Is the schizophrenia gene passed on to children?
The existence of genetic factors in the occurrence of schizophrenia is beyond doubt, but not in the sense of certain carrier genes.
Schizophrenia is inherited only when the life path of an individual, her fate, prepares a kind of soil for the development of the disease.
Unsuccessful love, life's misfortunes and psycho-emotional traumas lead to a person moving away from unbearable reality into the world of dreams and fantasies.
Read about the symptoms of the hebephrenic form of schizophrenia in our article.
What kind of disease is this?
Schizophrenia is a chronic progressive disease that includes a complex of psychoses that arise as a result of internal causes not related to somatic diseases (brain tumor, alcoholism, drug addiction, encephalitis, etc.).
As a result of the disease, a pathological change in personality occurs with a violation of mental processes, expressed by the following symptoms :
- Gradual loss of social contacts, leading to isolation of the patient.
- Emotional impoverishment.
- Thinking disorders: empty, fruitless verbosity, judgments devoid of common sense, symbolism.
- Internal contradictions. Mental processes occurring in the patient’s consciousness are divided into “his own” and external, that is, those that do not belong to him.
Associated symptoms include the appearance of delusional ideas, hallucinatory and illusory disorders, and depressive syndrome.
The course of schizophrenia is characterized by two phases: acute and chronic. In the chronic stage, patients become apathetic: mentally and physically devastated. The acute phase is characterized by a pronounced mental syndrome, which includes a complex of symptom-phenomena :
- the ability to hear one's own thoughts;
- voices commenting on the patient’s actions;
- perception in the form of dialogue;
- own aspirations are realized under external influence;
- experiences of impact on your body;
- someone takes away his thoughts from the patient;
- others can read the patient's thoughts.
Schizophrenia is diagnosed if the patient has a combination of manic-depressive disorders, paranoid and hallucinatory symptoms.
Who can get sick?
The disease can begin at any age, however, most often the onset of schizophrenia occurs at the age of 20–25 years.
According to statistics, the incidence is the same in men and women, but in males the disease develops much earlier and can begin in adolescence.
In females, the disease is more acute and is expressed by vivid, affective symptoms .
According to statistics, 2% of the world's population . There is currently no unified theory of the cause of the disease.
Congenital or acquired?
Is this disease hereditary or not? To this day there is no single theory of the origin of schizophrenia.
Researchers have put forward many hypotheses about the mechanism of development of the disease, and each of them has its own confirmation, however, none of these concepts fully explains the origin of the disease.
Among the many theories of the origin of schizophrenia are:
- The role of heredity. A family predisposition to schizophrenia has been scientifically proven. However, in 20% of cases the disease first appears in a family in which hereditary burden has not been proven.
- Neurological factors. In patients with schizophrenia, various pathologies of the central nervous system were identified, caused by damage to brain tissue by autoimmune or toxic processes in the perinatal period or in the first years of life. Interestingly, similar central nervous system disorders were found in mentally healthy relatives of a patient with schizophrenia.
Thus, it has been proven that schizophrenia is predominantly a genetic disease associated with various neurochemical and neuroanatomical lesions of the nervous system.
However, “activation” of the disease occurs under the influence of internal and environmental factors :
- psycho-emotional trauma;
- family dynamic aspects: incorrect distribution of roles, overprotective mother, etc.;
- cognitive impairment (impaired attention, memory);
- impairment of social interaction;
Based on the above, we can conclude that schizophrenia is a multifactorial disease of a polygenic nature . In this case, the genetic predisposition in a certain patient is realized only through the interaction of internal and external factors.
How to distinguish sluggish schizophrenia from neurosis? Find out the answer right now.
Which gene is responsible for the disease?
Several decades ago, scientists tried to identify the gene responsible for schizophrenia. The dopamine hypothesis has been widely promoted, suggesting dysregulation of dopamine in patients. However, this theory has been scientifically refuted.
Today, researchers are inclined to believe that the basis of the disease is a violation of the impulse transmission of many genes.
Inheritance - male or female?
There is an opinion that schizophrenia is transmitted more often through the male line. These conclusions are based on the mechanisms of manifestation of the disease:
- In men, the disease manifests itself at an earlier age than in women. Sometimes the first manifestations of schizophrenia in women can begin only during menopause.
- Schizophrenia in a genetic carrier manifests itself under the influence of some trigger mechanism. Men experience psycho-emotional trauma much more deeply than women, which causes them to develop the disease more often .
In fact, if a mother in a family has schizophrenia, then children get sick 5 times more often than if the father was sick.
Statistical data on the presence of genetic predisposition
Genetic studies have proven the role of heredity in the development of schizophrenia.
If the disease is present in both parents , then the risk of the disease is 50%.
If one of the parents has the disease, the probability of its occurrence in the child is reduced to 5–10%.
Studies using the twin method have shown that the probability of inheriting the disease in both identical twins is 50%, in fraternal twins this figure decreases to 13%.
To a greater extent, what is inherited is not schizophrenia itself, but a predisposition to the disease, the implementation of which depends on many factors, including trigger mechanisms.
Testing for multiple personality disorder can be taken on our website.
How to find out the probability in your family?
The risk of developing schizophrenia in a person with unaffected genetics is 1%. If one of the parents is sick in the family, then the probability of inheritance is 5–10%.
If the disease manifests itself in the mother, then the risk of the disease increases significantly, especially in a male child.
The chance of developing the disease is 50% if both parents are affected. If there were grandparents with schizophrenia in the family, then the risk of the disease for a grandson is 5%.
If the disease is detected in siblings, the likelihood of schizophrenia will be 6–12%.
Through what line is schizophrenia transmitted? Find out about it in the video:
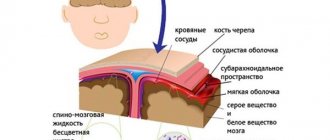
How is inherited - diagram
The likelihood of inheriting schizophrenia from relatives depends on the degree of relationship.
| Grandpa is healthy | Grandma is sick | Grandpa is healthy | Grandma is healthy |
| Father is sick (10%) | Mother is healthy | ||
| Brother's wife is sick | Brother (I) is sick (10%) | Sister is healthy (10%) | Sister's husband is healthy |
| Child probability of illness - 50% | Child probability of illness – 5% |
Compounded heredity can sometimes manifest itself in the form of personality changes, impaired cognitive processes, or manifest as mild forms of the disease.
What is child cognitive development? Find out about this from our article.
At what age can a child be diagnosed?
Schizophrenia in a child whose parents are sick can begin at any age.
Canadian psychiatrists admit the possibility of the onset of the disease in children under 3 years of age .
However, according to the results of many studies, the disease was diagnosed in children no earlier than 5 years of age.
Childhood schizophrenia is expressed by the following symptoms:
- fear;
- sadness;
- cognitive decline;
- speech disorder;
- sleep and appetite disorders;
- retardation in height and weight.
Children of primary school age experience disturbances in communication with peers, emotional impoverishment, a state of excitement, and lethargy of motives.
family aspects as a trigger in the development of the disease in children .
Special clinical and genetic studies of families of children with schizophrenia revealed that in 70% of cases the parents had schizoid symptoms.
A psychiatrist talks about the causes of schizophrenia in children:
Can it be avoided?
A burdened heredity does not necessarily imply the development of the disease. A person who has relatives with schizophrenia does not need to fear for their health and focus on the possible development of the disease.
As preventive measures you should:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid and not consume alcoholic beverages and other drugs.
- Share experiences and other emotional disorders with an experienced psychologist to avoid the development of apathy.
- Devote more time to sports and engage in active activities.
It is important to develop the right attitude towards life. You should not fall into despair when faced with any problems and experience various failures alone. You should approach problems calmly and judiciously, or solve difficulties together with a psychologist .
What methods does cognitive behavioral therapy include? Read about it here.
What to do if a diagnosis of schizophrenia is made during pregnancy? About this in the video:
Our interesting group:
Source: https://psyholic.ru/psihiatriya/peredaetsya-li-shizofreniya-po-nasledstvu.html
Risk groups for schizophrenia
There are several misconceptions among people regarding the possibility of hereditary transmission of schizophrenia.
Firstly, some “experts” believe that this disease is always transmitted to children, i.e. if one of the parents is sick, his heirs are doomed.
Secondly, some people believe that schizophrenia is passed down through generations, that is, for example, from grandmother to granddaughter.
Thirdly, there is speculation that only female or male heirs can get sick. Each of the above assumptions has absolutely nothing to do with reality. Such statements cannot be trusted.
According to average statistical data, a person whose ancestors did not have schizophrenia can get sick with a probability of about 1%. If there is a disease in the family history, the mentioned indicator increases significantly.
Approximate average patterns are as follows:
- if cousins and siblings are ill, the likelihood of schizophrenia increases to approximately two percent;
- uncles/aunts – similar;
- nephews – about 4%;
- grandchildren – about 5%;
- parents – up to 6-7%;
- If both parents and grandparents have the disease, the risk of developing the mental disorder being studied increases to 13-15%.
In some cases, schizophrenia is diagnosed in one of the twins. The risk that the second of them will also encounter the disease in the future is about 17-18%.
The above indicators, when first read, can frighten and plunge you into panic. In reality, the hereditary predisposition to schizophrenia is much less pronounced compared to a number of other dangerous diseases, for example, diabetes, oncology, etc. But the situation cannot be left without any attention either.
Is the disease schizophrenia inherited or not and how: diagram
Schizophrenia is a mental disease that is accompanied by affective behavior, impaired perception, thinking problems and unstable reactions of the nervous system.
It is extremely important to understand that schizophrenia is not dementia, but a mental disorder, a gap in the stability and integrity of consciousness, which leads to impaired thinking.
People with schizophrenia are often incapable of a full social life and have problems with adaptation and communication with other people. One of the reasons why the disease progresses and develops is heredity.
Stages of the disease ↑
Regardless of hereditary form, congenital or acquired pathology, schizophrenia has four stages of its development:
- primordial - during this period partial personal changes occur. A person becomes more suspicious of the outside world and the people around him, his behavior changes;
- The prodromal stage is manifested by the desire to isolate from the outside world, from any contact with loved ones, relatives and friends. The patient becomes distracted and uncollected, and his ability to work decreases;
- first mental episode. It is at this stage that pronounced symptoms begin to appear. Hallucinations, delusions and illusions arise;
- remission. During this period, the patient does not experience discomfort, all symptoms disappear. This period of time may vary in duration, but after a while, an exacerbation of the disease with all its clinical manifestations occurs again.
Mechanisms of heredity
Before talking about diseases, it is worth understanding what genetic heredity is. All information about us is contained in the DNA molecule, which consists of an unimaginably long chain of amino acids. The alternation of these amino acids is unique.
The fragments of a chain of DNA are called genes. Each gene contains integral information about one or more characteristics of the body, which is transmitted from parents to children, for example, skin color, hair, character trait, etc. When they are damaged or their work is disrupted, genetic diseases that are inherited occur.
DNA is organized into 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs, one of which is the sex chromosome. Chromosomes are responsible for gene activity, copying, and recovery from damage. As a result of fertilization, each couple has one chromosome from the father and another from the mother.
In this case, one of the genes will be dominant, and the other will be recessive or suppressed. To put it simply, if the father’s gene responsible for eye color turns out to be dominant, then the child will inherit this trait from him, and not from the mother.
So is it hereditary or not?
If the C4 gene is dominant, then why, if one of the parents is sick, the probability of having a child with schizophrenia is not 100%?
Numerous publications often prove the opposite: that genes are to blame, and the disease is inherited or not - and then they prioritize external influences.
No one can say for sure that a person with genetic defects will get sick, and vice versa. Only one thing can be said for sure: the more defective genes, the higher the risk of schizophrenia.
There is evidence that if a woman has the flu during pregnancy, it is not the virus, but an excessive reaction of her body with the release of interleukin-8 that causes mental disorders in the child.
However, not all women with an increase in the amount of IL-8 give birth to sick offspring, even if the pregnant women themselves are predisposed to the development of mental disorders.
It is not the disease itself that is inherited, but the pattern of its metabolic processes. Disturbances can occur not in 1, but in 3 genes that interact with each other, and in total about 30 mutations associated with schizophrenia have been identified.
The disease is not transmitted to all relatives, but everyone has a predisposition to it.
The risk of pathology increases with constant stress, alcoholism and drug addiction.
Is schizophrenia inherited?
Schizophrenia is a complex of mental disorders that affect a person’s thinking and consciousness. Both women and men are equally susceptible to the disease. For what reason does the disease occur, is schizophrenia inherited ? Scientists still cannot give an exact answer to the questions posed.
The priority of the hereditary theory in the past
The active study of genetic predisposition to this disease began in the 19th century. In those days, the hereditary, “family” theory was fundamental. There was an opinion among ordinary people: if there was at least one case of mental illness in the family, the mental disorder would certainly be inherited.
Such families became outcasts; they did not want to marry their members, for fear of being “infected” with mental illness.
Therefore, even isolated cases of schizophrenia in the family were carefully hidden, so as not to spoil the family reputation and not complicate the life of descendants.
This factor significantly complicated the diagnosis of the connection between a mental disorder and heredity. Patients could not tell for sure whether such cases of the disease had occurred in their family or not.
Nevertheless, in many case histories it was still possible to trace genetic involvement.
For example , in psychiatric medicine there is a known case that occurred in the second half of the 20th century. The family had four girls - identical twins. Their father suffered from mental illness.
Until adolescence, girls were no different from their peers - they studied well, communicated with friends, and graduated from school. Only one of them was unable to complete her studies - she was diagnosed with a catotonic form of schizophrenia.
However, at the age of 20-23 years, symptoms characteristic of this mental disorder were also noted in the remaining sisters. This case clearly proved the heredity of the disease.
If there have been cases of schizophrenia in your family, and you are afraid of a repetition of the situation with you or your relative, contact the “Balance” mental health center for advice.
We have experienced psychiatrists who will answer all your questions, give advice and recommendations, and, if necessary, conduct a comprehensive diagnosis.
All information received by the doctor will remain strictly confidential. You don't have to be afraid of publicity.
Make an appointment by phone: +7 (499) 495-45-03.
Modern theories
However, not every medical history is as clear-cut as the one described above. Scientists are still studying the question of how schizophrenia is transmitted and is it inherited? Despite the outstanding achievements and progress in the fields of neuroscience and molecular genetics, the problem of the hereditary factor of schizophrenia has become even more confusing.
Scientists have identified not just one “defective” gene, but a whole complex – 74. Their various combinations and each gene separately, under the influence of many environmental factors, can contribute to the development of the disease. And there are quite a lot of such factors that are provocateurs.
- Unfavorable social and psychological environment in which the child grows up.
- Injuries of various types - traumatic brain, psychological, sexual, physical, received during childbirth.
- Viral diseases that a woman suffered from during pregnancy - flu, colds, herpes, meningitis or encephalitis.
- Drug or alcohol use.
- Nervous stress , emotional and physical fatigue.
One or more of the above factors can trigger the “explosion” of a “genetic bomb”.
Scientists believe that the increased activity of “defective” genes disrupts the normal functioning of genes responsible for transmitting signals or impulses between nerve cells.
There is a malfunction in the functioning of the brain, which, in turn, leads to the development of mental disorders.
The likelihood of developing schizophrenia: myths and assumptions
The controversy of the hereditary theory has given rise to a number of myths that schizophrenia is transmitted:
- only from the father or only from the mother;
- strictly through a generation - from grandmother or grandfather;
- only boys, or only girls.
These statements are not scientifically substantiated or proven and should not be taken seriously.
For example, the misconception that schizophrenia is inherited only by boys has a reasonable explanation. In men, the course and development of mental disorder has its own characteristics that are different from women.
- It makes its debut early - at 15-20 years old. While female disease can be diagnosed already in adulthood, and even in old age.
- The course of the disease in men is often paroxysmal, with periods of acute psychosis that cannot be ignored. For women, sluggish schizophrenia, with mild or vague symptoms, is more typical.
- Manifestations of mental disorder in men are more pronounced. They are characterized by antisocial behavior, attacks of aggression, delusions and hallucinations.
The answer to the question along which line schizophrenia is transmitted does not matter. Scientists have proven the fact that both women and men are equally susceptible to this mental disorder.
Statistical data
Long-term observations of the clinical picture of the disease and the study of risk factors, including genetic ones, allowed scientists to collect statistical data. Using them, you can trace how schizophrenia is inherited with a percentage probability.
| Relatives with schizophrenia | Risk of developing the disease in % |
| Identical twins | 50% |
| Fraternal twins | 17% |
| Both parents | 40% |
| First degree relatives – one parent, brothers or sisters | from 4% to 10% |
| Second degree relatives - grandparents, uncles, aunts, cousins | 2% |
| There was no case of the disease in the family | 1% |
Doctors note that the predisposition is inherited. Even both sick parents can have a healthy baby. The hereditary factor is a certain risk. However, no one knows in advance whether the defective gene will “work” or not.
Each case of the disease is unique and the reasons for its development depend not only on “bad” heredity, but also on many associated environmental factors.
A child raised in a socially dysfunctional family, where he is constantly beaten, humiliated, and psychologically suppressed, has a much greater chance of “activating” his genetic predisposition, compared to one who grows up in a good, full-fledged family with healthy moral and spiritual attitudes.
Prevention measures
If you know for sure about cases of schizophrenia in your family, we advise you to consult a specialist. This does not mean that you will necessarily enter the risk zone. But taking care of your health, including mental health, will never be superfluous.
Call our clinic by phone: +7 (499) 495-45-03. We provide services:
- diagnosing;
- outpatient and inpatient treatment;
- emergency medical care;
- 24-hour doctor call at home;
- transporting the patient to the hospital.
If you are planning a pregnancy, be sure to get tested by a geneticist. A specialist will help identify the approximate likelihood of the baby developing pathology, as well as determine the most favorable period for pregnancy.
A person prone to developing schizophrenia should pay special attention to preventive measures.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle - exercise, eat right.
- Give up bad habits - smoking and alcohol, as much as possible.
- Avoid stressful situations and emotional overload.
If necessary, consult a specialist by phone .
Source: https://nevroz.com/psihiatriya/shizofreniya/shizofreniya-po-nasledstvy/
So is it all hereditary or not?
The question is quite complex, and even after many dissertations have been published, experiments have been carried out, experiments have been carried out, experts do not stop arguing on this topic.
“Schizophrenia is inherited,” this is what experts of the past believed. They argued: those who had relatives in their family with such a mental disorder, the illness would manifest itself sooner or later, and in the absence of such relatives, they assumed that the patient simply did not know about it.
Evidence from modern medicine refutes the fact that genes are to blame and states that only in half of cases schizophrenia is hereditary; in other cases, the disease occurs due to a persistent transformation of the genotype of the parent's germ cells and the reasons for their mutation are unknown.
Each cell of the body has 23 pairs of chromosomes and at conception, 2 copies of genes are transmitted (one from the father and mother). There is an assumption that only a few structural hereditary units have a risk of inheriting schizophrenia, but they do not have a big impact on the development of the disease. The process of disease formation not only from hereditary factors, but also from the environment:
- Infectious diseases caused by viruses.
- Poor nutrition of the embryo while in the womb.
- Poor psychological situation in the family or at work.
- Injuries to the child during childbirth.
Figures of hereditary schizophrenia
1% of the country's population has a group of mental disorders, but if parents have it, then the risk of developing the disease becomes 10 times greater. The risk of inheriting schizophrenia increases even more if second-degree relatives, for example, a grandmother or cousin, suffer from it. The peak risk is the disease of one of the homozygous twins (up to 65%).
The location of the chromosome in the gene is very important. A defect in chromosome 16 will have less destructive force on the brain than a defect in the 4th or 5th structural element of the cell nucleus.
Science and schizophrenia
Californian scientists conducted a study in which stem cells from mentally ill patients were taken. They were given different levels of development, their behavior was observed, creating unusual or stressful living conditions in an unnatural way. And for good reason! The study revealed oddities in the behavior and movement of these cells, that is, several groups of proteins.
According to scientists, the experiments should help in diagnosing schizophrenia in the early stages.
Schizophrenia: heredity and its features – Izvilina
In those suffering from schizophrenia, central nervous system disorders are recorded. They are caused by damage to brain tissue by toxic and autoimmune processes that occur in the first years of life or during the perinatal period. At the same time, according to studies, similar central nervous system disorders were recorded in healthy relatives of the patient.
Given the relevance of the data obtained, experts believe that multiple disorders of impulse gene transmission may underlie schizophrenia.
Contrary to popular belief, pathology is not always transmitted to close relatives. Often, schizophrenia can occur only in grandchildren, bypassing sons and daughters.
How is schizophrenia inherited? transmission scheme
This is due to the following reasons:
- In men, the disorder manifests itself earlier.
- Schizophrenia usually appears after an event that has had a significant negative impact on the psyche of a child or adult.
- Since men perceive psycho-emotional trauma much more severely, their disease develops faster.
Statistics say otherwise. In fact, when only the mother in a family has schizophrenia, the chance that the disorder will be passed on to the child will be 5 times higher than if the father is sick. Boys are especially at risk.
However, there are some features:
- if schizophrenia was “activated” in a child of twins, then 50% of the second child will also have it, sooner or later;
- if both parents had schizophrenia, their children have a 50% chance of developing the disease;
- Identical twins have a 50% chance, fraternal twins are luckier - they get sick in 13% of cases.
When only one parent has schizophrenia, the chance of inheritance is 5-10%. If the disease is detected in a sibling, the manifestation of schizophrenia in other children varies from 6 to 12%. If a grandfather or grandmother had schizophrenia in the family, then the chance of transmission will be 5%. However, anyone with normal genetics also has a chance of getting this disorder. It is equal to only 1%.
A family history of schizophrenia may manifest itself as impaired cognitive function.
How to avoid being at risk
To do this you need:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- It is necessary to give up alcohol and any substances that can affect the psyche.
- It is also advisable to establish a diet and engage in physical activity.
- It is required to undergo regular examinations with a psychologist.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited. It is necessary to share experiences, this will help to avoid apathy and further development of pathology. Stressful situations or too high loads should not be allowed.
With the right approach, schizophrenia is quite treatable and the patient can live a fairly long life with a clear memory and mind.
Schizophrenia is a hereditary disease
Schizophrenia is an acute problem of our century. The true causes of schizophrenia have not yet been identified. The media publish different views on the etiology of schizophrenia.
From time to time, the scientific community explodes with new leads and innovative treatments that are successfully debunked by scathing articles and new studies.
Among the main causes of this disease, heredity is most often put in first place.
Symptoms of schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is characterized by a range of negative symptoms and personality changes.
Its peculiarity is that schizophrenia continues for a long time, going a long way through the stages of development and progression of this disease.
In addition, the disease may have periods of active manifestation, or it may be sluggish and unnoticeable. But the main feature of this disease is that it is always there. Even if its manifestations are not so noticeable.
Schizophrenia differs from other diseases in its variety of forms and varying duration of manifestation. The first signs of this disease shock both the patient and his loved ones. Many people perceive them as ordinary fatigue or overwork, but over time it becomes clear that these symptoms have another reason.
In schizophrenia, several groups of symptoms are observed:
- Psychopathic symptoms that manifest themselves in delusions, hallucinations, obsessions - signs of behavior and existence that are uncharacteristic of a healthy person. In this case, hallucinations can be visual, auditory, tactile, or olfactory. Patients tend to see non-existent objects or creatures, hear voices and sounds, feel touches and even aggressive influences, feel non-existent odors (usually smoke, rot, a decomposed body).
- Emotional symptoms. Schizophrenics exhibit completely inadequate reactions to what is happening around them. Outside of the situation, they begin to show unreasonable sadness, joy, anger, and aggression. It must be remembered that patients are prone to suicidal actions, which are accompanied by extraordinary joy or, on the contrary, low mood, sadness, and hysterics.
- Disorganized symptoms. In schizophrenia, there is an inadequate reaction to what is happening. Schizophrenics can behave aggressively, speak incomprehensible phrases, fragmentary sentences. Patients with schizophrenia do not determine the sequence of actions and events, and cannot determine their location in time and space. Schizophrenics are very absent-minded.
An interesting fact is that when analyzing these symptoms, close people associate the patient’s behavior with the behavior of one of the relatives, usually parents. Expressions like: “Your mother also forgot everything...” characterize the characteristics of human behavior that are inherited.
The very correlation of the patient’s behavior with similar manifestations of one of the relatives speaks of the heredity of schizophrenia, which is proven even at such an everyday level.
Schizophrenia, of course, can also be acquired. However, psychiatry does not determine the differences between the manifestations of acquired and hereditary schizophrenia.
Heredity of schizophrenia: truth or myth
The question of whether schizophrenia is a hereditary disease is very pressing. There is no consensus in medicine in this direction.
Numerous publications either eloquently prove the heredity of schizophrenia, or refute it, placing priority on external influence factors.
And yet, some statistical figures regarding this disease can serve as proof of its heredity:
- If one identical twin has schizophrenia, the risk for the other twins is 49%.
- If one of your first-degree relatives (mother, father, grandparents) had schizophrenia or exhibits signs of this disease in behavior, then the risk of the disease in subsequent generations is 47%.
- In fraternal twins, the risk of developing schizophrenia is 19% if one twin is affected.
- If there were simply cases of schizophrenia in the family at any degree of relationship: aunts, uncles, cousins, then the risk of illness for each family member is 1-5%.
To confirm this, history can provide facts about entire families suffering from schizophrenia. So-called crazy or “strange” families exist in many localities. Given the possibility of distant relationships, it is not surprising that many are interested in the question of the possibility of inheriting schizophrenia.
So is there a gene for schizophrenia? Scientists have repeatedly tried to answer this question. Medical science knows of cases of attempts to prove the genetics of schizophrenia, in which 74 different genes have already been identified. But not one of them can be called a disease genome.
But these theories most likely speak about the inheritance of a predisposition to schizophrenia rather than the disease itself. This theory is supported by the fact that not all relatives of a person with schizophrenia suffer from this disease.
Of course, we can assume that not everyone inherited this disease, but it is easier to conclude that numerous relatives have a predisposition to schizophrenia.
For the appearance of the disease itself, triggering mechanisms are needed, which may include stress, somatic diseases, and biological factors.
Can schizophrenia be inherited from parents to children?
Schizophrenia is a very serious illness, so many experts are studying in depth the question of whether schizophrenia is inherited. It represents a pronounced mental change that gradually causes complete degradation of a person’s personality. The disease is accompanied by a whole set of signs and symptoms, from which a doctor can make a diagnosis.
The likelihood of inheriting schizophrenia is very high. Many people are confident that it is close to one hundred percent. Both women and men suffer from the disease. Moreover, pathology does not always clearly affect immediate relatives. Sometimes its expanded form is found in grandchildren, nephews or cousins.
Risk factors
It is very important to know exactly how schizophrenia is transmitted from generation to generation. In fact, the genetic factor plays a fairly large role in the transmission of this disease.
Such danger is distributed with a certain frequency.
- If the disorder manifests itself in one baby of twins, then there is about a fifty percent chance that the second child will also suffer from it.
- A slightly lower risk is the circumstance if the disease is diagnosed in a grandfather, grandmother, only in the mother, or only in the father.
- Only one in eighteen people suffers from the disease if the pathology manifests itself in a distant relative.
- One person in fifty is likely to inherit it if an uncle or aunt, as well as cousins, great-uncles or grandmothers, were patients in a psychiatric hospital.
We can say with complete confidence that the person who has been diagnosed with the pathology, both through his parents and the older generation of relatives, will suffer from this type of mental illness.
The probability of developing the disease is close to fifty percent if the mother or father, or both parents, suffered from it. That is, transmission of the disease occurs autosomally.
If only one family member was schizophrenic, all the same, the risk factor for inheriting the gene remains quite high. It’s hard to even guess what percentage it will be. However, in order to judge this circumstance with confidence, it is necessary to undergo a chromosome analysis.
Influence of the male line
It is important to understand whether schizophrenia is most often inherited from the father, since men are often susceptible to this disease.
This happens because:
- representatives of the stronger sex become ill with mental pathology already in childhood or adolescence;
- their disease progresses rapidly;
- it affects their family relationships;
- the impetus for its development may be a not very significant and even acquired factor;
- representatives of the stronger sex more often experience neuropsychic overload, etc.
However, experienced psychiatrists have clearly established that inheriting mental illness from the father is much less common. There is a prejudice about male schizophrenia due to the fact that in the stronger sex the disease occurs in a more severe form.
The main symptoms in men are more developed and vivid. They hallucinate, hear voices, see missing people. Schizophrenics are often very mannered, prone to reasoning, or subject to certain manic ideas.
Some patients completely lose contact with the outside world, stop taking care of themselves, and often suffer from depressive symptoms. Sometimes suicidal tendencies reach the point where a person seeks to commit suicide. If he fails, then most often he immediately becomes a patient in a psychiatric ward.
Men are very often aggressive, constantly drink alcohol, take drugs, and exhibit antisocial behavior.
Male schizophrenics are simply conspicuous, unlike sick women, whose illness is often noticeable only to members of their families.
In addition, representatives of the stronger sex tolerate severe nervous and mental stress much worse, do not seek medical or psychiatric help on time, and often subsequently end up in prison.
Influence of mother and grandmother line
It is equally important to definitely identify the exact probability of transmission of schizophrenia through heredity through the female line.
It is in this case that the risk of disease increases many times. The likelihood of a son or daughter getting the disease from a mother increases at least fivefold. This figure far exceeds the risk level in cases where the pathology is diagnosed in the father of the children.
It is quite difficult to make any definite predictions with complete confidence, since the general mechanism of the development of schizophrenia has not yet been fully studied. However, scientists are inclined to believe that a chromosomal abnormality plays a huge role in the occurrence of the disease.
Not only this pathology, but also many other mental illnesses can pass from mother to children. It is even possible that the woman herself did not suffer from them, but is a carrier of a chromosomal mutation, which caused the development of the disease in children.
A difficult pregnancy, aggravated by toxicosis, can also become a risk factor.
Infectious or respiratory diseases that affect the fetus during gestation also give rise to various diseases.
It is precisely such influences that are responsible for the fact that people who were subsequently diagnosed with this severe mental pathology celebrate their birthday at the very peak of spring or winter infection with viral infections.
The hereditary development of schizophrenia in children is aggravated by:
- very difficult mental conditions of the early development of a daughter or son affected by the disease;
- lack of full care for the child;
- pronounced changes in the baby’s metabolism;
- organic brain damage;
- biochemical pathology, etc.
Therefore, it becomes clear that in order for the disease to be transmitted in an expanded form, a combination of a variety of important factors is required, and not just one hereditary one.
Whether the parents suffered from the disease on the male or female side is very important, but not decisive.
Very often, a woman is affected by schizophrenia in a sluggish form, which goes unnoticed by her family members, medical professionals, or psychiatrists.
Often, a special mutated gene that she happened to inherit from relatives is recessive, without having much of a chance to express itself in its entirety.
The likelihood of developing a disease associated with a chromosomal factor
There is no clear answer to the question of the transmission of schizophrenia from relative to relative.
A genetic disorder or hereditary predisposition are pronounced risk factors, but not a death sentence. Therefore, people who experience this problem should be observed by a psychologist or psychiatrist from early childhood, and should also avoid provoking factors in the development of the disease.
Even when both parents of a child are affected by schizophrenia, the possibility of him developing such a pathology still usually does not exceed a fifty percent probability.
Therefore, until evidence is fully supported by practical and experimental data, one can only speculate about whether schizophrenia is a hereditary disease or not.
Even though there are fairly accurate statistical data that the disease is transmitted along a chromosomal line, it is still very difficult to calculate the degree of its probability.
Many prominent scientists in this field have been engaged in relevant research, but there is no definitive data yet. This is explained by the fact that it is not possible to fully study the mental state and signs of schizophrenia in all relatives of the patient, his absent great-grandparents, or to identify the conditions for the formation and development of a teenager affected by the pathology.
Sometimes the disease can be transmitted from parents to children, but in such a mild form that it can be very difficult to say that a person has schizophrenia.
In cases where parents or children are in a very prosperous environment and do not suffer from any concomitant diseases, sometimes the disease manifests itself in the form of some odd behavior or even almost hidden carriage.
Circumstances of manifestation of pathology in expanded form
In order for schizophrenia to express itself in a generalized form, a combination of factors such as:
- biochemical;
- social;
- nervous;
- psychological;
- chromosomal mutation;
- presence of a dominant gene;
- constitutional characteristics of the patient, etc.
Therefore, making a final conclusion about the likelihood of inheriting schizophrenia should only be done with great caution. However, it is, of course, unacceptable to discount such a factor.
Practicing psychiatrists have long noticed a connection between an ill father or even an uncle and the presence of pathology in a son or nephew.
Moreover, there are cases when both twins were simultaneously affected by such a mental illness.
It should be recognized that schizophrenia is transmitted along a chromosomal line. This conclusion does not raise the slightest doubt. Geneticists and psychiatrists have even proven that female heredity is decisive. However, in order for such a serious and incurable disease to fully come into its own, a combination of many causes and factors is required.