Germinoma of the brain is a rare tumor that occurs during intrauterine development of the fetus. It arises from the germ layers, from which the formation of the baby’s organs and tissues occurs.
The formation consists of different tissues and can be located not only in the brain, but also in the reproductive system and spine.
This type of tumor accounts for only 2% of all cases, but this neoplasm is the most common among deep ones.
The tumor is mainly contained in the deep structures of the brain and is difficult to operate. The neoplasm can be benign or malignant; it progresses as the child’s body grows, and at an early age it may not show any signs.
The first signs of the disease appear at 12-13 years of age. But if the tumor is malignant, then symptoms appear much earlier.
Also, the tumor can progress very slowly and only appear at the age of 25-30. Statistics show that this pathology is more common in the male half of the population. If the tumor is malignant, it progresses and covers nearby tissues and structures of the brain.
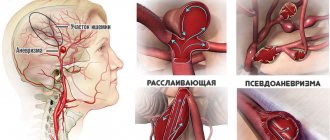
Located near the third ventricle. According to statistics, germinoma in a quarter of all cases is a benign tumor.
Causes of brain germinoma
There is no clear opinion about the cause of the formation of brain germinoma. Scientists and oncologists are more inclined to the version of the disorder in the process of embryogenesis. There is a so-called dysontogenetic theory of the occurrence of this type of tumor. According to this theory, brain germinoma occurs as a result of disorders of tissue differentiation and tissue migration at the very first stages of embryogenesis in the first trimester of pregnancy. The basis of this hypothesis is largely based on the fact that neoplasms are more often detected in people at a young age.
Germinoma is usually classified as a type of embryonic tumor, and these neoplasms arise and develop even before the full formation of the fetus from the rudiments of embryonic tissues. The reason is a violation of embryogenesis, which occurs as a result of changes in the structure of chromosomes and mutation of genes that control the normal development of embryogenesis.
Factors that induce changes and disturbances in embryogenesis may have an indirect or direct effect on the body of the expectant mother. Such provocateurs include contact with toxic substances during pregnancy, the influence of radioactive substances, various types of infections (measles, herpes, severe stages of influenza). The risk factor will also be the influence of carcinogens.
Etiology
To date, the exact cause of germinoma has not been established, but most doctors associate it with a disorder of embryonic development. The young age of the patients confirms this. In the first trimester of pregnancy, under the influence of unfavorable factors, deviations in the formation and correct formation of organs can occur. Toxicoses, taking certain medications, and viral and bacterial diseases of the mother can cause improper differentiation of fetal cells.
The most severe factors contributing to the development of pathology include:
ionizing radiation;- contact with toxic substances;
- influence of carcinogens;
- viral infections (herpes simplex, influenza, measles, chicken pox).
Symptoms of brain germinoma
The clinical picture of brain germinoma largely depends on its location. Localization of brain germinoma - deep structures of the brain - area of the pineal gland, third ventricle.
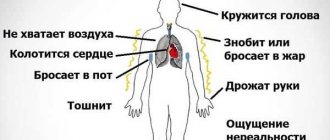
One of the first signs of this neoplasm will be impaired blood flow and hydrocephalus as a consequence. Patients often complain of a bursting headache that is not relieved by analgesics or other painkillers. There is also a feeling of pressure in the eyes, constant nausea, independent of meals, and at times even vomiting. Visual impairment is often observed. This is explained by the fact that germinoma is localized near the chiasm of the optic nerves and, growing, infringes on them. Patients focus on double vision, visual field defects, farsightedness or myopia.
The clinical picture of brain germinoma is also characterized by deterioration or partial loss of memory, mental disorders, and emotional instability. In some cases, various kinds of neuroendocrine syndromes such as diabetes insipidus, as well as menstrual irregularities, anovulation, amenorrhea in women and disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary system may be observed. Developmental disorders of puberty are also diagnosed. All these symptoms are explained by the location of the tumor near the hypothalamus.
general information
Among all brain tumors, germinoma accounts for only 2%. But among tumors affecting the deep structures of the brain, it is the most common. In approximately 56% of cases, germinoma is located in the region of the pineal gland, or pineal gland, and the pituitary gland area accounts for 25%. In the overwhelming majority, the neoplasm is a single conglomerate.
The period of occurrence of germinoma falls on the age range from 10-15 to 20-25 years. Some medical sources indicate that the tumor is more often found in men. This neoplasm often becomes malignant and grows into the surrounding tissue. A benign course of germinomas is observed in approximately 25% of cases.
Diagnosis of brain germinoma
The first diagnostic conclusions are made during the first examination by a neurologist. A neurological examination and questioning of the patient, his complaints and accents in the characteristics of general well-being makes it possible to establish or suspect the presence of hydrocephalus.
Methods for diagnosing brain germinoma:
- Echo-encephalogram. Firstly, it allows you to diagnose intracranial pressure, and secondly, in the case of a large tumor, this diagnostic method can reveal displacement of the deep structures of the brain.
- Tomographic methods - CT and MRI of the brain. They make it possible to identify the nature of the tumor, location and size. Almost half of patients diagnosed with brain germinoma have a clinical picture of tumor infiltration of the visual tuberosities and petrification in the middle (the so-called butterfly symptom). This diagnosis can be confirmed by the presence of tumor bodies in the lateral ventricles and metastases in the infundibular region of the third ventricle.
- Biochemical blood test - establishing markers of hCG, ACE, PAL.
- Steretactic brain biopsy. This method will be the most accurate in making a diagnosis, since a laboratory examination of the tumor body is performed. In some cases, such a study may not give accurate results if the tumor is heterogeneous.
- Morphological examination of tumor areas after its removal. The difficulty of this method is in localizing the tumor in the deep structures of the brain, so doctors often prefer stereotactic biopsy.
Brain germinoma has a similar clinical picture to a number of neoplasms in the central nervous system, and therefore requires careful diagnosis and differentiation from diseases with similar symptoms. Among these diseases:
- astrocytoma;
- glioma;
- ganglioneuroma;
- hematoblastoma;
- medulloblastoma;
- brain abscess;
- intracerebral hematoma;
- cystosis in the third ventricle.
Histology[ | ]
The tumor is homogeneous in appearance, consists of two types of cells: large cells (are true tumor cells) with vesicular nuclei and transparent or fine-grained cytoplasm, which is eosinophilic. Small cells located in clusters or randomly mixed with tumor cells[2]. Microscopic examination reveals uniform cells that resemble primordial germ cells. Typically, the stroma contains lymphocytes, and about 20% of patients have sarcoid-like granulomas. The immunohistochemical research method determines that more than 70% of lymphocytes are T-lymphocytes, the rest are B-lymphocytes.
Germinomas containing giant syncytiotrophoblast cells were classified as a separate group (K. Sano)[3].
Treatment of brain germinoma
The most common treatment strategy for brain germinoma is radiation therapy. If the patient’s age is too young, their general condition does not allow radiation therapy, or there are contraindications, then polychemotherapy is prescribed. Sometimes surgery will be a mandatory and forced method of treatment and may be accompanied by radiation or chemotherapy. But such a complex method of treating this disease is extremely undesirable for young or child patients, as it entails severe intoxication of the entire body.
Treatment[ | ]
The inaccessible location of germinoma makes it difficult for neurosurgeons to remove this type of tumor. Currently, CyberKnife or Gamma Knife (stereotactic radiosurgery) is used for minimally invasive treatment. Since radiation therapy negatively affects an undeveloped child’s body, polychemotherapy is often used for treatment. In an integrated approach, chemotherapy (cisplatin, bleomycin, vinblastine, cisplatin and etoposide) is also used [3].
Forecast[ | ]
Timely treatment gives good prognosis for recovery: the average survival rate of patients within five years is 75-90% after diagnosis. Early diagnosis and initiation of treatment increases the likelihood of success.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of brain germinoma can be carried out in various ways and is performed when an accurate diagnosis is made and the location, nature and size of the tumor is established. Often, surgical treatment is the only possible method, since other methods will be ineffective. In some cases, surgical intervention requires additional procedures - ventriculocisternostomy or ventriculoperitoneostomy.
Contraindications for surgical treatment of brain germinoma may include inoperable location of the tumor or disseminated tumor growth, as well as multiple foci. If the size of the tumor is small, then it is advisable to use radiosurgery methods. The essence is a single exposure to the location of the tumor with a high dose of radiation.
Treatment of the disease is within the competence of specialized departments of neurosurgery, which are equipped with equipment and a computer imaging neuronavigation system.
Tumor treatment
Treatment of a tumor process in the brain is carried out in various ways.
The increased sensitivity of such formations to chemotherapy and radiation allows these treatment methods to be chosen as fundamental ones.
The use of radiological therapy is contraindicated in pediatric patients, since such exposure negatively affects developing brain tissue.
Therefore, young patients are more often treated with antitumor drugs; if the tumor process is widespread, then polychemotherapy is prescribed.
If the tumor is not large, then it is better to use radiosurgical treatment, which involves a single exposure to a high dose of radiation to the tumor site.
Sometimes chemotherapy and radiation are used as additional therapy to surgical treatment. Surgery is often the only possible treatment option for germinoma.
But removal surgery also has its contraindications:
- Disseminated germinoma growth;
- Inoperable localization of the formation;
- Multiple focality of the tumor.
Surgical removal of germinoma is a technically complex neurosurgical and neurological task. The main difficulty is access to the tumor, because it is located deep in the brain.
But fortunately, today, thanks to the availability of neuroimaging techniques, specialists have the opportunity to plan the entire operation in seconds. Therefore, surgical removal of germinoma is the method of choice.
The specific method of removal is selected individually by the neurosurgeon. Tumor removal is often complemented by shunt surgery such as ventriculocisternostomy or ventriculoperineostomy.
Prognosis and prevention of brain germinoma
The main methods of preventing brain germinoma can be considered the exclusion of any negative impact on the body of the expectant mother. A pregnant woman should lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid contact with radioactive and toxic substances.
This disease, if detected in the early stages, responds well to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In the future, to monitor your condition and the course of the disease after treatment, you must consult a neurologist at least once a year. Even with surgery, the prognosis can be quite encouraging - the survival rate after such operations is approximately 85 percent.
Literature[ | ]
- Small medical encyclopedia. — M.: Medical encyclopedia. 1991–96
- Sadler, TW 2006. Langman's medical Embryology, 10th Edition, Chapter 15, pp. 251-252. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Pub.
- Keene D, Johnston D, Strother D, et al. (2007). "Epidemiological survey of central nervous system germ cell tumors in Canadian children." J. Neurooncol
.
82
(3): 289-95. - Balmaceda C, Heller G, Rosenblum M, et al. (1996). “Chemotherapy without irradiation—a novel approach for newly diagnosed CNS germ cell tumors: results of an international cooperative trial. The First International Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumor Study.” J. Clin.
Oncol .
14
(11): 2908-15 - Ueba T, Yamashita K, Fujisawa I, et al. (2007). "Long-term follow-up of 5 patients with intracranial germinoma initially treated by chemotherapy alone." Acta Neurochirurgica
.
149
(9): 897—902, discussion 902 - https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/record/ui?name=Germinoma
What is pinealoma
A pinealoma is a tumor of the pineal gland of the brain - the pineal gland. It is formed from pineocytes - cells that produce hormones (melatonin and serotonin). It is more common in children and young adults, with peak detection occurring in adolescence. In general, it is considered rare, occurring in less than 1% of brain tumors, but before the age of 14 years it accounts for almost 8% of all tumor diseases. It mainly affects boys.
If it is benign (adenoma), it is called pineocytoma. It grows slowly in the form of a node (cluster of cells), has clear boundaries, a capsule, and appears only when large in size. Malignant pineoblastomas grow very quickly, grow beyond the epiphysis, and their metastases spread throughout the body.
Mixed forms are also possible, occupying an intermediate position between cancerous and benign. They are considered completely unpredictable, since it is not known in which direction they will develop.
We recommend reading the article about the pineal gland in the brain. From it you will learn about what the pineal gland of the brain is, the structure and functions of the pineal gland, characteristics in children, as well as the main diseases that you may encounter. And here is more information about the epiphysis cyst.