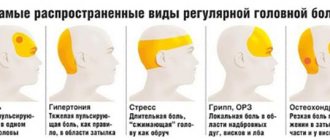
Etiology of the syndrome
Headache is a common cause of many pathologies. It can radiate to different areas, including temples, eyebrows, and eyes.
If the syndrome is permanent and severe, self-medication is contraindicated.
Experts say the main reasons why headaches appear in the eyebrow area are neurological pathologies.
Less commonly, this clinical manifestation appears in ENT diseases. Among other disorders, the leader in the etiology of long-term and frequent pain in the area of the right or left eyebrow is migraine.
The pain syndrome in this case is severe. The attack lasts for a long time.
It can cause discomfort to the patient for several hours or days. The pain initially appears in the forehead area, and then moves to the eyes and eyebrows.
The pain syndrome associated with migraine is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. After a few days, the patient begins to feel tired and irritated.
The symptom in question also appears when a nerve is pinched in the back of the head.
In this case, the pain spreads to the eyes, temples and forehead.
A pinched nerve occurs during severe stress and depression. During nervous and emotional shock, the neck muscles rapidly compress the nerve.
The pain first appears in the back of the head, and then in the forehead, between the eyebrows.
The clinic in question may appear when the vessels of the neck are pinched.
In this case, the blood vessels narrow, causing oxygen starvation. The patient experiences the following symptoms:
- pain in the forehead;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- impaired memory;
- problems with thinking.
The patient may experience fainting conditions against the background of the above-described clinic.
If the signs under consideration are associated with the course of neuralgic pathology, the following clinical picture may additionally be observed:
- noise in ears;
- changeable vision;
- damage to the optic nerve;
- problems with pupil movement.
Headache in the area of the right and left eyebrow appears in women against the background of a sharp hormonal imbalance, which is associated with the onset of the cycle and pregnancy.
Other reasons why the syndrome in question appears:
- inflammation;
- puberty;
- menopause;
- intoxication;
- abuse of spicy foods.
Diagnostics
If pain of unknown etiology occurs, you should consult a therapist. The doctor will conduct a survey and initial examination of the patient. Depending on the results of such an examination, he refers the patient to the appropriate specialist.
In some cases, additional diagnostic methods may be required:
- general or biochemical blood test;
- brain tomography;
- cardiogram of the heart.
Such research methods help to most accurately establish the clinical picture.
Often the factor that provokes the appearance of pain in the frontal area is a foreign object entering the eye. In this case, it is enough to simply eliminate it, but doing it yourself is not recommended, since you can damage the retina.
Diagnosis of eye pathologies
Depending on the presence of any additional headache symptoms, the therapist may refer the patient to the following specialists:
- An otolaryngologist is a specialist who examines all ENT organs, most often using x-rays. If the picture shows areas of darkening, this indicates the development of an inflammatory process, accompanied by the formation of pus.
- A dermatologist is a doctor who examines the condition of the skin. To do this, a smear is taken under the skin and under the eyelid.
- Neurologist - most often this specialist deals with the treatment of headaches. Usually, to make a diagnosis, it is enough for a doctor to examine the patient and study the complaints.
In some cases, treatment may be carried out by cardiologists, infectious disease specialists, and allergists. Conclusions about the method of therapy are made after all the necessary diagnostic measures have been carried out.
Brain and head injury
If you have a headache between the eyebrows after a blow or fall, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan.
This area contains blood vessels, so when injured, severe bleeding occurs.
Pain after a fall indicates infection in the wound.
If the patient is not given timely assistance, the infection will penetrate deeper, affecting nearby tissues, including the brain.
If an infectious process with a cut eyebrow is not observed, but the pain itself appears, the patient has a more serious injury - high intracranial pressure, concussion.
With this diagnosis, nausea, vomiting, and spatial orientation are disturbed.
To prevent serious complications, it is recommended:
- if the injury is closed, apply an ice pack to the site of the bruise;
- if the injury is open, the bleeding stops, and the edges of the wound are treated with iodine;
- study of anamnesis;
- calling an ambulance;
- constant conversation with the patient before the doctor arrives.
If your head hurts after an injury and there is heavy bleeding, urgent help from a surgeon and neurologist is required.
Do you have a headache above your eyebrow or forehead? Find out more about tension headaches
Tension headaches affect almost every person throughout their life. This is the most common headache. The exact definition of the disease is very difficult.
Therefore, in the literature this pain has received a number of designations: psychogenic, stress, idiopathic pain, etc.
in accordance with the International Health Society, the term “tension headache” is used, for the chronic form – “tension episodic headache”.
The disease can be characterized as a dull ache associated with fatigue, often preceded by stress. Usually the attack begins sporadically, sometimes the illness goes into a chronic stage, when the head hurts almost every day, and the initial motivating phenomena are often not defined and not understood.
It hurts mainly in the eyebrow area, often between the eyebrows, in the temple area (both on the right and left side) or forehead.
Pathogenesis
There are many factors involved in the pathogenesis of tension cephalgia. Hereditary predisposition has not been proven, as has hormonal dependence. On the other hand, psychosocial stress, domestic disputes, non-physiological work position, anxiety, depression and various emotional influences are indicated.
When studying the pathogenesis of tension cephalgia, attention is focused, in particular, on changes in tone and blood circulation in the muscles, changes in blood flow in the vessels of the brain and biochemical changes in the blood. Some of the results may help identify and understand the mechanisms that influence the occurrence of headaches.
Clinical signs
The pain is usually bilateral, most often it hurts in the forehead and temples, between the eyebrows, less often it hurts in the occipital region; The pain is stable, but may fluctuate in intensity. The onset is usually gradual.
This phenomenon distinguishes the disease from a typical migraine attack, which is characterized by pain in one half of the head, mainly in the temple area, rarely in the area between the eyebrows.
Headache (in the forehead, temples, or between the eyebrows) lasts for several minutes to days (30 minutes to 7 days), often occurring at night or in the afternoon.
Frequent various sensations in the head area: patients complain of a feeling of pressure, a hard hoop around the head, sensitivity is often manifested and the scalp hurts when combing, and there are frequent cases of stiff neck muscles.
The trigger for pain in the area between the eyebrows can be not only stress itself, but also the anticipation of stress and repeated conflicts. Provoking moments can be small but frequent daily troubles.
Accompanying symptoms may include mild photophobia and phonophobia, nausea is no exception, and there is no vomiting. Along with headaches, depression and anxiety may occur, especially in chronic conditions, sleep disturbances are common.
Fatigue and dizziness may occur. Subjective symptoms increase with physical activity or alcohol consumption.
According to the international classification of headaches, tension pain must meet the following criteria:
1. Recurrent episodes of pain that last from a few minutes to several days.
2. Intensity – weak or moderate.
3. Localization is two-way.
4. The pain does not worsen with physical activity.
5. Nausea, phonophobia or photophobia are also not uncommon.
6. Attacks occur less than 180 times a year, respectively, less than 15 times a month.
Differential diagnosis
For the differential diagnosis of headache, the most important is the medical history. Many specialists use questionnaires in which the patient fills out basic data, after which, over the course of several months, the characteristics of the attacks are recorded.
It is always necessary to exclude other causes of headache. The doctor inquires about the past history of injuries, especially to the cervical spine, and the presence of prolonged work in a fixed position.
It is necessary to eliminate inflammation of the conjunctiva or paranasal sinuses, refraction, and glaucoma. Myofascial dysfunction may occur in the area of the temporomandibular joint.
When these disorders are observed, the sensitivity of the joints and the presence, sometimes barely audible, crunching sound while moving the stethoscope are examined.
Spondylosis of the cervical spine causes cervicocranial syndrome. Dental disorders, especially in the upper jaw, can also be reflected by pain in the head.
Drug abuse should also be excluded. The cause of pain is mainly caffeine, Aspirin, Ibuprofen, sleeping pills, barbiturates.
Hypothyroidism can cause muscle pain and chronic headaches.
It is always necessary to repeat the diagnostic differential consideration if there is a change in the nature of the painful sensations.
Other pathologies
Many heart pathologies are accompanied by pain between the eyebrows and in the head. This is due to pressure surges.
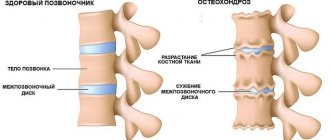
Another modern disease that provokes headaches that radiate to the eyebrows is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
The syndrome manifests itself against the background of compression of the roots in the spinal cord. The patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- tingling;
- problematic coordination when moving;
- dizziness.
Eye pathologies also provoke pain in the eyebrows and head. High intraocular pressure, which often accompanies eye diseases, provokes discomfort in the eyelids.
With this etiology, the help of an ophthalmologist is required. If you have a headache and the syndrome radiates to the neck, the muscles in this area are under high and prolonged tension.
In this case, the pain can radiate to the forehead, back of the head, and temples. The syndrome is oppressive in nature, which is associated with stress.
If there is pain in the temples, between the eyebrows, and the symptom is permanent, the help of an oncologist is required.
At an early stage of the pituitary gland, treatment is carried out by a neurologist.
Treatment options
Depending on the cause and intensity of the pain, the doctor will prescribe certain medications that can reduce the symptom or eliminate it for a while. However, painkillers cannot completely get rid of the problem.
If the pain is of low intensity, you can use medications made on the basis of drotaverine (No-Shpa). This substance allows you to relieve vascular and muscle spasms for a while.
Pain that occurs as a result of a minor head injury, hormonal imbalance or increased blood pressure can be eliminated with the help of analgesics (Nimesulide, Analgin, Nise).
To eliminate the symptom caused by impaired vascular activity or intoxication of the body, it is recommended to use medications containing acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin, Upsarin Upsa). This substance helps relieve vascular spasm and reduce pain.
Eye exercises
In case of infectious or viral origin of pain, it is better to give preference to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen and Nurofen.
If severe pain occurs, complex medications should be used, for example Sedalgin, Pentalgin.
To alleviate the condition, you can massage the eyebrows and forehead and take sedatives and vitamin-mineral complexes.
ENT diseases
Experts identify some ENT diseases that cause headaches, and the discomfort is associated with the eyebrow.
Such pathologies include frontal sinusitis - inflammation of the frontal sinuses. Against the background of this process, the sinuses are affected.
The cause of frontal sinusitis is a prolonged runny nose due to allergies and ARVI. ENT specialists say that frontal sinusitis often manifests itself as a complication of influenza, ARVI, or infection.
The pathology is severe. The main symptom of frontal sinusitis is severe pain in the head and eyebrows, which spreads evenly across the forehead.
The maximum intensity of the syndrome is observed in the morning. During this period, the discomfort is unbearable.
The pain subsides after cleaning the sinus. Then it appears again. At the same time, swelling occurs above the eyes and in the area of the diseased sinus.
The sense of smell is also impaired, and photophobia is added. If inflammation is a complication of a cold, the patient’s temperature rises and the skin tone of the forehead changes.
The pain may increase if you press on the eyebrow. To eliminate or reduce symptoms, it is recommended to rinse the new sinuses.
For this, Naphthyzin and sea salt solution are used.
If there is no fever, the pain syndrome is reduced by inhalation, for which an aerosol with an antibiotic is used.
Blue lamps are also used to warm up the problem area.
If your forehead, eyebrows and head hurt, ENT specialists may suspect the following diseases:
- sinusitis - the clinical picture of general poisoning manifests itself, the pain syndrome radiates to the corners of the eyes and cheekbones, the forehead bothers you when you tilt your head. Inflammation provokes high temperature, pus may be released;
- ethmoiditis - pathology is accompanied by migraine and symptoms of general poisoning.
Pain above the eye
Neuralgia ranks first among the causes of pain above the eyes. But the list of pathologies is wide.
If the eyebrow above the eye, the frontal or temporal part of the head often hurts, and attacks recur periodically, accompanied by specific symptoms, contact a neurologist. The pain that the patient encounters for the first time is relieved with antispasmodics.
When choosing a medicine, take into account the dosage and contraindications. Do not self-medicate: pain above the eye is sometimes caused by serious health problems.
There are primary pain, both an independent disease and secondary, symptomatic.
The main causes of the appearance are considered to be diseases of the nose and ears, pathology of the development of the jaw and nasal passage, inflammation or pinched nerves of the cervical spine.
Also, pain above the eye in the eyebrow area appears due to high blood pressure, hormonal imbalance or tumor formations of the upper eyelid.
ontakte
Odnoklassniki
When a pain syndrome occurs, pay attention to its nature and the specific place where the headache is above the eye. This is due to the nerve endings located in the forehead area, and the eyes themselves remain sensitive. Neuralgia can begin when the eyebrow twitches or hurts.
Photo 1. Pain above the eye
Pain is differentiated by time, strength and frequency of occurrence. Primary, or independent, pain is divided into subtypes:
- Beams. During attack attacks, they are repeated every 10 - 20 minutes, lasting up to 3 hours, sometimes the localization covers the dental nerves, eyebrow area, temples. Cluster pain in the eyebrow above the eye occurs at night and lasts up to 10 hours. It is accompanied by a decrease in body temperature, chills, anxiety, inflammation of the outer membrane of the eyes, runny nose or nasal congestion. Recurrence of attacks can last up to several months. The reasons are not fully understood, but a properly selected treatment regimen can prolong remission.
- Headache above the eyes occurs from tension. It occurs more often in older people and women. It is described as compressive and diffuse. It resembles the feeling of a tight hoop on the head. In addition to the pain above the eye under the eyebrow, accompanying symptoms arise: nervousness, lack of appetite, weakness. The pathology develops due to “muscle stress”: prolonged concentration of attention, tension in the eye muscles, neck or back.
- Migraine, which was described by the doctors of Pontius Pilate. The temporal part of the head is most often affected. Painful attacks are caused by vasoconstriction, pain affects one temple or half of the head, rarely both. Painful sensations of a pulsating nature are associated with disruption of the functioning of the head vessels. They are caused by stress, fatigue, abuse of chocolate, cheese and fish products, dehydration, alcohol, and sudden changes in weather.
The pathology is accompanied by fear of bright light, loud sounds, strong odors, nausea, apathy, and drowsiness.
But sometimes the eyelid above the eye hurts due to other factors, not having a primary nature.
Photo 2. Photophobia
Common diseases with symptom of pain above the eye
Soreness also occurs against the background of leading diseases, as a concomitant symptom.
Among the reasons why there is pain above the eye above or below the eyebrow are:
- Infectious diseases. During the flu or an acute viral infection, the body tries to get rid of the infectious agent, and the area of the forehead or above the eyes hurts because of this. Doctors call this condition somatogenic. With a cold, the eyes may become swollen, red and watery, and pain above or inside the eyeballs is a secondary symptom of the disease.
- Intoxication. Poisoning with alcohol, its breakdown products, or general intoxication during a viral infection are also causes of pain. They are accompanied by swelling and bulging of the eyeballs.
- Diseases of the ENT organs, when inflammation or infection first affects the nose or larynx.
Sinusitis is a common condition that causes pain above the eyes.
If sinusitis or frontal sinusitis is developed, the general body temperature rises; when you tilt your head down, the pain in the nasal sinuses or in the forehead between the eyes increases, and intensifies when pressed. Possible purulent discharge or photophobia, lack of smell.
Photo 5. Sinusitis as a cause of pain above the eyes
Ophthalmic diseases also lead to painful sensitivity above the eyes:
- Barley and damage to cartilage tissue or sebaceous glands - chalazion. Most often covers the inner edge of the lacrimal canal. Inflammation of the ciliary bulbs or sebaceous glands around the eyes is internal and develops under the eyelid. It is dangerous due to the possible breakthrough of pus into the eye or into the brain. Symptoms: redness, swelling of the eyelid tissues, their enlargement. Styes not inside are also a threat, but they are easier to diagnose.
- Conjunctivitis. There are allergic, viral, bacterial, etc. With it, the mucous membrane of the eye becomes inflamed and acquires a red tint. Accompanying burning, itching, pain in the eyes.
- Phlegmon of the orbit. Purulent inflammation is characterized by the absence of clear boundaries and can lead to pus entering the brain tissue through the venous bed. Sometimes accompanied by blurred vision due to swelling or inflammation of the eye. The disease is rare, occurring in 1 case in 100, but it is life-threatening. It is caused by general infections, dental diseases, and injuries to the facial part of the skull.
- Ocular myositis, or inflammation of the eye muscles. Hypothermia, injuries, stress, and prolonged eye strain while working at the computer lead to it.
Skin diseases are also characterized by pain above one or both eyes: these are boils, molluscum contagiosum, herpes viruses.
If pain over the left eye or pain over the right eye does not subside for a long time, or repeats periodically, contact a specialist.
Photo 6. Ocular myositis
Neurological diseases
Frequent pathologies of neurological etiology that cause severe headaches include:
- cluster pain syndrome that occurs in the forehead area is accompanied by lacrimation. The pain syndrome is intense, and it is difficult for the patient to sleep. The main provoking factor for this condition is smoking and alcoholic beverages. Relapse occurs in spring and autumn;
- neuralgia - develops due to damage to the trigeminal or optic nerve, which is located between the eyes. Symptoms are triggered by changes in weather;
- migraine – accompanied by unilateral pain, nausea, tinnitus;
- neuroses – develop after excessive aggressiveness or irritation.
If the above symptoms develop, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination, including differential diagnosis.
Based on the data obtained, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
Why might your eyebrow hurt?
If the eyebrow hurts slightly, then most people do not pay attention to the condition that has arisen. But the reasons why an eyebrow hurts are not always harmless; sometimes the symptom that arises is the first sign of the development of a serious illness. Let's consider what can hurt above the eyebrow and whether you always need to see a doctor.
1. Frontitis
The pathology most often appears as a complication of sinusitis, but can also occur as an independent disease. The frontal sinuses are located in the eyebrow area, on either side of the center of the face.
© shutterstock
Symptoms
Signs of frontal sinusitis are similar to manifestations of sinusitis:
- headache;
- a runny nose appears;
- temperature rises;
- the pain intensifies when pressing on the eyebrow.
The headache is localized in the area of the brow ridges and intensifies when bending forward.
Patients often note that not only their eyebrows hurt, but also their eyes and bridge of the nose.
Where to contact
When the pain above the eyes in the eyebrow area intensifies when pressed, you should visit an otolaryngologist.
Cervical osteochondrosis
Disease in the upper part of this spine can cause pinching of a nerve root in the back of the head.
© shutterstock
Who will help
When your eyebrow hurts due to osteochondrosis, you need to visit a vertebrologist or neurologist.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Innervation of the facial muscles is carried out by 3 branches of the facial nerve: upper, middle and lower. Damage to the upper nerve plexus results in pain in the eyebrows and eyes.
© shutterstock
Provoking factors
The causes of damage to the upper part of the trigeminal nerve are different. Commonly encountered ones include :
- hypothermia;
- bruises of the eyebrows and forehead;
- infectious inflammation of soft tissues (most often provoked by the herpis virus);
- neoplasms;
- vascular spasms.
Often the cause of the development of neuralgia of the upper part of the nerve is atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels or disturbances of cerebral blood flow.
Who to contact
If you have pain above the eyebrow caused by neuralgia, you should visit a neurologist. If there is a history of injury to the eyebrow, then additional consultation with a traumatologist will be required.
4. Myositis
Inflammation of the facial muscles leads to eyebrow pain.
© shutterstock
Colds
Seasonal infections are often accompanied by complaints that the eyebrows and bridge of the nose hurt.
© shutterstock
Who treats
The first signs of meningitis do not always appear immediately. Therefore, if there is pain in the eyebrow area and there is a fever, you should visit a therapist. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe a consultation with an infectious disease specialist or refer you for hospitalization in the infectious diseases department.
6. Migraine
The disease is not life-threatening, but excruciating headaches cause severe discomfort. More common in emotionally unbalanced women.
© shutterstock
Non-pathological factors
Eyebrows do not always hurt due to serious illnesses. Sometimes the reasons are relatively harmless :
- Long work at the computer. Pain appears between the eyebrows and a feeling of pressure on the eyes. The intensity of the symptoms decreases if you lightly massage the bridge of your nose and forehead.
- Bad habits. Smokers or people who abuse alcohol have a tendency to vascular spasms. There are many small vessels near the eyebrows, which, when compressed, provoke pain.
- Overwork. Great emotional and physical stress can cause spasm of facial vessels.
- Wrong food. Abuse of spices and fatty foods leads to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques and can cause complete blockage of the vascular lumen. Impaired blood supply is accompanied by moderate pain and sensory disturbance.
Despite the fact that under the influence of external factors, pain in the eyebrows is moderate and goes away quickly, the symptoms that arise should not be ignored. If the cause of the pain syndrome is not eliminated, a serious pathology may develop.
When to go to the doctor
If your eyebrows begin to hurt often, you need to undergo an examination. But before you go to the doctor, it’s worth analyzing your condition a little :
- Lightly press on the eyebrow. When the eyebrow above the eye hurts when pressed, this may indicate neuralgia, frontal sinusitis or colds.
- Additional symptoms. The appearance of a temperature will indicate an infectious process.
- One or two sided pain. The eyebrow on one side always hurts when there is illness or injury. The resulting condition requires medical treatment.
If, in addition to pain in the eyebrows, the temperature rises sharply, severe weakness and cephalalgia appear, then an ambulance is required. The resulting condition may indicate a severe course of frontal sinusitis or meningitis.
If your eyebrows hurt, it's not always safe. The symptom that arises is the first sign that not everything is fine in the body and a medical examination is required to identify the cause. Ignoring the symptom that has arisen will prevent the disease from being detected in the early stages and will complicate subsequent treatment.
Source: https://PrichinyBolej.ru/1976-pochemu-bolit-brov.html