The brain is one of the most mysterious structures in the human body. Thanks to him, a person breathes, walks, thinks. It is the brain that sends signals to all systems of the body so that they perform certain tasks.
The whole universe - this is how the human brain can be characterized. Billions of neurons forming up to several tens of thousands of connections - sometimes even specialists find it difficult to understand such a plexus. What can we say about ordinary people?
The country even has a special Brain Institute, which literally studies this organ far and wide from the point of view of both its physiology and capabilities. Naturally, against the backdrop of such a complex organization, many myths and speculations are born regarding the work of the organ.
Is 10% our limit?
Everyone knows the theory about the 10% of brain capabilities that people use. She was often voiced in cinema. According to it, a person fully works with only one tenth of all the capabilities that the brain can give him. One of the sources of this belief today is the work of the American scientist and psychologist William James and Boris Sidis . Back in the 1890s, they tested the theory of accelerated child development on who had the highest IQ in history. Dale Carnegie made a similar assumption .
Question answer
Why does the brain “erase” dreams?
There is another theory about why humanity could believe in this belief: it is believed that the idea of 10% was born on the basis of an incorrect interpretation of neurobiological research. The cerebral cortex is so complex that some lesions can be difficult to trace. And misunderstanding of functions could well become the basis of the “decimal theory”.
This theory has long had a refutation, which, however, did not turn out to be so loud that people remembered it. Neuroscientist Bariri Gordon called the theory "ridiculously wrong." He also noted that a person uses almost all parts of the brain and they are active almost constantly. Several facts debunk the 10% theory. First, proven scientific evidence indicates that evolution usually discards everything unnecessary. The brain is quite energy-intensive and requires a lot of oxygen and various nutrients. It can take up to 20% of energy. If 90% of this organ were not used by people and were essentially not needed by the body, the brain would become smaller in size. The theory about the degeneration of unused neurons and connections between them is also similar. If the organ were not used to its maximum, the cells would die en masse, which is not observed in healthy people.
The theory is also confirmed by instrumental techniques: MT and PET scanning. They allow you to see the work of the brain in real time. And it was with the help of such devices that it was proven that the brain is active even during sleep.
In addition, the fact that the brain has several sections, each of which is responsible for its own functions, does not favor the 10% theory. So far, brain researchers who have studied the organ in detail have not yet discovered any redundant or unused sections.
When it's short-circuited in the brain. Neurologist on the origin and treatment of phantom pain Read more
Indications and contraindications
The presence of a tumor is the only important indication for its elimination (in the absence of contraindications). Only removal of the tumor leads to a positive result, since drug therapy is only temporary. An important point is to determine how effective and safe the use of surgical treatment is. It all depends on the location of the tumor, its size, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient, such as general condition, age category and others. It is necessary to clearly predict the likelihood of successful surgery and the patient's life expectancy. Difficult-to-reach localization, bilateral location and other complications significantly increase the possible risk.
Brain surgery for tumors is actually the most common method of treatment, but the following contraindications should be taken into account:
- When a tumor is detected in a vital part of the brain.
- An elderly patient has a large tumor.
- Localization of pathological formation in an inaccessible place.
The final decision to perform the operation is made by the neurosurgeon, who takes into account the opinion of the oncologist, chemotherapy and a number of other specialists. They also determine the possibility of treating the tumor with non-surgical measures.
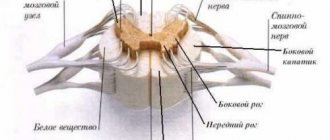
Hemispheres separately - how does it work?
There is a theory, and quite a tenacious one, according to which a person has either one hemisphere of his brain or the other. Moreover, people even often diagnose themselves as “right-hemisphere” or “left-hemisphere” based on the skills inherent in a particular individual. It is believed that creative people are precisely those who have a developed right hemisphere, which is also the working one. Left-handers are logicians.
Question answer
What is the left hemisphere of the brain responsible for?
However, scientists have already debunked this myth a long time ago. The results of a two-year study published in the journal Plos One showed that both hemispheres work equally and simultaneously. Neuroscientists at the University of Utah scanned the brains of 1,000 people of different ages - from 7 years to 29. At this moment, the subjects either lay quietly or read. Measurements were taken at this time on each side of the brain at 7,000 points at once. The results showed that it is true that brain connectivity may be more left-sided or right-sided, but there was no evidence that only one side was working. “The brain is not as clear-cut as the myth makes it out to be. For example, the right hemisphere is involved in processing some aspects of language, such as intonation and stress,” said Jeff Anderson, lead author of the study and a professor of neuroradiology at the University of Utah . This would be extremely ineffective if one half of the brain had to constantly be more active than the other, the scientist says.
What is the right hemisphere of the brain responsible for? More details
Neurologists have discovered how the human brain compensates for the absence of an entire hemisphere
In extremely severe cases of epilepsy, when debilitating attacks are repeated again and again, and all tried treatment options are ineffective, specialists resort to the last option to alleviate the patient’s condition and perform surgery.
In this procedure, called a hemispherectomy, the patient has one of the hemispheres of the brain removed. It is noteworthy that many who undergo such surgery are cured of seizures and retain basic motor, speech and cognitive skills.
To understand how the brain adapts to such extreme changes, neuroscientists at the California Institute of Technology studied six such rare cases.
The age of people without one hemisphere ranged from 20 to 30 years, and they underwent hemispherectomy at the age of three months to 11 years.
The research team performed functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) on the operated volunteers and two healthy controls.
With its help, neurologists assessed the participants' brain activity at rest. This means that the volunteers were not performing any specific task while in the machine's scanner, but were simply in a relaxed state.
The experts were interested in the functioning of neural networks in the parts of the brain that control vision, movement, emotion and cognition.
Let us briefly explain that it is thanks to such networks, that is, connections between cells and various areas of the brain, that a person has the ability to walk, talk and perform many other functions.
The scientists compared the data obtained not only with the results of the control group, but also with almost one and a half thousand other archival MRI images of a healthy brain.
The scans showed that the neural networks in people with a missing hemisphere were surprisingly intact. Moreover, in participants who underwent surgery in childhood, the number of contacts between certain brain regions was noticeably increased compared to the norm.
For example, regions of the brain that control walking function had more active and pronounced connections with areas responsible for speech.
“We found that despite the loss of an entire hemisphere of the brain, [the volunteers] retained all the same basic networks that we see in a healthy organ. The neural networks [of people with hemispherectomies] appear to cooperate more closely: although the networks themselves look completely normal, the level of interaction between them is increased in all six patients studied,” comments lead author of the scientific paper Dorit Kliemann in an institute press release .
Previously, experts from the California Institute of Technology had already established that people born without a corpus callosum (the “bridge” connecting the left and right hemispheres) eventually develop a normal bilateral brain organization.
Now scientists know that the main organ of the central nervous system is capable of developing neural networks even within one hemisphere and thus compensating for the absence of a large part of the brain.
In the future, neurologists intend to study in detail how hemispherectomy affects behavior. For example, what happens in the brain when performing a certain task or how various stimuli affect its work.
And this is a very important question. The fact is that usually a touch on one side of the body is registered and processed in the opposite side of the brain. However, in the absence of one of the hemispheres, a global reorganization of this process should occur, which still needs to be studied.
The researchers note that one of the most important goals of their work is to provide medical professionals with as much information as possible about the consequences of extensive brain surgery and the recovery process after them.
Data obtained from examining people with a high level of compensation after undergoing hemispherectomy will make it possible to improve this type of treatment and achieve an optimal result.
“The abilities of our patients are truly amazing. Yes, they have some difficulties, but their level of cognitive ability is surprisingly good considering half the brain is missing. How this is possible with only one hemisphere is an important question of plasticity [of the brain], its ability to restructure and compensate. And we have to study it in detail,” concludes Dorit Kliemann.
The results of the work of American neurologists are published in the public domain in the publication Cell Reports.
Let us add that earlier the authors of Vesti.Nauka (nauka.vesti.ru) talked about a method of influencing the deep structures of the brain without surgical intervention and about a brain implant that helps with severe forms of epilepsy.
To keep abreast of the most interesting scientific news, subscribe to our groups on social networks: , Facebook, Twitter, Odnoklassniki. We are also in Yandex.Zen.
Classic won't help?
For many years it was believed that you can raise a harmonious person if you play classical music for him from childhood. Various musical compositions written by Mozart , Bach, Chopin and other eminent masters were supposed to develop the brain. In reality, everything turned out to be wrong. Already in 1993, a study was conducted at the University of California at Irvine, which showed that listening to Mozart can improve spatial thinking in a person, but... exclusively and for no more than 15 minutes. Moreover, this result is also subject to doubt, since scientists have not been able to obtain a similar result in any other study or experiment.
Another study on this topic was structured like this: one group was given to listen to Mozart, the other was given to read Stephen King . And the results after reading the books were similar to the results after listening to the maestro. So the researchers concluded that a person’s spatial imagination improves when they are in a good mood, either caused by listening to music or reading a book.
Treatment of brain cancer
There are three main methods:
- Removal of the tumor.
- Chemotherapy.
- Radiation therapy.
Surgery for detected oncology is the main method of treatment if the tumor does not border on healthy tissue.
Chemotherapy is used in conjunction with surgery and is aimed at destroying abnormal fast-growing cells. There are different ways to take medications. The consequences of chemotherapy are very diverse (from hair loss to infertility).
Radiation therapy is used for both malignant and benign tumors. When the tumor is located in hard-to-reach places, when surgical intervention is impossible, this type of treatment is almost the only possible one. In some cases, radiation therapy is used as an addition to the main treatment.
It should be noted that most often for such diseases, brain surgery is chosen as a treatment; the tumor must be completely removed.
Expert commentary
Surgical treatment is not indicated for seizures that do not affect the quality of life, for generalized idiopathic epilepsy or benign epileptic syndromes, for severe concomitant pathology and severe mental disorders. In the case of symptomatic drug-resistant forms of epilepsy, surgical treatment eliminates seizures in 26-72% of patients. If there are indications for surgical treatment, then the sooner the operation is performed from the onset of epilepsy, the higher the effectiveness.
Cancers in newborns
Oncology in infants is usually associated with genetic factors or congenital diseases. In addition, negative impacts may come from the environment. During childbirth, a child may receive injury, which can also cause the development of cancer.
In 90% of cases, with timely diagnosis, pathologies are completely cured, so it is very important to immediately contact a specialist when the first symptoms appear. It is customary for doctors to examine a child at certain intervals.
Symptoms of a brain tumor in infants are less pronounced, they are expressed as follows:
- Loss of appetite, weight loss or slower weight gain.
- Moodiness.
- Increased fatigue.
- Periodic rises in body temperature.
For the common cold, the nature of the symptoms is very similar, which is why constant consultation with specialists is necessary. Even the appearance of some symptoms may be a sign that the child will need surgery to remove a brain tumor. Just like in adults, when cancer is detected in areas of the brain that are important for life, radiation therapy is used. A brain tumor is removed if it can be separated from unaffected brain tissue.
Rehabilitation after surgery
The patient needs to understand that surgical treatment can bring both positive and negative results. In both cases, the patient will undergo postoperative rehabilitation, but its specificity primarily depends on the results of the operation.
On this topic
Usually, during rehabilitation after surgery, doctors recommend that patients not stop taking antiepileptic drugs. In some clinics in Russia, doctors are of the opinion that medications should be present in the patient’s life for at least another three to five years, even after a successful surgical intervention. This will help the body suppress residual epileptic outbreaks that may occur even after treatment.
Seizures after surgery occur in the first six months. It is very difficult to judge the outcome of surgical intervention in the early stages, since seizures occur in all epileptics and they are not complications as such. However, at this time it is not entirely clear whether the operation was successful, or whether the person did not get rid of the disease.
After a considerable period of time (about a year), one can judge what results surgical treatment gave the patient. If a patient reduction in the number of attacks by one year, we can expect that in the future this positive trend will only continue, and he will be completely cured.