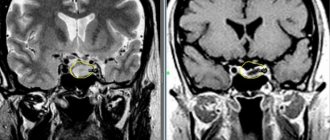
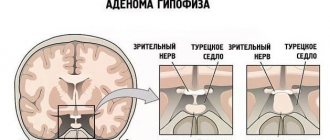
Under the cerebral cortex there is a depression (sella turcica), which houses the endocrine gland - the pituitary gland. This department is responsible for the production of multiple protein hormones and the body's metabolism. Changes in its activity and structure inevitably lead to endocrine diseases, which include pituitary adenoma. According to the international classification of diseases (ICD-10), it belongs to benign neoplasms.
The tumor is concentrated, in most cases, in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. In terms of prevalence among other brain tumors, it is located on the list after meningioma and glioma. It is believed that at least 15% of the world's population is affected by this disease, and most patients are women aged 30 to 40 years.
Pituitary adenoma is characterized by a fairly slow growth and small size - so small that many people go undiagnosed for years, especially if its symptoms are not expressed for a long time.
Tumors are divided into those that produce hormones and those that are hormonally inactive (incidentalomas). Among the first, those that produce prolactin (prolactinomas) are common. In Itsenko-Cushing disease, during diagnosis, a neoplasm is discovered that increases the level of adrenocorticotropin (corticotropinoma develops). Acromegaly, the symptoms of which are expressed by expansion and increase in the size of individual parts of the body (limbs, skull), is caused by the production of the hormone somatotropin (under the influence of somatotropinoma). The production of thyroid-stimulating hormone by thyrotropinoma leads to dysfunction of the thyroid gland. Gonadotropinoma is to blame for the increased synthesis of sex steroid hormones.
Also, neoplasms of the pituitary gland vary in size: there are micro- and macroadenomas.
Another classification is based on the location of the tumor relative to the sella turcica. A pituitary adenoma can be located in the saddle itself, without protruding beyond its edges (endosellar neoplasm). But what often happens is that it goes beyond the boundaries of the hole and grows:
- upward (and is called an endosuprasellar tumor);
- down (endoinfrasellar);
- sideways, destroying the wall (endolaterosellar).
Classification of adenomas according to various criteria is of key importance for choosing the method by which treatment will be carried out.
Classification
In clinical neurology, pituitary adenoma is divided into:
- hormonally inactive, in which there is no increased production of hormones;
- hormonally active, causing abnormally increased secretion of biologically active substances.
The first type of adenoma is treated by a neurologist, but the second requires the intervention of an endocrinologist. Benign pituitary tumors are divided into groups depending on which hormone caused their formation:
- Prolactinoma is a benign tumor formed from prolactotrophs. A concomitant deviation of this disease is increased production of the hormone prolactin.
- Gonadotropinoma is a neoplasm formed by gonadotrophs. Accompanied by elevated levels of LH and FSH.
- Somatotropinoma. It is formed from somatotrophs and is accompanied by a jump in growth hormone levels.
- Corticotropinoma is a benign neoplasm formed from corticotrophs. Accompanied by increased synthesis of ACTH.
- Thyrotropinoma. A benign tumor formed from thyrotrophs. With this disease, there is an increased production of TSH.
Hormonally inactive pituitary adenomas include oncocytoma and chromophobe adenomas.
Depending on the size, tumors are divided into:
- picoadenomas having a diameter of less than 3 mm;
- microadenomas with a diameter of up to 10 mm;
- macroadenomas with a diameter greater than 10 mm;
- giant adenomas – from 40 mm.
Depending on the direction of growth, adenomas are:
- endosellar (the neoplasm is localized in the cavity of the sella turcica);
- infrasellar (the tumor grows downwards, reaching the sphenoid sinus);
- suprasellar (adenoma grows upward);
- retrosellar (tumor grows posteriorly);
- lateral - spread to the sides;
- anesellar - the adenoma grows anteriorly.
If the tumor grows in different directions, it is classified according to the direction in which it grows.
Therapy methods
There are many ways to treat microadenoma. Usually the doctor selects several methods, based on the characteristics of the tumor, the degree of its hormonal activity, the patient’s health status and other factors.
The following approaches to adenoma treatment have been developed:
- observation. If the tumor is small, does not grow in size, and does not affect the patient's hormonal levels, observation may be the optimal strategy. The patient should regularly undergo an MRI or X-ray of the skull, as well as donate blood for hormones. If during follow-up there is no negative dynamics, other treatment methods can be abandoned;
- drug treatment. Taking special medications is recommended if the patient is diagnosed with somatotropinoma or prolactinoma. The doctor selects drugs that block the production of hormones, as a result of which the patient’s condition returns to normal. Additionally, symptomatic treatment is prescribed, for example, immunomodulators and calcium supplements for Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, painkillers to relieve pain in acromegaly, etc.;
- radiosurgery. This method is relatively new. Thanks to radiosurgery, it is possible to destroy a tumor, while avoiding both extensive surgical intervention and destruction of tissues adjacent to the tumor, which is extremely important when performing brain surgery. Removal of microadenoma is carried out through targeted exposure to radiation;
- surgical intervention. This method is the most traumatic. It is used only if other methods are ineffective or are not suitable for a particular patient. The pituitary gland is accessed in one of two ways: through the nasal passages and by opening the skull. For microadenoma, the first option is safer, and therefore the most preferable. Surgical treatment is often used if a microadenoma is detected in a pregnant woman for whom radiosurgery and drug treatment are contraindicated.
Reasons for development
The causes of the disease have not been fully established, but there are several hypotheses for its development:
- Internal defects. According to this theory, when genes are damaged in one of the pituitary cells, its transformation into a tumor is provoked, which then begins to grow.
- Violation of the hormone-producing function of the pituitary gland. The amount of hormones produced is regulated by statins and liberins. Against the background of a decrease in the former and an increase in the latter, hyperplasia of the glandular pituitary structures develops. This is the root cause of the development of the tumor process.
People at risk include:
- survivors of TBI;
- those suffering from neuroinfections (poliomyelitis, encephalitis, meningitis, etc.);
- undergoing hormone therapy (this is especially true for women who have been using COCs for a long period of time).
An unfavorable course of the gestational period with mechanical impact (trauma) on the fetus can in the future lead to the development of this disease, both in childhood and in adulthood. Despite the fact that pituitary adenoma is a benign neoplasm, some of its varieties can develop into cancer over time.
Microadenoma and pregnancy
Prolactinoma, gonadotropinoma or corticotropinoma can lead to secondary infertility. If a woman manages to become pregnant with such a microadenoma, then she needs to be constantly monitored by an endocrinologist. After the baby is born
Obstetricians and gynecologists advise immediately switching him to infant formula and interrupting lactation. Breastfeeding causes the release of prolactin, which can negatively affect this tumor.
Pituitary microadenoma usually does not pose a serious threat to the patient. However, it can cause pathological manifestations that worsen the quality of life. Therefore, timely treatment of microadenoma and compliance with all recommendations of the attending physician will help achieve long-term remission of the disease.
Symptoms
Features of the manifestation of adenoma depend on the type of tumor and the hormones produced by it. Also, the symptoms of pituitary adenoma can manifest as ophthalmic-neurological or endocrine-metabolic syndromes. A radiological symptom complex of neoplasia may occur.
Thus, the development of ophthalmo-neurological syndrome occurs at a time when the tumor begins to increase in size. When the surrounding tissues are compressed, the adenoma can cause discomfort in the patient in the form of headaches, double vision, as well as decreased, partial or complete loss of vision.
Cephalgia is often dull, local in nature, and its source is located either in the temporal or frontal part of the head. As a rule, taking analgesics gives a short-term effect or does not bring relief at all.
Visual disturbances are observed with large adenomas. In this case, the tumor compresses the optic nerves and their chiasm. With adenomas of 1-2 cm in diameter, nerve atrophy can occur, resulting in complete blindness.
The cause of endocrine metabolic syndrome is changes in the production of pituitary hormones. And since this part of the brain regulates the functioning of the peripheral glands, their hyperactivity develops with adenoma.
Prolactinoma
Prolactinoma is the most common type of adenoma among women. It is caused by hypersecretion of the hormone prolactin, and is manifested by the following symptoms:
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle up to amenorrhea - complete cessation of menstruation;
- white discharge from the nipples;
- secondary infertility;
- sudden weight gain;
- seborrhea;
- hirsutism (male pattern body hair growth);
- decreased sexual desire.
Prolactinoma also occurs in men, and they more often suffer from ophthalmo-neurotic syndrome. The main symptoms include discharge from the nipples, impotence, and enlarged mammary glands.
For comparison: it is much more difficult to suspect prolactinoma in men than in women. In male patients, only sexual disorders are clearly manifested, which the patient himself does not associate in any way with a pituitary tumor. Therefore, the adenoma in this case is detected already at the later stages of its development. In women, the disease can be detected at the microadenoma stage.
Corticotropinoma
With this pituitary tumor, there is an increased production of ACTH, which affects the adrenal cortex. Due to hypercortisolism, patients experience symptoms such as:
- significant weight gain;
- the appearance of age spots on the skin;
- formation of stretch marks (stretch marks) on the abdomen and thighs;
- hirsutism in women;
- increased hair growth – in men;
- mental disorders.
The above symptoms form the clinical picture of Itsenko-Cushing's disease. It is corticotropinomas that are more prone to malignancy than other tumors of the adenohypophysis.
Somatotropic adenoma
Somatotropic adenoma is accompanied by hypersecretion of somatropin - growth hormone. It is its excess in the child’s body that causes such a deviation as gigantism. In adults, acromegaly often develops against this background.
With gigantism, rapid growth of the entire body is observed. Patients with this deviation are tall, have long arms and legs. But that's not the worst thing. The fact is that with gigantism, the functioning of internal organs is disrupted due to the active growth of the body and the creation of an increased load on the entire body.
Acromegaly is characterized by enlargement of only certain areas of the body - the hands or feet, or the face. At the same time, the person’s height remains normal, normal.
Somatotropinoma is often accompanied by the development of diabetes mellitus, obesity and thyroid diseases.
Thyrotropinoma
Thyrotropinoma is one of the rarest types of pituitary adenoma. It produces false thyroid hormones, resulting in the development of thyrotoxicosis. This deviation is characterized by sudden causeless weight loss, general malaise, attacks of heat, dizziness, nausea, headaches, etc.
Gonadotropinoma
With gonadotropinoma, uncontrolled synthesis of hormones occurs, under the influence of which the gonads are stimulated. However, the clinical picture for this type of adenoma remains blurred. As a rule, it manifests itself as sexual disorders, infertility or impotence (in men). If we talk about other symptoms of gonadotropinoma, then most often it manifests itself as ophthalmo-neurological disorders.
Large adenomas of the medullary pituitary gland provoke compression not only of the nerve structures, but also of the parenchyma of the endocrine gland itself. The consequence of this is a violation of the hormone-producing function.
Against the background of reduced secretion of biologically active substances, weakness, fatigue occur, and the rate of metabolic processes in the body decreases, which leads to obesity. Insufficient production of adenopituitary hormones is called hypopituitarism.
Corticotropinoma
Corticotropinomas disrupt the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone. As a result, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome is formed, which has the following manifestations:
- persistent arterial hypertension;
- obesity. The bulk of fat in Itsenko-Cushing syndrome is deposited on the face (it becomes round, moon-shaped) and in the abdominal area. In this case, the limbs may remain thin, which is why the patient’s figure takes on the appearance characteristic of the syndrome;
- the appearance of numerous pustular rashes on the skin;
- in areas of increased fat deposition, in particular on the abdomen, stretch marks (striae) appear;
- decreased libido;
- the appearance of male pattern hair in a woman;
- increased bone fragility (osteoporosis). With severe osteoporosis, even a minor injury can lead to a fracture;
- decreased immunity. With Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, patients experience more frequent infectious diseases that take a protracted course.
Diagnostics
Despite such a wide variety of clinical presentations, diagnosing pituitary adenoma is a rather complex process. This is explained, first of all, by the absence of specific signs that would indicate this particular disease. Therefore, referring a patient to highly specialized specialists rarely helps to identify pathology. But when adenoma is diagnosed, the patient requires mandatory observation from several doctors at once.
Previously, the most reliable diagnostic method was radiography of the sella turcica. But those deviations that are detected with its help arise already in the later stages of adenoma. But for early diagnosis, it is more advisable to perform an MRI or CT scan of the brain. However, even this procedure may not be effective when it comes to certain types of microadenomas.
Another important diagnostic measure is the study of venous blood for pituitary hormones. Increased or decreased levels of certain biologically active substances can help in making a diagnosis.
Forecasts for recovery, prevention
In 9 cases out of 10, the patient overcomes the disease and is completely cured. In some cases, to maintain the general condition, the patient has to take medications, for example, Dostinex, for the rest of his life.
Complex cases leading to disability are rare. As a rule, they are associated with lack of timely treatment or very late seeking of medical help.
If you write about the prevention of the disease, then it does not exist, since there are no proven causes of pituitary adenoma.
Treatment of pituitary adenoma
Treatment of pituitary adenoma depends on its type, location and size. To begin with, the patient is closely monitored. The doctor must track the dynamics of the development of the tumor, assess the degree of risk of complications and record the intensity of tumor growth.
If the tumor tends to increase, and at the same time the patient’s well-being worsens, a decision is made to immediately carry out certain therapeutic measures. In the absence of complications, monitoring of the patient's condition continues.
Drug treatment
This therapy is prescribed mainly to patients with prolactinoma or somatotropinoma. Drug treatment is based on the use of drugs that block the production of hormones. Thanks to this, it is possible to normalize hormonal levels and restore the physical and psychological state of the patient.
Radiosurgery
Radiosurgical treatment of adenoma involves destruction of the tumor using radio rays. This is a highly effective modern method of instrumental therapy used for various tumor pathologies.
Surgical excision of the tumor
Surgery to remove a pituitary adenoma is an intervention with the advantage of being highly effective. The downside is the high risk of trauma to brain tissue during tumor excision. Small tumors are removed through the nose, but for large adenomas, or when they are localized in hard-to-reach areas of the brain, an “open” operation is performed to excise the adenoma.
Often, to achieve the desired result, doctors combine several therapeutic techniques at once. The whole process is controlled by a specialist, so there can be no talk of any self-medication in this case!
Microadenoma and pregnancy
Pituitary microadenoma is not a contraindication for planning pregnancy. If a woman has a hereditary predisposition or characteristic symptoms, then she needs to be examined before conception. If the hormonal background is stable, doctors allow pregnancy, but recommend regularly monitoring hormone levels.
With increased activity of the microadenoma, the patient is prescribed medications or offered surgery. Breastfeeding with microadenoma is contraindicated.
Forecast
Pituitary adenoma is a benign neoplasm, but if left untreated it can become malignant. However, timely diagnosis of the disease makes it possible to completely remove the tumor without complications for the patient’s health. Although the possibility of complete excision of an adenoma directly depends on its size.
The prognosis also depends on the type of adenoma. With microscopic corticotropinomas, in 85% of cases, complete restoration of vision occurs after surgical removal of the tumor. But with somatotropinoma and prolactinoma, such a favorable outcome is observed only in 20–25% of cases, respectively. But it is interesting that often the hemorrhages that occur with prolactinoma go through a self-healing phase and do not cause significant harm to human health.
(Visited 103 times, 1 visits today)
Thyrotropinoma
Thyrotropinomas cause an increase in the blood level of thyroxine, a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. In this case, the woman develops the following symptoms:
- sweating: patients may sweat even with minor physical exertion;
- irritability and increased emotional lability;
- increased heart rate;
- a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart;
- rapid loss of body weight in the absence of diets and increased exercise;
- exophthalmos, that is, bulging eyes. Eyes with thyrotoxicosis become shiny and appear larger; for this reason, patients in the initial stages of the disease often report that they feel more attractive.
Complications
The most common complications of pituitary adenoma include the following:
- cystic degeneration. The development of this complication is indicated by symptoms such as severe headaches, progressive visual impairment, frequent increases in blood pressure in the absence of diseases of the cardiovascular system. Occasionally, patients experience mental changes, for example, increased irritability, causeless decrease in mood, etc.;
- hemorrhage in the adenoma tissue. Prolactinomas are especially often complicated by hemorrhage. Hemorrhage is a rather dangerous, but usually not fatal complication. Its development is indicated by symptoms such as a sharp headache, sudden blurred vision, as well as pituitary insufficiency. Sometimes there are cases where, after hemorrhage into the adenoma, spontaneous self-healing occurs.
It is important to remember that if the patient has a diagnosed microadenoma, if the above symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a medical facility.