The list of progressive muscular dystrophies (PMD) includes myodystrophies:
- pseudohypertrophic Duchenne;
- pseudohypertrophic Becker-Keener;
- Emery-Dreyfus-Hogan;
- Rottauf (fibrosing myopathy);
- juvenile Erba-Rota;
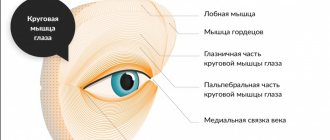
- ocular (Graefe's ophthalmoplegia);
- humeroscapulofacial (Landouzi);
- oculopharyngeal;
- Dreyfus;
- mitochondrial.
Clinical features
Symptoms of the disease appear up to 5 years of age. The earliest signs of Duchenne muscular dystrophy include delayed development of speech and walking.
This is followed by gradual weakening and loss of the hip and pelvic muscles.
The victim has difficulty climbing stairs from a chair.
Over time, a noticeable thickening of the lower leg muscles is observed.
Find out more All features of Klippel syndrome Trenaunay Weber
With progressive involvement of the muscles of the chest, shoulder, and back, a typical posture can be seen.
The child has difficulty balancing and constantly falls. Soon, he begins to walk on his toes due to the contraction of tissue on the heels.
The shoulder blades, knees, hips, and spine are affected as the disease progresses, leading to scoliosis (curvature of the spine).
The victim is limited to a wheelchair until he is 12 years old.
Although most patients have a normal level of intelligence, signs of mental retardation may be observed in a small percentage of cases.
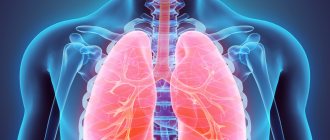
The muscles of the heart and lungs also suffer, leading to death from respiratory or heart failure.
Once the diaphragm/respirator muscles become involved, the patient finds it difficult to breathe and is dependent on a machine for breathing support.
Prognosis for muscular dystrophies
The prognosis of hereditary myopathies depends on the form. Since in most patients the disease is steadily progressive, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Patients with pseudohypertrophic Duchenne muscular dystrophy usually die in the 3rd decade of life, most often from progressive heart failure.
With pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy Becker-Keener and muscular dystrophy Emery-Dreyfus-Hogan, patients usually live up to 40-60 years. With Rottauf-Mortje-Beyer muscular dystrophy, patients often live up to 30-50 years. The article was prepared and edited by: surgeon I.B. Pigovich.
Video:
Healthy:
Related articles:
- Muscular dystrophies in children Muscular dystrophies in children are a group of hereditary diseases that are characterized by progressive muscle weakness in the absence of…
- Increased levels of transaminases in muscle diseases in children Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are markers of liver damage, but to a large extent these enzymes...
- Eye myopathy Eye myopathy (ocular myopathy, oculo-pharyngeal myopathy) is manifested by ptosis and limitation of…
- Lambert-Eaton syndrome Lambert-Eaton syndrome is caused by a disorder in the mechanisms of acetylcholine release from presynaptic vesicles. It is observed in cancer patients, more often...
- Myopathies Myopathies include hereditary diseases with progressive muscle atrophy, accompanied by increasing weakness in the limbs,...
- Myopathies in children The following forms of congenital myopathies in children are distinguished: disease of the “central rod” (Shaya-Mezhi); nemaline myopathy; myotubular (centronuclear)…
Diagnostics
Clinical examination
Clinical examination raises suspicion of DMD
Creatinine phosphokinase assay
When muscle cells die, the affected ones release the enzyme creatinine phosphokinase (CPK) into the blood. Thus, patients with Duchenne disease have high levels of the enzyme in their blood (20 times the upper limit of normal). This test was the only available method to detect the presence of the disease until 1982.
Electromyography
A test that tests the electrical activity of muscles. In Duchenne dystrophy, the affected muscles show decreased electrical activity.
Muscle biopsy
A test in which a small part of the affected muscle is examined under a microscope for changes.
Dystrophin assay
Because patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy have a defective gene, there is an abnormality in the production of the protein dystrophin. As a rule, its complete deficiency is observed in 99% of victims. The test is used to distinguish DMD from other forms of dystrophy.
This form of diagnostic tool provides accurate results and can therefore be used to make a diagnosis.
Causes
The disease is hereditary, linked to the X chromosome, so boys are almost always affected. Girls are carriers of a pathological gene (boys rarely survive to adulthood, and, moreover, are usually sterile). A change in the structure of the gene responsible for the synthesis of the dystrophin protein occurs on the chromosome.
Although the content of dystrophin in skeletal muscles is extremely small (thousandths of a percent), without it necrosis of muscle tissue quickly develops and progressive muscle dystrophy develops. If the gene is damaged in a site that completely destroys the synthesis of the dystrophin protein, Duchenne dystrophy develops. When insignificant parts of the protein are involved in the process, the disease takes the form of Becker's dystrophy.
Treatment of DMD
Despite the disease being described as early as 1868, there is no reliable treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
However, it is possible to slow the progression of the disease and preserve muscle strength and joint function by allowing the patient to walk and sit.
Find out more MDS, diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome: diagnosis and treatment
Because DMD affects almost every muscle in the body, those involved in the treatment process face a number of challenges. Effective management of a disabling disease requires a multidisciplinary approach.
Various forms of treatment are used, including light braces, physical therapy, pulmonary therapy (breathing support), and surgery.
The choice of specific treatment largely depends on the clinical condition of the patient.
After identifying the gene, researchers developed animal models that mimic the disease. Such clinical experiments improved previously existing knowledge about the disease.
Active research is being conducted to test whether injecting normal muscle cells (from healthy patients) or introducing a corrected form of the dystrophin gene into muscle cells (gene therapy) can reverse the disease process.
Treatment of muscular dystrophies
Primary treatment is aimed at slowing the rate of development of the disease and maximizing the patient’s ability to self-care.
PMD treatment tactics:
- diet therapy in order to avoid the development of excess body weight in the patient;
- Exercise therapy and physical activity, in particular, to maintain the functions of supporting joints and prevent contractures;
- breathing exercises;
- drug therapy;
- socio-psychological rehabilitation;
- orthopedic care.
In some forms of muscular dystrophy, in particular in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, the use of glucocorticoids can sometimes delay the onset of immobility of the patient for years. Since such treatment is long-term and usually accompanied by many complications, judicious administration of glucocorticoids is necessary. For PMD, prednisolone 1-2 mg/kg in the morning, every other day is used (taking into account possible contraindications). Prednisolone can also be taken daily for muscular dystrophy (single dose in the morning at 0.75 mg/kg/day). The authors also suggest using a drug of the same group - deflazacort, which has fewer side effects, at approximately the same dose (the effectiveness of 6 mg of deflazacort corresponds to 5 mg of prednisolone). The duration of treatment depends on the effectiveness and severity of side effects of the drug.
Symptomatic and restorative therapy is indicated. In particular, the use of adenosine phosphate, triphosadenine, vitamin E, coenzymes (for example, cocarboxylase), non-hormonal anabolic agents (ethylthiobenzimidazole, orotic acid), inosine, and potassium preparations is recommended. It should be borne in mind that there is no evidence of objective evidence of the effectiveness of these drugs.
Recommended drug treatment regimen for PMD:
Prednisolone orally (in the morning) 1-2 mg/kg/day every other day, the duration of therapy is determined individually, or Prednisolone orally (in the morning) 0.75 mg/kg/day daily, long-term or Deflazacort orally 6 mg, long-term.
Methods for diagnosing Duchenne-Becker disease
A neurologist diagnoses the disease. To confirm the presence of pathology, a number of studies are carried out:
- DNA test. Allows you to accurately determine the presence of a gene mutation.
- Biopsy of muscle tissue. Rarely used, it involves taking a sample of muscle fibers and determining the presence of dystrophin using a special dye.
- Prenatal testing. Done at 11 weeks of pregnancy to identify the risk of neuromuscular disorders, especially if one or both parents are carriers.
- Fetal blood collection. It is carried out at the 18th week of pregnancy, used in extreme cases by a geneticist.
Attention! Expectant parents should be careful with tests during pregnancy. However, if such a need arises, then preference should be given to early testing in order to minimize the likelihood of miscarriage.
Prognosis and prevention
To prevent complications of the disease, the patient must lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and spend enough time in the fresh air. It is prohibited to restrict a person’s movements and keep him on bed rest. Without at least minimal attempts at walking, muscles are destroyed very quickly.
Due to the fact that with Duchenne dystrophy, not only skeletal muscles, but also the heart and respiratory organs are quickly damaged, a person cannot live long in this condition. Even if they take medications that alleviate the condition, patients rarely live beyond 35 years. More than 50% of them die in adolescence, without appropriate help - even faster.
With mechanical ventilation, heart support medications, and the use of a wheelchair and feeding tube, some patients live 40 to 50 years. However, they need constant care and supervision, as they cannot independently perform basic hygiene procedures or even ask for help.
It is impossible to cure Duchenne muscular dystrophy, but medications and orthopedic drugs will help alleviate the patient’s condition. Due to significant damage to internal organs, patients usually die at a young age. But modern advances in the use of stem cells make it possible to hope for an increase in the average life expectancy of people suffering from this disease.
Treatment of Duchenne myopathy
Currently, there is no cure for this disease. However, there are a number of methods that can alleviate the patient’s condition at different stages of myopathy development and, perhaps, somewhat slow down the progression of the disease.
Treatment methods for certain age groups are described below, but often when treating one patient it is necessary to combine several treatment methods at once.
Preschool patients
Children with Duchenne myopathy usually do not yet need treatment at this age. Parents may be offered:
- More information about Duchenne myopathy. The doctor will talk with the parents and talk in detail about how this disease will affect the child’s condition, and what the patient’s life expectancy is (most people with this diagnosis only live to be 20-25 years old). If desired, parents can turn to other specialists (for example, a psychologist), as well as support groups;
- Recommendations regarding acceptable physical activity for a child;
- Genetic consultation for family members. Many parents want to know if they are carriers of the Duchenne gene. This is especially important for those who plan to have a child again in the future.
Already at preschool age, the child begins to be regularly examined so that, when necessary, treatment can be started on time.
Patients aged 5-8 years
Children this age may require support for their leg muscles. For example, they may be advised to wear ankle splints or longer shin splints at night.
Symptoms
Symptoms begin to appear before the age of three. The child begins to experience increased fatigue, which occurs quite quickly. In addition, it is noted:
- Developmental delay;
- Difficulties with walking and mastering this skill (often the child begins to walk on his toes);
- An attempt to stand up is accompanied by active assistance with the hands, which is called Govers' symptom.
The latter occurs due to the fact that the leg muscles cease to cope with the load placed on them.
The disease gradually progresses and by the age of 12 the patient usually needs crutches. By the time he was 16-18 years old, he was already confined to a wheelchair.
Disease prognosis
During this period the following signs of Duchenne muscular dystrophy occur:
- Inability not only to stand up, but also to sit down independently;
- Skeletal deformity;
- Pseudohypertrophy of the calf muscles;
- Difficulty moving your arms;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Cardiomyopathy and other heart disorders;
- Deterioration in the functioning of the respiratory muscles;
- Less commonly, mental disorders.
If the disease has already taken over the heart and lungs, then there is no way to help such a patient. That is, the disease is irreversible and leads to death in a short time.
The photo shows the symptoms of myodystrophy
Therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: old and new approaches
According to Olson, the main difference between the new strategy using a vector containing genome editing components and other therapeutic methods is that it addresses the cause of the disease. What other approaches are scientists developing?
Figure 3. Animal models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. a — Manifestations of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice and dogs. Above: mdx mice only show symptoms in old age and are prone to forming rhabdomyosarcomas, tumors of muscle origin. Mice with knockouts of the utrophin/dystrophin and integrin/dystrophin genes are significantly smaller than their wild-type counterparts (BL10 and BL6). Below: manifestations of the disease in a five-month-old sick dog. Differences between healthy and sick two-year-old dogs. b — Comparison of life expectancy of healthy and sick people, dogs and various strains of mice.
[17]
One promising approach is cell therapy . Although experiments with intramuscular injection of myoblasts from healthy donors have failed, technologies using stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have so far been successfully tested in models of not only Duchenne muscular dystrophy, but also Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, spinal muscular atrophy, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , autism and schizophrenia [14–16]. For example, in 2013, researchers from Boston Children's Hospital's Stem Cell Program used a mixture of three small molecules (forskolin, basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF and glycogen synthase kinase inhibitor-3) to reprogram iPSCs from the skin of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy into muscle cells , which then successfully took root in mice. Cardiomyoblasts and neurons have now been obtained from iPSCs [2].
Other studies show that restoring normal levels of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis , which is reduced in patients due to impaired NO synthase (nNOS) activity, reduces inflammation, increases the activity of intrinsic stem cells, and reconstructs skeletal muscle morphology and function [3].
Givinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor that slows disease progression in a mouse model, is already in phase II clinical trials.
This massive experimental attack on Duchenne muscular dystrophy gives us hope. Will CRISPR/Cas9 technology lead the way in developing therapies that can be adopted by clinicians? Perhaps the publication of similar works on other diseases is not far off, where it is necessary to get rid of mutations in a single gene? We will learn this from the upcoming issues of Science (as well as other honorable journals).