Headaches, or cephalgia, are a fairly common symptom of many diseases and conditions.
It is believed that headaches are more common in women than in the stronger sex.
In this case, the causes of frequent headaches should be sought in the physiological characteristics of women, due to their more complex anatomical structure and functionality.
The main, but far from the only, cause of headaches in women under thirty years of age is considered to be hormonal fluctuations in the body.
They are associated with the functions of ovulation, gestation and childbirth.
It should be borne in mind that frequent headaches in women of different age groups are symptoms of pathological disorders.
Classification
There is an ICD 10 disease classifier. Cephalgia belongs to the International code R51.
According to the international classification of diseases, cephalalgia is divided into the following types:
- vascular;
- tension cephalgia;
- vasomotor cephaly;
- headache when using medications;
- migraine;
- post-traumatic headache.
Vascular headaches are considered the most common type of cephalalgia.
The pathology manifests itself in the form of throbbing pain with a sharp expansion or narrowing of blood vessels.
The causes of headaches with hypotension are increased blood flow, stretching of small arteries, poor outflow of blood (venous) from any part of the head.
The pain intensifies when tilting the head and lying down. Outflow improves in a standing position.
Pain can be caused by compression of the neck vessels (tight tie, prolonged tilt of the head down), stress, hypertension.
This type of cephalgia manifests itself in various pathologies of internal organs, neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD).
A characteristic feature of headaches with hypertension are the following factors: increase after exercise; occurrence after sleep; manifestation in the back of the head.
Stroke (hemorrhagic) is characterized by acute development of headache against the background of increased blood pressure.
The causes of pain are the accumulation of blood escaping from a blood vessel in any part of the brain.
The nature of the pain is severe and unexpected, accompanied by vomiting, nausea, photophobia, and loss of consciousness.
Tension cephalgia occurs in many people. Frequent headaches of aching nature occur when working, sitting in an uncomfortable or incorrect position in the form of spasms of the muscles of the neck and head (scalp).
Prolonged muscle tension leads to stretching of the meninges and affects numerous nerve endings.
Such pain can be prevented by taking breaks from work and performing gymnastic exercises.
Vasomotor cephalgia manifests itself as pressure in any head area.
Frequent headaches are provoked by: tension in the muscles of the shoulders and neck; sedentary lifestyle; lack of rest; large doses of medications; smoking; stress.
A unilateral spasm of the blood vessels of the brain during migraine affects the trigeminal nerve, causing severe, unbearable headaches of a pulsating nature.
Migraines are often accompanied by vomiting and nausea. During attacks, the patient cannot tolerate noise or light.
Migraine is considered a neurological hereditary disease.
Arterial hypertension
Headache may be associated with hypertension. This is a chronic condition of the cardiovascular system, a disease characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure (abbreviated as BP) from 140/90 mm Hg. Art. and higher.
People suffering from arterial hypertension have high blood pressure and headaches in the early hours. The location of pain is the occipital region. It is worth noting that pain may not occur with a slight or moderate increase in pressure. They are always observed only with a rapid increase in blood pressure over 200/120 mm Hg. Art.
If you often have a headache, what could be the reasons? One answer to this question is arterial hypotension. This is a condition in which the blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. Art. and less. It is characterized by headache.
- weakness;
- lethargy in the morning, drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- emotional instability;
- sensitivity to weather conditions;
- pallor;
- palpitations and shortness of breath during exercise.
Experts have created a classification of arterial hypotension. There are acute and chronic varieties. The latter is divided, in turn, into physiological, primary and secondary. Acute hypotension is a sharp decrease in blood pressure. A similar condition is observed with blood loss and acute myocardial infarction.
Low blood pressure, headache... Such symptoms are sometimes noticed by absolutely healthy people. Athletes serve as an example. They experience low blood pressure during constant physical activity. This feature is an adaptive reaction of the body, a protective measure. This type of arterial hypotension is called physiological.
The primary type is considered an independent disease. It is not a consequence of any pathologies and does not occur against the background of existing diseases. Doctors see primary hypotension as a special form of neurosis-like disease of the vasomotor centers of the brain.
Hypertension manifests itself in the form of temporal and occipital pain. A common reason is inattention to one’s body, expressed in excess weight, a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, and mature age greatly intensifies attacks, turning them into chronic headaches.
Arterial hypertension affects the functioning of the entire body. It causes disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels, negatively affects the heart and kidneys, and significantly reduces visual acuity.
Pulsation of blood vessels is accompanied by nausea and sometimes vomiting. In addition to contacting a therapist, an examination by a cardiologist is also required with the prescription of complex treatment. In addition, if attacks occur in the morning, there is a risk of having a brain tumor.
MORE ABOUT: Pain and heaviness in the legs: 20 folk recipes
Causes
The main causes of headaches in women are pathological disorders and negative conditions.
- Viral and infectious diseases.
- Aneurysm.
- High or low blood pressure.
- Diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
- Meningitis.
- Intracranial pressure.
- Nervous and physical overload.
- Diseases of internal organs (genitourinary, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal systems).
- Trigeminal neuralgia.
- Iron deficiency (anemia).
- Optic nerve tension.
- Temporal arteritis.
- Apoplexy.
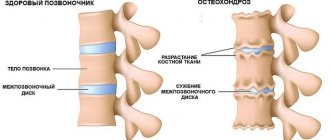
- Cervical osteochondrosis.
- Stress.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Eye diseases.
- Inflammation or swelling of the brain.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Muscle strains.
- Violation of sleep and eating patterns.
- Oxygen starvation.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Strict diet.
- Change of weather.
- Heatstroke or sunstroke.
- Fluid deficiency.
- The impact of medications on the body (exceeding the norm).
The list of factors that provoke headaches is long. So why does cephalalgia often occur?
According to statistics, the frequency of headaches in women is higher than in men. The causes of frequent headaches are hidden in physiological differences.
Sharp changes in hormonal levels and organ function (increased load) occur during ovulation, at different stages of pregnancy, during the prenatal and postpartum periods.
Possible concomitant causes of headaches during these periods are chronic diseases.
The following factors contribute to the manifestation of cephalalgia:
- tension and compression of the muscles of the skull;
- irritation of the occipital or trigeminal nerve;
- blood thickening (viscosity);
- psychogenic;
- eye diseases;
- nasal infections.
One of the common types is muscle tension cephalgia (80% of the world's population).
It manifests itself as a result of prolonged muscle contraction and compression of blood vessels.
Blood flow decreases, and oxygen starvation of the muscles occurs, which leads to the accumulation of toxic substances and effects on the nerves.
They transmit a signal to the brain. The result is a constant headache.
With such cephalgia, pressure in the temporal or frontal part increases.
The duration of unpleasant sensations depends on the individual characteristics of the person and ranges from half an hour to several days.
Compression of blood vessels in the neck area manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- low mobility of the neck muscles;
- dull, stabbing or shooting pain;
- vomit;
- blurred vision;
- dizziness;
- ringing and tinnitus (should be differentiated from hypotension);
- manifestation when tilting the head and (physical) loads.
The female population is more susceptible to irritation of the occipital or trigeminal nerve. Deterioration of blood flow and compression of the nerve leads to primary neuralgia.
Infectious diseases and the formation of tumors become the culprits of secondary neuralgia.
Pain occurs with neuropathic complications.
Of particular note is the cause of cephalalgia, such as blood viscosity. As the level of the liquid part of the blood (plasma) decreases and the red blood cells increase, viscosity increases.
Blood thickening occurs for the following reasons:
- eating salty, sour, difficult to digest foods;
- disruption of the structure of blood vessels and their inner lining;
- liver dysfunction;
- incomplete breakdown of food by enzymes;
- deficiency of microelements and vitamins;
- smoking;
- food contamination with pesticides, toxins, insecticides;
- increased spleen function;
- abuse of strong alcoholic drinks;
- increase in red blood cells;
- adhesion of leukocytes, erythrocytes, formation of blood clots;
- depressive state.
Chronic diseases, worms, and poor lifestyle negatively affect the systems that produce blood components and various hormones.
Accordingly, the effect is on viscosity. Thickened blood is poorly transported through the blood vessels and the body's main pump - the heart - begins to work in increased mode.
When viscosity increases, the following conditions occur: unexpected headache; heaviness in the legs; varicose veins, nodes; dry mouth; frequent coldness of hands and feet; absent-mindedness; depression; despondency; general weakness; forgetfulness.
It is not always possible to detect increased blood viscosity during examination and medical history.
Sometimes the disorder is asymptomatic. To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive blood test, coagulogram, and hemoscanning.
During laboratory testing, the condition of blood vessels and blood clotting indicators are checked.
To determine the root cause of cephalgia, an electroencephalogram of the brain and computed tomography are prescribed.
Treatment
After conducting research and establishing a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medications that strengthen blood vessels and thin the blood.
To strengthen the walls of blood vessels, the following drugs are prescribed:
The doctor prescribes blood thinning medications.
- Warfarin or analogues.
- Chimes.
- Thrombo ACC
- Cardiomagnyl.
- Aspecarda.
- Lospirin.
- Aspirin Cardio.
- Coumadin.
To keep the blood in proper condition, experts recommend a special diet containing the following types of foods:
- fruits (grapefruit, apples, pomegranate, all citrus fruits, lime);
- seafood (crabs, mussels, squid, scallops);
- sea fish;
- cocoa, chocolate (dark);
- berries (plum, raspberry, cherry, strawberry, blueberry, cranberry);
- vegetables and grains (onions, garlic, fresh cucumbers, tomatoes, beets, sprouted wheat grains, sunflower seeds, artichoke, beets, ginger, cinnamon).
It is recommended to drink at least two liters of tested drinking water per day.
You should exclude or limit the consumption of sugar, salt, smoked, fried, spicy foods, and marinades.
Types of headaches in women
The reason why a woman has a headache may lie in various diseases. Depending on the nature of the occurrence of headaches, there are:
- primary. These include migraine in women. Attacks sometimes occur more than three times a week. They can appear when drinking too much coffee and are accompanied by nausea. Unpleasant sensations may occur when the weather changes. Sometimes patients complain of pain in the orbital area;
- secondary. In this case, headache appears against the background of other diseases. Only a specialist can determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe effective treatment.
The types of headaches can be:
- Beams. The location is the orbital area. The attacks last for more than half an hour. In some patients, the pain does not go away for several hours. Attacks may continue for several months.
- Neurological. These include migraine. Painful sensations occur approximately once every two weeks.
- Chronic. Most often, pain is felt in the temples, as well as in the back of the head and forehead. The patient suffers from attacks once every 2 days.
- Tension (tension). This type of pathology occurs most often. In this case, attacks do not depend on age characteristics.
When a pathology appears, it is necessary to determine its type, which will allow the most effective treatment to be prescribed.
Low or high blood pressure
Headaches often occur in women predisposed to low blood pressure. Due to low pressure, the blood supply to the brain deteriorates, so it experiences oxygen starvation and sends signals of discomfort. For some, to cope with the problem, it is enough to drink an extra cup of coffee, since caffeine increases blood pressure, or take a few drops of tincture of lemongrass, eleutherococcus, or ginseng.
An obsessive headache in the back of the head and neck associated with high blood pressure is most often a response to nervous tension or stress. However, a systematic rise in pressure and the associated squeezing or throbbing pain in the head are a reason to consult a doctor. Hypertension is treated with appropriate medications, and only a doctor can prescribe a drug that is suitable for your case, since the cause of high blood pressure may be a pathology of the heart, kidneys or blood vessels.
Why do women often have headaches?
Determining the causes of frequent headaches in women is a very important aspect in the treatment of pathology. In the case of vascular disease, there is a deterioration in blood circulation in the brain, which causes unpleasant symptoms. The causes of headaches may be diseases of the lining of the brain of an infectious-inflammatory nature.
Periodic attacks are characteristic of migraines or cluster headaches. The cause of severe attacks of cephalalgia may be the development of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine. Hormonal headaches are often observed in women, which is explained by disruption of hormone production.
When disorders such as cerebral atherosclerosis appear in the body, patients experience cephalgia. Headaches often occur during pregnancy, which is explained by hormonal imbalances. For the same reason, pain in the head occurs during menstruation. During menopause, this symptom often appears.
Cephalgia is observed after injuries, even if the woman suffered them several years ago. This is due to irreversible damage to blood vessels and deterioration of blood circulation in the brain.
When the body is intoxicated, acute or chronic, the patient experiences a headache.
There are a large number of causes of head pain, so accurate diagnosis is necessary to prescribe treatment.
Pregnancy
Women who suffered from constant headaches and migraines before pregnancy note that during pregnancy the course of the disease acquired positive dynamics, attacks either decreased significantly or did not bother them at all. Most often, such an improvement in condition occurred in the second and third trimester of pregnancy; explanations for this phenomenon can be simple - stabilization of estrogen production, equalization of the emotional background and stabilization of mental balance inherent in the body of a pregnant woman.
During lactation, when using any medications, it is strongly recommended that during therapy you stop breastfeeding and switch to artificial feeding. After completing the course of treatment, you can return to breastfeeding at the same rate.
Headache in pregnant women is a common manifestation of toxicosis, especially in the first trimester. This is explained by dramatic hormonal changes and mild intoxication. Pregnant women should not take medications, but you can do breathing exercises, drink more clean water, and walk in the fresh air.
If a frequent headache bothers the expectant mother in the second half of pregnancy, this may be an alarm bell. Firstly, headaches are caused by high blood pressure, and for pregnant women this is dangerous because the blood supply to the fetus deteriorates, partial placental abruption or premature birth may occur.
Secondly, pain in the head can be a sign of late gestosis and preeclampsia, which poses a direct threat to the life and health of the mother and the unborn baby. In any case, you should immediately inform your gynecologist about recurring headaches. The doctor will prescribe a number of additional tests and decide on treatment at home or in a hospital.
Provoking factors
Most patients wonder why cephalalgia may appear.
There are a number of provoking factors due to which women often have headaches. Experts identify such factors as constant headaches, such as nervous tension and anxiety. A headache attack can be triggered by excessive mental or physical stress. Stress is often the cause of pain. The appearance of symptoms can be caused by prolonged work at the computer. Headaches often occur after watching television or reading for a long time.
Mysterious migraine
We should also talk about migraines. Women experience this debilitating pain more often. Overall, every fifth woman suffers from migraine, but only one in 15 men suffers. But finally, the reasons why women suffer more are not clear, as are the causes of migraines in general.
Scientists estimate that about 10 percent of the world's people suffer from migraines—severe, debilitating headaches that throb and affect half of the head.
In men, cluster pain is more common - severe one-sided pain, usually around the eye, which may be accompanied by watery eyes and swelling around the eyes. Migraine is still very little studied. Doctors don't know what exactly is causing this pain.
Among scientific hypotheses, there are even genetic factors, so there are studies that prove that two thirds of migraine sufferers admitted that one of their parents or older relatives had the same illness.
How to relieve pain
Initially, it is recommended to determine the causes of a woman’s headache, which will allow us to develop an effective treatment regimen. This requires complex diagnostics using instrumental methods - ultrasound, electrocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalography. To identify the inflammatory process, laboratory tests are prescribed.
Frequent headaches in women are most often treated with medications. When symptoms appear, the use of analgesics is recommended. Taking anti-inflammatory drugs that have an analgesic effect also helps.
During pregnancy, before taking a medication, a woman should consult a doctor, as the medicine may be contraindicated for her due to unwanted side effects.
If cephalgia occurs against the background of low blood pressure, then it must be treated with appropriate medications. You can drink a cup of tea or coffee. If the disease appears due to increased blood pressure, it is recommended to take antihypertensive drugs.
If headaches are caused by hormonal disorders, hormonal medications are used.
To eliminate the unpleasant symptom, manual therapy is often used. It helps relieve tension headaches and migraines. Another additional method of treating pathology is massage. It is highly effective if the patient has a chronic form of the disease or a consequence of injury.
Some patients are recommended to use acupuncture. It consists of influencing certain points with needles, which helps to activate the functioning of organs. Most patients note an improvement in their condition after just a few sessions.
An effective method of treating pathology is osteopathy. This therapeutic method is used if cephalgia occurs against the background of pathologies of muscles, joints and organs.
Treatment can be carried out using physiotherapeutic procedures that use alternating current, laser radiation, magnetic field and other physical factors. This treatment method can be used for any type of headache.
If cephalgia occurs against the background of atherosclerosis, then extracorporeal hemocorrection is used for treatment. Thanks to this method, excess cholesterol is eliminated from the blood, which promotes proper blood circulation in the vessels of the brain.
Quite effective auxiliary methods are physical therapy and traditional medicine.
There are a huge number of therapeutic techniques that are used to eliminate headaches. The doctor chooses the treatment method based on the severity of the pathology.
What is she talking about
According to many experts, an absolutely healthy person can experience pain up to 2 times a week , but still continue the usual rhythm of work.
Main symptoms of tension headache :
- Appears on both sides.
- It lasts quite a long time, causing severe discomfort, but is not characterized by excessive intensity.
- A person can engage in work activities, even carry out sports loads. This does not change the nature of the pain.
- Not all patients classify unpleasant symptoms as headaches. They indicate a feeling of constriction and believe that they need rest.
- The symptoms are not accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the gastrointestinal tract, and patients practically do not react to certain irritants coming from the environment.
Migraine symptoms:
- Pulsating in nature, usually appears on one side only.
- Medium or high intensity, unpleasant sensations are expressed, affect work activity.
- Physical activity provokes a change in the nature of pain, usually leading to its intensification. Even unnecessary movements are dangerous.
- There is a fairly wide variability in the duration of an attack; it can last several hours or 2-3 days. One patient may experience both long-term and short-term attacks.
- Painkillers can only act at the beginning of pain symptoms, after which they are useless.
Headache: one symptom - three solutions! “Live Healthy!” Program:
This publication will tell you how to make original bookmarks for books with your own hands.
How to determine your facial skin type? Our article will help you figure it out.
What not to do if you have a headache
Only a doctor can determine the method of treating pathology.
If the patient self-medicates, she may experience serious problems. That is why, with frequent attacks, a woman is advised to consult a doctor. After carrying out appropriate diagnostic measures, the specialist will develop an effective treatment regimen. It is strictly forbidden to take antispasmodics without a doctor’s recommendation. These drugs can eliminate the symptom, but they do not fight the cause of the disease. In addition, after taking medications of this group, the process of diagnosing pathology becomes more complicated.
When to see a doctor
To determine the cause of headaches in women, you need to consult a specialist.
This symptom occurs in a variety of pathologies, so the patient should pay attention to when and under what circumstances it appears. The doctor also needs to know about the patient’s age, whether she is menstruating, pregnant or menopausal. If, in addition to cephalgia, changes in the functioning of the body were observed or additional symptoms appeared, then this should be reported to a specialist.
Thanks to the data obtained, the doctor will be able to determine the cause of the pain and prescribe effective medications.
Tips & Recommendations
To prevent the problem from developing, avoid the following situations :
To get rid of them, you need to follow certain recommendations , and if there is no desired effect, consult a doctor to receive full treatment.
Headaches or Cephalgia are a fairly common symptom of many diseases and conditions.
It is believed that headaches are more common in women than in the stronger sex.
In this case, the causes of frequent headaches should be sought in the physiological characteristics of women, due to their more complex anatomical structure and functionality.
The main, but far from the only, cause of headaches in women under thirty years of age is considered to be hormonal fluctuations in the body.
They are associated with the functions of ovulation, gestation and childbirth.
It should be borne in mind that frequent headaches in women of different age groups are symptoms of pathological disorders.
Let's consider the important questions that most concern people: “Why do women often have headaches?”; types of cephalgia; ways to combat the disease.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of constant headaches in women, it is necessary to carry out their prevention in a timely manner. It consists of the patient following certain rules:
- elimination of stressful situations and nervous tension;
- adherence to sleep and rest patterns;
- ensuring rational nutrition;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- sports and daily walks in the fresh air;
- Drinking caffeinated drinks in limited quantities.
By following all of the above recommendations, the patient will be able to avoid painful attacks.
Cephalgia is a rather unpleasant symptom that occurs due to the fault of the woman herself or against the background of various pathological processes. In order to eliminate a symptom, it is necessary to first determine its cause. The choice of treatment method is made by the doctor in accordance with the type of disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
Almost all people, when a headache occurs, try to quickly take a painkiller pill. Ubiquitous advertising also contributes to this behavior. Not only do headaches become chronic without adequate therapy, but regular use of analgesics can aggravate the course of the disease.
The most rational tactic is to search for the cause of pain. And in this case, the following information will help - the location of the pain, its nature and intensity, duration and frequency of occurrence. As a rule, one or two cases of headaches are not dangerous. However, frequent and repeated symptoms are a symptom of serious disorders in the human body.
Symptoms of tension pain
Symptoms are divided into 2 categories:
- The episodic variant is accompanied by painful sensations lasting less than 20 days over six months. The severity of episodic pain symptoms is insignificant.
- Chronic headaches lasting more than 21 days for 6 months. The first symptom of pathology is pain of moderate or high intensity. The intensity of the pain is moderate. It is easier to determine what to do with the disease than with other forms, since self-medication can be used against the background of drug treatment.
Tension headaches do not interfere with daily activities and are well tolerated by patients. The duration of the disease is from 30 minutes to two days.
There are specific features of tension cephalgia:
- Bilateral localization of pain;
- Transition of pathology to the back of the head and forehead;
- Pulsating character;
- Does not cause vomiting or nausea;
- Same frequency in elderly and adults.
Thus, tension headaches do not interfere with a person’s physical activity and performance. Its treatment can be carried out at home.
We determine the cause by localization of headaches
Why does my head hurt - looking for the cause
Based on what part of the head the source of pain is located, it is impossible to determine exactly what exactly triggered it. However, there are clear trends - which diseases most often cause pain in the temples, the back of the head, the forehead, or the entire head.
Pain that surrounds the head occurs when working at a computer for a long time due to overstrain of the neck muscles and incorrect body position (tilting the head forward, crooked posture), as well as due to eye strain.
Regularly occurring shingles pain may indicate psycho-emotional exhaustion, which is a consequence of prolonged stress (unresolved conflicts, the need to always be on alert, chronic lack of sleep, etc.).
Although such pain is rarely extremely intense and is the easiest to treat, frequent episodes of pain have a significant impact on a person's well-being and negatively affect the quality of life, causing irritability and worsening depression.
Pain in the temples - this complaint can often be heard from hypotensive patients. Low blood pressure associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia or anemia. At the same time, during the day the patient notices a pain spread throughout the head, but in the morning the symptom appears suddenly. The sensations are localized precisely in the temporal region and are accompanied by dizziness and loss of clarity of vision.
Frequent headaches in the temples are a sign of worn-out cerebral vessels. This condition often indicates an increase in intracranial pressure, while arterial pressure may be within normal limits or even low.
A sharp, throbbing headache in one temple, spreading to the entire half of the head, is a sign of a classic migraine. A migraine attack is preceded by blurred vision and photophobia.
Other causes of pain in the temples:
- Hypoxia - lack of oxygen when working in a stuffy room, with atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels
- Intoxication is chronic poisoning of the body with various kinds of poisons: smoking, inhalation of strong odors (even pleasant ones), excessive consumption of spices in food and poor quality food. Even the constant use of plastic containers for storing food releases toxic substances that can cause chronic poisoning.
- Trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by paroxysmal, extremely intense pain in the temples. Appearing more often at night, an attack can be triggered by any irritant - loud conversation, temperature exposure, tactile sensations and even food intake. Lack of treatment leads to more frequent attacks, an increase in their duration and the spread of pain to the eye area and the back of the head. Neuralgic pain always occurs on one side. A common cause of their occurrence is carious teeth, chronic inflammatory processes in the ears and eyes.
- Malocclusion and pathology of the jaws - excessive clenching of the jaws leads to constant muscle tension in the temple area, which provokes frequent pain. In this case, grinding of teeth at night is noted.
- Hormonal changes - the cause of periodic headaches in women can be pregnancy and breastfeeding, serious disorders leading to a prolonged absence of menstruation (including the physiological or postoperative onset of menopause). Hormonal surges are observed during puberty, including in teenage boys. This also explains frequent headaches in women during the premenstrual period. This is not a whim, it is the normal course of physiological processes in the female body.
Prolonged pain localized in the frontal region most often indicates an inflammatory process in the sinuses. Sinusitis and sinusitis are accompanied by difficulty breathing through the nose, heaviness in the area between the eyebrows or on both sides of the nose (especially when the head is tilted forward). Soreness in the forehead may indicate low intracranial pressure, and the pain may spread to the temples on both sides and the back of the head.
Pain in the forehead is a companion to high temperature. The most common causes of this are viral respiratory tract infections and sore throat. However, intense, frequent headaches may indicate the development of encephalitis, malaria, tuberculosis and other serious diseases.
Dehydration (insufficient fluid intake) and fasting, practiced for the purpose of healing, often provoke headaches localized in the forehead or temples.
Pain in the occipital region is often associated with high blood pressure. However, such a symptom - throbbing pain in the back of the head - occurs only with constantly significantly high blood pressure or its sharp rise. Frequent pain in the back of the head is most common with cervical osteochondrosis, less often with spondylosis.
Diseases leading to illness
If you've recently hit your head, been in a car accident, or suffered a whiplash injury, you may be experiencing frequent headaches. It happens that cephalalgia suddenly intensifies several weeks or months after the injury, so it is quite difficult to establish the cause of the pain.
- Headache due to brain tumors
A tumor pressing on the brain causes frequent headaches. Severe pain appears after sleep and during physical exertion: coughing, sneezing, bending or defecating. These symptoms can be observed in a large number of neurological diseases, as they are the result of structural damage to the brain and central nervous system. Unfortunately, in some cases, symptoms appear when the disease is already in an advanced stage.
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain (meningitis and meningoencephalitis)
With inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord, frequent pain in the head is accompanied by fever, disturbances of consciousness, painful sensitivity to light and sounds, and stiffness of the neck muscles. The patient is unable to tilt his head to his chest and straighten his knees. Such diseases require hospitalization and treatment in a hospital setting.
- Infectious diseases not related to the brain
Bacterial and viral diseases that develop in any part of the human body can begin with a headache. A little later, other symptoms join it: chills, fever, weakness, drowsiness, lack of appetite.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
Often inflammation is associated with pathologies of the oral cavity, teeth, eyes, ears, and nose. They cause pain not only at the site of development of the inflammatory process, but also in the head. Sore throat, rhinitis, sinusitis, otitis media, conjunctivitis, pulpitis and other diseases are accompanied by obsessive headaches.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
People who have a sedentary job, or those who spend a lot of time at the computer, have probably noticed that they periodically experience attacks of headaches localized in the cervical-occipital region. The pain may spread to the temples or forehead. Sometimes cephalalgia does not go away for a very long time, so you cannot do without painkillers.
People suffering from cervical osteochondrosis experience painful stiffness in the muscles of the back and neck, as well as limited neck movements. Pain is caused by staying in a static position for a long time, sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow, and work involving bending and turning the head to the sides. At some point, pinched nerves or compression of the artery supplying the brain with blood may occur, causing a headache attack.
- Headache caused by medications and chemicals
Side effects of some medications include headaches. This applies to nitroglycerin, caffeine, codeine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, contraceptives, etc. Frequent headaches in women taking hormonal contraceptives may occur during treatment or after their discontinuation.
Additional symptoms: what to look out for?
Pay attention to other signs!
It is important to consider headaches in conjunction with other symptoms. This will allow you to determine the area of the pathological process and carry out the appropriate diagnosis.
- Headache and stiff neck - muscle tension in the back of the neck, first of all, makes it necessary to rule out meningitis. In this case, there is often an increase in temperature, lack of urination, and blue-purple spots appear on the body. Infectious-toxic shock is rapidly developing, and medical care must be urgent.
- A sharp, tearing headache, blurred vision, the appearance of neurological signs (changes in sensitivity, paralysis/paresis, changes in speech, distortion of the face on one side) and often loss of consciousness are a sign of a developing hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain).
- Pain and dizziness are a sign of insufficient blood circulation to the brain. The reason for this may be low blood pressure, anemia, cerebral atherosclerosis.
- Constant headache with a gradual increase in visual impairment, noise or congestion in the ears, nausea leading to vomiting, regardless of food intake, require the exclusion of brain cancer.
- Headache with nausea is a sign of pathology of the brain or its blood supply: high arterial and intracranial pressure, etc. The following sign will help to distinguish brain pathology from food poisoning or intestinal infection: with brain diseases there are no other intestinal symptoms (abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea etc.), nausea disappears when the headache is eliminated. Vomiting is not associated with food intake, sometimes (increased intracranial pressure) brings relief.
- Headache and frequent urination are a tandem that often accompanies migraines. At the same time, the a/d remains normal. Possible vomiting and blurred vision.
- Headache and fever are a sign of an inflammatory process. Its location is indicated by other patient complaints. However, in our time, filled with stress and nervous tension, thermoneurosis cannot be ruled out.
Acute angle-closure glaucoma
The term “glaucoma” refers to an eye disease that is characterized by an increase in intraocular pressure. There are 2 forms of this disease. One of them is called angle-closure glaucoma.
It occurs due to contact between the trabecular meshwork and the iris. When the disease occurs, the outflow of intraocular fluid from the eye becomes difficult, and the functioning of the trabecular meshwork is disrupted. As a result, intraocular pressure increases.
MORE ABOUT: Causes of pain in the popliteal fossa
Acute angle-closure glaucoma is something that gives some people headaches every day. With this disease, people complain of pain in the eye area, seeing rainbow circles around a light source, and blurred vision. Intraocular pressure is measured to confirm or rule out angle-closure glaucoma.
How to relieve a headache at home?
First of all, let's determine what not to do if you often have a headache:
- Drink alcohol (including during a hangover - the pain will ease, but quickly return with a vengeance) and smoke.
- It is not always advisable to use a heating pad with ice. For example, with a hypertensive crisis and concomitant atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels (found in most elderly people), cold will cause spasm of damaged vessels and can cause their rupture and hemorrhage.
- Re-take painkillers. Overdose is fraught with negative consequences. In this case, analgesics only block the pain syndrome and do not eliminate its cause.
- Citramon, which contains caffeine, is not used for headaches associated with high blood pressure. Citramon is indicated for headaches and normal/low blood pressure!
- Although one cup of coffee (not instant!) is not prohibited for hypertensive patients, it is not recommended with a significant increase in a/d.
- Taking Aspirin is contraindicated for children. It is replaced with safe paracetamol. Also, drugs with acetylsalicylic acid (Cardiomagnyl, Thrombo ACC, etc.) cannot be used for hemorrhagic stroke, but are advisable for cerebral ischemia.
- Take painkillers for more than 15 days (combined - 10 days). With long-term use of analgesics, not only addiction is possible, which means a decrease in the effectiveness of the drug, but also the development of drug-induced migraine.
What to do if you have frequent headaches:
- Ensure sufficient oxygen access - regularly ventilate the room, take daily walks.
- Avoid dehydration - drink at least 1.5-2.0 liters of water daily.
- Adequate rest - sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Monitoring blood pressure and timely taking antihypertensive drugs prescribed by the doctor.
- Avoid stress. In case of emotional stress, take light sedatives (preferably herbal ones - valerian, motherwort).
- Adjust your diet - give up canned foods that contain chemical additives, soda and alcohol, and limit your sugar intake.
- If these rules are followed regularly, tension headaches will be eliminated without taking any medications.
Effective measures for headache attacks:
- Ensure peace - lie down, exclude loud sounds and bright lights.
- Measure the pressure and act in accordance with the obtained values.
- For pain that occurs while working at the computer or due to osteochondrosis, do neck exercises: bending and turning the head to the sides, circular movements. Such gymnastics quickly eliminates muscle tension, compression of the vertebral artery and, as a result, headaches.
- In case of nervous tension, it is advisable to take sedatives. Sometimes an hour's rest or sleep is enough.
- Widely advertised MIG-400 (Ibuprofen), as an effective remedy for headaches, really quickly eliminates pain. Headaches, especially when overexerting, go away in about 15 minutes. However, this drug is approved for one-time use in people over 40 years of age. In the United States, this drug is not prescribed to children under 12 years of age due to the risk of sudden death.
Intracerebral hemorrhage
If you often have a headache, what are the reasons? An unpleasant symptom can be caused by various brain formations (hematomas, tumors, abscesses). The pain is most often diffuse. Sometimes it occurs in the place where the space-occupying formation is localized.
In the early stages of the disease, it makes itself felt in the morning and is weak. As the disease progresses, the nature of the pain changes. It becomes permanent and stronger. Other symptoms indicating the presence of space-occupying lesions include:
- vomiting that occurs without nausea;
- the appearance of oculomotor disorders;
- memory impairment;
- behavior change, etc.
It is worth noting that pain sometimes occurs when tilting the head, coughing, straining, or physical stress. This symptom may be characteristic of tumors of the posterior cranial fossa. The pain that occurs in the listed situations and is short-term, can occur without intracranial pathologies.
When you often have a headache, the cause may be a long-term head injury. The pain may persist for a long period. Its character is dull, diffuse and intensifies with physical activity.
In some cases, suspicious signs such as an increase in headache, drowsiness, confusion, changes in pupil size, and asymmetry of reflexes are observed. They may not be consequences of TBI, but symptoms of chronic subdural hematoma.
Headache - when do you need a doctor?
If you experience frequent headaches, even mild ones, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Prolonged pain is a sign of problems in the body. A visit to the doctor is required if the intensity of symptoms gradually increases. Immediate seeking of medical help is necessary in the following cases:
- sudden increase in headache;
- the appearance of neurological symptoms - numbness of the limbs, loss of sensitivity.
- rigidity (stiffness) of the neck muscles;
- headache accompanied by uncontrollable vomiting;
- against the background of pain in the head, a disturbance of consciousness develops.
Which doctor should I consult if I have frequent headaches? Usually the patient is recommended to make an appointment with a therapist. The doctor, taking into account other complaints, will prescribe the necessary initial examination, may identify the range of diseases that caused the headache, and refer you to a specialist.
Often, with frequent headaches, patients turn to a neurologist, especially if neurological symptoms are already present. To determine the nature of the disorder in the head, a specialist will prescribe an ultrasound of the brain, an encephalogram, and tomography. Only after an accurate diagnosis has been established, the doctor prescribes treatment. In this case, the list of drugs, their dosage and duration of use depend on the nature of the pathology and the patient’s condition.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses
If you often have a headache in the forehead area, or you feel heaviness near the nose, then this is sinusitis. This term means inflammation of the mucous membrane lining one or more paranasal sinuses. Sinusitis occurs as a complication of flu, runny nose, and infectious diseases. Bacteria and viruses provoke inflammation.
Pain and heaviness with sinusitis are not the only symptoms. Other signs of the disease are:
- nasal congestion;
- fever;
- purulent nasal discharge;
- pain when tapping the affected sinus area.