In Ozhegov's dictionary
BONE, -i, f. 1. The inflorescence and fruit of conifers and certain other plants are round or oval in shape, covered with scales. Pine, spruce, alder highway. Cedar * sh, (filled with nuts). 2. Tubercle, rounded convexity. Put a bump on your forehead 3. A hard ball at the end of something. pre meta. A cane with a metal lump. 4. With an important, influential person (colloquial irony). He's a big one there. You are important now nov sh. * A cone out of the blue (colloquial irony) is the same as a cone (in 4 digits). || adj. shishkovy, -aya, -oe (to 1 meaning) and (in some special names) shishkovy, -aya, -oe.
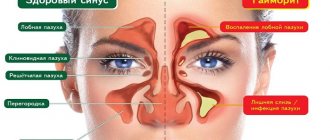
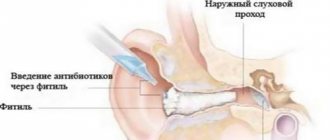
Cervical myositis
The causes of pain in the back of the head can be caused by cervical myositis. Neck myositis is an acute inflammation of the muscles and a very common ailment that knows no age restrictions. Among the causes of occurrence are :
- Infectious diseases;
- Passive lifestyle;
- Neck injuries;
- Prolonged stressful situations;
- Hypothermia;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- Diabetes;
- Alcohol and drug use.
© shutterstock
This disease can have a purulent, non-purulent, chronic, infectious, ossifying form.
Signs of cervical myositis
The headache in the back of the head is intense and gradually intensifies. It hurts a person to move his neck, which is why he tries to limit its work. The pain affects not only the back of the head, but also other parts of the head, including the shoulders and arms. When the inflammatory process becomes extensive, the muscles swell, forming a swelling.
With purulent myositis, the temperature rises, the skin becomes covered with red spots, fever and poisoning of the body begin.
In the non-purulent form of the disease, pain occurs in the back of the head, temples, and jaw, which even prevents the person from eating food normally.
The severe stage of myositis is manifested by cough, shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing . If the case is advanced, suffocation may occur.
If any of the above symptoms occur, you should contact a specialist who will diagnose and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Treatment options
To cure cervical myositis, an integrated approach is required, consisting of medication and physiotherapeutic procedures.
The doctor prescribes to the patient:
- Anti-inflammatory and painkillers;
- Antibacterial drugs;
- Gels and ointments that improve blood flow;
- Therapeutic complex of physical exercises;
- Massage.
It is also recommended to adhere to a certain diet, avoid smoking and alcoholic drinks, in order to avoid recurrent pain in the back of the head and other parts of the body.
In Vasmer Max's dictionary
I cone, Ukrainian shishka “bump, knob”, Old Russian. cone “fir cone, ball”, Serbian-cslav. shishka “bump, tuber”, Bulgarian. cone - the same, Serbohorv. cone "ink nut", Slovenian. šȋška “bump, ankle, loop”, Czech. šiška “bump, dumpling (type of bun)”, Slavic. šiška “fir cone”, Polish. szysza – the same, v.-luzh. šiška – the same, n.-luzh. šуška “fir cone, flax head.” The cone “a man walking at the head of barge haulers” is interesting. Based on this last value. It might have been possible to get closer to shish I and shish II (see). The meanings of the word šišьka make the borrowed origin incredible; see also Brückner 562. II coneII “foal”, Ryaz. (Dahl), cf. above - shinka - the same.
Symptoms of inflammation
Lymphadenitis is very difficult to miss. The first signal that indicates an inflammatory process in the lymph will be an enlargement of the lymph nodes. But other symptoms also appear in parallel: redness, pain on palpation, induration. Headaches, weakness in all muscles of the body, purulent inflammation, and a sharp increase in temperature occur less frequently.
If inflammation of one lymph node occurs, it is too early to talk about the need for concern. This may be the body’s reaction to infection and the active work of this particular lymph node. After a short time, even without treatment, the inflammation goes away. But if reductions do not occur for a long time, then it is advisable to consult a doctor.
In the dictionary D.N. Ushakova
BONE, cones, female. 1. Rounded bulge, tubercle. "A gray-haired old man with a bump on his head." Herzen. Put a bump on your forehead. A lump appeared on my forehead. | Thickening on the roots, stems or fruits of plants (bot.). 2. transfer Having great influence, a significant person (colloquial fam.). “He was a big shot. He managed some estates.” Kuprin. “It’s awkward to bury such a big shot without a speech.” Chekhov. 3. Round or oval inflorescence of some plants, for example. conifers, covered with scales and preserved when the seeds ripen. Pine cone. Fir cone. 4. Shape in the form of a rod, used. when casting hollow objects (tech.). 5. Hammer (reg., special). Battle cone (for breaking stones). Drill cone. 6. Leading barge hauler, leading man on a hike (old). • All the bumps are falling on poor Makar (colloquial) - pogov. about a person who is beset by various misfortunes.
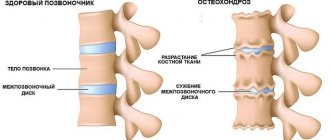
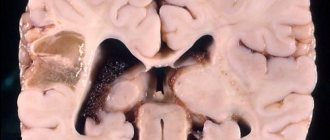
Osteochondrosis
The cause of a headache in the back of the head may lie in osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae. Today, this disease is faced not only by mature people, but also by young people who prefer to spend most of their time at the computer.
© shutterstock
The neck area is considered the most vulnerable, since the structure of the vertebrae is unreliable. They are located next to the arteries that supply the human brain. When the vertebrae become misaligned, they can put pressure on the artery, leading to various diseases.
Osteochondrosis, causing pain in the back of the head, occurs due to such factors:
- Sedentary, sedentary lifestyle;
- Scoliosis;
- Back injuries;
- Improper metabolism;
- Great physical activity;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Incorrect development of the cervical vertebra.
Signs of osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis manifests itself with the following symptoms::
- Pain in the back of the head;
- Weakness and numbness of the hands;
- A peculiar crunch in the neck;
- Dizziness;
- General malaise;
- Loss of vision and hearing.
Osteochondrosis of the neck is very dangerous for the entire human body. There is no need to endure pain in the back of the head and self-medicate; you should immediately seek medical help in order to avoid all sorts of complications.
Treatment options
When a person comes to the doctor with a complaint that a headache in the back of the head does not give rest, the specialist conducts an X-ray, computed tomography, MRI and duplex scanning to make sure that osteochondrosis is present.
There is one important point in the treatment of osteochondrosis - there is no single remedy that can eliminate this disease.
To get rid of pain in the back of the head and neck, you need complex therapy, which includes:
- Medications;
- Gels, ointments;
- Physiotherapeutic activities;
- Gymnastics;
- Massages.
There are cases when conservative therapy does not bring the expected, positive results. If after 5–6 months the treatment is unsuccessful, the doctor will be forced to resort to surgery.
In the dictionary of Synonyms 3
See nobleman" title='nobleman, nobleman synonyms, synonyms for nobleman, dictionary of Russian synonyms'>nobleman, elevation" title='elevation, elevation synonyms, synonyms for elevation, dictionary of Russian synonyms'>elevation, sublime" title='sublime , sublime synonyms, synonyms for sublime, dictionary of Russian synonyms'>sublime, main" title='main, main synonyms, synonyms for main, dictionary of Russian synonyms'>main...
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes on the head
Inflammation of the lymph nodes can occur for several reasons. Most often, it indicates the presence of a disease in the body.
Lymphadenitis is of two types:
- nonspecific,
- specific.
With nonspecific inflammation of the lymph nodes, the cause is the entry into the body from the environment of microorganisms that are the causative agent of serious diseases. These include infections such as: periodontitis, caries, abscesses, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, lymphangitis, allergies, toxoplasmosis.
Specific inflammations. Occurs as a result of damage to the body by a severe infectious disease. For example, tuberculosis, syphilis, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, AIDS, measles.
Where to contact?
If you notice the first signs of enlarged occipital lymph nodes, be sure to show your child to the doctor.
To establish the cause that caused this condition, additional examination is required. After a clinical examination of the baby, the doctor will prescribe appropriate tests to establish the correct diagnosis.
In some cases, in addition to general clinical tests (urine and blood tests), special instrumental studies may be needed. These include ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and kidneys, radiography of the lungs and chest organs. In difficult cases, a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan may also be required.
Causes of enlarged occipital lymph nodes
Lymphadenitis can take on a specific or nonspecific form. The first type of disorder is a symptom of various severe infectious pathologies. Among them are:
In addition, lymph nodes may become enlarged due to rheumatoid arthritis or leukemia.
The nonspecific form of lymphadenitis develops due to the fact that the infectious focus is located close to the lymph nodes of the occipital part. Their increase is usually provoked by chronic processes such as phlegmon, dental caries, tonsillitis or chronic pharyngitis. In addition, the cause may be otitis media or a trophic ulcer.
Reasons for the increase
Various reasons can lead to the appearance of enlarged lymph nodes. The basis for this increase is severe inflammation that occurs in the lymphoid tissue. The severity of symptoms depends on several main factors: the age of the child, the presence of concomitant chronic diseases, and the state of the immune system.
The following reasons lead to enlargement of the occipital lymph nodes:
- Bacterial infections
. Quite often the disease is caused by tuberculosis, childhood quarantine infections, measles, rubella, staphylococci and streptococci, and aerobic microorganisms. Bacteria easily penetrate the blood and reach the occipital lymph nodes. This causes them to become inflamed and noticeably increase in size. - Viruses
. Infectious mononucleosis often causes enlargement of the lymph nodes at the back of the child's head. Lack of treatment leads to the fact that this symptom persists for a long time. - Carious teeth.
An infection in the mouth quite often allows pathogens to spread throughout the bloodstream. This leads to microbes entering the nearest occipital lymph nodes. Typically, enlarged lymph nodes in this case are palpable on one damaged side. Deep caries, pulpitis and periodontitis are quite often the causes of occipital lymphadenitis in children.
- Oncological diseases.
Enlarged lymph nodes in such pathologies occur already at fairly late stages. This is due to the spread of metastatic cells to the lymph nodes. - Chronic tonsillitis.
In children who have had severe tonsillitis or suffer from constant inflammation of the tonsils, enlarged occipital lymph nodes are often found. - Purulent abscesses and phlegmons on the neck.
Typically, these conditions occur after severe bacterial infections. Such diseases require emergency surgical treatment and high doses of antibacterial drugs. - Chronic otitis media.
Inflammation of the ear often contributes to the spread of the inflammatory process to the occipital lymph nodes. In some cases, the appearance of this symptom is also facilitated by acute otitis media, which occurs with manifestations of intoxication and a severe course.
- Systemic diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
In these conditions, pronounced disturbances occur in the functioning of the lymphoid and circulatory systems. As a result, this contributes to the appearance of signs of occipital lymphadenitis. - Severe hypothermia.
Walking in frosty weather without a scarf often leads to inflammation of the occipital lymph nodes. According to statistics, it is during the cold season that a greater number of cases of this disease are recorded.
Course of the disease
There are two possible course of the disease.
- Non-purulent lymphadenitis.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is observed. They are mobile, quite dense and increased in size. Pain is felt only upon palpation. - Purulent lymphadenitis.
The immobility of the lymph nodes; they are also connected to each other. The painful sensations in them are strong. Possible exacerbation of the condition. This is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature, increased headaches, abnormal heart rhythm and general weakness throughout the body.
There are also two options that differ in the course of the disease.
- Spicy.
The period lasts for 2 weeks. Diseases occur unexpectedly. Lymph nodes increase sharply in size. A temperature change occurs. - Chronic.
The duration of the disease is more than 1 month. Arises as an advanced stage of acute lymphadenitis. There are no unpleasant symptoms.