08.05.2017
Among the types of benign brain tumors, about 10% are adenomas formed in the cells of the pituitary gland.
The role of the pituitary gland in overall health cannot be underestimated.
This gland controls the production of hormones and the development of the entire body. If a pituitary adenoma begins to form and grow, the activity of a number of organs and systems is disrupted - the endocrine and nervous systems suffer, vision decreases, and brain activity is complicated.
Symptoms of adenoma will depend on the hormonal function of the tumor. In particular, if the adenoma is of a special type, then patients complain of a sharp deterioration in vision. Tumors of a hormonally active type cause specific hormonal disruptions. Rarely, when a pituitary adenoma is manifested by an acute attack of headache and impaired consciousness - such a condition can cause involvement of the hypothalamus in the pathological process.
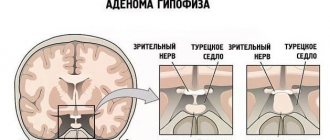
To choose the right method of therapy, the doctor must conduct a diagnosis, determine the parameters of the adenoma and the nature of its growth, localization in the sella turcica, hormonal activity and the degree of influence on neighboring areas.
Indications and contraindications
Transnasal removal of a pituitary adenoma is prescribed in advanced conditions, when drug treatment is powerless and does not lead to positive results. The main advantage of performing surgery through the nose is complete visualization of the tumor body from all sides and the minimally invasive nature of the technique.
Unfortunately, despite the slow progression of the pathology, patients often present at a late stage, when:
- pituitary gland dysfunction is clearly expressed;
- there is a hormonal imbalance;
- There are unpleasant signs of the disease: atrophy of brain cells, severe headaches, sleep disturbances, fatigue, memory impairment, decreased concentration.
If a pituitary adenoma is suspected, patients are asked to undergo a full diagnosis, including the following examination methods:
- angiography;
- taking fluid from the spinal cord for study;
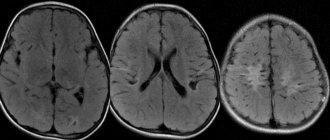
- CT, MRI;
- radiography;
- complete blood count and hormone test.
Based on the results of a consultation of specialists and interpretation of instrumental examinations, an appropriate operation using an acceptable technique will be prescribed.
If a malignant tumor is detected, then endoscopic removal of the adenoma becomes ineffective. Doctors will select alternative and more effective methods of surgery - radiochemotherapy.
Pituitary adenoma - advantages of treatment at the Top Ichilov clinic:
- highly qualified specialists in the field of neurosurgery and endocrinology;
- the latest high-precision laboratory tests;
- diagnostics at an advanced level using innovative techniques.
The following treatment options for pituitary adenoma are available:
- operational;
- radial;
- complex.
After any of the listed treatment options, the patient needs rehabilitation, as well as observation by an endocrinologist.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(16 votes, average: 3.6 out of 5)
Methods
Removal of a pituitary adenoma directly through the nose is carried out using the following methods:
- transsphenoidal by inserting an endoscope into the incision under the upper lip;
- transseptal - insertion of the device through an opening in the nasal septum;
- transnasal - immersing the endoscope into the nasal cavity at the back.
Each of the operations is minimally invasive and is performed under general or local anesthesia. Duration takes no more than 3 hours. The technique is selected taking into account the location and size of the tumor. The procedure is performed transnasally when the adenoma is localized directly in the sella turcica or near it, but extending beyond the limits by no more than 25 mm.
In particular, when removing an adenoma, other alternative methods are applicable:
- plastic surgery;
- radio emission;
- cryodestruction.
Minimally invasive intervention using an endoscope is now successfully performed by specialists to operate on hard-to-reach areas of the pituitary gland.
The main thing is to prevent the adenoma from becoming a malignant neoplasm and the tumor growing in size. The space is quite limited at the location of the pituitary gland, and an increase in tumor size can lead to serious complications: injury to the optic nerve, malfunction of many systems and organs.
Chromophobe pituitary adenoma
Which adenomas cannot be removed?
Those adenomas that respond well to conservative therapy, as well as those whose removal may pose a serious risk, are not removed. Some pituitary adenomas may not require treatment at all, in which case only medical supervision in the form of regular examination is recommended. These include hormonally inactive adenomas no larger than 1 cm in size (microadenomas).
The group of adenomas that can be treated conservatively and therefore do not require surgery includes prolactinomas (tumors that produce lactogenic hormone).
Removal of large adenomas located close to the cavernous sinus (plexus of cerebral vessels) and oculomotor nerves is associated with a high risk. In this case, the tumor is only partially removed (subtotal resection), then subjected to radiotherapy.
The essence of the transnasal method
Many modern clinics today have powerful automated equipment with lamps to ensure an almost 20-fold increase in the tumor body and the operated area. Thanks to the innovative method, it is possible to perform surgery to remove a pituitary adenoma through the nasal cavity, without opening the skull area. But the transanasal technique is effective in the presence of a small tumor, no more than 10 mm in diameter. It is a small tumor that can be quickly removed through the nose. With a strong increase in size, it is hardly possible to do without operating on the gland together with nearby tissues, so the operation often leads to dysfunction of the brain.
Taking into account the size of the tumor, it is possible to insert an endoscope into one or both nostrils at once, which significantly reduces the invasiveness of the procedure. To approach the sella turcica, specialists use a drill: they cut the septum and make holes in the front of the sinus. When the bottom of the sella turcica is clearly visible, trepanation of the tumor is performed, removing it in parts or all at once.
Possible complications during surgery
Modern techniques for performing brain surgery make it possible to reduce the number of surgical and postoperative complications to a minimum.
However, complications during surgery for pituitary adenoma cannot be completely excluded:
- injury to the pituitary gland, causing disruption of its activity;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- liquorrhea (leakage of brain fluid);
- compression of the optic nerves;
- secondary diabetes insipidus.
How is it carried out?
The operation is performed under anesthesia. Duration - no more than 3 hours. The flexibility of the endoscope allows you to make a hole in the upper walls of the sphenoid sinuses of the nose, thereby opening the dura mater and removing the tumor piece by piece. In case of severe bleeding, it is additionally stopped using electrocoagulation.
Thanks to the flexibility of the endoscope, it is possible to insert the tube into the nasal cavity at different angles for a more complete view of the cartilaginous septum and the opportunity for specialists to get as close as possible to the location of the tumor. The location of the adenoma directly above the sella turcica involves first, during the operation, separation of the tumor from the pituitary gland, then manipulation to lower the saddle down and, lastly, drilling holes in the bone tissue, removing the tumor-like body from the body, covering the place with synthetic materials or fixing it with a special bioglue.
Radiosurgery
This method is suitable for removing pituitary tumors and ensures minimal damage. The accuracy of the effect is 0.5 mm - this is why it becomes possible to perform a delicate effect without traumatizing neighboring nerve tissues. The radioknife performs the removal in one go, but you need to prepare for the procedure - the patient visits the clinic several times to create a special model based on MRI and computed tomography. The 3D image of the tumor is used as a task for the adenoma removal machine.
The operation begins with careful fixation of the patient to prevent accidental movements during the procedure. The removal device operates at a distance, sending waves to the location of the adenoma. In this case, painful sensations are excluded, and after the procedure there is no need to stay in the clinic. This eliminates unpleasant consequences that may occur after therapy with other methods.
Manifestations and diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of this disease are related to the type of adenoma the patient has. There are ophthalmo-neurological manifestations and endocrine-metabolic ones. The first include:
- visual disturbances, double vision;
- headache, often in the temples or forehead, for which painkillers are not effective;
- decreased vision, even to the point of blindness.
As the tumor grows, it compresses nearby tissues. With large adenomas, vision decreases more due to compression of the optic nerves by the tumor. Already with a tumor of 1-2 cm in diameter, atrophy of the optic nerves and complete loss of vision can occur.
Endocrine metabolic symptoms vary depending on which hormone malfunctions due to tumor development. The most common type of prolactinoma is prolactinoma, in which women's menstrual cycle is disrupted, body hair begins to grow in a male pattern, body weight increases, infertility develops, and sexual activity decreases. In men, the symptoms are usually less pronounced, but enlarged mammary glands, a drop in libido, and impotence are observed.
Corticotropinoma, in which the balance of adrenocorticotropic hormone is disturbed, is dangerous because more often than other adenomas it becomes malignant and metastasizes. Its manifestations are associated with Cushing's disease:
- purple stretch marks on the stomach and thighs;
- obesity;
- spots (pigmentation) on the skin;
- baldness in men and body hair growth in women;
- mental disorders are possible.
Somatotropic adenoma is associated with growth hormone. In pediatric patients, it causes gigantism, and in adults, acromegaly (a growth disorder in which the feet and hands appear enlarged compared to the proportions of the rest of the body). This pathology can be accompanied by diabetes and obesity. With gigantism, on the contrary, growth is high, and the functions of internal organs, which do not have time to increase with the body, are disrupted. Both forms can be accompanied by thyroid diseases.
Thyrotropinoma, directly related to the functioning of the thyroid gland, manifests itself with symptoms of hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. The patient's hands are shaking, he is emotionally unstable to the point of tearfulness, cannot tolerate hot weather, is losing a lot of weight, and has tachycardia.
Gonadotropinoma is an adenoma with the production of sex hormones. Its main manifestations are associated with decreased sexual function, but decreased vision and headaches are also noticeable.
With any type of large tumor, fatigue, weakness, suppressed libido, impaired sense of smell and signs of thyroid dysfunction are observed. This causes compression of the pituitary body, disrupting the production of all hormones.
Craniotomy
This method involves opening the frontal bones or the part under the temporal bone. The patient is usually placed on his side to avoid pinching the veins and arteries that transport blood to the brain. An alternative position is on your back. The patient's head is securely fixed during the operation.
Preparation involves several stages - hair removal in the area to be treated, disinfection. The doctor applies markings to the skin showing the location of blood vessels and important structures. Next, general anesthesia is provided and the operation begins - tissue incision and bone cutting. During a craniotomy, the surgeon puts on special glasses - this way the doctor carefully examines all the nerve structures and blood vessels.
If the pituitary gland is deep, an incision is made in the dura mater. The adenoma is removed using electric tweezers or the tumor is pulled out using an aspirator. In rare cases, the tumor grows inside the pituitary gland; therefore, the entire gland must be removed. After this, the bone flap is returned to its place, and sutures are applied.
This operation requires a stay in intensive care after the anesthesia wears off—to avoid complications, doctors constantly monitor the patient’s condition throughout the day. Next, hospitalization is provided for a week or up to 10 days.
Visual impairment and recovery after adenoma removal
Many patients are waiting for the restoration of vision, which was impaired due to the adenoma. It is impossible to name the exact period, but this process depends on the development of the adenoma and the time of deterioration in visual function. For example, if the diagnosis was not timely, and the patient delayed treatment for a long time, the prognosis cannot be called optimistic. Vision may not be restored to its original state.
And if you consult a doctor immediately, then you can give a favorable prognosis - within two weeks after the operation, visual acuity should return to its previous level.