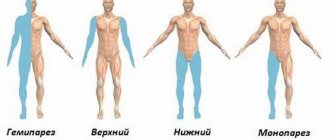
Duchenne-Erb palsy is a disease in which patients experience paralysis of the arm due to disruption of the innervation of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. This disorder can develop in adults as a result of an infectious process or intoxication, as well as in newborns due to birth trauma.
The neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital has the necessary equipment for diagnosing pathology, as well as experienced specialists using modern methods of therapy. The activities offered by rehabilitation doctors at the Yusupov Hospital to patients after treatment for Duchenne paresis help them return to an active life and eliminate residual effects.
Feature of the condition
Myodystrophy is a disease with a chronic course, which can have various variations in the development of symptoms. What unites all forms as a whole is the mechanism of manifestation of the disease. Skeletal muscles are most often affected.
Muscular or myodystrophy is manifested by a gradual increase in muscle weakness and degeneration. There is a gradual decrease in the thickness of muscle fibers.
The affected sections usually lose their ability to contract and undergo decay, being replaced by connective and adipose tissue.
According to the ICD-10 code, the disease is coded G 71.0.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
The fight against the pathological process involves the so-called positional treatment. A splint is placed on the affected limb, which can only be removed during hygiene procedures.
To maintain muscle tone, the following activities are recommended:
- massage of the affected limb (start from the second week);
- electrical stimulation of muscles;
- therapeutic exercises with passive exercises;
- acupuncture;
- paraffin applications;
- ozokerite.
A positive effect from conservative therapy is possible only if the fibers of the brachial plexus are partially damaged. They wait for about three months, after which they move on to evaluating the results obtained. If by this time the patient does not have active movements in the elbow joint, the issue of surgery is decided.
View gallery
Types and their features
The disease can occur in different forms and develop in a wide variety of areas. Accordingly, the type of symptoms will depend on this. Based on this, doctors prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen.
Duchenne
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is one of the most dangerous forms. It occurs chronically and affects entire muscle groups. it is also called pseudohypertrophic.
In most cases, it is detected in childhood, and usually in boys. This form is distinguished by:
- Development at approximately 2–5 years of age;
- Muscle weakness initially manifests itself in the legs and pelvic area;
- Slightly less often, the first signs appear in the arms and shoulder girdle, after which the disease begins to spread to neighboring areas;
- The muscles in the calf area begin to increase due to tissue degeneration and their gradual replacement with fat with the growth of connective tissue.
The disease progresses quite quickly. Literally by the age of 12, the patient is no longer able to move independently. By the age of 20, death most often occurs.
The photo shows manifestations of progressive dystrophy
Becker
This form is rare. If we compare it with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. A distinctive feature is that this condition manifests itself in most cases in short people. Moreover, for many years the condition of patients has been at a satisfactory level. Disability usually occurs either due to secondary pathologies that develop against the background of muscular dystrophy, or due to injuries.
Graefe
This type of muscular dystrophy is also called oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. This is a hereditary disease that can be of an autosomal recessive or dominant type of inheritance.
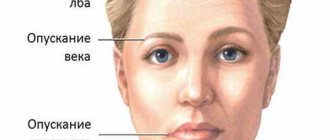
It usually appears in the area of the muscles located on the head and face. Symptoms include dysphagia (simply, swallowing disorder), weakness of facial muscles, eyelid ptosis, and ophthalmoparesis. General weakness appears a little less often.
Important! It is noteworthy that the disease affects both sexes equally, but differs according to nationality. For example, Bukharian Jews and French-speaking Canadians may suffer from Graefe's muscular dystrophy more often than others.
Landouzy-Dejerine
This species affects the area of the shoulder blades, shoulder girdle and face.
It most often debuts in adolescence, that is, around 10-15 years, although it can be diagnosed from 6 to 52 years.
The muscles of the face are the first to be affected, with a gradual transition to the shoulder girdle and shoulder blades. The process then spreads to the torso and limbs.
Moreover, at an early stage, insufficient closure of the eyelids and lips is noted as the first symptom. The latter can affect diction.
Important! The pathology shows slow progression and after diagnosis, usually 15-25 years, the patient can be considered able to work. But then the pelvic muscles are affected by atrophic processes, which makes movement difficult.
Erba-Rota
This type of myodystrophy is also called juvenile, as it develops at 10-20 years of age. The beginning falls on the muscles of the shoulder girdle, then – the arms, pelvis and legs, that is, according to a descending pattern. The main differences between patients with this condition are a waddling gait, a protruding stomach, and a pushed-back chest. Progresses quite slowly.
Erb-Roth dystrophy
Secondary
The secondary form develops against the background of other diseases, and therefore, in addition to muscle weakness and loss of function, signs typical of the provoking factor may be present.
Dreyfus
This is another type of hereditary type. With it, there is a slow progression of symptoms. Elbow contractures develop early, as well as retractions of the neck muscles and Achilles tendons. Gradually, the disease spreads to other muscle groups, causing concomitant impaired cardiac conduction. Hypotrophy and muscle weakness most often occur in the proximal arms and legs.
Manifestations of dystrophy
Duchenne-Erb paresis: causes of the disease
Before answering a question from a patient diagnosed with Erb's palsy of the right arm about how to treat the disease, specialists conduct an examination to determine the causes of the pathology. Thus, in newborns, the development of Duchenne palsy is preceded by a birth injury, as a result of which tension or rupture of the trunks of the brachial nerve plexus occurs. Risk factors for the development of paresis in newborns are: high weight of the baby, narrow pelvis in the mother, long labor, which requires the use of auxiliary methods.
The causes of Erb's paresis in adults are mechanical damage. Thus, rupture of nerve fibers in the shoulder often occurs in car accidents when a person is wearing a seat belt. The main mechanical damage leading to Duchenne-Erb's paresis is:
- shoulder bruise;
- sharp traction on the hand;
- sprains;
- neck injuries.
Erb's palsy can also develop due to the action of other factors on the body, one of which is toxic damage. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital, when a patient presents with signs of this disease, conduct a comprehensive diagnosis to identify the causes.
Symptoms
The symptomatic picture is usually limited to:
- Decreased muscle tone;
- Skeletal muscle atrophy;
- Frequent falls;
- Weakness;
- Feeling tired;
- Gait disturbance;
- Loss of physical skills;
- Impaired sensitivity;
- Complete absence of pain.
It is noteworthy that as the disease progresses, the affected area increases. This is explained by the fact that dead muscle tissue is replaced by connective and/or fatty tissue. To a greater extent, this condition can be observed in the calf muscles.
What do you need to remember?
- Duchenne-Erb's palsy is a disorder of the innervation of the upper limb due to damage to the roots of the brachial bundle.
- Birth trauma is the most common cause of the disease.
- The main symptoms are the inability to perform active movements, free hanging of the shoulder, and impaired sensitivity.
- To establish a diagnosis, the typical clinical picture of the disease plays a major role.
- Treatment is aimed at restoring the integrity of the nerve bundle and returning lost limb functions.
- The prognosis in most cases is favorable, provided that medical instructions are followed.
Literature
- Bershtein N.A. Physiology of movements and activity M. - 1990. - P. 140.
- Bondarenko E.S., Shanko G.G. Neurology of childhood. Diseases of the nervous system of newborns and young children. Minsk: Higher School. -1990.- P. 343.
- Dolnitsky O.V. Treatment of birth paralysis of the upper limbs, Kiev. - 1985. - P.127.
- Dolnitsky O.V., Yatsenko V.P., Dolnitsky Yu.O. Birth injuries of the brachial plexus in children. Clinical and morphological parallels // Klin. hir. 1981.- No. 6.- P. 46-48.
- Ivanov M.A. New elements in the treatment of obstetric paralysis // Author's abstract. dis. . Ph.D. honey. Sciences. - Kuibyshev. - 1981. - P. 27.
- Komarevtsev V.D., Diagnosis and treatment of birth paralysis of the upper limb in children // Dissertation of Doctor of Medicine. Sci. Yaroslavl 2000.-P.227.
- Anand P., Birch R. Restoration of sensory function and lack of long-term chronic pain syndromes after brachial plexus injury in human neonates // Brain.-2002.-Vol. 125.-No. l.-Pl 13-122.
- Andersen J., Watt J. et all. Perinatal brachial plexus palsy // Pediatr Child Health.- 2006.- 11(2).- P.93-100.
Diagnostics
Myodystrophy can be diagnosed using:
- Ultrasound;
- Electromyography;
- Biopsies;
- Blood tests;
- DNA analysis;
- Electroneurography;
- MRI;
- ECG;
- Echo-CG;
- X-ray.
The specific examination scheme is determined by the specialists involved in treatment. In this case, it may be necessary to visit a neurologist, orthopedist, cardiologist, and so on.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of pathology in the baby, the mother needs to take care of this during pregnancy.
In case of viral diseases, it is necessary to cure them in a timely manner. Do not expose your body to stress, do not take medications without consulting a doctor. During pregnancy, eat right, eat fresh vegetables and fruits. If necessary, take vitamin complexes, but only after consultation with your doctor. During childbirth, doctors must be attentive and use obstetric supplies with caution. After the baby is born, parents should prevent the child from becoming infected with viral infections, not overcooling the baby, and monitor his general condition.
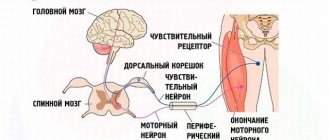
Obstetric paralysis is a disorder in the upper limb of a newborn baby that occurs due to incorrect obstetric tactics during childbirth. The immediate cause of this disorder is the brachial plexus - a “tangle” of nerve endings.
The main symptoms of the pathology are deterioration in mobility and sensitivity of the upper limb on the affected side. The pathology is complicated by contracture - “jamming” of the arm in the shoulder joint and the inability to perform any movements in it.
A preliminary diagnosis is made based on clinical signs and information about how the birth took place and whether pregnancy pathology was observed.
Additional research methods are used to clarify the degree of violation. The pathology is treated with drugs that improve nerve conduction. Table of contents:
How is myasthenia gravis treated?
Treatment of the disease is usually symptomatic, since the condition itself cannot be cured. In the process, two goals are usually set - relief of symptoms and suspension of progression.
Affected and already replaced tissues cannot be regressed. Drug therapy is used, which includes:
- Pentoxifylline;
- Neostigmine;
- Corticosteroids;
- B vitamins;
- ATP inhibitors.
Treatment may also be required to help support the functioning of internal organs, including the heart, if there are associated risks. In addition to medication, exercise therapy, water procedures, massage, electrophoresis and heat treatment are used. If contractures have formed, the following techniques are used:
- Tenotomy;
- Elimination of contractures in the elbows by surgical method;
- Tenolysis of the Achilles tendon and so on.
These are all orthopedic surgeries. If the condition affects the heart, you may need to install a pacemaker or cardioverter-defibrillator.
Exercises for muscle dystrophy
Signs of pathology
Clinical manifestations of the disease are divided into three stages, characterized by different symptoms:
1. Acute stage. It begins immediately after injury and lasts for a month after it. During this period, the arm is in one position - extended at the elbow, pressed to the body, fingers brought to the palm. The patient cannot independently move his arm forward, up, to the side, or rotate the inner surface of the limb to the front position. Any manipulations or attempts to change the position of the limb cause pain and discomfort. The biceps reflex is not recorded on the affected side. Infants lack a grasp reflex on the side of paralysis. When the child is placed in a horizontal position, a “limp” hanging of the arm is observed. Muscle tone is reduced, the skin is cold and discolored, and the sensory system is little susceptible to pain applied to the skin.
2. Recovery stage. Depending on the severity of the injury, the timeliness of therapeutic care and the adequacy of medical manipulations, the following symptoms will appear. With mild paralysis, sensitivity and activity are gradually restored to full functionality. However, in children by the age of three, a slight shortening of the affected arm and muscle weakness are noticeable.
3. Stage of residual effects. Since functionality does not return to full extent during the recovery period, subsequent disorders develop. If the paralysis is moderate or severe, the patient complains of “doll hand” syndrome. It is manifested by a clearly defined fold between the sternum and shoulder area. The structure of muscle tissue changes, the elbow joint loses its flexion ability. A pronounced rotation of the scapula is clearly visible, the fingers remain in palmar presentation. Since the muscles atrophy, subsequent chronic dislocation of the shoulder area is possible. The consequence of the altered anatomy of the upper spinal column is the curvature of the latter, scoliosis manifestations.