- Causes of development of brain tumors
- Early symptoms and first signs
- Types of neoplasms
- Methods for detecting brain neoplasia
- Brain tumors - treatment with modern methods
- Survival prognosis
- Is it possible to prevent central nervous system cancer?
Brain tumors or neoplasia are neoplasms localized in the cranium and developing from brain tissue, its membranes, cells of other tissues present in the cranium, as well as metastases of malignant tumors from other parts of the body.
Risk factors
There are no factors proven to provoke the development of brain tumors. But there are 6 factors that, in theory, can increase the risk.
- Floor. Some cancers, such as meningiomas, are twice as common in women, while medulloblastomas are more common in men.
- Age. The incidence of cerebral neoplasia increases with age and is more common in people aged 65 years and older. Children are at high risk of developing medulloblastomas, while gliomas are more common in adults.
- Immune system disorder. People with compromised immune systems are at increased risk of developing intracranial lymphomas.
- Genetic connections. Family history can affect your likelihood of developing certain diseases. Hippel-Lindau disease, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and neurofibromatosis (NF1 and NF2) are found in families with rare cranial neoplasias.
- Chemical exposure. Exposure to industrial chemicals or solvents is associated with an increased risk of developing brain tumors in workers in the oil refining, rubber and drug industries.
- Previous radiation treatment. Exposure to radiation therapy, especially at a young age, can increase the chance of developing brain cancer.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of these neoplasms depend on which part of the brain is involved and the functional system it affects (eg, motor, sensory, language, etc.). For example, vision problems may result from a tumor near the optic nerve. A tumor in the front can affect the ability to concentrate and think.
Early signs
The symptoms of brain tumors often mimic those caused by other diseases, so you should consult a healthcare professional to get an accurate diagnosis.
First signs:
- headache that varies depending on the time of day and head position and gets worse over time;
- seizures;
- numbness in the limbs.
Common symptoms may also include:
- nausea or vomiting;
- memory loss;
- muscle weakness;
- speech disorders;
- mood or personality changes;
- unexplained fatigue;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- impotence or infertility;
- overproduction or underproduction of breast milk;
- Cushing's syndrome (a condition marked by weight gain);
- high blood pressure;
- diabetes.
Some patients may have problems with vision, speech, or coordination. Symptoms may be hidden, smoothed out or develop very slowly.
Types of neoplasms
According to the ICD (International Classification of Diseases) classifier, there are more than 120 types of brain tumors.
Primary tumors form in brain cells and are classified by cell type, or where they first develop. For example, astrocytomas form in star-shaped cells called astrocytes.
Most brain tumors are secondary . They are metastatic tumors that have spread from another area in the body. Lung cancer most often metastasizes to the brain, followed by breast cancer.
Are these neoplasms malignant?
More than 60% are malignant. For example, more than half of all gliomas diagnosed in adults are glioblastomas (a very aggressive brain cancer). Ependymomas and oligodendrogliomas can also be malignant.
But not all brain tumors are like this. Many meningiomas, craniopharyngiomas, and pituitary tumors are benign.
It is important to understand that even benign tumors can damage brain tissue and cause side effects such as headaches, fatigue, or blurred vision. Even if the tumor is benign, timely and appropriate treatment can be decisive for your health.
Astrocytomas
Astrocytomas are the most common tumor of the central nervous system. Occur anywhere in the brain and develop from small star-shaped cells called astrocytes.
gliomas are a type of astrocytoma that forms in the brain stem and controls many vital functions such as body temperature, blood pressure, breathing, hunger and thirst. Tumors in this area are difficult to treat. Most gliomas are high-grade astrocytomas.
Glioblastoma multiforme or grade IV astrocytoma is a fast-growing, aggressive type of malignant tumor of the central nervous system. Glioblastomas can appear in any lobe of the brain, but most often develop in the frontal and temporal lobes.
In addition to astrocytomas, there are other primary tumors that arise from glial cells. These include:
- Ependymomas, which usually arise in the lining of the ventricles or in the spaces of the brain. Although ependymomas can develop at any age, they are most common in children and adolescents.
- Oligodendrogliomas develop in cells that produce myelin, the covering that protects nerves. They are very rare, grow slowly and do not spread to surrounding tissues. Oligodendrogliomas most often occur in middle-aged adults and have a more favorable prognosis than astrocytomas.
- Mixed gliomas have two types of tumor cells: oligodendrocytes and astrocytes.
Nonglial neoplasias
There are a number of tumors that do not start in glial tissue.
Meningioma develops in the cells of the membranes that surround the brain. Meningiomas account for 15% of all intracranial neoplasias. Most of these neoplasms are benign. Some meningiomas may not require immediate treatment and may go undetected for many years. Most meningiomas are diagnosed in women aged 30 to 50 years.
Craniopharyngiomas develop in the area near the pituitary gland. These neoplasias are usually benign. However, they can create pressure or damage the hypothalamus and affect vital functions.
Germinoma is the most common type of embryonal malignant neoplasia in the brain. In addition to the brain, germinomas can form in the ovaries, testicles, breasts and abdomen. Most of these neoplasms occur in children.
Pineal neoplasias occur in or around the pineal gland, a small organ located in the center of the brain. They can be slow-growing (pineocytoma) or fast-growing (pineoblastoma).
Medulloblastomas are fast-growing neoplasias that develop from cerebellar neurons. The cerebellum controls movement, balance and posture. They are usually found in children or young adults.
Primary CNS lymphomas develop in the lymphatic tissue of the brain. This type of neoplasia usually occurs in people who have a compromised immune system.
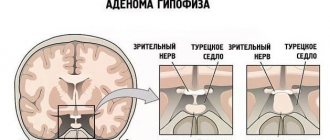
Pituitary tumors
The vast majority of pituitary neoplasias are pituitary adenomas, benign growths that do not spread beyond the skull. Although these tumors are benign, they often cause problems because they can cause the pituitary gland to produce excess hormones.
The latest cancer treatment methods: immunotherapy and virotherapy
After weighing the risks associated with repeated brain surgery and potential complications, the patient decided to seek advice from Professor Slavin, under whose supervision she was during this entire period. According to Professor Slavin, it was possible to achieve a reduction in the volume of the tumor mass using a conservative method, without surgery. However, it was necessary to take into account the resistance of the cancer tumor - its acquired resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Based on this, Professor Slavin recommended an alternative treatment strategy, proposing to shift the focus towards immunotherapy.
The goal of immunotherapy is not to directly destroy malignant cells, but to turn them into a target for the immune system, which is normally capable of recognizing and attacking substances foreign to the human body.
Additionally, the patient received oncolytic virotherapy. Genetically modified oncolytic viruses are harmless to humans, and at the same time they specifically infect cancer cells, causing their death. But even if a cancer cell remains viable after a viral attack, it becomes a carrier of specific viral antigens that serve as a signaling target for the immune system.
Another group of drugs, called immune checkpoint inhibitors, have been used to stimulate the natural antitumor activity of T cells.
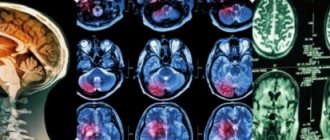
Diagnostics
Visual tests used in diagnosis
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI is used to look for brain tumors because it provides more detail than a CT scan. However, for skull bones, MRI does not provide the same image quality as a CT scan and may not show the impact of pathology on the skull.
CT scan (computed tomography): A CT scan provides greater detail of the bone structures near the tumor and may be used when an MRI is not appropriate. For example, for patients with excess body weight or claustrophobia.
PET (positron emission tomography): PET scans are more often used for high-risk, fast-growing tumors. After treatment, a PET scan helps determine whether tumor tissue remains.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves removing a small amount of tissue. This helps evaluate the tumor to develop a treatment plan. Fine-needle biopsy may be performed for tumors in hard-to-reach or critical areas.
Angiography
This procedure uses X-rays to produce multiple detailed 3D images of the blood vessels. Angiographs can be used to plan surgical resection near an area rich in blood vessels. Sometimes this test is used to embolize (close) blood vessels feeding a tumor before surgery.
Preoperative preparation
Preparing for treatment involves performing the following actions:
- reducing the patient’s intracranial pressure (with the help of medications or directly on the operating table);
- normalization of the patient’s body condition (during the operation, the cardiovascular and respiratory systems must function normally).
Before a patient has a tumor removed, he is asked to undergo the following examinations:
- a biopsy, which is the removal of a particle of tumor tissue for subsequent analysis of its structure (may pose a danger to human health due to the development of bleeding, therefore it is used only for certain types of pathology);
- magnetic resonance therapy or computed tomography of the brain;
- an electrocardiogram to determine whether the cardiovascular system is functioning normally;
- fluorography;
- angiography (contrast x-ray examination of the blood vessels of the affected organ).
In addition, before proceeding with the operation, the doctor recommends that the patient undergo urine and blood tests. All the manipulations described above are necessary so that a specialist can remove a tumor from a person with maximum confidence that this will not lead to the development of complications.
Treatment of brain tumors
Surgery
Surgical removal is the main treatment option for primary brain tumors. For low-risk neoplasias, this is usually the only treatment.
During surgical resection, the tumor can be completely or partially removed. In the second option, the positive effect is that the pressure on nearby brain structures is reduced and neurological symptoms are alleviated.
Surgical resection has also become the standard treatment for single metastases larger than 3 cm and in noncritical sites.
Surgical resection is more effective than radiosurgery. The survival rate of patients after surgery is almost twice as high as with radiosurgery. Only 13% of patients treated with surgery showed local recurrence, whereas 39% of patients treated with radiosurgery showed local disease progression.
Innovative cranial surgery techniques used in Belgium
- Intraoperative neuronavigation uses an advanced MRI system to map areas of the brain responsible for important functions. This visual map allows the operation to be performed accurately, without damaging important areas of the brain.
- Intraoperative electrophysiological mapping (motor mapping or language mapping) is like GPS navigation for the brain. Small electrodes are placed on the outer layer of the brain to stimulate the areas around the tumor. This helps to accurately determine the boundaries of an area, for example, responsible for speech or movement.
- Biofluorescence . The patient is given an injection of 5-aminolevulinic acid before surgery. This compound is actively absorbed by atypical cells. As a result, they begin to glow, which makes it possible to remove them as completely as possible.
- Laser ablation allows you to remove tumors without a large-scale opening of the skull (craniotomy). This ensures a faster return of the patient to normal life.
- Robotic surgery . Minimally invasive endoscopic surgeries using neurosurgical robots make it possible to remove tumors in the most critical areas. The movements of the robot's manipulator are 100 times more accurate than the movements of the surgeon's hands. This allows tumors to be removed literally cell by cell without resorting to craniotomy.
Multimodal surgery in clinics in Belgium
Intraoperative chemotherapy (BCNU) is the direct application of chemotherapy to the tumor area during surgery, which helps reduce the side effects associated with systemic chemotherapy, such as nausea and vomiting.
Another treatment option was intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT). With this technology, the tumor resection area is irradiated directly during surgery, helping to avoid damage to adjacent normal structures, especially the scalp and meninges.
Radiation therapy and radiosurgery
Radiation therapy (WBRT) is usually used to prevent relapses. Its effectiveness in the treatment of brain tumors is controversial, since it has been proven that, despite a decrease in the number of relapses, overall survival does not improve. For neoplasias that are well localized in the brain, conformal radiation (spot therapy) is recommended. This is radiation delivered strictly to the tumor and a small surrounding area.
However, irradiation of the entire brain is sometimes recommended when there are multiple tumors in the brain.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is also available for brain tumors in Belgium. This is high-intensity radiation that is very precisely aimed at a small area.
Clinics in Belgium use the most advanced options for stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).
- Advanced Linear Accelerators, or LINACs, provide up to five times greater accuracy than previous generation sources, allowing for finer adjustments. LINAC can also be used to successfully target small lesions or deep, previously inaccessible tumors.
- Frameless Neurosurgical Stereotactic Radiotherapy (CyberKnife) - Unlike the outdated Gamma Knife technique, the new one no longer requires a frame to hold the head in place for highly focused radiation therapy, making surgery easier, more precise and with better protection of surrounding brain tissue for neurological improvements results.
- Stereotactic fractional radiosurgery (SBRT) is a high-intensity form of radiation where the total dose is divided into fractions. Several procedures are carried out throughout the week. This method provided more than 90 percent pain reduction and more effectively controlled tumor growth after one year of treatment.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is usually given to patients with high-grade brain cancer as maintenance therapy. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, including surgery and/or radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy drugs can be given orally in tablet form or injected into a vein.
In Belgium, methods of injecting chemotherapy (and biological) drugs directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or into the brain are being investigated. These methods increase the concentration of drug at the tumor site while reducing the side effects typically associated with systemic chemotherapy.
Biological therapy
Targeted therapy targets specific pathways or abnormalities in tumor cells. Targeted therapy is often combined with other treatments such as chemotherapy. This treatment is often an option for patients whose tumors recur after repeated treatments. The main drugs used in 2020 for brain tumors are bevacizumab and larotrectinib.
Immunotherapy is carried out in Belgium using modified T cells and dendritic cells. These methods are still at the stages of clinical trials and there are no approved protocols for their use.
Brain surgery to remove tumors for cancer: rehabilitation after the procedure – Molodushka
According to statistics, brain tumors occur in 5–8 percent of all cancers.
Surgery to remove the tumor is the optimal method, since it minimizes the risk of damage to adjacent tissues that limit the tumor. Modern medicine allows the use of non-invasive or minimally invasive surgical methods, which significantly reduces the risk of complications.
Indications and contraindications
Surgical intervention to remove tumor foci is necessary when:
- the location of the tumor is an accessible area, and the likelihood of complications is much lower than if the operation is not performed;
- there is no further growth of benign neoplasms, but their negative impact on the performance of brain structures is noted;
- there is evidence that the neoplasm is malignant;
- The condition and age category of the patient allow the operation.
In most cases, after eliminating the tumors, there is a significant improvement in the condition of the patient being operated on, and proper rehabilitation helps to increase life expectancy.
Among the contraindications to the use of surgical intervention are the following:
- inoperable tumor (the tumor is located in a place inaccessible for removal);
- exhaustion of the body due to pathological processes or age-related changes;
- a neoplasm that is malignant and grows into surrounding tissues;
- the prognosis for survival after surgery is not as favorable as without it;
- voluntary refusal of the patient.
When only conservative treatment methods are used, the probability of death is almost 100 percent.
Kinds
When diagnosing a brain tumor, the following types of operations can be used:
- Stereosurgery. This method involves removing tumor cells by exposing them to special rays. There is no need to make an incision.
- Open operation . In other words, it is called a craniotomy. The tumor is removed through a hole drilled into the skull bone. In some cases, partial removal of the skull bones is possible. This need arises when the inflammatory process spreads and the formation of metastases to bone tissue.
- Endoscopy. It differs from the previous method in that the entire process is displayed on the monitor using a camera. In addition, such an operation requires a much smaller hole through which the tumor will be removed.
Preparatory process
First of all, it is necessary to carefully calculate the location of access to the brain and choose the optimal method for removing the tumor formation. The surgeon must foresee all possible risks associated with damage to brain structures.
In Russia, most experts are of the opinion that the preservation of brain activity should be as maximum as possible. However, this often provokes relapses - repeated formations, since as a result the pathological cells are not removed.
Israeli neurosurgeons-oncologists are more inclined to ensure that the removal is as complete as possible. The likelihood of risking unintentional brain damage will depend on the qualifications and professional experience of the specialist.
Before the operation, if necessary, the following actions can be performed:
- Decreased intracranial pressure. This is done with the help of medications or while the patient is on the operating table.
- Biopsy. A small piece of tumor tissue is taken for subsequent study of its structure. However, we should not forget that this analysis is not always used, since it can pose a serious threat to the patient’s life.
- Stabilization of the condition. The operation is possible only if blood pressure, pulmonary and cardiovascular indicators are normal.
In addition, the following examinations must be carried out:
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- electrocardiogram;
- angiography;
- taking urine and blood tests;
- fluorography.
Only after receiving the results of all studies can you proceed to the operation process.
Anesthesia
In almost all cases, the patient is given general anesthesia. An endotracheal tube is inserted into his throat, which is necessary to maintain breathing. Throughout the entire operation, the patient will be in a state of sleep and will not feel anything.
Sometimes the patient is required to be conscious. For these purposes, local anesthesia is used or the patient is taken out of sleep for some time. By asking questions, the doctor checks the activity of the brain and also determines whether certain centers that are responsible for speech, thinking and memory have been affected.
Stereosurgery is performed under local anesthesia or without anesthesia at all, since no punctures or incisions are required in this case.
Possible complications
The brain is a vital center that controls the body as a whole. If its structure is disrupted as a result of any type of surgical intervention, the likelihood of consequences increases.
Depending on which method of tumor removal will be used, as well as on the degree of development of the pathology, location and type of tumor formations, complications may develop both as a side effect and with irreversible consequences.
As a result of craniotomy, the risk of developing complications such as:
- intracerebral bleeding;
- edema ;
- complete loss of activity of the site affected by the operation;
- further spread of pathological cells;
- incomplete removal requiring re-intervention;
- fatal outcome.
In addition, the loss of many functions is possible, which leads to:
- loss of speech, memory, vision;
- paralysis;
- mental disorders;
- involuntary urination.
If chemotherapy is prescribed after surgery, the following consequences are added to those described above:
- loss ;
- rapid weight loss;
- respiratory and heart diseases
- changes in blood composition;
- reduced immunity;
- neurological disorders ;
- inability to bear children.
Under any circumstances, the outcome will depend on how successful the surgery to remove the tumor was.
Rehabilitation period
After surgery, the patient requires rehabilitation. A set of recovery measures is developed individually for each specific case.
The main objectives of the rehabilitation program are as follows:
- Prevent possible relapse. This is necessary in case of incomplete elimination of the tumor and its tendency to grow.
- Restore damaged and lost functions.
- Re-teach the patient life and everyday skills.
- Carry out psychological adaptation to get a person accustomed to his limitations in order to prevent the manifestation of panic and the development of a depressive state.
The rehabilitation process must be comprehensive and carried out by more than one specialist. The team must include:
- psychologist;
- neurosurgeon;
- neurologist;
- oncologist;
- radiologist and chemotherapist;
- ophthalmologist;
- physiotherapist;
- speech therapist;
- physical therapy specialist;
- nurses.
The rehabilitation period should be carried out immediately after the completion of surgery to remove cancer cells. If the outcome of the operation is positive, the recovery period takes 2-4 months. During this period, not only the patient, but also loved ones need special patience and a positive attitude.
Depending on the type of operation, the type of tumor formation and impaired functions, some of the following measures may be prescribed:
- Massage – helps normalize blood flow, also restores neuromuscular conduction and sensitivity in case of paralysis of the limbs.
- Chemotherapy – its use is advisable if the tumor has not been completely eliminated.
- Exercise therapy – prescribed for loss of musculoskeletal and vestibular functions.
- Speech therapy exercises help restore speech.
While the rehabilitation period lasts, and also after it, you must also adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid physical fatigue;
- completely give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- avoid contact with chemicals and toxic substances;
- do not stay in the sun for a long time, but also do not overcool the body;
- try to avoid exposure to irritating factors that can provoke stress and depression;
- Don't fly on airplanes for a while .
Provided that all necessary recovery measures are taken and the recommendations of doctors are followed, the likelihood of possible disability is significantly reduced, and the patient’s chances of returning to normal life will increase.
Result and forecast
Often in the postoperative period it is possible to restore all lost functions.
According to statistics:
- in 14 percent of cases, vision is not restored;
- 60% of patients regain the ability to move;
- mental disorders appear rarely and only in the first 3 years after the operation;
- only 6 percent have disorders of higher brain that were obtained during surgery.
Among the most unfavorable consequences is the development of new cancers. This depends, first of all, on the type of tumor and the percentage of pathological cells removed. Such a confluence of circumstances is rarely predictable or preventable.
Depending on the condition the patient will be in during the postoperative period, he may be assigned a certain disability group. It is possible to extend sick leave, as well as some restrictions related to work activity.
Survival, as well as life expectancy, are directly related to the patient’s age and the nature of the tumor:
- at the age of 22-44 years, in 50-90 percent of cases, patients live 5 or more years;
- from 45 to 55 – this outcome is reduced by about 1/3;
- from 55 years of age – reduction by another 15-20 percent.
The term of 5 years is not the maximum. This is most likely an indicator of relapse. If cancer does not return during this period, then the likelihood of its formation in the future is minimized.
There are cases when, after surgery, the life expectancy of patients is 20 years or more.
A brain tumor is a serious disease that can lead to serious consequences, including death. Therefore, it is so important to detect it in the early stages of development and take timely measures to eliminate it.
Source: //sevgb2.ru/dieta/operatsii-na-golovnom-mozge-po-udaleniyu-opuholej-pri-rake-reabilitatsiya-posle-protsedury.html
Forecast
- Tumor resectability, location, patient age, and tumor histology are major factors for survival.
- Without radiation therapy, the average life expectancy of a patient with brain metastases is 1 month. Radiation therapy can prolong survival to 4-6 months.
- Patients with seizures secondary to a brain tumor typically experience overt neurological deterioration over a 6-month course.
- Most patients with brain metastases die from progression of their primary malignancy rather than from damage.
A study of 69 pediatric brain tumor survivors found deficits in executive function, memory, and attention. Whole brain radiation therapy, tumor size, young age at diagnosis, and male gender were risk factors for late cognitive outcomes.
Adult survivors of childhood brain tumors have an increased risk of mental illness, including depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation, schizophrenia and related psychoses, and behavioral problems.
Perhaps no other cancer is as dangerous as a brain tumor, as severe disability can occur, including paralysis, seizures, gait disturbances and cognitive decline.
Contraindications to surgery
In some cases, a council of doctors decides not to undergo surgery if there is reason to believe that in this case the patient will live longer. Also, according to the law, the patient can make an independent decision to refuse surgical removal of the tumor.
Neurosurgical surgery is contraindicated if the tumor affects an important brain center and the intervention will lead to death or loss of vital body functions. The operation is not performed in cases where the tumor gives numerous metastases.
Useful to know: Is epilepsy treatable? Features of the recovery process
Also, a contraindication to surgical tumor removal is the localization of the pathological process in an area inaccessible to intervention.
to contents ^
Prevention
Since the exact causes of the development of brain tumors have not been established, it is impossible to talk about reliable preventive measures.
However, it is worth adhering to the general rules for the prevention of cancer in terms of reducing the impact of proven carcinogens on the body. These are, first of all, ionizing radiation and chemicals such as 3-4-benzipyrene and asbestos.
Also, as a preventive measure, you can use MRI at the slightest suspicion of a brain tumor. This will help to identify a dangerous pathology at an early stage and carry out its effective treatment.
Find out more about life-prolonging new treatment options for intracranial neoplasia in Belgium. Write to us or request a call back. We will provide you with detailed advice on all issues of interest.
Where can treatment for recurrent brain cancer be performed?
Our website presents many foreign medical institutions that are ready to provide high-quality medical care for the treatment of recurrent brain cancer. These could be, for example, clinics such as:
The Korean National Cancer Center provides effective treatment for most cancers known today. In addition to direct treatment programs, the Center conducts scientific research in the field of oncology, and also works on training and education of specialists. Go to page >>
The Severance Oncology Center, located in South Korea, uses the most innovative medical equipment and technology to date for the treatment and diagnosis of oncological diseases: MRI, CT, PET, PET/CT, equipment for tomotherapy, radiosurgery, hyperthermia. Go to page >>
One of the main activities of the Mayo Clinic in the USA is the diagnosis and treatment of malignant neoplasms. The clinic uses an individual approach to each patient, developing a treatment program for various types of cancer, taking into account all its individual characteristics. Go to page >>
The Center for Therapeutic Oncology and Hematology, established at the Nuremberg Clinic in Germany, specializes in the treatment of malignant tumors of various types using modern methods of drug therapy, intensive chemotherapy, and bone marrow transplantation. Go to page >>
St. Mary's Hospital in Germany has been involved in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of cancer diseases for many years. For this purpose, the hospital established an Interdisciplinary Oncology Center, equipped with the most modern medical equipment and devices. Go to page >>
One of the most important areas in the work of the South Korean Hospital at Chung-Ang University can be considered the implementation of high-precision diagnostics and effective treatment of various oncological diseases. The oncologists of the Hospital have extensive experience and high qualifications. Go to page >>
Doctors at the Barmherzige Bruder Order Clinic in Germany have achieved excellent results in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer of various forms and locations. The medical equipment at the clinic’s disposal allows us to successfully treat cancer of the lungs, stomach, prostate gland, etc. Go to page >>
Clinic named after Johann Wolfgang Goethe in Germany, among other services, provides its patients with highly accurate diagnostics and effective treatment of oncological diseases. The Clinic successfully operates one of the largest oncology centers in Europe, Rhein-Main, headed by Professor Mitrou. Go to page >>
The German clinic “Maria Hilf” considers the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of oncological diseases to be one of the priorities in its activities. The technical equipment of the clinic meets the highest standards; it has linear accelerators, gamma cameras, etc. Go to page >>
Nutrition for cancer
What should nutrition be like for cancer patients? What foods are absolutely contraindicated for this or that form of cancer?
Find out more >>
Herbal medicine in oncology
Herbal medicine can provide significant assistance not only in the treatment of cancer, but also in their prevention.
Find out more >>
Heredity and cancer
Many people who have cancer in themselves or in their relatives are interested in the question: is cancer inherited?
Find out more >>
Cancer during pregnancy
Treatment of cancer during pregnancy is quite difficult, because most medications are toxic.
Find out more >>
Pregnancy after cancer
What are the prospects for pregnancy after cancer? Should you wait until after cancer treatment?
Read more Delivery of goods without a contract, judicial practice
Find out more >>
Cancer Prevention
Prevention is an important part of the overall fight against cancer. How to reduce the likelihood of cancer?
Find out more >>
Palliative treatment of cancer
What is palliative cancer treatment? How can it affect the quality of life of a cancer patient and change it for the better?
Find out more >>
New cancer treatments
Scientists have developed quite a lot of promising methods for treating cancer, which have not yet been recognized by official medicine. But everything can change!
Find out more >>
Cancer statistics
Cancer incidence statistics, unfortunately, are disappointing: there is an increase in the number of cases, while the disease is getting younger.
Find out more >>
About “folk” medicine
Sometimes it is possible to defeat cancer using “folk” methods, but there are many more of those who relied only on them and ended up leaving this world ahead of time.
Find out more >>
How to fight cancer?
How to find strength to fight cancer? How not to fall into despair over possible disability? What can serve as hope and meaning in life?
Find out more >>
How to help your loved ones?
How can you help a loved one live with a cancer diagnosis? Is a “white lie” necessary? How to behave so that loved ones suffer less?
Find out more >>
Stress and cancer
There is an opinion that constant stressful situations can lead to the development of cancer. Is it so?
Find out more >>
Fighting cachexia
Many cancer patients often suffer from sudden weight loss. What causes this and is there any way to deal with this problem?
Find out more >>
Caring for bedridden patients
The rules for caring for patients who are forced to constantly remain in bed have their own characteristics and must be known.
Regular medical supervision and “healthy” behavior are now a way of life. And, above all, to prevent cancer from recurring.
New tumor growth is usually preceded by a period of remission. Its duration depends on how long the body takes to recover. Relapse of a malignant tumor can be early (the formation of a cancerous tumor occurs 2-4 months after the end of the main course of treatment) and late (secondary cancer is diagnosed 2-4 years later).
“It is very important that the operation to remove the tumor is performed professionally,” says oncologist Alexey Dikarev . – Cancer relapse may be associated with inadequate or poor-quality treatment, which provokes secondary manifestations of the disease.
Patients who are diagnosed with cancer at an early stage have the best hope for a complete cure. It is easier for doctors to take all measures to destroy “bad” cells when they are clearly localized and have not yet penetrated into other organs (have not metastasized).
The most difficult thing for oncologists to treat is patients with so-called advanced forms of cancer, where the tumor has begun to grow.
Grigory Roytberg, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, President of the Clinic of OJSC “Medicine”:
– At different stages of cancer, it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and the extent of the process. Therefore, it is very important that the patient undergoes timely examinations - modern medicine has high-tech diagnostic tools.
A multidisciplinary approach to treating patients ensures not only high-quality diagnostics and a properly selected course of procedures, but also post-clinical rehabilitation, social adaptation and assistance from a professional psychotherapist. The task of our specialists is to defeat the disease and fight for the quality of life of Russian cancer patients.
In older people, it has been observed that cancer relapses are more common.
Doctors note that it is very important that the first stage of treatment is performed professionally.
After a person defeats cancer, there is a high probability of going to extremes. In food, this is reflected in a radical change in diet. A lot of high-calorie food appears on the tables due to the need to gain weight. In the second option, the diet is replete with those foods that supposedly fight cancer. All this food is consumed uncontrollably and to the detriment of everything else.
However, a cancer patient needs to adhere to the same principles of proper nutrition as other people. Focus on vegetables and fruits, more foods containing fiber, less meat and more fish, limit animal fats, meat cooking, baking, and minimize salt intake.
You also need to maintain your weight. You should especially avoid being overweight and overweight. In addition, you should not get hung up on searching for specific products with supposed antitumor activity. Their effect is usually questionable, but excessive consumption can be problematic.
Regular and moderate physical activity helps strengthen the immune system and help avoid relapse of cancer.
– Numerous studies have proven that even the most weakened patient (not necessarily cancer), even the bedridden one, can benefit from regular physical activity and improve their prognosis and quality of life! While you have the strength to move, you must do it! – advises Dr. Alexander Myasnikov. – As for the overwhelming number of people who have undergone cancer treatment, the common postulate of all doctors applies to them: everyone should devote at least half an hour a day to some type of physical activity, five times a week!