Naturally, every woman is familiar with those few days of unpleasant discomfort that cannot be avoided. For more than half of the female sex, menstrual days are manifested by pain in the lower abdomen, brittle joints, severe rashes on the face and décolleté, as well as strong and sudden mood swings. But, unfortunately, these are not all unpleasant symptoms; many women often suffer from severe headaches, which simply worsen during menstruation. What could be the reasons for such injustices? Why can a headache occur several days before such unpleasant and painful days, and also appear directly during menstruation? It is these questions that we will try to find answers to in this article. A woman’s body is a kind of holy place that gives life to a new generation. After all, only the beautiful female sex gives new life, and this opportunity appears precisely from the moment of menstruation. Since hormonal changes occur in the body (during each menstruation), in the female sex an egg is released into the uterus and if conception does not occur during this period, then the process of cleansing the uterus and preparing for the release of the next egg occurs. Of course, for many women these days are accompanied by such unpleasant and painful sensations, which are sometimes very difficult to cope with.
Headache before menstruation
Headaches during menstruation can be considered as a component of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which affects almost half of all women.
This condition is characterized by the appearance of unpleasant symptoms a few days before the onset of menstruation. They disappear with the arrival of periods.
At the moment, it is not accepted in medicine to consider PMS as a result of hormonal imbalance.
On the contrary, it has been proven that premenstrual syndrome is observed in women with a regular cycle, in which all phases are clearly visible, while in patients with disorders (anovulation, amenorrhea, long delays) no changes occur.
Interesting! During pregnancy, when the concentrations of progesterone and estrogen are constantly high and stable, such signs are not observed!
In addition to behavioral abnormalities, increased appetite, fluid retention, autonomic reactions, abdominal pain, cephalgia (headache) comes to the fore in some women.
It is usually bilateral, localized in the frontoparietal region, and sometimes resembles a “helmet”. Patients describe it as a feeling of pressure, heaviness; They, as a rule, do not feel sick or vomit.
Possible complications and consequences
Menstrual migraine itself can lead to severe maladjustment in patients, causing long-term disability, physical or emotional exhaustion.
Most of the risks and possible complications of migraine are associated with taking medications, in particular hormonal therapy.
There are multiple studies examining the relationship between migraine and stroke. Taking oral combined contraceptives in the presence of migraine can greatly increase the risk of developing ischemic stroke and cardiovascular pathology, but in fact, this is more typical for the form of migraine with “aura”.
If you have a headache after menstruation, you need to pay attention to some of the possible ailments that accompany this symptom.
The main causes of the syndrome are considered:
- Intestinal problems. Weakened peristalsis leads to the fact that waste products, which are released into the gastrointestinal tract during blood loss, do not leave the body. As a result, additional stress on the body occurs. Unpleasant sensations occur in the abdomen, against which other symptoms of mild poisoning appear.
- Taking oral contraceptives. With their constant use, a very sharp drop in the level of hormones in the blood occurs.
Some blood diseases also become active after menstruation. This is due to the fact that a woman loses a very significant amount of various substances necessary for functioning during PMS.
Menstrual migraine
Menstrual migraine is a special type of headache that occurs during menstruation against the background of a sharp decrease in the level of sex hormones (estradiol and progesterone). It is observed in half of women suffering from migraines.
According to the international classification, there are 2 forms of menstrual migraine:
- 1 True menstrual migraine (10-20%). It is characterized by the occurrence of attacks a couple of days before and in the first 3 days of menstruation in at least two out of three cycles. On other days of the cycle, pain does not occur.
- 2Migraine without aura associated with menstruation. It differs from the first form only in that attacks occur on other days of the cycle.
The main causes of such pain are a sharp drop in the level of sex hormones and an increase in the concentration of prostaglandins in the bloodstream before menstruation and in the first 2-3 days after their onset.
Interesting! It has been experimentally proven that the introduction of estrogen into a woman’s body immediately before menstruation delays the time of the next attack!
What changes occur in the body during menstruation?
Every month, the female body prepares for the possibility of conception. Every month, the endometrium grows, and then peels off again. Menstruation does not provide therapeutic differentiation, is not a cleansing action in the body system and is not able to remove harmful particles from it, as many people think.
Almost at the end of the cycle, the mucous membrane covering the surface of the uterus from the inside is ready to attach a fertilized cell - a zygote. If fertilization does not occur, the level of estrogen in the blood decreases sharply, and a whole chain of changes occurs. The mucous membrane disintegrates and peels off, as a result of which it is released with blood.
These manifestations do not occur immediately throughout the entire mucous membrane of the organ, but gradually. The leaking blood is a consequence of fragmentary bleeding that continues for some time until particles of cells from the uterine mucosa are completely rejected over the entire surface.
The intensity of bleeding varies from woman to woman.
For every woman, the length of menstruation, as well as the abundance of blood coming out, are not the same. And the cyclical environment can change. The duration and abundance of menstruation are closely related to the density of the mucous membrane. The average, normal course of the menstrual cycle is three to five days.
But it is not an anomaly when menstruation lasts longer - up to eight days or less - up to two days. The duration may increase due to the use of an intrauterine device, and the days may be shortened due to the use of birth control pills.
Difference from other headaches
This is a special pain, it has specific signs. We can talk about migraine if a woman has at least 5 attacks of this nature:
- 1The pain is one-sided.
- 2 Its character is pulsating, localization is often in the frontal, temporo-suciliary and parietal regions.
- 3The intensity can vary: from moderate to unbearable, and the duration of 1 attack is from 4 to 72 hours.
- 4 Associated symptoms: nausea, sensitivity to bright light, sound, stuffiness, smells, vomiting that does not bring relief, dizziness, various visual disturbances (flickering “flies”, flickering spots before the eyes).
- 5The headache gets worse with any physical activity, for example, walking up the stairs significantly increases the discomfort.
To make a diagnosis, at least two of these signs and a history of at least 5 seizures are required.
Menstrual migraine differs from ordinary migraine in its more severe course and high resistance to therapy.
Diet therapy
In addition to the fact that menstrual migraine may begin during critical days, the patient’s appetite also increases greatly. And this can result in excess weight gain. Therefore, switching to a healthy diet will help you avoid both. Let's consider the basic recommendations for menstrual migraines:
- You will need to give up too spicy, salty, sweet and fatty foods.
- The diet must include natural foods rich in vitamins and microelements. For example, seasonal plant foods, dairy products, lean meats, legumes, berries, grains.
- The drinking regime should be quite plentiful, at least two liters of clean still water per day.
- It is better to avoid strong tea and coffee.
- You should completely avoid alcohol-containing drinks.
- Overeating will make the pain worse. It is better to let the meals be small, but there will be five or six of them.
- It is better not to eat two hours before going to bed.
You need to remember, so that menstrual migraine does not bother you, similar nutritional principles will need to be followed on an ongoing basis.
Provoking factors
A number of factors increase the risk of seizures:
- 1 Taking oral contraceptives (COCs) . The content of estradiol in them gradually decreases, by the end of the cycle it is minimal in one tablet. On the one hand, this provokes the onset of uterine bleeding, and on the other, it causes menstrual migraine. The way out of this situation is to select another drug.
- 2 A state of emotional tension , stress, prolonged experiences, depression and other neurosis-like conditions can increase existing discomfort during menstruation and contribute to the appearance of pain.
- 3 Nutrition . As you know, some foods are triggers. These include chocolate, coffee, hard cheese, red wine, nuts, red meat. Taking them in large quantities before and during menstruation can negatively affect a woman’s well-being.
- 4 Existing vascular disorders during menstruation can provoke headaches due to changes in the tone of the arteries and veins, as well as fluid retention.
- 5 Chronic anemia . A low level of hemoglobin cannot fully supply the brain neurons with oxygen, which leads to brain hypoxia.
- 6 Meteor dependence . This phenomenon has been poorly studied, but some women experience headaches during rain, snowfall, or sudden changes in weather.
Anemia
Normally, the body loses about fifty milliliters of blood during menstruation, but heavy and prolonged periods lead to more significant blood loss, which causes anemia. At this time, the level of hemoglobin, which is involved in oxygen transport, drops. Brain cells receive insufficient oxygen, as a result cellular respiration is disrupted, hypoxia of brain structures develops, and cephalalgia appears. Fair-skinned women with red hair are more susceptible to developing anemia.
Menorrhagia can cause anemia
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is based on complaints and the typical picture of the disease. If the attacks meet the criteria described above, then additional diagnostic methods are not used.
Every woman is recommended to keep a diary where all headache attacks, accompanying symptoms, and connections with the cycle are recorded. This is necessary to select adequate therapy and control it. It is convenient to keep a diary in applications - women's calendars.
In case of intolerable attacks, their frequency, or the appearance of danger signals, an additional examination is carried out, including:
- 1Consultation with a neurologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, therapist.
- 2 Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs, neck vessels and their Dopplerography.
- 3MRI, CT scan of the skull and brain, angiography of cerebral vessels.
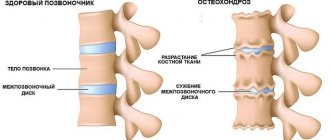
Osteochondrosis
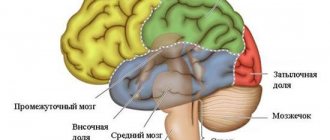
Cervical osteochondrosis is the cause of frequent headaches during menstruation. With osteochondrosis, changes occur in the vertebrae: salt shoots (osteophytes) appear. They compress blood vessels (carrying blood to the brain) and nerve fibers (connecting the brain center with other organs). Between menstruation (which is physiological stress), the body adapts, pain is not felt. On critical days, the adaptive reaction is not enough. The brain and other organs require increased amounts of oxygen. And a compressed vessel is not able to ensure its supply. A headache appears.
Lack of oxygen causes dizziness and loss of consciousness. Dizziness during menstruation is less common, but is also a consequence of an exacerbation of an existing disease.
Menstrual headaches associated with osteochondrosis can be treated with a massage of the neck and shoulder area and exercises for the cervical spine.
Danger signals
The following signs should alert both the attending doctor and the woman herself, as they may be a manifestation of other life-threatening situations:
- 1 Thunderous, severe pain (usually sudden) occurs with hemorrhagic stroke, rupture of a cerebral artery aneurysm.
- 2 Pain that first appeared after age 50 , during pregnancy or after childbirth, as well as pain that has changed recently.
- 3 Progressive deterioration and intensification of attacks (metastases to the brain, growth of tumors).
- 4 The appearance of pain in women who previously had cancer.
- 5 Focal symptoms (paresis, paralysis, sensory disturbances), weakness, changes in consciousness, atypical aura, combination with prolonged fever.
- 6 Lack of effect from the treatment.
Any of these symptoms should be a reason for urgent additional examination of the woman.
Main signs of the syndrome
Often, cramps appear before menstrual periods or during PMS. Sometimes they are observed after menstrual bleeding. Discomfort before “natural” discharge makes itself felt by the following symptoms:
- Prolonged pulsating spasms.
- Painful perception of sharp sounds, bright lights, smells.
- Changeable mood.
- Lack of appetite.
- Localization of spasms at one point.
- Feeling pain in the eye sockets, lack of clarity of vision.
- Sudden surges in pressure.
- Painful sensations in the heart, arrhythmia.
- Weakness, insomnia, vomiting and feeling of nausea and increased sweating.
There may be discomfort in the lumbar region and back. Headaches and cramps during menstruation, which are sometimes difficult to identify, may be accompanied by bloating or cramps. On critical days, the condition improves.
How to treat?
Therapy for headaches during menstruation is based on three basic principles:
- 1Behavioral therapy, that is, lifestyle changes.
- 2 Direct elimination of the resulting attack of pain.
- 3Prevention of subsequent attacks (relevant for migraines).
7.1. Behavioral therapy
The doctor explains to the woman the cause of the headache and talks about the triggers. In the future, the patient can control her lifestyle, nutrition, work and rest schedule, and make notes in her diary.
It is necessary to give up bad habits and take large amounts of painkillers, which only aggravate the situation and lead to chronic pain.
7.2. Drugs
To reduce the intensity and duration of pain, you can drink one of the NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): Aspirin, Paracetamol, Nimesulide, Movalis, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac.
It is not recommended to take combination drugs containing caffeine, codeine, or barbiturates. Taking analgesics too often leads to more frequent attacks, this is called overuse pain.
For vomiting and nausea, you can use metoclopramide (Cerucal).
In case of a severe migraine attack, the doctor will prescribe triptans: sumatriptan (Amigrenin, Imigran), eletriptan (Relpax), naratriptan (Naramig), etc. The drugs are prescription drugs, so you cannot do without consulting a doctor.
Triptans are most effective when used at the very beginning of an attack. If they are insufficiently effective, they can be combined with NSAIDs.
Important! Triptans should not be used more than 9 days in one month; there should be a break of at least 2 hours between taking two doses. They are used only to relieve a migraine attack and are ineffective for other headaches!
7.3. Seizure prevention
Preventative treatment is usually used only for migraines. For the purpose of prevention, different groups of drugs are used. This is due to the fact that the causes and pathogenesis of the disease are not fully understood.
The doctor may prescribe:
- 1Beta blockers (metoprolol, propranolol, bisoprolol).
- 2 Anticonvulsants (valproate, topiramate).
- 3Antidepressants (amitriptyline, venlafaxine).
- 4Calcium channel blockers (verapamil), etc.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that both a gynecologist and a neurologist (if necessary, an endocrinologist) should treat headaches associated with menstruation.
It is necessary to take into account the intensity, duration and nature of pain, monitor dynamics and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.
When should you see a doctor?
You should consult a doctor if headaches interfere with your usual life activities.
If headaches interfere with daily life tasks, women should consult a doctor.
When PMS is the cause of your headache, a variety of medications can help, including hormonal birth control pills, antidepressants, and calcium supplements.
The choice of treatment for headaches depends in part on their specificity and severity.
Your doctor may recommend measures to prevent migraine headaches. In addition, he may prescribe stronger pain medications if he sees the need.
Constant headaches may indicate preeclampsia. If a woman suspects she has this problem, she should seek medical support from a doctor.