The human body is unique, but even it can get sick. Even the simplest disturbance in the regulation of vascular tone has a bad effect on a person’s condition. The simplest disruption of organ function provokes a disruption of the normal functioning of the vascular and nervous systems. This complex of work disorders is called headaches due to vegetative-vascular dystonia.
How does a headache occur with VSD?
Vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) is not included in the international classification of diseases. The diagnosis “somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the nervous system” is considered more correct. Many doctors still use the term VSD in the old fashioned way.
It is accompanied by many disturbances in the functioning of the body, which are provoked by disruptions of the nervous system or somatic diseases.
The following diagnoses may be hidden under VSD:
- Depression;
- Anemia;
- Diabetes;
- Systemic diseases;
- Oncology;
- Viral infections;
- Hepatitis;
- Hypothyroidism;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Chronic fatigue syndrome.
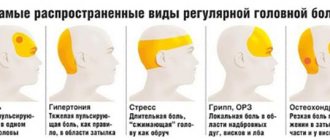
The nature, intensity, and regularity of headaches in each person will depend on the specific diagnosis and characteristics. Doctors distinguish 3 types of cephalalgia.
| Name | Character | Intensity | Regularity |
| From voltage |
|
| Occasionally or constantly. |
| Migraine |
| severe, to the point of nausea and vomiting. | From several hours to several days. |
| Cluster pain (Horton's migraine) | The pain syndrome is localized in the orbit, in the temple, above the eye. There is lacrimation, redness of the eye, and nasal congestion. | Sharp, sharp, strong. | Attacks for a week or a month with periods of remission. |
The human brain cannot be sick. Discomfort is experienced by the muscles, ligaments, blood vessels, and nerve endings covering the head.
Causes of cephalgia with VSD
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, the cause of headaches is a change in the state of the brain vessels - their spasm, expansion or narrowing. This happens under the influence of external factors or in the presence of certain pathologies and characteristics of the body. In the first case, headache appears due to:
- stress and psychogenic situations caused by troubles in personal life, at work or study, tragic events;
- overwork;
- poor quality sleep;
- bad habits;
- unbalanced diet;
- exposure to harmful radiation and chemicals;
- head injuries;
- effects of infections and viruses on the body.
Pathological features that provoke the development of cephalgia in VSD include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- hormonal surges;
- excessive suspiciousness and emotionality;
- the presence of diseases of the blood vessels and heart, gastrointestinal tract, nervous and endocrine systems, kidneys;
- susceptibility to allergies;
- obesity caused by diseases of the metabolic system or low mobility.
Due to the large number and variety of factors that cause headaches in vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is quite difficult to determine the true cause of deterioration in well-being. To do this, in case of regularly occurring painful sensations characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia, you need to consult a neurologist, undergo an examination and take measures to eliminate the external stimulus or internal pathology.
How to treat ailments
Since vegetative-vascular dystonia is a non-existent diagnosis, it is important to correctly establish the cause of the ailment. Symptoms are treated using an integrated approach.
Non-drug methods
According to statistics, 80-90% of headaches arise from tension.
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Stress;
- Poor nutrition;
- Negative worldview.
To reduce discomfort, you need to adjust your lifestyle and work on your outlook on life. Additional non-drug methods of getting rid of headaches include massage of the cervical-collar area, water procedures, and psychotherapy.
Inhalation of pure oxygen helps with cluster pathology.
Medication methods
Vegetative-vascular disorders can be normalized with medications.
For tension pain, take standard painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs:
To ensure that the medication helps and is not addictive, you should not take more than 15 tablets per month.
For migraines, conventional painkillers are ineffective. To treat this group of pathologies, drugs called triptans are used.
Triptans are available in the form of tablets, nasal sprays, and injectable solutions.
Depending on the severity of the disease, additional medications will be prescribed. This:
- Sedatives;
- Tranquilizers;
- Hypotensive;
- Antidepressants;
- Nootropic.
Entrust the decision on the selection of competent therapy to your doctor after examinations and analysis of complaints.
Which doctor should I contact?
Often, after physical exertion or mental stress, people feel worse. The nature of the pain can be varied. Compressive, pressing, throbbing pain in one side of the head is possible.
Pain during exercise is often functional in nature. They can occur for many reasons:
- Changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure;
- Stressful state during physical activity;
- Heat and stuffiness in the room;
- Dehydration is often the cause of headaches;
- Eat a large meal before training;
- Overweight people often suffer from hypoxia during exercise.
The likelihood of illness is higher in people with specialties: programmer, accountant, driver, who spend many hours at the computer or constantly strain the muscles of the eyes and neck.
The initial appointment should be made by a therapist. He will conduct a general examination, measure blood pressure, write out directions for tests and refer you to specialists.
If you have unpleasant sensations in the head and neck area, it is good to have a home blood pressure monitor, with which you can track pressure surges in different life situations. A rise in blood pressure after physical activity can often be the cause of pain.
The doctor gives a referral to an otolaryngologist to rule out chronic otitis media, sinusitis or inflammation of the maxillary sinuses (sinusitis).
The doctor can give a referral to an ophthalmologist to identify changes in the fundus and possible vision defects.
Most of the causes of discomfort in the head are associated with neurological symptoms, so diseases accompanied by head pain syndrome are treated by a neurologist.
What tests are usually prescribed?
At an appointment with a neurologist, a physical examination of the patient is performed: basic neurological reflexes are checked and the neck muscles are examined.
The doctor writes out a referral for tests: general blood test, biochemical blood test, blood sugar test.
A general blood test with an increase in ESR or an increased content of leukocytes indicates inflammation in the body.
Low blood glucose levels are often accompanied by cephalgia, dizziness and weakness.
The doctor may write a referral for additional tests:
- The gas composition of arterial blood can reveal cerebral hypoxia.
- A blood test for hormones determines various abnormalities in the functioning of the hypothalamus.
A neurologist can give a referral to one or more diagnostic methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - excludes the presence of various neoplasms (tumors and cysts), aneurysms. The photographs clearly show post-traumatic defects, neurodegenerative abnormalities, and changes in blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis.
- Computed tomography (CT) is the most informative method for studying the brain. It gives a clear idea of pathological changes in the skull and brain, pathology of bone tissue, blood vessels and brain structures. Provides information about the consequences of traumatic brain injuries. The disadvantage of this method is the significant radiation dose during the study.
- Electroencephalography gives an idea of the presence of pathological changes in blood vessels and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Doppler ultrasound (ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck) - shows the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries; narrowing and tortuosity of the arteries, leading to brain hypoxia; peripheral vascular resistance.
- Rheoencephalography (REG) - gives an idea of the tone and blood flow of blood vessels. Using REG, the following are diagnosed: hypertension, atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- MRI of the cervical spine - the presence of cervical osteochondrosis can cause pain in the head and neck, which intensifies when turning the head.
- Rheovasography of cerebral vessels (RVG) - shows the quality of blood flow through the great vessels, evaluates collateral circulation.
- Radiography will be less known. In the image you can only see the bone structures of the skull, soft tissues are not visible.
What is vegetative-vascular dystonia
When you have a very bad headache, you should first think about the possibility of vascular problems, because in most cases they are the main causative factor. There are quite a lot of variants of the pathology that causes headaches, and most often it will be vegetative-vascular dystonia, which has several names:
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- angiodystonia;
- angiovegetodistonia.
Any of the names indicates the essence of the problem - a violation of blood flow that arose against the background of changes in the nervous and vascular system. The problem can be throughout the body (systemic dystonia) or only in the head area (regional). Vegetative-vascular dystonia can manifest itself not only as spasm and narrowing of arteries with impaired blood flow, but also as pathological relaxation of tone and dilation of blood vessels, leading to accumulation of blood. In both cases, a person may experience a headache of varying severity from very severe to aching and boring.
The cause of the pain syndrome must be clarified with the help of a doctor, because self-medication or uncontrolled use of painkillers can lead to serious health problems.
Safe medications and pills
When planning a visit to the doctor, the patient should be prepared to answer questions about how often pain occurs and what its intensity is. This will help the doctor develop the correct treatment tactics.
Groups of drugs effective for episodic attacks of pain
Medicines for the treatment of pathology are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They have an analgesic effect, relieve inflammation, and eliminate swelling.
- Ibuprofen-400 mg per day;
- Ketoprofen-100 mg/s;
- Naproxen-500 mg/s;
- Meloxicam-7.5-15 mg/s;
- Celecoxib-200 mg/s.
Most NSAIDs have a negative side effect: with long-term use, they negatively affect the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, including the development of drug-induced gastritis.
Medicines Meloxicam and Celecoxib are new generation drugs that do not have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract. The disadvantages of using these drugs include the relatively high price.
Analgesics are often used at home to relieve an attack. They do not treat the disease, but only relieve pain. Drugs in this group are suitable for stopping episodic attacks, but their systematic use leads to the occurrence of abuse syndrome.
During an attack of pain, you can take Paracetamol-100 mg, Citramon, Analgin-500 mg or Mig 200-400 mg.
If the examination revealed the appearance of cephalgia after exercise as a result of increased blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe medications prescribed at an early stage of the development of hypertension. These include: vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, diuretics, calcium channel blockers.
Self-prescribing antihypertensive drugs is unacceptable. Self-medication leads to serious consequences.
For muscle tension, drugs from the group of muscle relaxants are used as part of complex treatment. They relax the spasmodic muscles of the head and neck, relieving pain of a spastic nature, and help restore blood flow.
- Mydocalm-150-450 mg per day;
- Sirdalud (Tizanidine) - 4 mg/s;
- Baclofen-15 mg/s.
Nootropic drugs are often prescribed as part of complex treatment: Phenibut, Nootropil, Glycine. Nootropics have an activating effect on brain function and increase its resistance to damaging factors. The drugs improve cerebral circulation and eliminate the consequences of traumatic brain injuries.
Sedatives in combination with basic drugs lead to muscle relaxation and decreased vascular tone. Taking tranquilizers helps relieve pain, but this type of medication quickly causes drug dependence with withdrawal symptoms.
Sedatives that are not addictive: Afobazol, Atarax; alcohol tinctures of valerian, motherwort, Maryina root.
For severe attacks, a combination of drugs is used: Sirdalud 2 mg + Aspirin 500 mg or Analgin 250 mg + sedative.
The use of vitamin B complexes has proven itself. Vitamins B1, B6, B12 have a beneficial effect on the central nervous system and restore the structure of nerve tissue. Vitamin complexes are often prescribed: Neuromultivit, Milgamma, Neurovitan.
If attacks of pain recur more than 10 times a month, a course of treatment with Ibuprofen at a dose of 400 mg per day for 2-3 weeks and treatment with muscle relaxants is prescribed for 2-4 weeks.
There is no single scheme for pain relief. Depending on the cause, each patient needs an individual selection of drugs.
Treatment of chronic disease
Sometimes cephalalgia becomes chronic. The pain occurs every day, continuously, with varying degrees of intensity.
Amitriptyline 10-100 mg/s is most often prescribed, the dose is increased gradually. The drug relieves pain well, but has many negative side effects and is addictive.
As an alternative, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are prescribed: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline. The course of treatment is at least 2 months. These drugs have less toxicity.
In addition to prescribing drug therapy, the doctor will recommend massage, a course of physiotherapy or acupuncture.
Headaches with vegetative-vascular dystonia are one of the main symptoms of the disease. They are oppressive in nature. Most often, painful sensations appear in the back of the head and frontal area. Less commonly, it is a throbbing pain without a clearly defined location.
If vegetative-vascular dystonia is not treated, every year its symptoms will progress and darken a person’s usual life. Including headache, dizziness, drowsiness, feelings of panic and anxiety will become increasingly stronger.
There is only one way out - take action!
Why does my head hurt?
Before starting drug treatment, the patient should find out about the characteristics of his illness. Pain and pressing sensation in the skull or migraine with VSD differ in their etiology from other similar diseases.
The very first reason why headaches occur with VSD is a sharp expansion or narrowing of blood vessels in the brain . The reasons may be different - diseases and abnormalities of brain development, inflammatory processes, malignant or benign tumors.
Basically, this pain in the head with VSD is provoked by the stress with which a person lives. Moreover, the anamnesis often also includes panic attacks, insomnia, sudden mood swings, depression, and depression.
The second cause of pain in vegetative-vascular dystonia is hypotension or constantly high cranial pressure.
In this case, the patient’s vessels are constantly working under increased load, they lose tone and stretch. When excess blood enters the brain, pain develops. As a result, the person suffers from chronic pressing pain in the skull.
Preventive measures
The disease is easier to prevent, this is a known truth. Prevention of headaches due to VSD includes the following measures:
- in this case, the disease will not allow you to drink alcohol, drugs and you will have to completely give up smoking,
- this disease requires a person to strictly adhere to a daily regimen,
- you will need to change your diet, necessarily including vegetables and fruits in large quantities,
- if a person has to do too much physical activity during the day, he will have to reduce it,
- you need to accustom yourself to daily long walks,
- It is advisable to sign up for yoga classes, learn how to do breathing exercises,
- you need to try to change your lifestyle so that there is as little room for stress as possible,
- reduce the intake of medications that have a vasoconstrictor effect to a minimum.
For headaches that torment a person, there is no need to immediately take medicine without finding out the cause. With vegetative-vascular dystonia they will not go away. Some stubbornly try to self-medicate. This cannot be done. Any pain in the head, especially if it occurs frequently, requires a thorough examination in a medical facility and the appointment of a professional course of treatment.
Characteristics of pain in the head with VSD
Stress negatively affects human health at the biochemical level. When stressed, the body releases adrenaline, which dilates blood vessels, increases heart rate, and accelerates blood circulation. If a person experiences stress regularly, then he no longer pays attention to this state of the body. But as a result, he gets headaches, muscle spasms, emotional reactions and a number of chronic psychosomatic diseases. For example, allergies, obstructive or asthmatic bronchitis, asthma, osteochondrosis, eczema, dermatitis, etc.
With VSD, headaches vary. It can be sharp or long lasting. It occurs only on one side or has a floating character, wandering from the temporal lobe to the back of the head, and from there to the frontal part, pressing on the eyes.
Along with cephalalgia, accompanying symptoms often appear:
- ringing or noise in the ears;
- "fireflies" or white spots before the eyes;
- vomiting, nausea;
- dyspraxia, disturbance of gait and coordination of movements, so-called “clumsiness”;
- decreased attention, unable to concentrate on something;
- confusion;
- changes in blood pressure (sharp decrease or increase);
- chronic pain in the head goes away only during sleep;
- decreased vision, blurry image.
How to effectively relieve a migraine attack
Headache due to VSD - how to treat and save it if it’s difficult to continue to live and work happily? First of all, the patient should undergo a diagnostic examination and identify the causes of pain in the head. Since this symptom is extremely dangerous and may indicate the development of a tumor in the brain or an inflammatory process.
Self-massage of the head will help relieve a sharp attack of headache. During the massage, you need to press on biologically active points until slight discomfort appears, without causing pain.
Breathing practices, meditation, or just walking in the fresh air are no less effective. While walking, it is recommended to take deep breaths, control your breathing, and walk slowly, without haste. Additionally, you can also do light exercises or yoga.
It is especially effective to do massage or exercises in combination with medications.
After the examination, a neuropathologist or neurologist prescribes an individual treatment regimen for the patient, which is based on the root cause of the exacerbation of VSD.
For example, for osteochondrosis, the doctor prescribes medications against inflammation in the thoracic or cervical spine, drugs to relieve vasospasm, vitamin complexes, exercise therapy, yoga, etc.
Tablets for quick relief of spasms are not able to completely rid a person of the problem, but they can alleviate his condition at this time.
Depending on the situation, the doctor may prescribe Ibuprofen, Citramon and No-shpu, Papaverine for high blood pressure.
For severe migraines , a shower will help by directing a stream of warm water to the back of the head, shoulders or neck. You can try taking a bath with aromatic essential oils and salt, but it is important not to bathe in hot or too cold water to avoid stress on the blood vessels of the brain.
Why are pills dangerous?
It is important to know that treatment only with medications that relieve pain, dilate or constrict blood vessels, and improve blood circulation in the brain is ineffective and often dangerous for the health and quality of life of the patient.
An integrated approach to treating the disease includes:
- relief of an acute condition (severe headache during VSD, attacks of hypertension, panic attack, etc.);
- getting rid of inflammation (for example, with osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine);
- strengthening blood vessels through medication and other means (walking and running in the fresh air, hardening, breathing practices, yoga);
- psychotherapy (for chronic stress and psychosomatics);
- relaxing massage course;
- maintaining a daily routine (healthy sleep, activity, self-care);
- proper nutrition;
- a complex of vitamins and minerals (especially B vitamins, Omega 3, vitamin E, etc.);
- herbal medicine (soothing herbal teas instead of black tea and coffee);
- in difficult cases, the doctor may prescribe sedatives or nootropics.
Head pain with vegetative-vascular dystonia is an extremely insidious and difficult disease.
At the same time, it forces a person to pause and pay attention to his health, the lifestyle and values by which he lives. After all, treatment with pills alone does not work, and with VSD it is important to change habits and lifestyle.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a complex of symptoms caused by disruption of the autonomic nervous system. One of the most common and striking manifestations of VSD is headache. Usually it is paroxysmal in nature, may not go away for a long time and can be quite strong. It exhausts a person, making him tired and irritable. Painkillers usually do not help; during the examination, as a rule, no serious disorders are revealed.
How to get rid of headaches
The treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia with frequent headaches must be approached comprehensively. Medical prescriptions will include the following groups of therapeutic effects:
Drug treatment
Getting rid of fainting and very severe headaches with the help of medications largely depends on the condition of the blood vessels. For low blood pressure, it is necessary to use means that increase tone. If it is high, reduce blood pressure. After the examination, the doctor will be able to select the necessary medications.
Herbal sedatives will have an excellent effect. If your sleep disorder is serious, your doctor will recommend medications for insomnia. If you have heart problems (pain, rhythm disturbances), you will need to take heart medications. As a rule, a course of treatment includes a complex of medications.
Non-drug treatment
In addition to medications, the doctor will give recommendations on diet, lifestyle and the use of other treatment methods. The following factors will have a good effect on angiovegetodystonia:
- refusal of night work, overexertion and bad habits;
- physiotherapeutic treatment using sedative and vascular effects;
- physical therapy, moderate exercise, swimming or moderate walking;
- therapeutic and prophylactic effects in a sanatorium or dispensary.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia with headaches and fainting often occurs in youth, very rarely causes serious disorders, and gradually disappears with age. However, in some cases, vascular changes in young people lead to health problems in the future, causing cerebrovascular disorders, arterial hypertension and heart failure. That is why if you have a very bad headache and fainting, you should consult a doctor to find out the reasons and carry out a timely course of treatment, followed by strict adherence to preventive measures.
Ivan Drozdov 09/07/2017 0 Comments
Headache that occurs with vegetative-vascular dystonia is one of the main signs of disorders of the autonomic system. It is exhausting with regularity and different types of sensations, interferes with full-fledged activities, contributes to the loss of interest in life and the occurrence of psychosomatic diseases. To determine the cause of pain, a person suffering from it must undergo a series of examinations and consultations with specialized doctors.
Causes
Headaches and dizziness with VSD are of vascular origin and develop against the background of chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, overwork, etc. It is believed that the main cause of headaches and dizziness is stress. With various difficulties in life, a person is under tension, while his blood pressure rises and his pulse quickens. Staying in this state for a long time gradually leads to headaches.
Autonomic disorders are formed or aggravated against the background of such events as conflicts in an educational institution, at work, in the family, the loss of loved ones, preparing for and passing exams, etc. If there are disturbances in the autonomic nervous system, the body reacts to such events with headaches and dizziness.
Thus, the causes of headaches with vegetative-vascular dystonia can be divided into external and internal. The first include:
- infectious diseases;
- constant stress;
- bad habits;
- unhealthy gastronomic habits;
- frequent overwork;
- brain injuries;
- chemical exposure;
- radiation.
Internal factors include:
- heredity;
- individual characteristics of the body;
- allergies;
- internal illnesses;
- hormonal changes;
- personality traits: suspiciousness, tendency to take everything to heart and worry about trifles;
- sedentary lifestyle.
What are the causes of headaches
Vegetative-vascular dystonia can occur due to the following reasons:
- severe emotional stress;
- hormonal imbalance associated with insufficient functioning of the central endocrine organs;
- congenital and hereditary disorders of vascular tone, when relatives have migraine attacks or vascular diseases in the family;
- heart disease with disturbances in heart rhythm and blood flow.
In each case, the doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination to identify the main causative factor. Only after it is clear why the headache is very bad can treatment effectively rid a person of a vegetative-vascular problem. And, most importantly, try to prevent these troubles in the future.
Types of headaches with VSD
Doctors distinguish three types of headaches that occur with vegetative-vascular dystonia:
Tension pain
When do they arise?
- due to shocks, strong experiences;
- after severe stress;
- against the background of work that requires constant concentration and memory;
- due to high mental stress.
Nature of pain
Usually the pain spreads to both parts of the head, is dull in nature, and causes the feeling of a squeezing hoop on the head.
What will help
- complete rest;
- switching to another occupation;
- breaks during strenuous activities;
- the ability to avoid stressful situations.
Migraine
Migraine is a common manifestation of VSD, more often observed in women.
Main causes of attacks
- noise and large crowds of people;
- great physical activity;
- visit to the steam room;
- drinking alcohol;
- stress.
Nature of pain
- severe throbbing pain on one side of the head,
- usually concentrated in the temple, spreading to the forehead or eyes.
Associated symptoms
- nausea;
- sometimes vomiting;
- light intolerance;
- noise intolerance;
- chills, cold extremities.
What to do
Lie still, ensuring complete silence and darkness. After some time, the pain will begin to subside.
Cluster pain
These pains are more common in men. A characteristic symptom is the occurrence of attacks at night and cessation in the morning. They are especially strong at the beginning of an attack.
Nature of pain
- localized on one side of the head;
- usually hurts in the brow ridge, forehead, temple, crown of the head, eyes;
- can be observed in the jaw, chin, cheek.
Associated symptoms
- increased sweating;
- lacrimation;
- facial redness;
- drooping eyelid.
What to do
- get enough sleep;
- do not overwork;
- to refuse from bad habits.
Symptoms and types of pain
Thanks to the presence of a number of specific signs, doctors are able to distinguish cephalalgia due to autonomic dysfunction from other types of headaches. The difference between the symptom under consideration in VSD and the pain syndrome in dental diseases and stroke is its lower intensity.
Headaches begin to bother the patient after waking up, in stressful situations, under the influence of stuffiness. Circular, squeezing pain may be observed that does not go away over a long period. Sometimes cephalalgia accompanies a person suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia from morning to evening.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is accompanied by aching, dull, squeezing cephalgia. Vascular spasm and a sudden decrease in pressure can cause loss of consciousness and cause unexpected disorientation in space. The patient feels weak, cannot concentrate on doing ordinary things, and mental exercises are difficult.
Pain rarely appears at night. This symptom may only bother those who sleep poorly or are nocturnal. Violation of the “wakefulness-rest” regime leads to headaches appearing unexpectedly, at any time of the day. Cephalgia is more pronounced in those who sleep less than 7-8 hours per day.
The occurrence of headaches with NCD is usually not affected by blood pressure (its surges). Sometimes there is still a connection between cephalgia and hypo-, hypertension. Low pressure increases pain due to oxygen starvation of the brain, and high pressure increases pain due to increased intracranial pressure, venous intracerebral hypertension.
The distinctive features of cephalgia in neurocirculatory dystonia are:
- presence of fog in the head;
- the appearance of a symptom in the morning (after waking up);
- dizziness with vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- ineffectiveness of pain medications;
- nausea, weakness;
- increased causeless anxiety;
- tinnitus;
- continuation of pain throughout the day;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- increased pain, pulsation after bending the body forward.
Headaches that constantly occur with vegetative-vascular dystonia are different. This is due to the presence of certain pathologies (failures in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, anemia, impaired neurohumoral regulation). In addition to typical cephalgia, the patient is concerned about:
- migraine. It is a neurological pathology of unspecified etiology. Migraines with VSD are not uncommon. They usually occur together with a deterioration in health, photophobia, a desire to protect themselves from noise, strong odors;
- tension pain. It appears in the form of the body’s reaction to increased mental and emotional stress (reading, working on a computer, driving a car). Dull pain occurs due to constant tension of the eye muscles, shoulder girdle, and neck. Increased pain is observed when trying to concentrate (reading text);
- cluster cephalgia. This type of headache is considered the least studied. Its appearance provokes damage to blood vessels, nerves of the brain, face, and neck. The condition is characterized by a one-sided manifestation. Paroxysmal pain spreads to the cheek, eye, neck, temple. Their duration is 1 – 30 minutes.
Important: An attack of cluster cephalgia requires immediate qualified help. You won't be able to relieve it with painkillers on your own.
Morning headache
The main symptom of neurocirculatory dystonia is considered to be morning headache. This serious condition begins almost immediately after rising (3-5 minutes after the patient wakes up). The headache begins to hurt gradually, sometimes rapidly, after abruptly getting out of bed. The duration of the pain syndrome varies (1 – 2 minutes, about half an hour, the whole day). Most often, the pain does not leave the patient from morning to night, its subsidence is replaced by intensification.
An attack of morning cephalgia significantly worsens the well-being of a person suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia. The feeling of lethargy follows him throughout the day. Headache is accompanied by other signs indicating disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system:
- irritability;
- apathy;
- feeling of depression, indifference to what is happening;
- the presence of an increased reaction to loud sounds;
- manifestation of outbursts of anger;
- nervousness;
- hearing impairment;
- loss of appetite;
- dizziness;
- tearfulness;
- constant fatigue;
- manifestation of anxiety.
If the morning pain in the head is migraine-like in nature, it will not be possible to eliminate it with medications. Sleep can alleviate a serious condition. Cephalgia recedes with complete loss of consciousness. If the patient cannot sleep due to its manifestation, then the cause of severe pain is not vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Pain in the head area appears in the morning or at night. Associated symptoms may include: sore eyes, stuffy ears, pulsation in the temples. Cephalgia has a different character (a feeling of squeezing or bursting). Blood pressure during headaches is usually normal.
Treatment
Before taking painkillers for headaches and dizziness due to VSD, you need to undergo an examination. All symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are associated with functional disorders of the autonomic nervous system, so you need to not just relieve the headache, but treat the entire body.
How to treat without pills
Manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia are treated comprehensively. Before moving on to drug therapy, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that provoke headaches and other symptoms.
It may be possible to do without medications. These common activities include:
- Visiting a doctor who diagnoses and treats VSD. Not so long ago, neurologists dealt with this; today, vegetative-vascular dystonia is under the purview of psychiatrists.
- Lifestyle changes: frequent exposure to the air, adherence to work schedule, proper rest.
- Proper nutrition: include in the menu more foods that strengthen blood vessels, speed up metabolic processes, and improve immune defense. The diet should contain more greens, fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Moderate exercise and sports: morning exercises, walking, swimming, cycling.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol forever.
- Do not stay in a stuffy room, ventilate it constantly.
Only these simple actions can effectively combat the manifestations of VSD, provided that they are performed constantly and become a way of life.
Drug treatment
In advanced cases, it is impossible to do without medications. The main thing is not to prescribe them to yourself. Only a doctor can select the optimal medications, their dosage and duration of use. The main means for treating manifestations of VSD include:
- Sedatives based on medicinal herbs: tinctures of valerian, motherwort.
- Nootropics. Drugs in this group stimulate blood flow and improve brain function.
- Tranquilizers. They are usually prescribed for panic conditions, increased anxiety and tension.
- Sedative medications.
- Cerebroangiocorrectors normalize blood circulation in the brain.
- Antihypertensive drugs are needed for high blood pressure.
If you have an attack
During an attack, the patient may require emergency care. It will depend primarily on what type of attack you are dealing with - vagoinsular or adrenal.
Signs of vagoinsular
- dizziness;
- headache on one side;
- sweating;
- rare pulse;
- low pressure;
- visual impairment;
- lack of air;
- loss of consciousness.
What to do
- calm the patient down by giving him Corvalol;
- rub the ears;
- massage the central fossa of the foot.
Signs of an adrenal attack
- excited state;
- tachycardia;
- cold extremities;
- tremor;
- increased blood pressure;
- feeling of fear.
What to do
- breathe deeply, holding a short pause with each breath;
- massaging the supraclavicular area and eyeballs;
- warming up the back of the neck.
If symptoms of both types of attacks are combined during an attack, assistance should be provided based on the prevailing symptoms.
Treatment of headaches with vegetative-vascular dystonia
Walk in the fresh air
Headache is only a symptom of VSD, which must be eliminated by treating the disease or disorder that provoked it. In such cases, you should not take painkillers uncontrollably, since their effect only briefly relieves the unpleasant symptom, and the main cause of the disease continues to have a negative impact on the autonomic system.
Treatment of VSD includes two approaches: lifestyle changes and drug therapy. In the first case, the patient must follow general recommendations:
- observe the rest and work regime;
- regularly spend time in the fresh air;
- develop physically by engaging in moderate sports (swimming, race walking, cycling);
- quit bad habits;
- include in the menu products that have a beneficial effect on blood vessels, the immune and metabolic systems.
If headaches continue to bother you and significantly worsen your overall well-being, the patient is prescribed medications:
- sedatives in the form of herbal tinctures;
- nootropics;
- sedatives;
- means that normalize blood circulation;
- drugs that increase or decrease blood pressure;
- tranquilizers.
Feel free to ask your questions right here on the site. We will answer you!>>
Folk remedies can be used for headaches caused by vegetative-vascular dystonia only after finding out the exact cause of the disorder and agreeing on the prescription with the doctor. This is due to the fact that most herbal components that effectively relieve headaches as a symptom may be contraindicated for use due to existing diseases of internal organs and systems.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a complex of symptoms manifested by a disorder in the functioning of body systems. The most unpleasant sign indicating a malfunction of the autonomic-vascular system is a headache. It can be treated with antispasmodics and analgesics, but these medications only help temporarily. Headaches with vegetative-vascular dystonia disrupt normal life activities and can cause a number of psychosomatic pathologies and loss of interest in life.
Cephalgia (headache) with VSD has a vascular etiology. The following factors contribute to its occurrence:
- lack of sleep;
- nervous tension;
- overwork.
More often, headaches bother teenagers due to the instability and lability of their nervous system. Cephalgia in neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD) is provoked by factors of an exogenous and endogenous nature.
Among the external reasons for the development of an unpleasant symptom, we indicate:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- injury to the neck, collar area;
- intoxication of the body;
- past infections (viral, bacterial);
- lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction;
- unfavorable climatic conditions.
Headaches with VSD are provoked by the following endogenous factors:
- allergic reaction;
- genetic predisposition;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- characteristic personality traits (suspiciousness, impressionability, nervousness);
- individual reaction to stimuli (flashing, bright light, loud noise, sound, strong smell);
- hormonal dysfunction;
- disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system;
- failure of the endocrine system.
Cephalgia can be caused by insufficient oxygen supply to brain cells. Patients experience hypotonicity, spasm of vascular walls, and impaired blood flow.
Experts have found that the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia provokes disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are responsible for the production of endorphin and serotonin (pleasure hormones). They are responsible for the functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems. Failures in the operation of the mentioned systems provoke headaches, worsen general well-being, and cause increased nervousness.
Important: If VSD is suspected, ultrasound of neck vessels, EEG, and ECG are prescribed for timely visualization of impaired patency of veins and arteries.
Constant pain in the head is a concern in the presence of the following pathologies:
- eye diseases;
- arterial hypertension;
- asthenic syndrome;
- hypotension;
- neurotic state;
- chronic infections;
- CNS disorders;
- diseases that cause hearing impairment.
Even glasses or a squeezing headgear can cause cephalgia in vegetative-vascular dystonia.