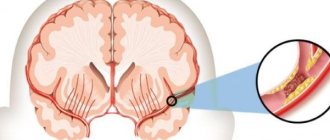
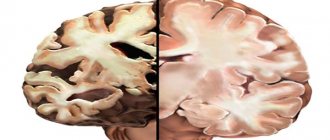
Stroke is an extremely dangerous condition that claims many lives. Once a cerebral infarction has occurred, the necessary therapeutic actions must be taken. This is the only way to save the patient. The rehabilitation period is long and difficult.
Nutrition after a stroke plays a major role in the patient’s full recovery. The diet for stroke must be selected individually, based on the general condition of the patient. This way the rehabilitation process will be the shortest and most effective.
If the patient has swallowing problems and cannot feed on his own, a special probe is used. Tube feeding is discussed in more detail in this article.
General principles of proper nutrition
The specialized diet after the hemorrhagic form of the disease, as well as after an ischemic stroke, is approximately the same.
The principles include the following elements:
- In the first days or even weeks, tube feeding is indicated. Such nutrition allows you to provide the body with the necessary substances if the patient is not able to take food on his own. Also, tube feeding is required if the patient is unconscious (feeding for bedridden patients). The preparation method consists of grinding the products through a meat grinder twice, grinding them with a blender or rubbing them through a sieve. Only liquid food is suitable for tube feeding.
- Mode. It is necessary to develop a clear eating regimen. After an acute cerebrovascular accident, all organs and systems are in dissonance. There are problems with digestion. To ease the work of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to eat by the hour.
- It is worth eating in small portions at each regular meal so as not to overload the digestive tract.
Dietary factors influencing recovery after stroke
The location, extent and type of cerebral infarction (ischemic or hemorrhagic) largely determine the recovery of brain function. Recovery is primarily hampered by the involvement of larger areas of white matter and damage to or disconnection of the hippocampus, a critical structure for learning.
Older people tend to recover less well than younger people. The reserve capacity of the brain plays an important role, in particular, freedom from previous damage caused by subclinical vascular lesions. In assessing the chances of recovery from a stroke, the factor of previous injury is more important than the patient's age.
Early and post-stroke rehabilitation are currently largely in the hands of private institutions. In the case of acute stroke, the interaction of medical personnel with scientific experimental and intervention studies has significantly expanded the quality of services in Russia. Early neurological rehabilitation helps to quickly return to everyday life.
Andrey Yurievich
Healthy foods
What can you eat after a stroke? Nutrition for cerebral stroke depends on the patient’s condition. During the period of tube intake of nutrients, the consumption of lean meats and side dishes is indicated. Also vegetable and fruit purees.
In the future, the diet expands and includes:
- Bakery products . For the vessels of the brain of a patient after a stroke, such products are useless, however, bread creates the necessary ballast load in the intestines, cleanses the tract, normalizing motility and accelerating the evacuation of feces. It is acceptable to consume stale bread made from rye and wheat flour, soaked crackers, and bran.
- Vegetables, fruits and juices. These are ideal products for blood vessels: they normalize blood circulation and lower blood pressure (diet for hypertension should also consist mostly of foods of plant origin). The most useful fruits are: apples (dilate blood vessels, are good for veins and normalize blood flow), pears, oranges and citrus fruits (prevent oxidative processes, help thin blood in blood vessels, lower the concentration of lipid structures, eliminate cholesterol), peaches (lower the concentration of lipids , normalize arterial blood circulation).
- The most effective vegetables : zucchini, eggplant, cabbage, onions, etc. The main active beneficial substances that determine the therapeutic effect of this food are B vitamins, vitamin C, other vitamins, minerals, organic acids, antioxidants. You need to consume at least half a kilogram of fresh fruits per day. This approach reduces blood pressure and helps nourish blood vessels.
- If brain damage has not yet occurred, you can urgently clean the blood vessels with juices.
- What foods thin the blood? Fruits and vegetables also come to the rescue here. Citrus fruits and apples are especially effective. The anticoagulant effect is necessary to normalize blood flow.
This diet includes not only foods after a stroke. The same nutrition with high blood pressure will help prevent acute ischemia of cerebral structures.
Why is diet important?
The trouble has already happened. But cholesterol levels are still high, the tendency to form blood clots has not gone away, and obesity does not disappear with the wave of a magic wand. This means that the right diet for a stroke becomes issue No. 1. By adjusting diet and lifestyle, a person significantly reduces the risk of another stroke and speeds up the rehabilitation process.
To summarize, dietary nutrition after a stroke has the following goals:
- Providing the body with the necessary set of nutrients. Without this, vital organs will not be able to function fully.
- Creating conditions under which blood thickening decreases and ceases to be hazardous to health. This is especially important for diabetics.
- Normalizing weight and preventing its increase, since obesity affects the functioning of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
There is no fundamental difference in what caused the stroke. Diet after a stroke is selected according to similar rules in both cases.
Foods you should avoid
The list of harmful products is no less extensive:
- Sweet bakery products. They increase the concentration of cholesterol, cause worsening of atherosclerosis and worsen the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, these are harmful products for the heart and blood vessels.
- Sweet products. They increase glucose levels and cause increased insulin production. This process increases blood pressure. After a brain stroke, you should give up sweets.
- Salty food. Causes stenosis (narrowing) of blood vessels in the brain and neck. Salt is definitely not included in the nutritional structure for strengthening blood vessels.
- Fatty fermented milk food products , including butter, kefir, cottage cheese, sour cream.
- Fried foods.
- Fat meat.
- Ethanol. Alcoholic drinks contribute to stenosis of arteries and veins.
- Ketchup, mayonnaise, sauces.
- Coffee, teas. They tone blood vessels and increase tonometer readings.
A few words about salt
Immediately after a stroke, salt is not added to food at all. It leads to fluid stagnation. Moreover, it draws fluid from the tissues surrounding the vessels, thereby increasing the load on the vascular system. Consuming salt often causes high blood pressure, and this should not be allowed. The diet after a stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) should be salt-free.
When the patient's condition noticeably improves, he can refuse fresh (not salty) food. In this case, minimal addition of salt is allowed. But the ideal option is when a patient after a stroke gets used to being content with lightly salted dishes.
The diet for stroke necessarily includes sea fish. It is sea fish and river fish that do not contain the necessary omega-3 acids. Many exclude this product because they consider fish expensive, but it is necessary, at least as a source of phosphorus, which has a beneficial effect on the brain, improving metabolism.
Meat lovers should give preference to rabbit, turkey, and veal. Duck and chicken meat can only be cooked without the skin. But you will have to refuse offal (brains, liver and other liver). These foods are high in cholesterol. By the way, it is especially important that the diet for ischemic stroke keeps the level of cholesterol in foods under control.
Menu
A sample menu is compiled together with your doctor or nutritionist. The structure of the diet includes products that strengthen blood vessels (products for cleaning blood vessels).
You can distribute your diet using the Daily Routine diary.
An approximate diet could be:
- Breakfast. Oatmeal or other cereal porridge with pieces of fruit (dried fruits can be used), weak tea or a decoction of blueberries/rose hips.
- Next breakfast (lunch). Juice squeezed from vegetables or fruits, a small amount of low-fat cottage cheese.
- Dinner. Soup or broth with fish or lean meat, a piece of bread, jelly or berry broth.
- Afternoon snack. Fresh vegetable salad seasoned with carrot or citrus juice.
- Dinner. Buckwheat porridge or rice with chicken breast cutlets. Kissel or weak tea.
- At night, you can drink a small amount of milk or kefir with minimal fat content.
Exactly the same nutrition is indicated for high blood pressure.
Menu for cerebral stroke
- It is preferable to include orange or dark green vegetables, peas and beans in the diet after a stroke;
- fruits can be consumed daily in frozen, dried and fresh form;
- grain products for the menu after a stroke should be included from the whole grain category;
- low-fat dairy products;
- fats on the menu can be represented by fish and nuts;
- Lean poultry is the main permitted source of protein.
Nutritionists, together with other specialists, have developed recommendations for creating a menu to reduce the likelihood of relapse. The daily menu should be varied so that the body receives the substances necessary for recovery. It is important to include brightly colored vegetables and fruits in the menu, as they are rich in macroelements and vitamins.
Basic directions of proper nutrition
The optimal diet is prepared not only for the health of the body. The dietitian has a difficult goal to achieve. It consists of a number of tasks. The menu being compiled is aimed at solving these problems.
Among the main tasks:
- Reducing the concentration of cholesterol in the bloodstream. As a result of an increase in the amount of lipid structures in the veins and arteries, fatty deposits known as atherosclerotic plaques are deposited on the walls of blood vessels. They clog the lumen of blood supply structures and prevent normal blood flow. According to statistics, it is such atherosclerosis that causes stroke in 40% of cases (or so). Moreover, the age of the patient does not matter. The primary task of a proper diet is to eliminate hypercholesterolemia.
- Normalization of calorie intake. Excessive calorie intake leads to increased cholesterol concentrations. Excess sweets provokes increased insulin production. What this leads to has already been said.
- Avoid taking substances that excite the nervous system. This is strong tea, coffee, alcohol, especially narcotic substances. All of them have a stimulating effect on the central nervous system.
- Getting rid of salt in the diet. Salt is an extremely dangerous substance for a hypertensive patient, and even more so for a patient who has suffered a cerebral infarction.
- Stabilization of the amount of fluid consumed (drinking regimen) . You should drink no more than one and a half liters of liquid per day. Exceeding the amount leads to edema and increases blood pressure.
Rules for eating
Rapid restoration of health and prevention of complications is possible by following medical recommendations after a stroke, which are based on control of blood pressure and weight. In addition to changing your diet after a stroke, you should adjust your diet. Recommendations for diet after a stroke:
- a diet after a stroke involves frequent meals, the time interval between which is no more than 3 hours;
- after waking up, eating should be no later than an hour later;
- before going to bed, eating should be no earlier than 2 hours later;
- Snacks between meals are undesirable, as they burden the stomach.
A stroke is a serious shock to the body, after which a long recovery is required. Rehabilitators at the Yusupov Hospital will help restore lost body functions, psychologists will provide psychological assistance and support, and specialists will organize a comfortable stay for the patient in the hospital.
During the period of treatment and recovery at the Yusupov Hospital, special attention is paid to the nutrition of patients. The daily diet consists of fresh dietary products that do not affect blood pressure and do not contribute to weight gain. The menu is developed individually for each patient, taking into account the recommendations of the attending physician.
The need for diet when sick
After suffering a stroke, the patient can no longer afford the usual hamburgers, fried potatoes and chips with beer.
Increased salt intake leads to fluid accumulation in the body, which worsens the condition of people with high blood pressure, which almost always occurs in patients who have had a stroke. Pressure surges can not only worsen the current condition and increase the duration of rehabilitation, but also provoke a second stroke.
Help: It is vital for the patient to monitor cholesterol in the blood to prevent the formation of plaques that can continue to clog blood vessels. This also requires adjustments to your diet.
To strengthen and cleanse blood vessels, it is necessary to enrich the menu with vitamins, microelements and fiber. After a stroke, weakness, dizziness, increased fatigue often appear, and the level of iron in the blood drops. To eliminate these symptoms, you need to add as many vegetables, raw and steamed, as well as lean meats and fresh fruits to your diet.
As you can see, this diet is not at all difficult to maintain at home.
What can you drink?
During the day, it is important to drink water, clean, plain, not carbonated. Drinks you can include in your diet include fruit drinks and uzvar (dried fruit compote). Rosehip decoction, not very sweet jelly, kvass, preferably homemade, and fresh juices are suitable. Tea is acceptable, but only weakly brewed, but coffee is completely prohibited. Under no circumstances should you drink sweet soda; it increases sugar levels, interferes with the fight against obesity, and damages small blood vessels.
You need to forget about alcoholic drinks after a stroke, they will only do harm.
The principle of diet composition
By following a certain diet, you can significantly speed up recovery after a brain injury. What recommendations do doctors usually give?
- The most important rule for stroke patients is a sharp reduction in salt and sugar in the daily menu. There should be no more than five grams of salt in the diet per day - this is a level teaspoon.
- It is allowed to cook food only boiled, baked and steamed .
- It is necessary to add as many fiber-rich foods as possible - vegetables, not too sweet fruits, whole grain cereals, bread and herbs.
- It is necessary to sharply limit animal fats , as well as “bad” carbohydrates - sugar, white bread, baked goods.
It is best for the patient to eat frequently and in small portions. The number of meals should be at least five - this will prevent sudden drops in blood sugar, which are detrimental to stroke survivors.
What to exclude from the diet and why?
- Salt retains water and causes swelling, raising blood pressure.
- Alcohol has a detrimental effect on the nervous system and blood circulation.
- You can’t eat fatty meat, butter, baked goods, ice cream, fatty dairy products, chocolate - it provokes the formation of cholesterol plaques.
- All types of preservation are due to the salt and vinegar content.
- Sausages, fast food products - many chemical components that are contraindicated for the patient.
- Semolina and carbonated drinks are easily digestible carbohydrates that provoke obesity.
- Strong tea and coffee - increases adrenaline in the blood.
- Mushrooms in any form are prohibited.
Features of nutrition after illness
Proper nutrition after a stroke is important for the recovery of the entire body . This is the only way to ensure the normal functioning of all internal organs.
And when the body is ready to fight, having a strong immune system, then the recovery period is less painful and much faster.
After an illness, there is a high risk of receiving nutrients through food or drink in insufficient quantities for the body. This often causes rapid weight loss and slows down the healing process.
Poor nutrition may be due to the following factors:
- problems with thinking and memory, the patient may forget how and what to eat;
- complete loss of appetite, caused by lack of hunger;
- problems with swallowing appear in almost 70% of people who have suffered a stroke; paralysis of the throat muscles occurs, which causes dehydration;
- probing;
- motor disorders of the upper extremities.
During the first days of hospital stay, patients are regularly weighed. After discharge, they must monitor their weight on their own. If the patient’s motor functions are impaired, relatives help feed the patient.
Nutrition for stroke patients
How to cook properly
The diet for stroke is not too strict. It is advisable to discuss this issue with your doctor and nutritionist. Experts will give qualified recommendations according to which you can create a varied menu from suitable products. If you feed a person who has suffered a stroke the same dishes, he will begin to refuse food, since his sense of taste is impaired, and the monotony simply causes an aversion to food.
You should not give fried or smoked foods to the patient. If he does not like steam and boiled cuisine, then cook in the oven, but without oil. Be sure to prepare soups and broths. If the patient has impaired swallowing function, grind food in a blender or prepare a smoothie. Never serve food that is too hot or very cold. All food should be warm or at room temperature.
Instead of salt, add mild spices and herbs, this improves the taste, smell and reduces the feeling of lack of salt.
Post-stroke diet - menu options for the week
A nutritionist will help organize proper nutrition and create a menu for a patient after a stroke. You can expand your knowledge yourself by studying the publications of some recognized authors. In them you can easily find information about the physiology of nutrition, hygiene and feeding techniques for the patient. Learn the nutritional characteristics of patients with vascular diseases. Such literature will help to properly organize the rehabilitation of a patient who has suffered a stroke.
Post-stroke diet goals:
- Reduce and normalize the patient's blood pressure.
- Normalize the operation of the system.
- Avoid thrombosis.
- Prevent blood from thickening.
Fresh vegetables and fruits, poultry and fish dishes, porridges and soups made from whole grain cereals will help avoid or reduce the risk of disease by 30–40%. Compliance with the diet and a special menu for stroke is the key to successful rehabilitation of the patient and his complete recovery.
| Day of the week | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
| Monday | Barley porridge, green tea | Carrot and apple pudding | Vegetable rice soup, chicken fillet with vegetables, apple compote |
| Tuesday | Dumplings, wheat porridge, rosehip decoction | Fruit puree | Broccoli and cauliflower soup, vegetable stew, fruit drink |
| Wednesday | Omelet, buckwheat porridge with raisins, green tea | Charlotte | Vegetable broth, chicken cutlet with buckwheat, compote |
| Thursday | Boiled egg, rosehip infusion | Baked fruits | Vegetarian soup, cauliflower baked with chicken fillet, jelly |
| Friday | Lazy cottage cheese dumplings, compote | Carrot pudding | Rice soup, vegetables stewed in sour cream with vegetables, berry juice |
| Saturday | Omelette, oatmeal, chicory | Baked apple | Green cabbage soup, 100 g boiled beef with rice, weak tea |
| Sunday | Boiled egg and compote | Banana and apple puree | Vegetable soup with lentils, steamed cutlet with steamed carrots, jelly |
| Day of the week | Afternoon snack | Dinner | |
| Monday | Rose hip decoction | Fishballs and zucchini | |
| Tuesday | Green tea with biscuits | Cottage cheese with banana | |
| Wednesday | Morse and bread | Puree and fish balls | |
| Thursday | Berry fruit drink | Carrot pudding, boiled pollock with vegetable garnish | |
| Friday | Pear compote | Casserole with cauliflower and chicken fillet | |
| Saturday | Berry compote | Fish fillet with cucumber salad | |
| Sunday | Rose hip decoction | Potato side dish and steam cutlet, tea |
An hour before bedtime, you can offer the patient a glass of kefir
It is very important not to overload the patient with food. Meals must be split up and overeating avoided.
Four to five meals a day will relieve the burden on the patient’s body and ensure quality sleep.
Success in the treatment of stroke largely depends on the organization of proper nutrition. The diet will help not only to avoid the development of the disease, but also to lose extra pounds, which put stress on the blood vessels and heart, increasing the risk of another attack. The more attention is paid to healthy eating, the less likely you are to become another victim of this terrible disease.