Neurosis is a functional disorder of the nervous system. Men, just like women, suffer from similar pathological conditions. Without correct treatment, the problem gradually worsens, leading to serious dysfunction of organs and systems. At the same time, there are quite effective therapeutic regimens that affect both the root cause and the consequences of disorders. Symptoms of neurosis in men are varied, as are the factors that trigger a pathological but reversible process in the nervous system. Following preventive measures and maintaining a healthy lifestyle will help prevent the problem.
Symptoms of neurosis in men
A depressive state usually occurs in people who are unsure of their own abilities and indecisive. They find it difficult to adapt to new conditions. Categorical, overly restrained persons are also prone to frustration. Classic symptoms of neurosis in men:
- depression;
- decreased activity;
- slow speed of thinking.
At 45-55 years of age, the development of menopausal neurosis is possible. The condition is accompanied by psychogenic disorders and neurovegetative problems. Pathology appears:
- sudden rush of blood to the face;
- irritability;
- increased fatigue.
Nervousness is noted in 90% of patients. Approximately 51% develop tachycardia. Memory loss of varying degrees accompanies 75% of patients.
Hysteria is quite rare and usually appears before the age of 30. Symptoms of hysterical neurosis in men also do not involve organic disorders. The diagnosis is confirmed if at least 25 of 60 signs are present, affecting all body functions.
Neurosis is a disorder of the nervous system caused by prolonged stressful situations and leading to changes in the psycho-emotional state, decreased performance, obsessive thoughts and hysteria. Symptoms of neuroses initially do not cause alertness and are mistakenly interpreted as ordinary fatigue. However, according to the World Health Organization, neurosis is the most common mental illness that needs to be treated promptly.
Neurosis concept
So, what is neurosis?
Useful advertising. We recommend that you pay attention to insurance against the COVID-19 coronavirus. The cost of the policy is from 1,690 rubles, there are tariffs for the whole family. Together with Zetta Insurance.
Neurosis is a mental disorder characterized by destructive changes in a person due to prolonged exposure to stress factors. With such a mental disorder, the nervous system suffers, the psycho-emotional background is unstable, and performance drops to zero. The individual develops obsessive-compulsive disorder syndrome, hysteria, and asthenia.
This term appeared in the twentieth century thanks to William Cullen, a Scottish doctor. The concept has undergone several interpretations and had different meanings, but has never received a single interpretation. Today, nervous disorders are common to most people from all over the world. They are perhaps the most popular disease in recent years. There are 25 times more patients with neurosis than 70 years ago. And many patients do not go to the doctor at all, so the statistics may actually be much more significant.
These days, the number of social problems has increased. Political and news wars, global warming, a large number of poor people, deadly diseases, terrorist threats, natural disasters - such events will not leave anyone indifferent. Every year there are more and more people suffering from neuroses.
Causes of neuroses
The main cause of neuroses is prolonged stress and overload, both mental and physical. In women, they are most often caused by problems in the family and interpersonal relationships, low self-esteem, complexes, excessive passion for introspection, and worries about loved ones. Neurosis is often provoked by hormonal changes, so women who have recently given birth to a child and women who have reached menopause are at risk.
In men, a state of neurosis, the symptoms of which in most cases do not cause physical pain, is caused by problems at work, excessive stress, alcoholism, self-doubt, and emotional instability.
Signs and symptoms of neuroses in adults
The main signs of neurosis include:
If symptoms of neurosis appear in adults, first of all, you need to change the environment and not be afraid to seek professional help. The insidiousness of this type of disease lies in the fact that emotional symptoms are often attributed to fatigue, and pain symptoms are often attributed to certain chronic pathologies. It is not uncommon for people to treat cardiac or gastrointestinal diseases for years without getting results. To avoid this, you need to listen carefully to yourself and consult a psychotherapist at the clinic in time.
If symptoms are identified, treatment of neurosis should begin without delay. This category of mental illness has a favorable prognosis and can be completely cured if you consult a specialist in a timely manner.
There is a stereotype that women are more susceptible to neuroses than men. However, practice shows that a neurotic state occurs in both those and others equally. If correct treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the disease may worsen, which will cause serious disruptions in the functioning of organs and systems. The most common symptoms of neurosis in men:
- depressed state;
- decreased activity;
- slowing down the speed of thinking;
- flushes of blood to the face that come on suddenly;
- increased fatigue;
- memory impairment;
- presence of tachycardia.
A person’s age also plays an important role. The hysterical state can manifest itself before the age of 30. After 45 years, the onset of menopausal neurosis is possible; neurovegetative diseases are added to psychogenic disorders.
The clinical picture of the disease is vague, so in the initial stages it is difficult to independently identify the disease. Often the initial signs are mistakenly considered to be overwork. But doctors call symptoms of neurosis in women, in the presence of which due attention should be exercised. The most characteristic are:
- prolonged apathy for no apparent reason;
- excessive emotionality;
- sudden change of mood;
- drowsiness;
- irritability;
- decreased appetite;
- slight anxiety;
- irregularities in the menstrual cycle;
- headache;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- increased sweating;
- attacks of nausea.
Neurosis - symptoms
A neurotic disorder has the following symptoms: the presence of cynicism, emotional distress for no apparent reason, indecision, communication problems, low or high self-esteem, anxiety, phobias, panic disorder, fears, anticipation of an alarming event, panic attacks, uncertainty in system of values, as well as contradictions in preferences and life desires, contradictory ideas about oneself, about life, about others.
Symptoms of neurosis include instability of mood and frequent, as well as sharp variability, irritability; high sensitivity to stress, manifested in despair or aggression; The symptoms of neuroses are characterized by tearfulness, fixation on a traumatic situation, vulnerability, touchiness, and anxiety. When trying to work, neurosthenics quickly get tired, their attention, memory, and thinking abilities decrease; they are very susceptible to loud sounds, temperature changes, and bright light.
Neurosis also includes symptoms such as sleep disorder; it is often difficult for a person to fall asleep due to overexcitation; his sleep is superficial, very disturbing and does not bring any relief; In the morning, drowsiness is often observed.
Physical symptoms are also characteristic of neurosis: headaches, as well as heart pain, increased fatigue, chronic fatigue, abdominal pain, decreased performance (emotional burnout), VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia), dizziness, and darkening from changes are often observed. pressure in the eyes, disturbances in the vestibular apparatus: difficulties in coordinating movements for balance, frequent dizziness, eating disorders (bulimia - overeating or undereating - anorexia); feeling of hunger and at the same time very rapid satiety during meals; insomnia, unpleasant dreams, hypochondria – concern for one’s health, psychological sensation and experience of physical pain (psychalgia).
Neurosis also has the following vegetative symptoms: sweating, surges in blood pressure, palpitations, stomach disturbances, cough, frequent urination, decreased libido, loose stools, decreased potency
Types of neuroses
Obsessive-compulsive neurosis. Conditioned reflexes developed as a result of some event participate in the formation of this form of neurosis. This disease manifests itself in constant fears and doubts, frightening memories, anxiety, repeated repetition of the same actions (for example, checking whether the door is closed).
Hysterical neurosis. This form is typical for people of a certain type and stems from the desire to attract attention, excessive egoism, and the habit of achieving one’s goals by manipulating other people. As a result, this behavior leads to uncontrollable emotional reactions, memory impairment, seizures, hallucinations and suicide attempts.
Neurasthenia. This type of neurosis is the most common, as it is the result of prolonged mental and physical overload that most modern people experience. The disease manifests itself in the form of fatigue and irritability, sleep disturbances, impotence, gastrointestinal disorders, etc.
There are other types of this group of diseases: anxiety, gastric neurosis, postpartum, traumatic, etc.
Diagnosis of neuroses at the Doctor SAN clinic
Our clinic provides comprehensive treatment for all types of neuroses. Usually, at the initial appointment, the specialist conducts a thorough analysis of complaints and medical history, performs a neurological examination, and if other diseases are suspected, he refers for additional examinations (laboratory, instrumental).
In addition to medications, we prescribe a course of physiotherapy and psychotherapy. When patients with severe mental trauma come to us, we use hypnosis to treat neuroses, which effectively helps even at an advanced stage of the disease.
The main task of the doctors at our clinic is to help patients return to a full, colorful life.
Neurosis is a protracted disorder of the central nervous system in which the mental and emotional state is constantly changing. But it is important for a person to understand for himself what the symptoms and treatment are, because it is the clinical picture that does not allow him to live a full life.
Selection criteria
The main criteria for distinguishing neurotic disorders from mental disorders in general are:
- the leading role of psychogenic factors in the occurrence and decompensation of painful manifestations;
- functional (reversible) nature of mental disorders;
- absence of psychotic symptoms, dementia, or increasing personality changes;
- egodystonic (painful for the patient) nature of psychopathological manifestations, as well as the patient maintaining a critical attitude towards his condition.
Description of the pathology
This is a reversible mental disorder that can occur in both adults and children. It is caused by a psychotraumatic factor, but on condition that the person’s psychological defense is currently reduced.
This pathology can be classified as a protracted disease.
People who suffer most often are those who experience frequent overwork, emotional distress and lack of sleep.
They have a logical question - how to treat the disease, but to do this it is necessary to understand the cause of its occurrence.
In medicine, there are several types of pathology:
- Depressive, in which a decadent mood and problems with intellectual development are manifested.
- Anxious, in which a feeling of fear, depression and anxiety is clearly manifested.
- Hysterical, during which there is low self-esteem, a feeling of lack of attention to oneself, as a result of which an overestimation of personality occurs. As a rule, this condition appears in childhood.
- Asthenic, in which fatigue, depression and mood problems come to the fore.
- Bulimic, characterized by uncontrollable eating of food, especially high-calorie foods.
All of them arise for individual reasons, as a result of which their symptoms may be different. It is believed that the disease is a protective function of the body, namely the brain, from unfavorable psychological and social factors.
Causes
Experts identify the following causes of mental health problems:
- Excessive stress on the brain caused by the field of activity or emotional distress.
- The inability to resolve existing problems, an example of this is debt, illnesses of loved ones, etc.
- Forgetfulness, which leads to serious consequences, which haunts a person, since he is unable to correct the situation and a feeling of guilt for what happened settles in his soul.
- Deviation in the development of the central nervous system, which causes an inability to perform mental and physical activity, this leads to asthenia.
- Exhaustion of the body due to a serious illness or drug addiction.
Interestingly, for some people, a neurotic condition has become common, and they do not try to fight it, but others try to find solace in medications. But another option for the development of the disease may occur - addiction to religion, alcohol or work.
Psychological reasons are:
- the claim of parents to their child;
- the influence of certain educational techniques;
- relationships in society;
- personal development.
Biological reasons include the following:
- injuries;
- functional impairment;
- developmental deviations that arose due to congenital pathology;
- trauma of a woman during a difficult birth.
Naturally, depending on the cause of the occurrence, the symptoms may differ.
Neurosis - what is it?
Neurosis is a combination of psychogenic disorders that have a reversible course, but last quite a long time. Symptoms of neurosis are obsessive and can manifest as hysterics, asthenic syndrome, and decreased physical and mental performance. Psychoneurosis and neurotic disorder are all synonyms for neurosis.
In adult patients, neuroses most often have an uncomplicated course. After recovery, the psyche is completely restored. This is the main difference between neurosis and psychosis. Statistical analysis indicates that about 20% of the world's population suffers from neuroses of varying severity. Depending on the specific social group, the percentage of patients may vary.
The disorder is based on a disorder of brain activity, which under normal conditions is the main adaptive mechanism of a person. As a result, the patient develops disorders in various areas: somatic and mental.
Neurosis, as a medical term, was introduced into use in 1776. It belongs to the Scottish doctor William Cullen.
Symptoms in women
In women, the clinical picture is somewhat different; for example, they more often experience neurasthenia, that is, an asthenic appearance that is caused by irritability, which often leads to problems with sexual life.
In addition, with neuroses, women more often develop hypochondria, depression, and melancholic disorders.
In females, the disease can take three forms.
The following symptoms of neurosis occur in women:
- Irritable, during which there is increased excitability, but there are pronounced symptoms of fatigue. In this condition, even exposure to excessive noise leads to loss of self-control. In the second stage, girls become even more depressed and aggressive, even dangerous.
- Hypersthenic, which occurs at the initial stage, and the excitement here is insignificant. A woman reacts negatively to bright light and noise, feeling excessive discomfort in society. She begins to react emotionally even within her family, especially to her own children.
- Hyposthenic, referring to the last stage, which makes it difficult to treat neuroses. Here, even in the absence of provoking factors, the woman feels aggression, but at the same time exhaustion. The last stage is characterized by a constant desire to rest.
Symptoms in men
As a rule, depression occurs in those people who are not confident in their abilities and find it difficult to adapt to the new prevailing conditions.
The most common symptoms of neurosis in men are:
- decreased activity
- depression,
- slow thinking.
Often, after reaching the age of forty-five, men experience a menopausal type, which is accompanied by a psychogenic disorder.
This condition is characterized by the following clinical picture:
- irritability,
- flushed face,
- fast fatiguability.
At the same time, half begin to develop tachycardia, and in the vast majority, the symptoms of neurosis in men are diluted by memory problems.
Frequently occurring neurotic conditions lead to the fact that a person cannot respond adequately even to a weak stimulus.
Many often confuse the disease with widespread psychosis, although they differ in that with psychosis the person does not consider himself sick and perceives his reaction as the norm, while with neurosis the patient feels that something is wrong with him.
Experts consider it a reversible pathology, but some people suffer for a long time because they do not try to get rid of the disease at the initial stage.
The longer a person experiences negative symptoms, the more radically his psyche changes. When the disease becomes chronic, problems arise with the gastrointestinal tract, heart and genitals.
Mainly chronic neurosis is characterized by a clinical picture of the following type:
- sleep problems,
- drowsiness,
- teak,
- pressure change,
- obsessions,
- dizziness,
- bouts of crying.
Stages of development of neurosis
If neurosis is treated, then all the changes it causes can be eliminated. The disease leads to organic damage to the brain. Neuroses often have a long course. This largely depends on the individual characteristics of a person, as well as on how developed his adaptation mechanisms are that allow him to adapt to traumatic situations. Of no small importance is the character of a person, the degree of formation of psychological defense.
Neurosis has three stages. Each of them has a different set of symptoms:
- First stage.
The disease is just beginning to develop. A person experiences increased irritability and excessive excitability.
- Hypersthenic
or intermediate stage.
In humans, the excitability of the peripheral nervous system increases. - Hyposthenic
or final stage.
The patient is in a depressed mood all the time, drowsiness increases, he is apathetic, and shows no interest in life. This is due to severe inhibition of nervous system processes.
If neurosis is not treated, the disease will certainly affect a person’s behavior. The patient begins to understand that not everything is all right with him. Neurotic personality development occurs 6 months to 2 years from the first symptoms of the disease (if it is not treated).
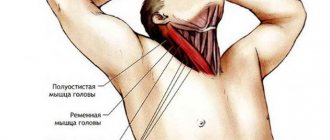
Muscle tension
The most obvious symptoms of muscle tension are the following:
- decreased potency,
- excitability,
- weakness,
- muscle spasm,
- sleep problems.
Muscle tension during neurosis is the most painful and unpleasant symptom, so the main goal of treatment is muscle relaxation.
Muscular neurosis is local in nature, that is, it affects only one area of the body.
There are four types of MN:
- facial,
- chest muscles,
- muscles of the cervical spine,
- limbs.
In this case, the person does not feel severe pain, he simply has limited movement in the affected area. This type of neurosis is best treated with massage.
Treatment
During treatment the following methods can be used:
The main one is psychotherapy, which is divided into:
- Pathogenetic, which affects the causes of occurrence.
- Symptomatic, which is effective only in conjunction with the first, since in itself it has a temporary effect that alleviates symptoms for a short period of time.
It is important to understand how to treat the pathology and find out the cause of the development of the emerging disease.
If it begins at an early age, that is, transmitted at the genetic level, then treating neuroses only with the help of psychotherapy will not give the desired result.
The effect of medications is on processes in the brain, that is, it is excitation and inhibition. To stimulate inhibition, specialists use bromine, and for the opposite effect, caffeine.
To block acute neurosis, the following medications are prescribed:
The drugs are fast-acting, the principle of action of which is based on calming the central nervous system, which leads to a decrease in negative symptoms.
Muscle tension during neurosis requires massage, as it will help relax overstrained muscles, which will allow a person to live a normal, full life.
Treatment of neuroses
Many methods and techniques for treating neuroses help cope with this disease. In the treatment of neuroses, psychotherapy is successfully used, and in more severe cases, drug treatment.
The opinion of doctors is that it is advisable for the patient to become aware of his contradictions and build a more accurate picture of his personality. The main goal of psychotherapy is to help the patient understand the relationships that determined the development of neurosis. There will be a result in psychotherapy if the patient really correlates his life experience with the situation because of which they came into conflict and the disease manifested itself.
It is important to draw the patient’s attention to his personal subjective experiences, as well as to the external conditions of the social environment.
But Karen Horney argued that awareness of contradictions alone is absolutely not enough; it is very important to create psychotherapeutic conditions that will change the personality and allow her to forever forget neurotic ways of protecting herself from the outside world
Color diagnostics of neuroses
Personality neurosis is diagnosed by repeated preference for the following colors (gray, purple, black, brown).
The colors rejected by patients with hysterical syndrome are red and purple.
Treatment of neuroses includes many methods. These include feasible physical activity - physical exercise (aerobics, swimming, running, brisk walking). All this stimulates the heart and enriches it with oxygen. We conduct physical exercises up to 5 times a week for 15 minutes.
Treatment methods for neuroses include color therapy. The right color for the brain is beneficial, just like vitamins are for the body. To extinguish anger and irritation, avoid the color red. When you are in a bad mood, eliminate black and dark blue tones from your wardrobe and surround yourself with light and warm colors. To relieve tension, look at blue, greenish tones. Replace the wallpaper at home, choose the appropriate decor.
An effective method for treating neurosis is music therapy, which is selected according to the mood, then the music is changed in the direction of changing the desired mood. This is what Bekhterev advised. Simple music - songs, romances - gives a strong effect and good results. French researchers advise using the mechanism of action of music. First, we determine the melody that is responsible for the state of mind at the moment. Next, a melody is selected that can resist the effect of the first composition, neutralizing it. When choosing a second melody, they are guided by the fact that it should be airy and light; giving the desired consolation and instilling hope. When choosing the third composition, music with the greatest emotional impact is selected. Music should be dynamic, carrying confidence, will and courage.
Methods for treating neuroses include the gastronomic method. Pleasure yourself through food. Carbohydrates contained in cakes and sweets are very calming. Protein foods (seafood, chicken, young veal, beef) also give the desired result, but avoid drinking coffee, strong tea, Coca-Cola and the like. There is a direct connection with high consumption of these drinks and anxiety, depression, and irritability
Consequences
Pathology without proper treatment can lead to the following conditions:
- Low performance, which occurs due to the inability to concentrate for a long time, as well as memory limitations.
- The occurrence of diseases, which occurs due to the weakening of the body’s protective functions.
- Fluctuations in body weight, as hormonal levels are extremely unstable.
- Problems with communication in society, as a person experiences anxiety, tearfulness and touchiness.
- The emergence of obsessive thoughts.
At the same time, the feeling of anxiety can manifest itself in different ways, that is, it can be muscle strain, restlessness, trembling in the hands, and so on.
A person prone to neurotic conditions should limit contact with irritating factors and avoid stress. The latter can be achieved with the help of sedatives or by learning to control yourself. Otherwise, the consequences of neurosis may be unpredictable.