Why do temples swell?
Bumps on the head appear for various reasons.
Most often this is mechanical damage, the result of a blow or insect bite. This lump appears very quickly because tissue swelling occurs. It is painful, but goes away on its own over time. In all other cases, the lump should definitely be shown to a doctor; treatment or observation is necessary. Possible reasons for the appearance of a lump:
- neoplasm (atheroma, fibroma, hemangioma, lipoma);
- inflammatory process (enlarged lymph nodes, ulcers);
- congenital pathology (cephalohematoma).
There are several different reasons for the appearance of edema in the temporal region, these are:
- Injuries, blows, head concussions;
- Allergic reaction to cosmetics;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Neuroinfectious diseases;
- Inflammations on the scalp;
- Inflammation of the temporal or masseter muscles;
- Horton's disease.
Most often, swelling of the temple and lumps in the temporal part are provoked by local pathology. Systemic disease is rarely present in etiology.
The problem of fluid accumulation in the temples
There is a lot of information on the Internet describing swelling of the face or head. But few can find comprehensive articles on the topic of tumors in the temple area. It itself is formed from bone, which cannot accumulate fluid; only subcutaneous neoplasm occurs.
Swelling extending down to the cheek is often observed. Rarely does fluid accumulation occur on both sides, so why does swelling occur, for example, in the left temple?
Swelling of the sides of the head as a result of diseases
Diagnosing and establishing the causes of swelling in the temple area is not always easy. The examination of the patient is approached in a comprehensive manner with visits to doctors:
- ophthalmologist;
- neurologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- allergist;
- vertobroneurologist;
- a dermatologist if there are skin problems: rashes, discoloration;
- Additionally, a parasitic source of inflammation is excluded by visiting an infectious disease specialist and undergoing tests.
Why several areas of examination of the body are required can be understood after establishing signs of inflammation:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- heaviness around the affected area, spreading to the eyebrow, ear, neck;
- loose skin;
- swollen temple veins;
- pain in the temple area when pressed, which does not appear in all cases.
Sources of swelling of the side of the head
Swelling in the temple area is caused by the following reasons:
- chronic tonsillitis, accompanied by severe enlargement of the tonsils;
- persistent sore throat;
- inflammation of the adenoids;
- allergic reactions;
- an increase in blood pressure, which can occur due to nervous situations, resulting in swollen veins in the temples;
- inflammatory processes in the area of the parotid gland, causes of mumps can be hypothermia, infection, trauma;
The causes of swelling in the temple area may be the development of many diseases of the masticatory muscles and temporal bone. Allergic reactions can occur as a result of applying low-quality cosmetics, an insect bite or infection.
Vascular problems can be the cause of swelling in temporal artery disease.
This disease is also called arteritis Horton's disease. Similar consequences include Kawasaki and Takayasu disease, as well as periarteritis nodosa. The sources of such ailments, in turn, are hepatitis and herpes viruses.
In addition to causing swollen areas, Horton's disease can lead to partial or complete loss of vision, so this condition must be treated.
Diagnostics
The reason for undergoing diagnosis should be the presence of the following symptoms:
- persistent discharge from the eyes;
- cyclically recurring pain in the face and head;
- blurred vision of surrounding objects;
- lethargy of the eyelid, its drooping is observed.
In search of the main reason why the temple swells, the following types of examinations can be used in different areas of the body:
- heart electrocardiogram;
- tests for allergic reactions and infections;
- reencephalopathy of cerebral vessels;
- computer diagnostics;
- in case of disease of the temporal artery, ultrasound diagnostics of the head and biopsy of the vessels of the head are performed;
- examination of the eye vessels by an ophthalmologist;
- laboratory blood tests, detection of increased levels of leukocytes;
The ophthalmologist checks the patient's fundus pressure and vision. If a disease of the ENT organs is suspected, he is referred to an otolaryngologist.
If swelling of the temporal region of the face appears, you should go to any of the listed specialists.
You can start by visiting a therapist, who will analyze the existing symptoms, conduct initial tests and, if necessary, refer to the next specialist.
Prevention and treatment of swelling
Health measures are selected based on the complete picture of the disease and the establishment of the cause that caused it. It may be necessary to relieve facial swelling very quickly, due to its rapid development. In this case, powerful drugs that have an effective anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed. Among these are glucocorticoids.
At the initial stage, even before receiving the results of laboratory tests, large doses of medication are prescribed. Subsequently, the number of drugs is gradually reduced. Severe conditions are rarely eliminated promptly, because the vessels of the temple are very small. These operations are expensive and belong to the section of microsurgery.
To reduce swelling, follow an appropriate diet, which recommends reducing salt intake and fluid volume. All nutrition rules apply here for any swelling.
Diet for swelling
In addition to medical therapy prescribed by the doctor, proper nutrition will help reduce swelling in the temple area. It is recommended to limit the consumption of the following products:
- exclude mineral water, carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol for the duration of prevention;
- Tomatoes, celery, beets, and beans contain a large amount of salts;
- Semi-finished products, smoked foods, fried foods, and canned foods contribute to water retention in the body;
- fast foods, disrupted eating patterns, aggravating factors;
- working too hard upsets all systems of the body, restless sleep and nervousness contribute to the development of swelling of the temple and other more dangerous diseases;
- spicy dishes and pickled vegetables;
- reduce the number of servings per meal;
- remove yeast, sweets, and flour products from the diet.
There are a large number of diets that effectively help in reducing temple swelling:
- watermelon;
- herbal, tea;
- apple;
- vegetable;
- lactic acid;
- taking various juices.
Choosing a diet on your own when your temples are swollen is extremely dangerous. You can use the appropriate type of diet only after examination and receiving recommendations from a doctor. Each person has their own chronic diseases that need to be taken into account when choosing products. In some cases, a transitional preparatory period will be required to establish the functioning of all body systems.
Measures to reduce swelling
Drink clean water, without additives. Water alone can reduce swelling by half in a short time. Boiled and mineral liquids are not suitable. The speed of operation of almost all vital systems of the body depends on molecules unrelated to other substances.
Unbound water promotes the rapid removal of fluid and waste from the area of temple swelling. Among the products it is advisable to choose:
- lemon, fresh cabbage and cucumbers;
- drinks: berry juice, cranberry, green tea, lingonberry, pumpkin juices;
- herbal decoctions: birch buds, burdock, pine buds, parsnips;
- melon, strawberries, apples, currants, bananas, citrus fruits and brown rice.
Proper nutrition will help not only remove swelling from the temple, but also lose extra pounds. However, some of the listed products remove the important trace element potassium from the body. Such diets are contraindicated for people with heart disease and vascular problems. Light sports, walks in the fresh air and a positive attitude will be a supporting factor on the path to recovery.
Source: https://pro-oteki.ru/organy/skopleniya-zhidkosti-v-viskax
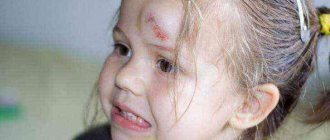
Girls, take care of the kids, they are already big!
The hemotomy will pass without a trace. My son has already forgotten about her, so it’s not scary. I would anoint it a little with Traxevazinchik. I feel sorry for Lyalechka
Yesterday I left the room for less than a minute, left Mishka on the sofa, lying on his back. He was doing what he loved - raising his legs and joyfully, loudly thumping them back on the sofa. And then I walked into the room, and he was already on the floor, crying.
I pick him up, I’m roaring, he’s even stopped, and he’s shaking me. Grandma says, calm down, put him in his crib, and I hold him close to me and continue to roar. He’s already smiling, but I still can’t calm down. I scold myself with all the bad words. .
Answer
In such cases, you need to immediately go to a doctor: a therapist, a surgeon, or maybe a neurosurgeon. The point is not that there is a lump, but that it is a head. Any complication, suppuration or incorrect self-medication tactics are fraught with very serious consequences. All my further thoughts are purely educational in nature, since the lump must be examined live.
Unfortunately, you did not indicate the color and consistency of the formation, so there may be several options. Let's look at each of them.
Bumps often appear for no apparent reason, so your case is no exception. There are several reasons for the appearance of such formations:
- inflammatory processes, with regional lymph nodes involved (there are no lymph nodes on the forehead);
- infectious diseases;
- blockage of the sebaceous glands;
- injuries;
- allergic reactions.
The lymph nodes and blockage of the sebaceous glands disappear immediately, so it is not a wen or a tumor. The secretion of the sebaceous gland could not organize such a large formation in such a short period of time. In any case, the atheroma is removed without any problems, does not cause complications with timely removal and is not a problem in 99% of cases after removal. The oncological option is eliminated, because no tumor grows like this - there are signs of a local reaction on the face.
What is confusing is that the itching in your forehead appeared after sleep, i.e. We cannot know for sure what happened to you before this moment.
Hypothetically, you could hit your forehead against a wall, bed frame, corner of a closet, or other hard objects. At the same time, your body did not want to wake up, you fell back into sleep. After some time, the impact mark became less intense, and tissue swelling with the formation of a lump occurred gradually during the day. If the lump is painful and dense, you can choose this option.
Another reason could be contact with an allergen or some aggressive substance. You may have been bitten by an insect or arachnid. This is not the season for spiders, and most of them are sleeping. In addition, spider venom is no longer very toxic at this time of year. However, with increased reactivity of the body, this option is quite possible: itching at the site of the bite, local swelling of the tissues. In this case, the lump will be soft and possibly itchy. If you are allergic, you can choose this version of what is happening.
There may have been a local infectious process , which can also lead to the appearance of bumps.
The infection enters the skin through minor abrasions or cuts, inflamed passages of the sebaceous glands. Once introduced, the infection causes itching, swelling and suppuration. A subcutaneous accumulation of pus is formed - an abscess. If the lump is red, the skin around the formation is also red, and you have signs of intoxication, you should immediately contact a surgeon.
Abscesses must be opened immediately in compliance with all surgical dogmas. An abscess on the head can end extremely badly, so delaying a visit to the doctor is deadly.
Some bacteria do not behave too aggressively, and the lump only marks the gates of infection, without the formation of massive purulent formations. For example, at the dermatovenous dispensary I once saw a syphilitic chancre on my grandfather’s forehead - “his granddaughter kissed him.”
In addition to opening (sanitizing) the abscess in this case, you will be prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy. It must be drunk completely to prevent relapse and spread of the process. An abscess of the skin of the forehead is a sign of severe immunodeficiency, because The scalp is well supplied with blood and must cope with such adventures without antibiotics.
If it turns out that the lump was of an infectious nature, you need to additionally visit an immunologist to prescribe an adequate course of immune correction. In addition to medications that affect the immune system, you need to take multivitamins (the season is appropriate, by the way).
In addition, it is necessary to strengthen local and systemic blood circulation and increase the overall tone of the body . Morning jogging, going to the pool and other general stimulating activities will be useful.
So the action plan looks like this:
We go to a surgeon or therapist, he determines exactly what it is:
- traumatic lump - consultation with a neurosurgeon and MRI of the brain. This is done to prevent bleeding in the brain after a stroke. There is no point in refusing in this case;
- toxic-allergic reaction - consultation with a dermatologist, prescription of skin (application) tests. The allergen will be determined for you, and you will be able to avoid further contact with this substance (or creature);
- abscess or phlegmon - the surgeon will immediately perform or refer for the opening and sanitation of the purulent focus, antibiotics will be prescribed.
Which specialist treats swelling of the temples
During a headache, many people notice that their temples swell. What is the reason for this condition? Why does swelling occur? A doctor can answer these questions after a detailed examination.
During a headache, vasospasm occurs. It may be accompanied by pain during chewing, double objects in the eyes, and swelling of the temples. Painful pulsation of blood vessels appears in the temporal zone and around the eyes.
Treatment or its individual dosage for swelling and bumps on the temples is strictly individual. Long-term monitoring for adverse complications is necessary. The cooperation of a therapist, immunologist, rheumatologist, ENT specialist, and neurologist is required.
Temporal arteritis
If the temples are swollen, a lump appears, the vein may have temporal arteritis - an inflammatory vasculopathy characteristic of older people.
Neurological symptoms:
- headache;
- memory impairment;
- dementia.
Eye signs:
- sudden and irreversible, usually significant decrease in visual function.
Systemic symptoms:
- fatigue;
- sleep disturbance;
- night sweats;
- weight loss;
- pain in the jaw and temporal region while eating (the jaw does not deviate to the side);
- muscle pain.
Important! When a lump appears on the temples, timely diagnosis is important for starting treatment; delayed identification of the problem is fraught with blindness.
Causes and types of bumps on the head of infants
Most often, bumps in infants are small, about the size of an average pea; such bumps are most likely lymph nodes. They move freely under the skin, without causing pain or discomfort to the child.
Another common cause of bumps in infants is birth trauma, that is, damage to the baby’s head during childbirth with gynecological instruments or other means. In such cases, small tumors or hematomas form in the newborn. As a rule, they disappear within the first days or weeks of life.
The third type of bumps in infants is cephalohematoma. Externally, it is a tumor filled with fluid and is usually small in size. If the skin above it does not change color when palpated, this can be considered normal. Cephalohematomas disappear completely and without consequences after two weeks.
There are also a number of symptoms, if they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor for advice. These include:
- redness and appearance on the bumps themselves or around the rashes;
- increase in tumor size;
- release of fluid from the formation;
- increased skin temperature over the bump;
- the emergence of new tumors.
Particularly dangerous symptoms are considered to be disturbances in the baby's sleep, lack of appetite, severe neurasthenic disorders, and anxiety. You should definitely pay attention to such signs and immediately contact your pediatrician or consult a pediatric surgeon when they appear.
In most cases, the cephalohematoma is relatively small in size, and the liquid inside is clearly felt to the touch. If there is blood inside the tumor, it can persist for up to 10 days. However, progressive and growing cephalohematomas are not uncommon.
MORE ABOUT: Flat feet in children: signs, degrees, treatment, prevention. How to correct longitudinal and transverse flat feet in a preschool child?
Then the skin over the bump in the baby becomes hot, and discharge may also be noted. All these symptoms require an urgent visit to a specialist. Otherwise, severe consequences may develop, such as impaired brain activity, paralysis, etc.
Cephalohematoma can form as a result of birth trauma and jaundice. In cases of normal and full development of the baby’s immune system, the child’s body successfully fights pathology. If the newborn has any developmental abnormalities, then the baby’s lump may begin to grow and develop, which leads to a threat to life and health.
As already mentioned, most often such bumps on the head of infants do not require special treatment. It is enough just to carefully monitor the condition of the cephalohematoma and note its changes. When the swelling begins to shrink quickly, it will mean that it will soon disappear completely, so you don't have to worry anymore.
With such bumps in infants, you need to show the baby to a doctor who will monitor the tumor provided that it steadily decreases. In this case, the child should not be rocked to sleep; one should also not touch, press or squeeze the formation. Bath the child carefully, without using soap or shampoo.
If the development of the disease and the growth of a lump in the infant are noted, then treatment is carried out using surgical methods. The doctor carefully punctures the tumor and removes fluid from it. After this, a tight bandage is placed on the child’s head.
How to remove a bump from a blow?
Almost every person throughout his life has encountered such a phenomenon as a swelling on the forehead. Bumps on the forehead can be of different types and arise as a result of various reasons, so you should not take this phenomenon calmly. It is imperative to identify the cause and nature of the neoplasm.
A bump on the forehead may not always be the result of solely physical impact on an area of the body.
If a hematoma has formed from the blow, then in a short time it is freed from it in the following way:
- First of all, apply an ointment that will help resolve the swelling that appears. This method is effective if there is a lump under the eyebrow.
- It is better to anoint the swelling after the child has applied cold.
- A similar procedure should be carried out 2 times a day; in addition, you should also use traditional methods of therapy.
Causes of bumps on the head with and without pain, diagnosis, treatment
Surely every person at least once in his life felt various tubercles, swellings, swellings and other formations on his head. The reasons for their appearance are different, as are the symptoms and treatment methods.
External damage
A bump on the head as a result of a bruise or injury appears after a strong blow and represents a hematoma (limited accumulation of blood under the skin) of a dense structure. It is painful when pressed. Color varies from light lilac to eggplant.
In the first two to three days, you should carefully monitor the condition of the hematoma, because it can fester. This occurs as a result of weak metabolism in the process of resorption of accumulated blood. In this case, the surgeon is involved in the treatment, he performs an autopsy at the site of blood accumulation and cleans the wound of clots and pus.
Cervical osteochondrosis often has unexpected manifestations that are difficult to associate with damage to the spine. But you cannot get rid of them if you fight the troubles themselves, but not their cause. One of these manifestations
First aid: you need to treat the skin by washing it with soap and apply something cold to the bite site. Locally, you can use ointments and gels with an antiallergic effect. If the swelling spreads, it will not hurt to take antihistamines orally and consult a specialist. Never scratch a lump that appears after a bite, even if it itches
Blows and bites do not require treatment. If necessary, you can alleviate the suffering by briefly applying ice wrapped in a soft cloth. An antihistamine will relieve itching and swelling from a bite. If the blow is not severe, you can treat the damaged area with a special ointment that relieves swelling.
Cases when you need to see a doctor:
- Cephalohematoma after childbirth. In most cases, the watery bump on the top of the head will disappear on its own over time. If this does not happen, a puncture is used - the doctor uses special needles to pump out the liquid from the lump.
- How to treat one small bump on the head that did not appear as a result of a blow? Atheromas, fibromas or warts may be located on the back of the head. This case often requires surgery.
- Enlarged lymph nodes are often the result of a recent illness (angina, infectious mononucleosis, tonsillitis, inflammation of the adenoids). Inflammation of the lymph nodes can be combated only by identifying the source of the disease. It is possible to use antibacterial or immunostimulating agents. As a last resort, surgery is indicated.
- Wen on the head is removed using cryodestruction. This treatment is effective and virtually painless.
Lumps that appear as a result of severe injuries require immediate medical attention. The following symptoms will indicate the seriousness of the situation:
- a sharp deterioration in health;
- dizziness and severe drowsiness;
- cramps in the limbs;
- constriction or dilation of the pupils;
- severe pallor of the skin;
- heavy bleeding from the wound;
- muscle paralysis.
Parents need to call a team of doctors, and until they arrive, place the child on his side and ensure peace. This position will prevent the child from choking if vomiting begins.
My son had a congenital hemangioma. For the first year we were observed by a surgeon, then he said that it was not growing and would go away over time. Now he is 8 years old, the hemangioma is practically invisible, I think that it will soon completely disappear.
For some reason, enlarged lymph nodes are in no hurry to return to normal on their own, as is written here. Usually they are simply cut out and the problem is solved that way. This happens to many boys, every second one walks around with scars on their necks
MORE ABOUT: Umbilical hernia: do we treat or wait?. What is an umbilical hernia and why is it dangerous?
Attention! All information on the site is provided for informational purposes only and is for informational purposes only. For all questions regarding the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, you must consult a doctor for an in-person consultation.
Today, the fundamental stone of treatment for lumps on the temples with temporal arteritis is treatment with corticosteroids. It should be started without delay, consisting of relatively high doses of steroids, preferably during hospitalization with intravenous methylprednisolone.
At the same time, antiulcer drugs (H2 receptor antagonists, proton pump inhibitors) are administered to prevent steroid-induced peptic ulcers, and potassium chloride is administered to supplement potassium in cases of increased urinary loss.
Bumps that go away and come back again
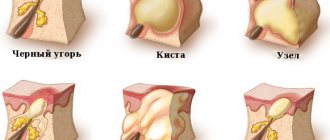
Recurring subcutaneous lesions should be a cause for concern. They indicate an infection that does not go away. A common cause of this problem on the face is a sebaceous cyst. These are purulent tubercles formed on the sebaceous glands or pores of the skin.
They are not cancerous and are caused by infection or blockage of the sebaceous glands. You should clean the skin area around the lump with antibacterial soap, apply a warm compress twice a day for 20 minutes for a week, and avoid scratching or squeezing as this increases the likelihood of infection.
You should consult a doctor for additional diagnostics if the swelling does not go away after doing all these steps.
Baby has a lump on his neck
All parents monitor the health and well-being of their little child, this is especially pronounced in the first months of his life. The appearance of any deviations from the norm often causes fear, anxiety, and sometimes panic, and even more so such as a bump on a baby’s head. Why might they appear, and what should be done in this case?
Bumps on a baby’s head usually appear with enviable regularity, because the child learns to sit, stand up, and walk, and at the same time, of course, it is difficult to do without bumps and falls. When hitting hard objects or falling, bumps are normal.
In addition to mechanical effects, other reasons can lead to the appearance of cones. For example, such a subcutaneous neoplasm may be a benign tumor. It is worth considering that such tumors are prone to growth and often grow over time. Lipomas, fibromas and warts most often appear in the head area of a small child.
Another name for lipoma, more common among people, is wen, since the basis of this neoplasm is sebaceous mass. There are many folk methods for treating such bumps in infants, one of them is applying a paste to the tumor, which consists of chopped boiled onions and laundry soap.
Fibroma is a neoplasm of a different type and nature; it is an accumulation of fibrous tissue of dense consistency; it is usually located on a kind of stalk. To cope with such a bump on the back of a baby’s head, lotions are used.
Warts are another common type of bumps in infants. Modern medicine easily eliminates this problem, using liquid nitrogen, electric current, a laser beam or another method.
According to popular belief, a lump on the back of the head in the lower part means that a person has magical abilities. But if such a lump in a baby is surrounded by severe swelling, cyanosis, pain or other signs of injury, then it is worth visiting a doctor. After all, such symptoms can accompany cracks and even fractures of the cranial bone.
Another cause of a lump on the back of a baby’s head can be a pilar cyst. It appears as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. Gradually, the secretion secreted by this iron accumulates, which is why a solid formation is formed on the baby’s head.
If a child has had a mechanical injury or blow, then immediately apply cold to the bump on the head; any cold object or compress will work well. Under its influence, the blood vessels narrow, which reduces swelling.
Ice can be used as a compress, but it should be wrapped in a thick towel to avoid frostbite on the skin. A salt compress is very effective in such cases; a towel or any piece of cloth is soaked in a high concentration salt solution.
Bumps in infants located on the back of the neck require special attention. Moreover, the younger the child is, the more urgently it is necessary to take action. A baby's prolonged crying in pain should be a direct indication for an immediate visit to the doctor.
Sometimes bumps in infants may appear behind the ears. Usually parents are frightened by such formations, and they begin to try to get rid of it in various ways. Some heat the lump, others give the child antibiotics, and others apply various agents to the tumor.
One of the most common causes of a lump behind the ear in a baby is enlarged lymph nodes. This may be caused by an illness in the recent past. When you have a cold or runny nose, bumps most often appear on both sides.
In this case, they do not require special treatment, since after some time the enlarged lymph nodes themselves will reduce their size to normal. Other causes of lymph node growth include infectious mononucleosis, tonsillitis, inflammation of the nasopharynx or adenoids, tuberculosis of the tonsils, tonsillitis and other diseases.
It is possible to determine that it was the enlarged lymph node that caused the appearance of a lump behind the ear of a baby by touch. The lymph node is practically immobile. And if the formation moves with the skin, then it is most likely a sebaceous cyst or fibroma.
The location of the lump in infants is also important. For example, a lump behind the ear located near the neck indicates damage to the sternocleidomastoid muscle located near the collarbone. A tumor directly behind the ear most likely means an enlargement or inflammation of the parotid gland.
In any case, you should not make a diagnosis yourself and determine the treatment method; for this it is better to consult a specialist. He will need all the possible information about the baby's lump, so he needs to keep an eye on it. The moment when the lump grows or shrinks is especially important.
MORE ABOUT: Knee arthropathy - what is it?
Lumps behind the ear of a baby should definitely be shown to a doctor. If a tumor forms in this area, a biopsy may be required. Of great importance for diagnosis is the appearance of the formation, its shape, density and time of occurrence. After making a diagnosis, the specialist will be able to determine the method of treatment required.
Removing tumors in this location is a rather complicated matter, requiring preliminary specialized examination.
The main cause of bumps on the forehead of a baby are mechanical injuries, blows and falls. The formation of a large lump after an impact is normal. Such tumors in most cases do not require seeking specialized medical care.
They represent swelling of the soft tissues as a result of a bruise, filling them with blood from damaged vessels and subsequent hematoma rising above the surface of the skin. The bumps on the forehead are the largest, because this is where a large number of small vessels pass. At the same time, this part of the head is more durable compared to the temple or back of the head.
First of all, immediately after a blow or bruise, cold should be applied to the damaged area or lubricated with a special ointment. The hematoma usually resolves completely within three weeks. If this does not happen, then you should seek medical help, as in this case a puncture and removal of the contents may be necessary.
In addition, a child who has received a blow to the head for any reason must be carefully observed, noting any unusual moments. With symptoms such as a noticeable decrease in reaction, lethargy, lack of reaction to light and different pupil sizes, sweating, drowsiness, constant moodiness, confusion, you need to consult a doctor.
Even more dangerous signs are convulsions, vomiting, loss of consciousness, speech impairment - all this is a reason to immediately call an ambulance, because these symptoms indicate a concussion. In cases of severe injury and a large lump, an x-ray may be taken to ensure there are no cracks in the skull.
Lumps on a child’s forehead may be an individual anatomical feature of the structure of a particular child’s skull. In this case, they are not dangerous and do not require any treatment. Most often, over time, the bump on the forehead smooths out and becomes less noticeable.
There are other types of bumps in infants that can appear on the forehead. These formations include benign tumors, characterized by an unchanged structure and gradual growth. One of the varieties of such tumors is wen (lipoma and atheroma).
They can occur on any part of the body, the reason for their appearance is clogging of the sebaceous glands. The distinctive features of these two types of neoplasms are the growth rate, as well as the fact that atheroma suppurates and becomes inflamed much more often. Both of these tumors are treated with surgery.
Another type of benign tumor that occurs on different parts of the body is fibroma. It can reach quite large sizes. The reasons for its appearance are still unknown. This lump does not cause significant harm to health, so if it is small in size, does not grow and does not interfere with normal life, it does not need to be removed. Otherwise, surgery is necessary.
Every mother worries about her baby, so any deviation from the norm can cause her anxiety and panic. The appearance of a lump on a baby's neck can greatly frighten parents. In this way, various diseases or conditions of the child may manifest themselves.
Small bumps on the neck in most cases accompany inflammatory or cold diseases, leading to an increase in temperature. In such cases, the appearance of a lump indicates that the baby's immune system is fighting the disease.
Such bumps in infants can occur due to various pathologies from a common runny nose to measles, mononucleosis and others. The lymph node increases in size and can be easily palpated, but the skin above it should not change its color, be hot, and the lump itself should not move.
A lump on a child's neck may be a fatty tumor. This can be determined by the rapid increase in its size, the unchanged condition of the skin over the bump and the mobility of the neoplasm itself. Metabolic disorders can lead to the appearance of fatty tissue, often due to poor nutrition.
Doctor's answer
It is difficult to judge the nature of this education from a distance. From the description it can be assumed:
- retention epidermal cyst;
- keratoacanthoma.
There are a number of other formations that fit the description, but they are less common.
Retention epidermal cyst (false atheroma) is a cavity formed in the sebaceous gland when it is filled with secretions due to obstructed outflow.
Atheroma is a dense, smooth, painless, flesh-colored formation. If the duct is not completely blocked, the false epidermal cyst may resolve spontaneously, but after a while it begins to grow again.
Factors provoking growth:
- increased activity of the sebaceous glands (manifestation – oily skin);
- increased secretion viscosity;
- increased sweating;
- thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin (especially with age).
As a rule, a small atheroma does not bother the patient.
- violation of the integrity of the wall with concomitant infection;
- cyst suppuration;
- compression of adjacent tissues by a cyst of significant size;
- malignant transformation (rare).
Treatment of epidermal cysts is surgical, with removal of the walls. When only the contents are removed, the atheroma is prone to recurrence.
Keratoacanthoma
Keratoacanthoma is a benign tumor of the hair follicle. It is a round or oval flesh-colored formation (sometimes with a reddish or bluish tint) with a depression in the center filled with horny masses. The tumor is observed mainly in elderly people.
Possible causes:
- a connection with infection with certain types of papillomavirus is suspected;
- hereditary predisposition;
- prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Keratoacanthoma can quickly grow up to several centimeters, then its size does not change for several months, after which regression occurs. Scars may remain at the site of the tumors. Sometimes the formation reaches gigantic proportions and does not regress for a long time.
The tumor is prone to malignancy (malignancy), therefore, if keratoacanthoma is suspected, a histological examination is necessary.
For accurate diagnosis and treatment, I recommend contacting a dermatologist or surgeon.
Swollen temples: causes, symptoms, possible problems and doctors' opinions
If your temples systematically swell and your overall health deteriorates, you should seek help from a doctor, since such a phenomenon may indicate that a serious illness is developing.
In this case, self-medication will provoke a deterioration in the patient’s general health.
Only after a thorough medical diagnosis, based on the results of the study, will the doctor prescribe an individual treatment regimen.
Features of temporal arteritis
With temporal arteritis, an inflammatory process develops that affects the arteries of the arms, neck, torso and head. Under such conditions, the temporal arteries are negatively affected. But they provide a complete blood supply to the eyes, optic nerves and head. There are several factors that can cause temples to swell:
- viral;
- genetic;
- ecological.
It is almost impossible to find out the exact cause of the pathology, but most often temporal arteritis is diagnosed in women after 50 years of age. Due to inflammation of the temporal artery, swelling of its wall may occur. Under such conditions, the delivery of oxygen and necessary elements through the bloodstream to the vessels of the head becomes difficult. If a blood clot forms, the person is at high risk of developing a stroke.
Among the main symptoms of this pathological condition are:
- swollen temples;
- painful sensations when pressing on the affected area;
- severe migraine;
- vision problems;
- weakness.
If your temples are swollen and another symptom of the disease appears, it is important to consult a doctor immediately, since the disease can progress and develop into more complex forms.
Therapy process
Treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor completely examines the patient.
The patient must undergo a complete clinical blood test to determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein.
Based on the identified symptoms of the disease, symptomatic treatment is prescribed, which will help improve the patient’s overall well-being.
If your temples are swollen, your doctor will prescribe medications. The effectiveness of treatment depends on timely contact with a specialist. At the initial stage of disease development, therapy is carried out much faster and more effectively with the help of medications.
During the treatment process, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs - glucocorticoids. Such drugs must be taken strictly according to the prescribed regimen. At certain intervals it is necessary to increase the dosage of medications.
After a few days of therapy, the patient’s general well-being will significantly improve, but in order to get a lasting result, drug treatment must be carried out for one and a half to two years.
All this time it is advisable to be under the strict supervision of the attending physician - this will help prevent the development of health problems.
Pain in the temple area can be caused by certain diseases. For example, migraine or increased intracranial pressure often cause an unpleasant symptom.
Why do temples swell? If discomfort occurs in an elderly person, then it is necessary to exclude arterial hypertension and serious pathological changes in the brain. When the body is intoxicated, the patient often feels a feeling of heaviness in the back of the head.
In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, since self-medication can only cause harm. Most often, pain in the temples occurs when:
- atherosclerosis;
- flu;
- alcohol intoxication;
- infectious sore throat;
- stroke;
- arterial hypertension;
- temporal arteritis;
- migraine and cluster pain;
- neuralgia;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- osteochondrosis;
- osteoarthritis;
- hormonal disorders;
- during pregnancy or menopause;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
After mental or emotional stress, pain in the temples may occur. Stress, regular lack of sleep, and taking certain medications provoke a deterioration in overall health. To prevent the development of an unpleasant symptom, it is recommended to regularly visit a doctor and not eat smoked foods, fast food and excessively salty foods.
What to do if your temples are swollen and painful?
To improve your overall well-being, you need to seek help from a neurologist. The following activities can help speed up the healing process:
- taking medications;
- performing acupressure;
- use of folk remedies;
- complete rest;
- regulation of diet.
If such recommendations do not help get rid of the unpleasant symptom, then you need to take a medication that will help temporarily eliminate pain in the temples.
What will help?
If the temple and eye are swollen, treatment must be started immediately. The medicine should only be prescribed by a doctor. Tablets can cause the development of health problems if they are not taken as recommended by a doctor.
Thanks to the anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and analgesic effect, you can eliminate:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- weakness;
- drowsiness.
The most effective means
If the temples are swollen on both sides, it is recommended to use the following medications:
- Analgin contains metamizole sodium. The drug effectively eliminates the inflammatory process and relieves pain, helps relieve a migraine attack. Among the main advantages of the drug are its affordable price and effectiveness. There are also disadvantages - the drug has a detrimental effect on the liver.
- “Citramon” is one of the most effective blood-thinning and analgesic drugs. The medicine contains caffeine and acetylsalicylic acid. The medication is effective and versatile, but has a number of contraindications for use.
- Ibuprofen effectively eliminates inflammation, relieves pain and relieves fever. Often, specialists prescribe medicine in the treatment of osteochondrosis or vascular inflammation. Among the main advantages of the medicine are its effectiveness and affordable price. Disadvantage – bad effect on the kidneys.
- “Imet” is one of the best non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Effectively relieves pain, dilates blood vessels and eliminates spasms. Ibuprofen is the main active ingredient. This is a universal drug that will help improve the patient’s well-being in the shortest possible time.
It is not recommended to systematically take medicinal painkillers to improve well-being, since the disease must be cured, and not just masked. Any medications can aggravate the course of the disease if the doctor’s instructions are not followed.
Note to the patient
It is difficult to answer the question of what swollen temples of the head indicate and how to cure this pathological condition. As noted earlier, there are many diseases that can trigger the appearance of an unpleasant symptom.
Only after a thorough medical diagnosis of the patient can a specialist make a diagnosis and prescribe an effective treatment regimen. Based on the laboratory tests obtained, the doctor will prescribe effective medications. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate.
This is a truly serious problem that requires a competent approach and comprehensive treatment.
The duration of treatment and dosage of drugs is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the unpleasant symptoms and the severity of the disease.
If your temples become swollen when chewing, you should visit a doctor immediately. This symptom often occurs with hypertension. Only after making a diagnosis will a specialist prescribe suitable medications.
Self-medication in some cases can lead to serious health problems.
Source: //FB.ru/article/453485/opuhli-viski-prichinyi-simptomyi-vozmojnyie-problemyi-i-mneniya-vrachey
First aid
First aid is advisable if a lump appears and the temples swell after an impact. It is necessary to follow the victim's breathing and call an ambulance. In all other cases, in order to get rid of a lump, an examination is required to identify the pathology.
Surgeon of the first category, candidate of medical sciences.
Areas of professional interests: — Providing emergency and planned surgical care — Hernia repair with alloplasty — Removal of benign formations — Minor purulent surgery — Operations for ingrown toenails — Use of electrocoagulation scalpel during operations
Consultation
Hello, I am 33 years old, mother of 3 children. About six months ago, a lump began to grow on the right side, just above the temple, 2 cm above the eyebrow, but not in the hair. Now the diameter is 1 cm, hard, under the skin, as if attached to the bone. Not disturbing, but noticeable. What could this be and how serious is it?
Guaranteed response within an hour
Clinical manifestations
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory reaction following the destruction of the structure of the node, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Swelling and swelling around the ear. The visible manifestation of edema is an increase in the size of the node and the appearance of a lump near the auricle. In addition, dysfunction of the lymphatic system can cause lymph retention, which leads to puffiness.
- Pain. It occurs as a result of compression of nerve receptors in the skin and tendons by swelling. The sensitivity of the receptors increases due to the influence of biologically active substances released during cell destruction. During this period, the pain may be pulsating and bursting. Then sensitivity decreases and is felt only when pressing on the node or when palpating the site of inflammation.
- Hyperemia. Visually detected by redness of the skin over the enlarged node, which is associated with dilation of blood vessels and stagnation of blood.
- Local increase in temperature. Increased blood flow and activation of the cellular process leads to an increase in the temperature of the integument in the affected area.
Depending on how exactly the disease develops, different clinical manifestations are observed, both acute and chronic.
- Chronic productive type. The “bump” grows slowly and almost imperceptibly over several months (2-3). The process may either accelerate or slow down, but the swelling does not subside completely. The appearance of the skin remains unchanged, and the tissue is not fused to the underlying tissue. The lymph node is mobile and when pressed it causes little or no pain.
- Chronic abscess type. The next stage in the development of the disease. A limited cavity filled with pus appears in the thickness of the lymph node. The lump thickens, becomes painful and begins to fuse with the underlying tissues, which reduces its mobility. The general condition of the patient against the background of intoxication also worsens.
- Acute serous-purulent type. The inflamed soft, elastic lymph node increases to one and a half to two centimeters, which is almost not accompanied by painful sensations and does not affect the condition of the skin (slight redness may occur). Both the “ball” itself and the skin are not welded to the underlying tissues and are mobile.
- Acute purulent type. Associated with an abscess (filling of an organic area with pus). Soreness ranges from moderate to severe. The skin over the formation turns red, and the soft tissue around it swells. The “bump” itself gradually loses its mobility, fusing with the underlying tissues. At the same time, the patient’s general well-being practically does not change.
- Acute adenophlegmon. A form of the disease that occurs when pus leaks from the capsule into the surrounding areas. Accompanied by intense throbbing pain of a diffuse nature. The general condition also worsens (fever, weakness, aches, lack of appetite).