Reasons for appearance
There are many reasons why tumors may appear:
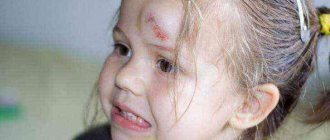
- Injuries and bruises. The most common problem after which bulges appear on the head. In this case, a small painful swelling appears, which looks like a growth from the outside.
- Allergic reaction to an insect bite. Depending on the degree of reaction to an insect bite, the neoplasm can be from 5 mm to several centimeters in diameter, accompanied by itching and unpleasant but tolerable sensations. To relieve itching and redness, you will need to use antiallergic medications; you should consult a specialist.
- Inflammation of soft tissues:
- Furuncle (purulent neoplasm, appears from a staphylococcal infection).
- Abscess (subcutaneous accumulation of pus, appears due to a focal bacterial infection).
- Enlarged lymph nodes (inflamed when adenoviral infections penetrate the body).
- Subcutaneous formations:
- Atheroma (cyst). Formed due to blockage of the sebaceous gland, it is painless and can reach the size of a fist. When infected and suppurated, it is accompanied by a feeling of pulsation at the site of the tumor and an increase in temperature.
- Lipoma (fat). Appears due to excess fat deposition in the skin, consists of fat cells and does not cause pain.
- Wart. Caused by the human papillomavirus, it usually appears on the head due to weakened immunity.
- Fibroma, sarcofibroma. Fibroma is hard to the touch and is itself a benign tumor. Sarcofibroma is malignant.
- Osteoma (benign tumor formed from bone tissue).
- Various types of blows and injuries.
- Insect bites.
- Atheroma.
- Osteoma.
- A lump on the head can form as a result of various inflammatory diseases.
- Lipoma.
- Wart.
- Allergic reaction.
Now it’s worth understanding each point in more detail.
The multiple reasons why a bump may appear on the head are divided into three main groups:
- Insect bites - a bump in the form of a tubercle and redness occurs at the site of the bite due to an allergic reaction caused by insect venom entering the bloodstream.
- Injuries - a painful lump and swelling of the soft tissues appears at the site of the injury. The size of the lump in such cases depends on the nature of the injury and the intensity of the blow.
- Subcutaneous tumors - benign and malignant formations appear due to improper division of soft and bone tissue cells. Some may cause painful sensations, while others may not manifest themselves at all. The rate of their growth depends on the type of tumor, which include hemangiomas, osteomas, lipomas, warts, atheromas, etc.
To understand what caused the bump on the head, you need to analyze the accompanying symptoms and consult a doctor for advice.
The reasons for the formation of a primary tumor in the head are currently poorly understood. Oncological science knows only the carcinogenic effect of ionizing radiation on brain tissue. Also, according to statistical data, there is a genetic relationship between brain cancer tumors among members of the same family.
Secondary malignant neoplasms of the head arise as a consequence of the spread of cancer cells from distant organs and systems.
Surely every person at least once in his life felt various tubercles, swellings, swellings and other formations on his head. The reasons for their appearance are different, as are the symptoms and treatment methods.
And you need to be able to understand this, because improper treatment can lead to serious consequences.
So, let's look at the reasons for the appearance of bumps on the head:
- injury or bruise;
- a bite of an insect;
- enlarged lymph node;
- lipoma (fat);
- atheroma (cyst);
- furuncle;
- trichoepithelioma;
- osteoma.
The reasons for the appearance of cones are varied, so they can be divided into several separate groups:
- bumps after injury. Impact or bruise of soft tissues is the most common factor in the development of a tumor. As a result, swelling forms, and the bruised area is very painful. As a rule, such bumps go away on their own without serious treatment. Cold compresses and applying heated cabbage leaves will help speed up the recovery process. Also in such a situation, iodine in the form of a grid is effective. Relevant for injuries to the forehead and back of the head. If tumors form, you should consult a doctor in order to exclude the possibility of traumatic brain injury;
- bump from a bite. Small swellings on the forehead, head, and body can occur as a result of an insect bite. This is an allergic reaction to the saliva secreted by the parasite. As a rule, you can see a small point on the surface through which the poison penetrates. The diameter of the affected tissue can reach 2-3 cm. Such bumps go away on their own or after using antihistamines. They are very itchy and have a dense consistency;
- lump in the form of a subcutaneous formation. Such tumors do not respond to standard treatment and slowly increase in size. Such growths include atheromas, lipomas, fibromas, hemangiomas, and warts.
Experts have identified several main factors for the occurrence of bumps under the scalp:
- Injuries. This reason is the most common. A person receives many injuries in the course of his life. The bruised area hurts and swells. Such bumps on the head disappear without medical help after a while. Applying a cold compress helps speed up the healing process of a bruise.
- A bite of an insect. After an insect bite, a bump appears on the head. This is an allergic reaction of the human body to the venom of the parasite. After taking antihistamines, the rash goes away on its own and does not require consulting a doctor.
- Subcutaneous formation. When cells divide incorrectly and uncontrollably, tumors appear on the head. These can be warts, wen, lipomas or hemangiomas. They can be both painful and sometimes do not bother a person for a long time.
Bumps that appear on the surface of the scalp are often a cause for great concern. Moreover, bumpy formations can appear both on the scalp and on the forehead and face. The reasons why bumps form on the head vary, and treatment often requires the intervention of a doctor.
When to see a doctor if you have a head injury
If the symptoms of a bruise are only swelling of the lump and pain at the site of the impact, which gradually subsides, then it is not necessary to go to the hospital; it is enough to use the remedies described above. But sometimes the situation can be much more serious. The injured person may experience not only a bump on the head from a blow, but also signs of a sharp deterioration in their condition as a result of a concussion, intracerebral bleeding, or a fracture of the skull. Urgent medical assistance is absolutely necessary.
Signs of such particularly severe conditions of the injured person are
- The appearance of open wounds and bleeding from them, which does not stop for more than 10 minutes.
- Feeling of severe pain in the head and neck area.
- Increasing nature of pain.
- Simultaneously with severe pain, attacks of nausea are observed.
- Blood or other fluid is leaking from the ears and nose.
- Increase in body temperature to a value greater than 38 degrees.
- Speech impairment.
- There is a feeling that there is “floating” in the eyes; the pupils are of different sizes.
- Confused consciousness.
If these signs occur, the victim must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible, and until the ambulance arrives, the person should be ensured complete rest and closely monitor his breathing and consciousness.
A bump on the head from a blow may appear to a lesser extent or not appear at all. It all depends on how quickly the situation is assessed and the necessary actions are taken to improve the condition of the injured person.
Types of head tumors
Based on the nature of the oncological process, tumors in the head are divided into benign and malignant.
Depending on the etiological factor, brain tumors are:
- Primary, when the cancer process initially develops from brain tissue.
- Secondary, the cause of which is considered to be the metastatic spread of tumors of internal organs and skin.
Leading experts from the World Health Organization have developed a unified classification of tumors in the head, which takes into account the histological structure of oncology.
- Neuroepithelial neoplasms are tumors of the brain tissue itself, which account for about 60% of all diagnosed brain lesions.
- Meningiomas are malignant neoplasms of the lining of the brain.
- Pituitary tumors, the localization of which is the pituitary gland.
- Neuromas are malignant lesions of intracranial nerves.
- Metastatic neoplasms. The source of such tumors in the head are cancerous lesions of other organs and systems.
- Dysembryogenetic oncology. This rare type of lesion is formed in the process of impaired embryogenesis.
Atheroma
Atheroma is a common phenomenon that occurs on the head of both men and women. Typical for any age. The development is caused by blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. The tumor can appear in different parts of the head and body. Even hair is not a hindrance.
- soft consistency inside, convex smooth shape, round appearance. Often has a yellow tint;
- a change in shade to brown indicates the beginning of the inflammatory process. Pus accumulated inside can cause fever, as well as a deterioration in general condition;
- atheromas can hurt if left untreated;
- lipoma and atheroma are very similar in appearance, so it is important to correctly determine the nature of the formation. A qualified doctor will help with this;
- often atheroma on the forehead resembles a cerebral hernia, which greatly complicates the diagnosis;
- cones may burst over time
- injury to the sebaceous ducts, resulting in blockage. The accumulation of fluid causes the tumor to enlarge. The size of such a cone can reach several centimeters in diameter. When a purulent process forms, atheroma requires urgent surgical intervention;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body, as well as problems in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- a sudden hormonal imbalance can cause the formation of lumps on the head and body;
- atheroma can be congenital. In such cases, it practically does not grow and does not bother throughout life;
- acquired is caused by a violation of the functionality of excretory processes in the body. Often appears after a long absence of normal hygiene.
Atheroma can be determined by external signs, so diagnosis does not cause any particular difficulties. To treat the disease, only surgical method is used. As a rule, the operation has only a cosmetic effect, as patients begin to feel embarrassed about their condition. The only medical factor for removing a tumor is its infection.
Since atheroma forms inside a kind of capsule, which is limited to it, removal consists of excision of the superficial soft tissue and extraction of its internal part.
After the incision, the atheroma is squeezed out, cleaned, the capsule is removed and sutured. Recovery after surgery is quick and leaves no visible defects.
Atheroma on the head
Lipoma
Lipoma is one of the most common benign growths on the head. It grows after damage to adipose tissue. It is predominantly diagnosed in the female half of the population over 30 years of age, as a result of hormonal imbalance.
- Poor metabolic processes can provoke development;
- heredity;
- violation of fat metabolism;
- clogging of the ducts of the sebaceous glands, which can be caused by impaired functioning of the liver and gallbladder. At the same time, the number of fat cells increases.
- soft consistency, round shape;
- may become infected, after which signs of intoxication are observed: weakness, high fever and general malaise;
- does not hurt, is mobile within the skin. Most often it forms on the forehead, neck and back of the head. It may also appear on other parts of the body.
Diagnosis is carried out by a qualified doctor after assessing general symptoms, external signs and after performing a cytological analysis. Ultrasound is also often prescribed to assess the structure of the formation. An x-ray is taken to determine the depth.
The prescribed therapy depends on the size of the tumor, stage of development and age of the patient. Both medical and surgical treatments may be prescribed. After taking medications, the wen resolves only at the initial stage of development; for larger sizes, only surgical intervention is relevant.
To do this, the outer tissue is dissected, the capsule and fat accumulation are removed. You should not be ashamed of your deficiency; you need to make drastic decisions in order to prevent further infection.
Fibroma
Fibroma is a benign formation consisting of connective tissue of the skin. They grow slowly and appear on the forehead, head and body. They don’t do much harm, but when they grow, they make you feel embarrassed about your appearance.
- bad heredity;
- frequent soft tissue injuries;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance.
- the tumor can be soft or hard, depending on the structure and composition of the formation. The hard one is formed in the form of a growth with a wide base. The color of fibroids does not differ from the main skin. It has a smooth and dense surface. Soft fibroma is much less common. It has the shape of a mushroom with a thin stem. Brown in color with flabby tissue on the outside;
- Fibroids rarely hurt, only when infected.
Since fibroids on the head can often become injured, hindering the patient’s normal life, it is imperative to treat the disease. To do this, the tumor is removed by surgical and laser methods.
- The surgical method is rarely used so as not to create unnecessary scars. During the operation, pathologically altered tissues are excised. There is a high probability of affecting healthy areas;
- Laser removal is the most common and popular method. The procedure is carried out using a laser and a microscope. Only a small scar remains at the site of exposure. The duration of the session is about 30 minutes.
Warts
Warts can appear on the head and other parts of the body. Since such a harmless benign formation can reach significant sizes, its owners are often embarrassed by their appearance.
The main causes of the disease are the human papillomavirus, as well as a decrease in the level of functionality of the immune system.
Warts develop slowly. Without treatment, the formations not only increase, but also multiply. By its nature it is an infectious disease.
- has a smooth, lumpy surface that rises above the skin level. Its structure resembles a ball located separately on the epidermis;
- reaches a size of about 0.5 cm;
- there is no skin pattern on the wart;
- With age-related warts, as a rule, there is no infectious etiology.
Wart on the head
There is no need to be shy here, you need to act decisively. For diagnosis, the doctor prescribes dermatoscopy, as well as histological examination. PCR examination is often used as an additional analysis to exclude the papilloma virus.
Warts can disappear on their own, but this happens quite rarely and sometimes it becomes unbearable to wait for this day. Therefore, without hesitation, you need to contact a specialist for advice. To begin with, drug treatment is prescribed, which is aimed at eliminating the lesion. For this purpose, fluorouracil, interferon, and special ointments are used.
To remove warts, the laser method, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation and surgical excision are used.
Hemangioma
A large growth on the head that occurs when the circulatory system is disrupted. The veins can grow uncontrollably, resulting in a red lump. Under the tubercle you can see a network of blood vessels.
Doctors consider hemangioma the most dangerous type of tumor. It is the hemangioma that leads to disruption and formation of the surrounding tissues of the head. Often this type of tumor is located under the hair. A small hemangioma can grow in size over time and become a malignant tumor. If a hemangioma emerges, you must seek specialized medical help.
A bump on the head occurs when the human body is exposed to certain allergens. An allergic reaction is caused by food, household chemicals or cosmetics. Such bumps itch and bring a lot of unpleasant sensations to a person.
A lump on a child’s head and its features
Why does the child have a lump and pain? Due to the active lifestyle of children, they most often find themselves in situations that cause bumps to appear. Most often, in children, large bumps form from bruises and small ones from insect bites, and you can find out why a ball might appear on the scalp from this article.
And in what case did a child’s lump appear not from a blow? The appearance of lumps is also observed in newborns, which occur after childbirth. What are these bumps on a child? They are called birth trauma and have a hard surface to the touch.
Attention! You shouldn’t leave bumps on children without a doctor’s examination and let the situation take its course.
Additionally, we advise you to follow the link https://vsemugolova.com/bolezni/kozhi/prichiny-i-lechenie-b-na-golove.html and read about other sores that can appear on the scalp not only in a child, but also in adult.
Bumps that appear on children's heads should not be ignored by parents.
The most common cause of their occurrence, regardless of age, is injury. A child may hit his head on a hard object as a result of excessive physical activity, unsteady walking, or during games.
A child’s skin is delicate and excessively sensitive, so after an impact the lump grows quickly. If the blow was strong and the bruise caused a rupture of blood vessels, then a subcutaneous hematoma forms at the site of injury.
The first aid for a child when a bump appears after a blow is a cold compress, which should be applied to the bruised area. If you have symptoms such as constant crying, nausea, vomiting, paleness or loss of consciousness, your baby should be taken to the doctor immediately.
Bumps in children can be the result of more than just injuries. They may be a consequence of the following pathological processes:
- Cephalohematoma is a small tumor, inside of which blood accumulates, typical for newborns. The reason for its appearance is a difficult birth, during which the baby’s head is injured when it passes through the narrow birth canal or when a gynecological instrument is used (for example, surgical forceps).
- Enlarged lymph nodes - painful lumps can be felt in the back of the head or behind the ears. The reason for their growth is the reduced functioning of the immune system and the development of inflammatory processes in nearby organs and vital systems.
- Atheroma (wen) - in children, the tumor appears mainly in the back of the head due to blockage of the duct of the sebaceous glands. The cause of the appearance of a wen is poor hygiene or improper functioning of the baby’s sebaceous glands.
Rarely, lumps in children can be caused by the growth of tumors such as fibroids, hemangiomas or lipomas. To exclude the development of oncological diseases and their transition to a malignant form, if a lump appears and grows on the head, not associated with a bruise or insect bite, the child must be shown to a doctor.
Bumps are also sometimes diagnosed in newborns. They arise during childbirth, during the passage of the birth canal. Such bumps are called birth trauma. This bump has a hard surface to the touch.
Medicines to get rid of lumps
To remove a bump on the head, medications are used that eliminate itching and inflammation, but most often surgical methods of treatment are used in therapy.
Treatment with drugs
Gel "Troxevasin"
The product strengthens capillaries and vascular walls, has an effect against swelling and emerging inflammation. The bump on the head is lubricated with gel in the morning and evening. In this case, the medicinal product is smoothly rubbed into the skin until absorbed.
Gel "Troxerutin"
Used to relieve swelling. Well absorbed through the top layer of skin. The product can only be applied if there are no open lesions or wounds. Places treated with gel should be protected from exposure to active sunlight.
Heparin ointment
The product promotes the resorption of blood clots and prevents the formation of new ones. Reduces pain. The ointment is applied in a thin layer in the morning, afternoon and evening until the symptoms of the bruise disappear.
Gel "Rescuer"
Promotes active cell growth and rapid restoration of injured skin. Has an antimicrobial effect. Quickly absorbed. Apply 1-2 times during the day. Apply a thin layer.
Symptoms and early signs
Brain tissue is located in a limited space in the skull, which causes two types of symptoms.
Focal signs of a tumor in the head are dictated by local damage to brain tissue and include the following manifestations:
- Impaired spatial, tactile or pain sensitivity. The patient does not control the position and movement of his body.
- Memory disorders. Often such patients experience loss of short or long-term memory.
- Paresis and paralysis of central origin. Disruption of nerve impulse transmission causes muscle blockage. The patient loses the ability to voluntarily move the upper and lower extremities.
- Epileptic seizures, which are formed due to overexcitation of certain areas of the brain.
- Impaired hearing, vision and speech recognition.
- Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in the form of rapid fatigue, decreased muscle tone and a sharp drop in blood pressure.
- Pituitary tumors provoke a loss of hormone balance.
- Visual and auditory hallucinations accompany most malignant neoplasms in brain tissue.
A tumor in the head, with further development, causes an increase in intracranial pressure and compression of parts of the brain, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Frequent attacks of intense headaches. Such pain, as a rule, does not go away after using traditional painkillers.
- Nausea and vomiting. Such symptoms are explained by the pressure of the tumor on the vomiting center in the midbrain.
- Dizziness and loss of consciousness, which indicate the spread of a tumor in the cerebellar tissue.
Hemangioma
Diagnostician
- Examination by a specialist doctor.
- Prescribing tests and studies (general blood and urine tests).
- Additional research:
- X-ray of the skull - helps determine the causes of cones, whether there is intracranial bleeding and concussion).
- Ultrasound diagnostics - helps to identify changes in tissues and structure.
- Making a diagnosis (in most cases, therapy is not required).
- If a malignant tumor is suspected, a person is asked to undergo an additional test - blood from a vein for tumor markers. When diagnosing cancer tumors, the patient must undergo complex therapy in a specialized hospital.
Be careful. Take care of your health in a timely manner!
Proper treatment of a tumor in the head requires an accurate diagnosis. Establishing a definitive diagnosis requires cytological and histological confirmation. But in such cases, performing a brain biopsy is very difficult for the oncologist.
An initial examination of the patient with testing of basic reflexes allows the doctor to suspect the approximate location of tumor growth.
A key role in the neurological diagnosis of brain tumors belongs to radiography, as well as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These techniques use digital processing of the result of an X-ray examination, which reveals the location and shape of a cancerous tumor.
At the first visit, the doctor examines the lump. After this, a series of tests and studies are prescribed. A complete blood and urine test may be required to assess the patient's overall health. Additionally, the following studies are prescribed:
- X-ray of the skull - helps to determine the causes of the lump;
- Ultrasound diagnostics - helps to determine any changes in tissues and their structure.
After receiving test results, the doctor makes a diagnosis. In most cases, no therapy is required. Only if a malignant tumor is suspected, a person is asked to take an additional test - blood from a vein for tumor markers.
Patient management tactics
For the most part, a bump on the head does not pose a serious danger, especially if it does not hurt. But even in this case, it is worth undergoing an examination to clarify the cause and nature of the formation and to be aware of the possible risks.
- Surgical diseases and injuries. Sukovatykh B.S., Sumin S.A., Gorshunova N.K. – 2020.
- Atlas of pathology of human tumors. Paltsev M.A., Anichkov N.M. – 2005.
- Acute purulent surgical diseases. B. M. Khromov - “Medicine”, 1965.
Ankylosing spondylitis and other autoimmune diseases
Back pain (dorsalgia)
Other pathologies of the spinal cord and brain
Other musculoskeletal injuries
Muscle and ligament diseases
Diseases of the joints and periarticular tissues
Curvatures (deformations) of the spine
Treatment in Israel
Neurological symptoms and syndromes
Tumors of the spine, brain and spinal cord
MORE ABOUT: How to check joint mobility
Answers to visitors' questions
Soft tissue pathologies
X-ray and other instrumental diagnostic methods
Symptoms and syndromes of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Vascular diseases of the central nervous system
Spinal and central nervous system injuries
Who and how can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment?
It is important not only to visit a doctor in a timely manner, but also to know who to contact. Unfortunately, not all tumors are benign. Many tumors from a harmless stage can develop into malignant tumors that require treatment under the supervision of a specialist.
With new growths, growths, bumps, you can contact:
- therapist;
- dermatologist;
- surgeon;
- oncologist.
Drug treatment
If an inoperable form of the tumor is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed maintenance therapy, which consists of drug elimination of the symptoms of the disease. For this, oncologists use the following means:
- Narcotic painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain attacks.
- Glucocorticosteroids that help reduce swelling of brain tissue.
- Antiemetics and sedatives (depending on the general condition of the body).
Surgical removal of the tumor
The surgical method is considered the most effective method of treating brain tumors and is carried out in two ways:
- Traditional surgery with craniotomy. A tumor in the head, the operation of which was carried out surgically, must undergo cytological and histological analysis in the laboratory.
- Radiological surgery. Removal of a tumor in the head in this method is carried out using highly active x-ray radiation. These are technologies such as “cyber knife” and “gamma therapy”.
Radiation and chemotherapy
Radiation therapy in patients with head tumors can be an independent therapy or an addition to surgical treatment. The technique involves remote irradiation of brain tissue with highly active gamma radiation.
Chemotherapy in such patients is so difficult that not all cytotoxic drugs penetrate the blood-brain barrier. An individual course of chemotherapy and method of drug administration are selected for each patient.
To avoid serious complications, do not neglect visiting a specialist. This could be a surgeon, therapist, ENT doctor, or less often an oncologist. In any case, you will be prescribed an examination in order to identify a diagnosis and eliminate a particular disease.
Soft structure, but the deeper, the denser.
It is not located deep.
Painful sensations when bruised.
- X-rays can reveal formations of bone density (osteoma) or detect the cause of inflammation of the lymph node (rhinitis, sinusitis, chronic periodontitis).
- Ultrasound makes it possible to determine changes in the structure of soft tissues, the presence of softening or a liquid component, as well as the degree of change in the structure of the lymph node during its inflammation.
For bruises and bites, it is enough to apply a cold compress to the site of the bruise. This can be a cold object or ice, wrapped in cloth before use. The following creams are used to resolve the tubercle: “Rescuer”, “Bodyaga” and “Troxevasin”.
They relieve swelling and help the bumps heal faster. The doctor recommends removing large atheroma, fibroma or hemangioma surgically. After the operation, the patient takes antibiotics.
Copying site materials is possible without prior approval if you install an active indexed link to our site.
The information on the site is provided for general information purposes only. We recommend that you consult your doctor for further advice and treatment.