through it, reaching the formed tumor, it will not allow the lumen to close and will not allow a new accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. This type of operation has a very serious drawback - there is a high probability of infection.
At the same time, one should not expect the complete disappearance of CP when examining patients, even in the long term. The purpose of the operation is to eliminate the valve mechanism of the gearbox and its volumetric effect on surrounding structures. The residual volume of the CP may be related to the anatomy of the septum pellucidum in a particular patient.
Treatment
The main therapy for Verge's cyst is based on:
- Observation.
- Conservative treatment.
- Surgical intervention.
The patient is observed for some time. If the detected cyst does not cause discomfort and does not affect the patient’s well-being, he is recommended to have a magnetic resonance scan twice a year. When the pathology does not grow, other treatment methods are not used. If it increases, a conservative technique is used.
The main goal of conservative therapy is to slow down the growth of the formation. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- Nootropic drugs.
- Osmotic diuretics.
- Drugs that stimulate cerebral circulation.
- Medicines that help resolve blood clots and hematomas.
By taking these medications, the patient should feel improvement. Symptoms of the disease either partially or completely disappear. If after the therapy no positive dynamics are observed, surgical intervention is used to restore the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- A probe is inserted into the area of the problem cavity.
- Using an endoscope, small incisions are made, thanks to which the accumulated cerebrospinal fluid flows out.
- A drainage tube is inserted into the problem area to avoid re-formation of the cyst and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
This treatment gives a 100% result if the formation is single-chamber. With a growth consisting of several cavities, in 20% of cases the cyst appears again. After surgery, the patient should be periodically examined so that if the pathology re-grows, it can be detected at an early stage and therapy can be started in a timely manner.
Self-medication is not acceptable here, since a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain can cause the most serious consequences if not treated correctly. It is especially dangerous to drink various infusions and decoctions: they can sharply worsen the patient’s well-being and accelerate its growth.
Diagnostic value of brain structure
The transparent septum of the fetal brain is one of the criteria for assessing the formation and degree of brain development in an unborn baby. Expectant mothers regularly undergo ultrasound examinations to identify possible developmental disorders of the child.
When examining the head on the monitor, the presence of a septum, the size of the gap between its sheets, and the correspondence of the size to the duration of pregnancy are studied. In the second half of pregnancy, its dimensions are 1.8–9.4 mm. If pathology is suspected, the study is carried out dynamically. After the birth of a child, it is recommended to conduct neurosonography through the fontanel to confirm or remove the diagnosis of a defect in the transparent septum of the brain in newborns.
Cyst formation
A cyst of the transparent septum of the brain (Verge's cavity) is a cavitary capsular formation located in the brain cavity; it has dense walls and fluid inside. This type of neoplasm is not a pathological deviation, but a developmental anomaly that does not pose a threat to life and the normal functioning of the body.
A cyst of the transparent septum is formed due to a violation of free circulation and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid; isolation of a certain area begins, which over time can grow under the pressure of the accumulated fluid.
When the capsule reaches its maximum size, it compresses the surrounding tissues and venous vessels, closing the interventricular space intended for fluid drainage, which contributes to an increase in intracranial pressure.
Although the cavity in the area of the septum pellucida does not pose any immediate danger, if this course of events is not stopped, irreversible changes occur in parts of the brain.
A similar disease is detected in a quarter of patients as a result of MRI.
There are several types of cysts in the brain area of a newborn baby:
- arachnoid;
- retrocerebellar;
- other liquor formations.
However, most experts classify a septum pellucida cyst as an arachnoid cyst, since it is a spherical formation located between the meninges with fluid inside. This type of formation occurs more often in men than in women.
Depending on the position, the formation is located in the region of the anterior sections of the interventricular septum or occupies the territory up to the cerebellum and corpus callosum.
A cyst of the transparent septum of the brain (Verge's cavity) is a cavity capsular formation located in the brain cavity; it has dense walls and fluid inside.
This type of neoplasm is not a pathological deviation, but a developmental anomaly that does not pose a threat to life and the normal functioning of the body.
Localization
In addition to the genesis of formation, the location of the cyst also plays a significant role. Often the formation is localized between the vault of the corpus callosum and the anterior part of the brain. However, in some patients the cyst may occur in the anterior part of the interventricular septum. In addition, sometimes it is localized in the cerebellar area.
The PPP is a buffer between the lateral ventricles (PPP exists in 100% of human embryos). The PPP contains cerebrospinal fluid that enters through pores in the leaves. Anteriorly, the PPP is limited by the genu of the corpus callosum; above - the trunk of the corpus callosum; behind - the anterior legs and columns of the vault of the brain; below - the anterior commissure and beak of the corpus callosum;
laterally - by leaves of the transparent septum. The size of the PPP is extremely variable; in some the cavity is completely closed, while in others there is almost complete non-closure (up to 46 mm in the coronal plane). In most cases, the PPP does not communicate with the cavity of the ventricular system of the brain, which makes it inappropriate to describe it as the “5th ventricle” of the brain, however, it is sometimes called the fifth ventricle.
The PPP itself is located at the level of the base of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles of the brain, and its extension in the posterior direction to the area of the bodies of the lateral ventricles is called Verge's cavity. During embryonic development, the cavities close in the posterior-anterior direction, which is why persistence of the Verge's cavity with a closed PPP is much less common.
Reasons for the lack of PPP:
- primary (induced by developmental anomalies) - holoprosencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, cortical malformation (schizencephaly), septo-optic dysplasia;
- secondary causes are hydrocephalus, porencephaly, hydroanencephaly.
Prevention
There are no preventive measures to prevent the appearance of Verge's cyst. But patients are recommended:
- Avoid head injuries.
- Treat infectious diseases in a timely manner.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Pregnant women need to do tests and ultrasounds in a timely manner, regularly visit an obstetrician-gynecologist and follow all his recommendations.
If a patient is diagnosed with such neoplasms, then there is no need to panic. In most cases, the prognosis for detecting a cyst in the early stages is favorable. The main thing is to undergo a series of prescribed procedures and get ready for recovery.
In most cases, especially in the early stages of detection, the prognosis is favorable.
However, with the rapid growth of a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain, incorrect treatment, or late detection, serious consequences can develop - due to compression of the tissues and blood vessels of the brain, a chronic increase in pressure occurs, loss of consciousness, deterioration in the supply of oxygen to the brain, deterioration in vision, hearing and motor functions, the occurrence of convulsive attacks.
In young children with a congenital form of the disorder, physical and emotional development occurs at the appropriate level if the neoplasm is independent and does not cause associated problems. Otherwise, the situation is complicated by various anomalies.
There are no preventive measures to prevent the appearance of a Verga cyst, but it is important to avoid traumatic situations, infectious diseases that can provoke its formation, and increased blood pressure.
If the formation already exists, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a neurologist every six months to a year, perform an MRI or CT scan, and do not engage in traumatic sports. The number of examinations may vary depending on the condition of the formation and the patient.
If the operation is postponed, the number of visits to a specialist increases to 1 time every 4–6 months.
This type of cyst does not pose a threat to human life and health, but this does not mean that everything can be left to chance; at the first symptoms, you should contact a specialist and constantly monitor its condition. Only in this case the usual course of life will not be disrupted.
Diagnostics
The secondary type of Verge's cyst progresses uncontrollably. Constant monitoring of the patient's condition is important. Regularly perform:
- magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- CT head;
MRI and CT differentiate a cyst from a malignant formation. A radiocontrast agent injected into a vein reacts to the tumor.
Additional diagnostic measures for septum pellucida cyst:
- ultrasound examination during pregnancy;
- electrocardiogram;
- blood pressure testing, identifying people with cardiovascular changes;
- general blood test, detection of infectious diseases
If a cystic formation is visible on magnetic resonance imaging, the factors responsible for the appearance of Verge's cavity are determined. Auxiliary diagnostic techniques:
- determining the location of the inflammatory formation;
- blood clotting;
- identification of disorders in the cardiovascular system: Doppler ultrasound is performed, searching for ischemic foci;
- identifying the cause of weak immunity;
- blood test for cholesterol: atherosclerosis - the cause of high cholesterol - a factor in the appearance of Verge's cyst;
- morphological study of functional changes of the heart
To prevent the tumor from growing to a large size, it is important for a patient with pathology to diagnose the disease in a timely manner by regularly doing MRI and CT scans.
What will be found out during the examination?
Ultrasound of the brain in infants allows you to evaluate:
- ventricles of the brain. During visualization of their sizes, contours, structures, the doctor diagnoses the presence or absence of hemorrhages, intraventricular cysts, hydrocephalus, as well as pathologies that subsequently develop rickets. Their timely elimination will help to avoid problems not only of a physical, but also of a mental nature;
- condition of large vessels of the head of children. During the procedure, an aneurysm may be detected. It appears to be an expansion of the vascular walls. As a result, it is difficult for blood to penetrate into the brain. What can cause various hemorrhages;
- the presence of hemorrhages as a result of prematurity. This problem needs careful monitoring. Since it can lead to death;
- cysts that have fluid in their cavity. This manifestation requires constant monitoring by a neurologist, since a child with this pathology is susceptible to epilepsy. This type of cyst does not resolve, they only tend to grow;
- ischemia. As a result, the child experiences a lack of oxygen, leading to the death of nerve cells;
- infectious processes causing meningitis. If the disease is detected in a timely manner, a complete recovery is possible;
- Tumor processes are diagnosed extremely rarely.
After the study, the ultrasound scan of the baby’s brain is deciphered, and the result is transmitted to the attending or supervising doctor.
Ultrasound characteristics
Ultrasound of the newborn's head is performed using neurosonography. It can be used to diagnose newborn babies and babies up to one year old. In rare cases, if his fontanel is not overgrown, it is carried out for up to one and a half years inclusive. Using high-frequency waves, an image is formed on the screen. Ultrasound of the brain of newborns is painless and safe.
This quality allows research to be carried out as needed to monitor treatment. In addition, this procedure does not require anesthesia. The baby may sleep or even cry. This will not affect the result in any way. Ultrasound studies of the brain study the structure of tissues, blood vessels, and the degree of blood supply to the organ. During diagnosis, the doctor analyzes the processes of the brain and their dynamics.