Many people have heard about epilepsy, but not everyone understands what kind of disease it is, why it occurs and how it progresses. In most cases, we imagine an epileptic attack when a person convulses and foam comes out of his mouth. However, such phenomena are only a small part of the possible options for the development of the disease, because there are many manifestations of such a pathological condition. Many patients can live without seizures at all, as long as they take their epilepsy medication promptly and undergo regular testing.
This disease has been known for a long time. Epilepsy is perhaps one of the oldest forms of brain diseases, which was recognized and tried to be treated with traditional methods hundreds of years ago. For a long time, people suffering from this pathology preferred to hide their diagnosis. This often happens today.
Ketogenic diet in adults: menu
The ketogenic diet is used to relieve the functionality of the brain.
The method is an alternative means of using anticonvulsants. The rational nutrition menu is aimed at restoring acidosis and ketosis. The condition eliminates hyperexcitability of the cerebral cortex. The ketogenic diet menu in adults brings a positive therapeutic effect for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
The mechanism of the therapeutic effect of the ketogenic diet remains unclear, but when treating children aged 2-5 years, dietary therapy is an excellent alternative to toxic anticonvulsant pills.
Features of the diet include a large amount of fat, so the menu is not recommended for people with severe obesity. The ketogenic diet is not prescribed for renal or liver failure, chronic diseases of parenchymal organs.
Diet therapy is not used for patients with atherosclerosis and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Ketogenic diet plan:
- A large amount of fiber (cereals, bran);
- Take food no later than 3 hours before bedtime;
- Fluid restriction;
- Fats – no restrictions.
Sample menu for a ketogenic diet in adults:
- Salad with cottage cheese and carrots;
- Borscht with meatballs;
- Big orange;
- Fish fillet with lemon;
- Kissel with breadcrumbs;
- Vermicelli soup with meat;
- Chicken roll with egg;
- Fruit salad with yogurt;
- Tea with crackers and milk;
- Stuffed cabbage rolls;
- A cheese sandwich.
The ketogenic diet for children contains a similar menu, but is prescribed without any special restrictions, since atherosclerosis does not occur in children, and acquired heart defects are quite rare.
Clonazepam
The drug is a derivative of the hypnotic-sedative benzodiazepine and has anxiolytic, sedative and anticonvulsant properties. The product promotes muscle relaxation and normalizes sleep. Prescribed for neuralgia, which is accompanied by myoclonic attacks and increased muscle tone.
Clonazepam treatment begins with small doses - 1.5 mg per day, dividing the tablets into 3 doses. Every 3 days the rate is increased to achieve the maximum effect of therapy. The average daily dose is 6 mg, but it can be changed at the discretion of the attending physician.
Anticonvulsants for neuralgia such as Clonazepam have some contraindications, so their use must be agreed with a specialist. Analogs of this drug: Klonopin, Ravatril, Antelepsin, Iktoril and others.
Practical experience of consumers
What is the situation with anticonvulsant therapy in practice? This can be judged by the reviews of patients and doctors.
I take Carbamazepine as a replacement for Finlepsin, since the foreign analogue is more expensive, and the domestically produced drug is excellent for therapy for my illness.
Since I tried both drugs, I can say that both are highly effective, however, the significant difference in cost is a significant disadvantage of a foreign product.
After several years of taking Finlepsin, on the advice of a doctor, I changed it to Retard, since the specialist believes that this drug is more suitable for me. I had no complaints while taking Finlepsin, but Retard, in addition to a similar effect, has a sedative effect.
In addition, the drug is characterized by greater ease of use, since in comparison with analogues it must be taken not three times a day, but once.
The drug Voltaren helps with pain syndromes of moderate severity. It is a good idea to use it as an addition to the main treatment.
Carbamazepine
The drug is an anticonvulsant, a representative of the iminostilbenes group. Carbamazepine has a pronounced anticonvulsant and moderate antidepressant effect on the patient’s body, and also helps improve mood. The use of Carbamazepine for neuralgia helps to significantly reduce painful manifestations, due to the analgesic properties of this drug.
The drug is prescribed to patients 0.1 g 2 times a day, but the dose is gradually increased, adding 0.1 g every day to the initial norm. The optimal daily dosage for patients with neuralgia is 0.3 mg, but if necessary it can be increased to 0.6 g. The effect of taking the tablets occurs mainly after 1–3 days, but despite the rapid decrease in the severity of symptoms, a course of therapy with Carbamazepine long term is prescribed. The duration of treatment with an antiepileptic drug is due to the fact that after premature cessation of its use, pain may resume.
Analogs of Carbamazepine are: Tegretol, Stazepin, Amizepine, Neurotol, Zeptol, Finlepsin and others.
Anticonvulsants: list of the best for epilepsy and seizures
Anticonvulsant drugs are used as a means to eliminate pain symptoms and muscle spasms, preventing the transition from a state of pain attacks to convulsive and epileptic manifestations.
The activation of a nerve impulse simultaneously by a group of specific neurons is similar to the signal produced by motor neurons in the cerebral cortex. When this type of lesion occurs, the nerve endings do not manifest themselves in tics or convulsions, but cause attacks of pain.
The purpose of using anticonvulsants is to relieve pain or muscle spasms without causing central nervous system depression. Depending on the severity of the disease, these drugs can be used from several years to lifelong use in severe chronic or genetic forms of the disease.
Attacks of convulsive activity are associated with an increase in the degree of excitation of nerve endings in the brain, usually localized in certain areas of its structure and diagnosed upon the onset of a condition characteristic of the onset of a convulsive syndrome.
The cause of cramps may be a deficiency in the body of necessary chemical elements, such as magnesium or potassium, pinching of a muscle nerve in the canal, or sudden prolonged exposure to cold. A deficiency of potassium, calcium or magnesium provokes disruptions in the transmission of signals to the muscles from the brain, as evidenced by the occurrence of spasms.
In the initial stage, the manifestation of the development of a neurological type of disease consists of local pain sensations emanating from the area of the affected nerve cells and manifested by attacks of pain of varying strength and nature of manifestation. As the disease progresses, due to the development of inflammatory processes or muscle spasms in the area of pinched nerve endings, the severity of the attacks increases.
In case of early contact with a specialist, a complex of medications is used for therapy that eliminates the causes and signs of damage to nerve endings. Self-diagnosis and treatment do not allow you to choose from a wide range of anticonvulsants the most suitable one for relieving pain symptoms and eliminating the cause of discomfort.
Most of the drugs used in the treatment of seizures have combined effects and have many contraindications, based on which, unauthorized prescription and use of these drugs can pose a danger to the patient’s health.
When observed by a specialist, he evaluates the performance of the prescribed drug based on its effectiveness and diagnoses the absence of pathological changes after taking it based on the results of blood tests.
Anticonvulsants used in complex therapy for neuralgia
Quite often, the cause of localized pain is a disease such as neuralgia. This common pathology affects the nerve endings, resulting in pain. Unpleasant sensations appear suddenly, in the form of attacks, and can be mild in the first stages of the pathology. But as the disease progresses, the pain intensifies and becomes more intense, causing serious concern to patients.
Treatment of neuralgia should be carried out as early as possible, by consulting a doctor when the first symptoms of the disease are detected. Therapy for this disease is based on the use of a complex of medications designed to eliminate the main symptoms and eliminate the main causes of nerve damage.
Anticonvulsants for neuralgia occupy one of the leading positions in its treatment. Taking anticonvulsants is necessary to prevent possible attacks of epilepsy, which often result from neuralgic attacks and seriously complicate the condition. Commonly used anticonvulsants include:
Antiepileptic drugs are presented in a large assortment, so in each individual case the specialist individually selects an effective remedy to suppress attacks of neuralgia.
General principles of therapy
The basis of therapy for the pathological process under consideration is the solution of several issues:
- Eliminate symptoms. The clinical picture against the background of a neurological disorder is painful and severe, which leads to avoidant behavior and the formation of phobias. The attacks themselves develop suddenly, sometimes at a dangerous moment. There is a risk of non-life-threatening injury. The first task is to eliminate symptoms, if any.
- The second goal is to prevent relapses. Seizure episodes are eliminated through the use of the same drugs, but in larger dosages or the use of second-line drugs, additional medications. The issue is resolved at the discretion of the treating specialist.
- The third problem to be solved is eliminating the root cause of the neurological disorder. It makes sense to undergo a full diagnosis. There are many treatment options; conservative correction does not always make sense.
In most cases, tablets alone are not enough. This is a key way of curation. However, psychotherapy may be required to eliminate anxiety and the phobic component (which, by the way, can provoke relapses and repeated more severe seizures). All assigned tasks are solved simultaneously; therapy may take more than one year. In most cases, patients are forced to take pharmaceuticals for life.
Basic drugs for the treatment of epilepsy
There are such concepts as a list of first- and second-line drugs for epilepsy.
The first-line drug for epilepsy is prescribed as monotherapy, while its therapeutic effect and side effects are monitored.
If treatment with one drug is unsuccessful, then additional drugs for epilepsy are prescribed (second-line drugs). Moreover, the list of first- and second-line epilepsy pills depends on the type and form of seizures.
The list of pills for epilepsy can be divided into the first and second row according to their effectiveness.
First line drugs:
- Carbamazepine and its analogs. Used for severe seizures accompanied by psychomotor impairment. Effectiveness for minor forms of the disease has not been proven. The drug is also effective for depression;
- A new generation drug for epilepsy, benzobarbital, is an analogue of phenobarbital and has less hypnotic and sedative effects when used in patients. In combination with other drugs, it is used for the treatment of non-convulsive and polymorphic seizures;
- Valproic acid is widely used in adults and children for various types of disease. The drug is effective against generalized seizures (minor and major) and focal motor seizures. For minor forms of the disease, they are limited only to the administration of valproic acid;
- Ethosuximide is the latest generation epilepsy drug, has minimal toxic effects and is widely used for the treatment of epilepsy throughout the world. Used to treat minor forms of the disease;
- Phenytoin is used in the treatment of generalized tonic-clonic and complex focal seizures. The drug also has a pronounced analgesic effect.
The above remedies are used primarily to prescribe treatment for epilepsy. If a significant side effect develops or there is no therapeutic effect, the attending physician selects a second-line drug. These medications for epilepsy are prescribed gradually under the supervision of a doctor, due to their mild effect or the presence of a significant side effect.
The most common drugs are:
- Phenobarbital has a pronounced anticonvulsant effect. The drug is limited in use due to significant side effects: depression of the central nervous system, mental retardation in children, carcinogenic effects.
- Carbamazepine drugs (carboxamide) can cause severe forms of anemia;
- Tiagabine blocks GABA reuptake and is used to treat treatment-resistant focal seizures. However, monotherapy with tiagabine is ineffective. Positive results can be achieved when complex treatment is prescribed;
- Lamotrigine is used to treat focal seizures. Side effects are associated with the presence of allergic reactions, depression of the central nervous system;
- Topiramate is a fructose derivative. It has limited use, especially in children, as it can cause delayed psychomotor development, personality disorders, and hallucinations;
- Therapy with clonazepam can cause persistent addiction, especially in people who have previously abused alcohol, so this drug is not included in their list of prescriptions;
- Gabapentin has limited use due to the risk of status epilepticus if the drug is abruptly discontinued;
- Nitrozepam has a pronounced inhibitory effect on the central nervous system;
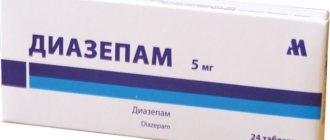
- Diazepam has a pronounced teratogenic effect.
Second-line drugs are prescribed with caution, usually under inpatient observation. The attending physician notes the presence of side effects and the severity of the therapeutic effect
It is worth noting that many medicines are used in modern medicine. The choice of one drug or another depends on the type and form of epileptic seizures. A patient suffering from epilepsy, as well as his family and friends, must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and know the name of the epilepsy pills and their dose. The effectiveness of treatment is achieved through the correct use of all medications.
Examinations and treatment
If epilepsy is suspected, the patient is thoroughly examined. First of all, the patient is examined by a neurologist and studies the history of the disease, including family history. The patient is prescribed the following tests:
- blood;
- fundus;
- X-ray of the skull;
- Dopplerographic study of cerebral arteries.
It is mandatory to visualize the structure, functions and biochemical characteristics of the brain using X-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Hours of electroencephalography (EEG) are of great importance in diagnosing the disease.
Such laboratory studies are aimed at determining the true causes of the disease and excluding pathologies that can cause seizures, but are not associated with brain diseases.
The main effect on epilepsy is medications. The result of medical care in the treatment of pathology depends both on the correct selection of medications and on the patient’s compliance with all doctor’s recommendations. The principle of medical intervention is an individual approach to each patient, continuity and duration of treatment. Antiepileptic therapy will be effective if:
- early onset of exposure to the manifestation of characteristic symptoms with antiepileptic drugs;
- desire for monotherapy;
- the correct choice of medication for epilepsy, depending on the type of attacks of a particular patient;
- if necessary, introduction of a rational combination of polytherapy (if there is no effect from the use of one drug);
- prescribing appropriate medications in dosages that provide complete therapy;
- taking into account the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of prescribed drugs;
- monitoring the presence of antiepileptic drugs in the patient’s body.
Epilepsy medications cannot be stopped at once. They should be taken until complete relief from pathological manifestations is obtained. Only in cases of individual intolerance to the components of the drug, allergies, or in the event of side effects, gradual withdrawal of the drug is necessary. Doses of drugs for the treatment of epilepsy are gradually reduced. If the doctor decides that the therapy does not bring the desired result, then new medications are also gradually introduced.
It has been proven that almost all patients newly diagnosed with epilepsy can completely control the occurrence of seizures with the help of antiepileptic drugs. After 2-5 years of full treatment, most patients can stop treatment without the risk of relapse.
Drugs of choice
The most effective and popular anticonvulsants include:
Phenobarbital is the reference drug of the group. It has a great effect on the central nervous system, but can cause shortness of breath and increased blood pressure. Not compatible with alcohol. Contraindicated for pregnant women. Finlepsin - blocks sodium channels, demonstrates the properties of an analgesic, antidepressant, relieves seizures when the trigeminal and glossopharyngeal nerves are damaged. Pregabalin is a tranquilizer, eliminates the feeling of fear, calms, the drug is used as a background or in combination with other drugs against seizures. Clonazepam – stops myoclonic, involuntary spasms by relaxing the muscles. Provokes discomfort when moving, apathy. The tablets are not compatible with alcohol. Contraindicated during pregnancy, lactation, and renal failure. Phenytoin - a drug indicated for epilepsy, is able to inhibit the excitability of nerve receptors, stabilizing cell membranes, can provoke vertigo and nystagmus, but always exhibits anticonvulsant properties. Primidone – relieves psychomotor seizures. The tablets locally relieve spasms in the affected area. Beclamid - indicated for generalized convulsive attacks, relieves spasticity. The drug is allergic. Carbamazepine is effective for prolonged attacks of seizures, improves the mood of patients because it calms the central nervous system, but at the same time causes drowsiness. The tablets are not prescribed to pregnant women. Lamotrigine - the medicine stabilizes brain neurons, prolongs remission between epileptic attacks until they stop completely
Reduces concentration and attention. Can cause excitement, therefore it is not used in the elderly and children
Contraindicated in case of impaired liver or kidney function. Valparin is a drug that relieves muscle spasms in epilepsy. Voltaren is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that can relieve seizures resulting from neurological disorders in the spine. Ketonal is an anesthetic tablet that relieves convulsive syndrome caused by pain of different localization. Benzobamil is minimally toxic, so the drug is used even in children; it gently soothes the central nervous system. Causes nystagmus and is contraindicated in pregnant women. Sodium valproate is useful for severe seizures. The drug blocks the generation of electrical impulses in the brain, exhibiting an anticonvulsant effect, and is not recommended for pregnant women, patients with endocrine pathologies, or impaired liver function. Keppra is a modern medicine for epilepsy. Xanax is a psychotropic, relieves leg cramps, fear, and has a hypnotic effect. Actinerval is an antidepressant, eliminates anxiety and convulsions.
Allowed list
When it becomes necessary to use antimicrobial tablets or injections, it is important to tell your doctor about concomitant diseases. He must know everything about the frequency of attacks, the time and duration of the last attack
He must know everything about the frequency of attacks, the time and duration of the last attack.
Based on the survey, examination and test results, he can recommend a specific drug.
Allowed:
- lincosamides (Lincomycin, Clindamycin);
- macrolides (Erythromycin, Linkosamine, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, Josamycin, etc.);
- nitroimidazoles (Metronidazole, Ornidazole).
As for others, the decision to prescribe should be made by the doctor. If you have the slightest doubt about the correctness of the recommendations, you should consult several specialists.
Epilepsy medications negatively impact mental health
An international team of experts led by Dr Patrick Kwan from the University of Melbourne has completed a study into the effects of epilepsy drugs on the human brain. Scientists have been able to establish that antiepileptic drugs cause mental disorders in some patients. The results of the study were published on August 8 on the website of the University of Oxford.
Epilepsy is quite widespread among the population, and it affects not only people, but also dogs, cats and mice. Symptomatically, the disease manifests itself in the form of sudden attacks of convulsions, which can lead to death due to hypoxia, acidosis, cerebral edema and many other different causes. In a new study, scientists have found that drugs that block seizures can cause mental disorders in a certain group of people. This indicates the need to create a new anticonvulsant.
Scientists found a relationship between drugs and mental damage by analyzing 2,630 patients with epilepsy. Among them, 3.7% had mental disorders, and in some of these patients - about 14 people - mental illnesses were caused by the use of antiepileptic drugs. At risk were women with temporal lobe epilepsy, which is characterized by attacks with loss of consciousness, which can lead to memory impairment. After completing the data analysis, the researchers concluded that one in seven people with epilepsy and a mental disorder acquired a second condition due to medication alone.
The percentage of people affected by antiepileptic drugs may seem small at first glance, but given the scale of the disease, which affects tens of thousands of people around the world, the need to develop alternative drugs against seizures becomes obvious. However, the researchers have not yet announced their future plans for scientific research.
List of drugs without prescriptions
Unfortunately or fortunately, the composition of these medications is such that they are prohibited from being sold without a doctor’s prescription on the territory of the Russian Federation.
If a pharmacist offers you to buy any anticonvulsant, saying that a prescription is not needed, know that this is illegal and he does it only at his own peril and risk!
The easiest way today to get drugs without a prescription is to order via the Internet. Formally, the courier, of course, will be obliged to ask you for a recipe, but most likely this will not happen.
List of drugs for children
Substances that can significantly reduce the excitability of the central nervous system are used as anticonvulsants for children. Unfortunately, many drugs of this type have a depressant effect on breathing and can be dangerous for the baby.
According to the level of danger, drugs are divided into two groups:
- The first includes: benzodiazepines, lidocaine, droperidol with fentanyl and sodium hydroxybutyrate. These drugs have little effect on breathing.
- The second group includes: chloral hydrate, barbiturates, magnesium sulfate. Substances more dangerous to breathe. They have a strong depressant effect.
The main drugs used in the treatment of seizures in children:
- Benzodiazepines. The most commonly used drug from this series is sibazon, also known as seduxen or diazepam. An injection into a vein can stop seizures within five minutes. In large quantities, respiratory depression is still possible. In such cases, it is necessary to inject physostigmine intramuscularly; it can eliminate the nervous system and facilitate breathing.
- Feitanil and droperidol. These drugs effectively act on the hippocampus (the area that triggers seizures), but due to the presence of morphine, babies under one year of age may have problems with breathing. The problem is eliminated with the help of nalorphine.
- Lidocaine. Almost instantly suppresses seizures of any origin in children when administered into a vein. During treatment, a saturating dose is usually administered first, after which they move on to droppers.
- Hexenal. It is a strong anticonvulsant, but has a depressant effect on the respiratory tract, and therefore its use in children is somewhat limited.
- Phenobarbital. Used for treatment and prevention. It is prescribed mainly for mild attacks, since the effect develops quite slowly from four to six hours. The main value of the drug is its duration of action. In young children, the effect can last up to two days. Parallel administration of phenobarbital and sibazon gives excellent results.
List of drugs for epilepsy
Not all anticonvulsants are necessarily used to treat epilepsy. About thirty medications are used in Russia to combat this disease.
Here are just a few of them:
- Carbamazepine;
- Valproate;
- Pregabalin;
- Ethosuximide;
- Topiramate;
- Phenobarbital;
- Oxcarbazepine;
- Phenytoin;
- Lamotrigine;
- Levetiracetam.
At the end of the article I would like to warn you. Anticonvulsants are quite serious drugs with special properties and consequences for the human body. Their thoughtless use can lead to very sad consequences. Such remedies can only be used after consulting with your doctor.
Do not self-medicate, this is not the case. Be healthy!
List
There are a large number of anticonvulsant medications used for epilepsy. These include the following:
- Phenobarbital (Luminal) has been used as an anticonvulsant for epilepsy since 1911. Can be used for all types of seizures other than absences. The dosage is 0.2-0.6 g/day.
It is worth noting that now this medication is not so popular due to the large number of adverse reactions. Among them, insomnia, rash, the occurrence of involuntary movements, decreased blood pressure and cognitive functions, toxic effects on the liver, aggression, and depression are possible.Contraindications include alcohol and drug addiction, myasthenia gravis, serious liver and kidney diseases, diabetes mellitus, severe anemia, pregnancy, and obstructive pulmonary diseases.
- Depakaine. Available in different dosage forms. There are also a large number of other drugs with the same active substance: Valproic acid, Calcium and sodium valproate, Convulex and others.
The drug is a first-line drug and is used to treat almost any seizure, both generalized and partial.The advantage of the medication is that it does not have a negative effect on any attacks, that is, even if it is not effective, it will not lead to an increase in their frequency.
The dosage is 15-20 mg/kg/day. When taken, there may be a negative effect on the liver, weight gain, bleeding disorders, nausea, vomiting, digestive disorders, and drowsiness. The drug should not be prescribed to children under 6 years of age.
Carbamazepine. Treatment of secondary generalized and partial seizures often begins with this remedy. It is not prescribed for myoclonic attacks and absence seizures. The dosage is 10-20 mg/kg, although it may increase.
In addition to the anticonvulsant effect, it also has an antipsychotic effect, which makes it especially useful for patients with concomitant mental disorders. Allowed for children over one year old.
Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal). second generation drug Carbamazepine, which is also used for generalized and partial seizures. The treatment regimen is also similar.
Moreover, in comparison with the previous one, this drug has a lot of advantages. It is better tolerated, has fewer side effects, is less likely to provoke allergic reactions, and does not require dosage adjustment.
Can be prescribed to children older than one month. In addition, it interacts less with other drugs, so if complex therapy is required, it is often prescribed.
The drugs are available with a prescription.
Read about the treatment of epilepsy:
- at home, folk remedies and surgical methods,
- drugs Cortexin, Mexidol and Pantogam,
- with folic acid, glycine and magnesium,
- and concomitant use of antibiotics.
Alternative Treatments
Among the variety of alternative treatment methods, homeopathic treatments occupy a special place. Although epilepsy cannot be completely cured, this treatment method has its advantages. For example, the use of homeopathic recipes brings a tangible therapeutic effect, affecting the entire body. Homeopathic procedures are non-addictive and easy to use. In addition, they have a low cost.
It is worth taking into account that such therapy is safe and gentle on the body. The obvious advantages of such methods include the fact that this is the only method that does not have a toxic effect on tissues and organs.
Treatment Goals
The overall goal of treatment for epilepsy can be divided into several basic principles:
- Pain relief for attacks occurs when the patient experiences pain during an attack. To do this, they regularly take anticonvulsants and painkillers. To alleviate the course of seizures, a diet with a high calcium content is prescribed;
- Preventing the occurrence of new attacks is achieved by prescribing appropriate medications;
- Reducing the frequency of attacks is the main goal of treatment if it is not possible to prevent the occurrence of new ones. Lifelong drug therapy is used;
- Reducing the duration of seizures becomes a treatment priority in the presence of severe seizures with breath holding for more than a minute;
- Achieve discontinuation of medications without resumption of attacks;
- Reduce the risks and side effects of drug treatment;
- To protect society from aggressive actions when a person suffering from this pathology poses a threat to himself and those around him. Compulsory inpatient observation and drug therapy are used.
The basic principles of treatment are selected after a detailed examination of the patient, establishing the form of the seizure, its severity, and frequency of occurrence. To do this, the attending physician carries out the necessary diagnostic procedures and identifies the main areas of therapy:
- Elimination of factors leading to an attack;
- Exclusion of causes of attacks that can only be eliminated surgically (tumor formations, hematomas, etc.);
- Determining the type and type of attack using the international classification list;
- Prescription of drugs against epilepsy of a certain group. It is advisable to use monotherapy with drugs of the same series. Only if treatment is ineffective, use complex therapy.
Correctly selected medicine for epilepsy in humans allows, if not cure the disease, then makes it possible to control its course.
Groups of anticonvulsants
In modern medical practice, anticonvulsants or anticonvulsants are divided into different groups depending on the main active ingredient.
These today are:
- Barbiturates;
- Hydantoin;
- Oxazolidionone group;
- Succinamide;
- Iminostilbenes;
- Benzodiazepine;
- Valproic acid;
Anticonvulsants
The main drugs of this type:
Phenytoin. Indicated if the patient’s seizures are of a pronounced epileptic nature. The drug inhibits the action of nerve receptors and stabilizes membranes at the cellular level.
Has side effects, including:
- vomiting, nausea;
- dizziness;
- spontaneous eye movement.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=g66BZCyUzh8
https://youtube.com/watch?v=g66BZCyUzh8
Carbamazepine. Used for prolonged attacks. In the active stage of the disease, the drug is able to stop attacks. Improves the patient's mood and well-being.
The main side effects will be:
- dizziness and drowsiness.
Contraindicated for pregnant women.
Phenobarbital. Possible use in combination with other drugs. This medicine perfectly calms the central nervous system. As a rule, it is prescribed for a long time. It should also be withdrawn gradually.
Side effects:
- changes in blood pressure;
- breathing problems.
Contraindicated for:
- initial stage of pregnancy;
- renal failure;
- alcohol addiction;
- and muscle weakness.
Clonazepam. Used in the treatment of myoclonic epilepsy. Fights involuntary cramps. Under the influence of the medicine, the nerves calm down and the muscles relax.
Also among the associated effects:
- increased irritability and apathetic state;
- discomfort of the musculoskeletal system.
During use the following is contraindicated:
- heavy physical activity requiring special attention;
- pregnancy at different stages;
- renal failure;
- Drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Lamotrigine. Successfully fights both mild seizures and severe epileptic seizures. The action of the drug leads to the stabilization of brain neurons, which, in turn, leads to an increase in the time between attacks. If successful, the seizures disappear completely.
Side effects may appear as:
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- skin rash.
During the reception, it is not recommended to engage in work with increased attention. Sodium valproate
Prescribed for the treatment of severe seizures and myoclonic epilepsy. The drug stops the production of electrical impulses in the brain, securing a stable somatic state of the patient. Side effects usually include stomach and intestinal upsets
Sodium valproate. Prescribed for the treatment of severe seizures and myoclonic epilepsy. The drug stops the production of electrical impulses in the brain, securing a stable somatic state of the patient. Side effects usually include stomach and intestinal disorders.
It is prohibited to take:
- pregnant women;
- for hepatitis and pancreatic disease.
Primidon. Used for psychomotor seizures, as well as in the treatment of myoclonic epilepsy. Slows down the activity of neurons in the damaged area and reduces spasms. The medicine can intensify arousal, therefore it is contraindicated in children and elderly people of the older generation.
Related actions include:
- headache;
- development of anemia;
- apathy;
- nausea;
- allergic reactions and addiction.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- liver and kidney diseases.
Beclamid. Eliminates partial and generalized seizures. The drug reduces excitability and eliminates spasms.
Possible side effects:
- dizziness;
- bowel irritation;
- allergy.
Benzabamil. It is usually prescribed to children with epilepsy, as it is the least toxic of its kind. Has a mild effect on the central nervous system.
Side effects are:
- lethargy;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- involuntary eye movement.
Contraindicated for:
- heart disease;
- kidney and liver diseases.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=bMJ_oU6QpN4
Effect of medications
It is known that if you regularly and promptly take anticonvulsant drugs for epilepsy, you can completely control the occurrence of epileptic seizures. Modern medications allow:
- block the excitability system of neurons of the epileptic focus;
- stimulate the activity of the inhibitory complex of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors;
- influence ion channels and stabilize neuronal membranes.
Prescribed tablets for epilepsy may have either one of these mechanisms of action or a complex of them. Modern antiepileptic drugs are conventionally divided into drugs of the 1st line (basic category) and 2nd line (drugs of the latest generations). Depending on the symptoms, the doctor recommends taking certain medications.
Main objectives of treatment
Complex therapy for epilepsy is primarily aimed at reducing its symptoms and the number of seizures and their duration. Treatment of pathology has the following goals:
- Pain relief is necessary if seizures are accompanied by pain. For these purposes, painkillers and anticonvulsants are systematically taken. To alleviate the symptoms accompanying attacks, the patient is recommended to eat foods rich in calcium.
- Prevent new recurrent seizures with appropriate tablets.
- If subsequent attacks cannot be prevented, then the main goal of therapy is to reduce their number. Medicines are taken throughout the patient’s life.
- Reduce the intensity of seizures in the presence of severe symptoms with respiratory failure (its absence after 1 minute).
- Achieve a positive result followed by discontinuation of drug therapy without relapse.
- Reduce side effects and risks from the use of medications for epilepsy attacks.
- Protect those around you from the person who poses a real threat during a seizure. In this case, drug treatment and observation in a hospital setting are used.
The method of complex therapy is selected after a full examination of the patient, determining the type of epileptic seizures, the frequency of their recurrence and severity.
For these purposes, the doctor carries out a full diagnosis and sets priority treatment areas:
- exclusion of “provocateurs” that cause a seizure;
- neutralization of the causes of epilepsy, which are blocked only through surgery (hematoma, neoplasm);
- establishing the type and form of the disease using the global list of classification of pathological conditions;
- prescribing medications against certain epileptic seizures (monotherapy is preferred; in the absence of effectiveness, other drugs are prescribed).
Correctly prescribed medications for epilepsy help, if not eliminate the pathological condition, then control the course of seizures, their number and intensity.
Duration of treatment
The cessation or reduction of epileptic seizures, reducing their duration, alleviating and improving the psycho-emotional state of the patient is already considered a positive trend in treatment. The use of the latest pharmacotherapy techniques makes it possible to achieve complete relief or significant minimization of seizures.
The duration of drug therapy is determined by the type of attacks and form of the disease, age and individual characteristics of the patient. Practical recovery can occur with idiopathic forms of epilepsy. A small percentage of relapses occur in idiopathic forms with absence seizures that occur in childhood or adolescence. Cancellation of treatment for low-recurrence epilepsy is possible after two years of remission. In other cases, the question of stopping therapy can be raised only after five years of remission. In this case, the EEG should show a complete absence of pathological activity.
Termination of therapeutic treatment is carried out gradually, with a reduction in dosage to 1/8 daily over 6-12 months. Antiepileptic therapy should not be discontinued in patients with severe symptoms.