What is lower extremity neuropathy?
Neuropathy is damage to peripheral nerves and the vessels that supply them. Initially, this disease is not inflammatory in nature, but later it can be layered with neuritis - inflammation of nerve fibers. Neuropathy of the lower extremities is included in the group of polyneuropathies, the basis of which is metabolic disorders, tissue ischemia, mechanical damage, and allergic reactions.
Neuropathy is classified according to the type of course:
- spicy;
- chronic;
- I'll sharpen it up.
Depending on the type of pathological process in nerve fibers, neuropathy can be axonal (encompasses the processes of neurons - axons) and demyelinating (extends to the sheaths of nerve fibers). According to the symptoms, the pathology is:
- Touch
. Symptoms of sensory impairment and pain predominate. - Motor
. It manifests itself mainly as movement disorders. - Vegetative
. Signs of vegetative and trophic disorders are noted.
The causes of the pathology are varied. Thus, the diabetic form is characteristic of metabolic disorders in neurons in diabetes mellitus. Toxic, alcoholic is caused by poisoning, intoxication. Other possible causes are tumors, deficiency of vitamins B, hypothyroidism, HIV, trauma, family history.
Vitamins
In complex vitamin therapy for PNC, the main role is given to B vitamins. The use of these neurotropic drugs promotes myelination of peripheral nerves and accelerates the transmission of impulses to muscles.
In addition, vitamin B 1 has an indirect analgesic effect and significantly accelerates regeneration processes, and vitamin B 6 has antioxidant activity and helps improve neuromuscular conduction.
Vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin) in PNK is necessary for the restoration of damaged nerve fibers, as it participates in the normal synthesis of myelin.
In addition, it ensures normal blood composition and has an analgesic effect. Complex administration of vitamins for polyneuritis has a positive effect on metabolic and regenerative processes in tissues, restores innervation and strengthens blood vessels.
Sensory disorders - the main group of symptoms
Manifestations of pathology in the leg area can be varied, often depending on the cause of neuropathy. If the disease is caused by injury, symptoms affect one limb. In diabetes mellitus and autoimmune diseases, symptoms spread to both legs.
Sensory disturbances can be so unpleasant that they cause depression in the patient.
Sensory disturbances occur in all cases of lower extremity neuropathy. Symptoms are usually observed constantly, do not depend on body position, daily routine, rest, and often cause insomnia.
In addition to the described signs, there are often sensory disturbances - slow recognition of cold and hot, changes in the pain threshold, regular loss of balance due to decreased sensitivity of the feet. Pains also often appear - aching or cutting, weak or literally unbearable, they are localized in the area of the affected area of the nerve.
Diagnosis of lesions of the peripheral nervous system
The main diagnostic method remains a clinical examination of a person, which tries to identify the cause of damage to the PNS. Usually these are paralysis and paresis, vegetative-vascular disorders, trophic ulcers and impaired sensitivity of certain parts of the human body.
There are different research methods in the arsenal of medicine:
- electromyography,
- electrodiagnostics,
- thermal invasive examination,
- histochemical and histological studies.
Early diagnosis makes it possible to minimize lesions and prescribe effective drugs for treatment.
Other signs of the disease
As the pathology of the extremities develops, the motor nerve fibers are damaged, and therefore other disorders occur. These include muscle spasms, frequent cramps in the legs, especially in the calves. If the patient visits a neurologist at this stage, the doctor notes a decrease in reflexes - knee and Achilles. The lower the reflex strength, the further the disease has progressed. In the final stages, tendon reflexes may be completely absent.
Muscle weakness is an important sign of leg neuropathy, but it is characteristic of the later stages of the disease. At first, the feeling of muscle weakening is transient, then it becomes permanent. In advanced stages this leads to:
- decreased activity of the limbs;
- difficulty moving without support;
- muscle thinning and atrophy.
Vegetative-trophic disorders are another group of symptoms of neuropathy. When the autonomic part of the peripheral nerves is affected, the following symptoms occur:
In patients with neuropathy, cuts and abrasions on the legs do not heal well; they almost always fester. Thus, with diabetic neuropathy, changes in trophism are so severe that ulcers appear, and sometimes the process is complicated by gangrene.
Neuropathy Treatment Basics
This disease must be treated comprehensively, always with correction of the underlying pathology. For autoimmune diseases, hormones and cytostatics are prescribed; for diabetes, glucose-lowering medications or insulin; for the toxic type of disease, cleansing techniques (hemosorption, plasmapheresis).
The goals of treatment for lower extremity neuropathy are:
- restoration of nervous tissue;
- resumption of conductivity;
- correction of disorders in the circulatory system;
- improvement of well-being;
- reduction of pain and other disorders;
- optimization of motor function of the legs;
- increasing metabolic rate.
There are many treatment methods, the main one being medication.
Surgical treatment is practiced only in the presence of tumors, hernias, and after injuries. To prevent muscle atrophy, all patients are recommended to exercise from a special exercise therapy complex; at first, they are performed under the supervision of a rehabilitation physician.
If you have neuropathy, you should follow a diet with an increase in the content of vitamins B, and you should also exclude alcohol, foods with chemical additives, marinades, fried, and smoked foods.
The disease is successfully treated with physiotherapy. Massage, magnetic therapy, therapeutic mud, reflexology, and electrical muscle stimulation have proven themselves to be excellent. To prevent the formation of ulcers, you should wear special shoes and use orthoses.
Basic drugs for the treatment of pathology
In the treatment of neuropathy, drugs play a leading role. Since the basis is degeneration of nerve tissue, the structure of the nerve roots should be replenished with medication. This is achieved by using the following medications:
B vitamins are mandatory in the course of therapy, especially B12, B6, B1. Most often, combined drugs are prescribed - Neuromultivit, Milgamma in tablets, injections. After taking them, sensitivity disorders are eliminated, all symptoms are reduced in severity.
What else is used to treat neuropathy?
Vitamins that are powerful antioxidants are very useful for the body in any form of neuropathy of the lower extremities - ascorbic acid, vitamins E, A. They are necessarily used in complex therapy of the disease to reduce the destructive effects of free radicals.
In case of severe muscle spasms, the patient will be helped by muscle relaxants - Sirdalud, Baclofen, which are used only with a doctor's prescription - if abused, they can increase muscle weakness.
There are other medications against this pathology. They are selected individually. These are:
Locally it is recommended to use ointments with novocaine, lidocaine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as warming ointments with red pepper and animal poisons. In case of bacterial infection of the skin of the feet and legs, bandages with antibiotics are applied (Tetracycline ointment, Oxacillin).
Traditional treatment of neuropathy
Treatment with folk remedies is used with caution, especially for diabetes. Recipes can be like this:
With timely treatment, the disease has a good prognosis. Even if the cause of neuropathy is very severe, it can slow or stop its progression and improve a person's quality of life.
5
Drug treatment of cerebral palsy depends on the stage of the disease, the structure of the defect, the mental and somatic status of the child and is aimed at:
- cessation of inflammatory primary and secondary autoimmune processes that began in utero, if they occurred;
- prevention of scar-adhesive processes resulting from inflammation, mechanical birth trauma and hemorrhages; consequences of asphyxia, including chronic metabolic acidosis;
- intensification of metabolic processes in nervous tissue, primarily redox and protein metabolism;
- ensuring energy processes in the brain;
Drug treatment of cerebral palsy aims to create favorable conditions for more successful physical therapy.
Drug treatment of cerebral palsy in the residual period includes the prescription of drugs that lower muscle tone, improve the conduction of nerve impulses in synapses, reduce hyperkinesis, normalize the course of metabolic processes in the nervous tissue, as well as anticonvulsants (in the presence of seizures), dehydrating agents (in case of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome) and restoratives.
Preparations
that lower muscle tone
(inhibit cells of the reticular formation, block mono- and postsynaptic spinal reflexes, have a central and peripheral anticholinergic effect): midocalm, baclofen, surdolite, amedine, norakin, cyclodol, tropacin, scutamil C, levodopa, nacom , sinimet, etc. These drugs are prescribed in gradually increasing dosages. It has been established that 40-60 minutes after taking one of the listed drugs, a decrease in muscle tone occurs and at this time it is recommended to carry out exercise therapy.
Sedatives
For mild forms of vegetative-vascular dystonia, adults and adolescents are most often prescribed:
- valerian preparations (Valdispert, tablets or valerian tincture);
- Bromenval drops (contain extracts of hawthorn, valerian, menthol and sodium bromide);
- Valemidin drops (contain extracts of valerian, motherwort, hawthorn, mint and diphenhydramine);
- motherwort tincture;
- tincture of evasive peony;
- Passifit syrup (contains extracts of valerian, hop cones, thyme, mint and hawthorn);
- Lotusonic tablets (contain extracts of oriental thuja seeds, seeds and germs of the nut-bearing lotus, dioscorea rhizomes, Chinese date seeds, mulberry leaves, longana euphoria fruits, erythrina leaves);
- Persen Night (capsules contain extracts of medicinal valerian, lemon balm, peppermint).
Persen Night
The drug has a mild sedative and antispasmodic effect, makes it easier to fall asleep, reduces emotional stress and eliminates nervousness. Effective for sleep disorders, nervousness, increased emotionality, and frequent mood swings.
Important. Persen Night is contraindicated for patients with low blood pressure, diseases of the biliary tract, children under 12 years of age, pregnant and breastfeeding women, patients with individual intolerance, as well as lactose and galactose intolerance.
With caution, Persen Night can be prescribed to patients with GERD.
Tranquilizers and neuroleptics
To reduce hyperkinesis, drug treatment for cerebral palsy includes tranquilizers
(Elenium, Amizil, Phenibut, Noofen, Relanium, Phenazepam, etc.),
antipsychotics -
containing drugs (Cyclodol, Orthan, Tropacin), as well as pyridoxine. In some cases, if conservative treatment is ineffective, they resort to so-called stereotoxic operations on the basal ganglia of the brain. In this case, a neurolytic mixture (usually with mayodil) is injected into the area of the globus pallidus or some nuclei of the optic thalamus. According to literature data, hyperkinesis ceases in 70% of cases and muscle tone decreases in 80% of cases. Chemopallidectomy is performed only by neurosurgeons in specialized departments.
In cerebellar forms of cerebral palsy, when muscle tone is reduced, duplex, securinin, echinopsin, and neurotransmitter stimulants are prescribed.
VSD - treatment, drugs
Treatment of VSD always begins with non-drug correction of symptoms. Medicines for vegetative-vascular dystonia are prescribed if non-drug treatment is ineffective.
For reference. It is important to take into account that if recommendations for lifestyle correction, normalization of physical activity, sleep and rest patterns are not followed, pills for vascular dystonia will also not give the desired effect.
The doctor must decide what to take for vegetative-vascular dystonia. The choice of drug depends on:
- type of vascular dystonia ( VSD of the hypotonic type , vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive type , mixed type of VSD);
- severity of VSD and frequency of development of vegetative-vascular crises;
- the prevailing symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia (thermoregulatory disorders, cardiac symptoms, gastrointestinal tract disorders, neurological or emotional disorders, blood pressure lability);
- patient's age;
- the patient has concomitant diseases or contraindications to the prescription of certain medications.
You should not choose your own medications for vegetative-vascular dystonia, since before starting treatment, the doctor must conduct a full examination and exclude the presence of other diseases that can give symptoms similar to VSD (arterial hypertension, thyroid diseases, neuroses).
Stimulation of metabolic processes
Preparations
that stimulate metabolic processes metabolism
, while simultaneously removing toxic breakdown products, increase respiratory activity, energy processes in brain tissue, improve blood supply, promote differentiation of nerve cells, myelination of pathways, improve the functionality of the brain): glutamic acid, aminalon, nootropil, piracetam, encephabol, cerebrolysin, diavitol, lipoic acid, cogitum, prefisone, carnitine, pantogam, pyridoxine, cyanocobolamin, neuromedin, etc. For seizures, stimulant drugs should be administered carefully, gradually increasing the dose, in combination with anticonvulsants and sedatives.
Herbal medicine for VSD
For reference. Most often, herbal remedies with a mild sedative effect are prescribed for VSD. Patients may be prescribed infusions with lavender, oregano, lemon balm, mint, motherwort, valerian, and St. John's wort.
Adaptogenic plants that are often prescribed include sea buckthorn, eleutherococcus, Chinese lemongrass, Rhodiola rosea, and ginseng.
To improve the flow of bile, milk thistle, immortelle, St. John's wort, and centaury can be prescribed.
Women may be prescribed preparations with phytoestrogens: red clover, oregano, licorice, flax, soy.
Anticonvulsants in the treatment of cerebral palsy
seizures
, drug treatment of cerebral palsy necessarily requires the prescription of
anticonvulsants ( phenobarbital, diphenine, antelepsin, carbamazepine, valproic acid derivatives - depakine, convulsofin, etc.). Anticonvulsant therapy for patients with cerebral palsy is prescribed individually, taking into account the characteristics of the underlying disease, the nature of epileptic paroxysms, their frequency, and the time of occurrence during the day. Anticonvulsants must be taken continuously, long-term (3-5 years of effective therapy), followed by gradual withdrawal.
In addition to such differentiated drug treatment, it is recommended to periodically take pharmacological agents that regulate metabolism in the nervous tissue and increase the body's resistance to adverse external influences. These are phosphorus preparations.
Increased conductivity of muscle fibers
The nervous system controls skeletal muscles through a network of neurons that are connected to muscle fibers through special connections. A nerve impulse (command signal) can activate all or some of the fibers with mild or intense excitation.
The nerve-muscle complex is called the neuromotor part of the body.
Different types of muscles can work in the same ligament to produce a compound muscle movement. All contractions of skeletal muscles are controlled by the brain. The better the conductivity of muscle fibers, the more intense the excitation can be and the excited muscle will work much faster and stronger. Therefore, the definition of a muscle of “highest quality” is primarily related to its nerve conduction.
The supply of muscle tissue with nerves ensures their connection with the central nervous system and is called innervation.
It has been noticed that the more innervated a muscle is, the stronger it is and the higher its ability to contract with greater ease and speed.
In addition, muscle innervation is directly related to the speed and intensity of anabolic processes. In fact, muscles that are connected to myelinated neurons (those surrounded by myelin sheaths that serve as a kind of insulating material and allow stronger neuronal signals to pass through) have greater strength and ability to grow.
If there really are "superior quality" muscles, then they must have superior nerve conduction, superior "executive abilities" and superior ability to utilize energy.
The question arises: is all this possible?
And the answer immediately suggests itself - more likely yes than no.
There is evidence that repeated intense stimulation signals the muscle to increase neuromuscular efficiency through innervation. As noted earlier, during the process of innervation, connections between the central nervous system and muscles are strengthened. The conclusion is that this process can significantly improve muscle strength and contraction speed even without any change in muscle mass. But different muscle actions require different stimuli with different neuromuscular regulators.
In other words, in order to have excellent performance, a muscle must be connected to a network of nerve endings that, with the help of impulses, will produce all the necessary muscle actions.
How to connect a muscle with the central nervous system?
This is a very broad topic, but we will try to explain everything briefly and simply. The same innervation must be involved in this process. The innervation of the muscle can be improved with the help of a set of stimulating signals, and, consequently, through a set of special exercises.
Changing the intensity of exercise is one way to influence innervation, and it is also the best method when it comes to improving qualities such as strength, speed, contractility and endurance.
This grueling combination of exercises that develop strength, speed, agility and endurance must be repeated several times a week.
A repeated set of exercises forces the muscles to adapt, increasing the efficiency of neuroconduction, improving all muscle qualities at the same time.
In doing so, we can achieve truly amazing results. For example, a long-distance runner can improve his speed without compromising his endurance, allowing him to break his own speed record over both short and long distances.
Martial arts and boxing athletes who train speed, agility and endurance can develop additional muscle strength and thus increase punching power, speed, grip strength, and overall resistance to fatigue during intense exercise.
Nerve conduction to a muscle is only part of what defines top quality muscles.
This text is an introductory fragment.
Everyone knows the catchphrase - “all diseases come from nerves.” This expression speaks perfectly about the true cause of many diseases.
As you know, nature has assigned to the nervous system
functions of managing the entire life activity of the human body - regulation of all physiological processes of the body, management of its activity and unity, connections with the outside world.
Partial or complete disruption of the nervous system
manifests itself in the form of a functional disorder or disease, mental disorders and emotional changes.
From the point of view of the functional activity of the nervous system, any disease is a disturbance in the control and regulation by the central nervous system of the physiological and mental processes of the body, the activity of organs or tissues. In this case, regulation consists, first of all, in the clear transmission of a nerve impulse from a certain center in the brain to an organ, tissue or system, i.e., the conductivity of nerve structures is important, first of all.
"The electrical network of our body"
Under the conduction of nerve structures
refers to the electrical conductivity of nerve fibers, i.e. the conduction of nerve impulses (electrical impulses) from the center (brain) along the nerve fibers to the periphery (organs, tissues) and back.
The causes of disturbances in the electrical conductivity of nerve fibers can be: overheating and hypothermia, bruise and pinched nerve, chemical and bacteriological exposure, overeating, smoking and alcohol, excessive grief and emotional stress, fright, anxiety, fear, etc. All of these conditions lead the body to overstrain.
As a result of overstrain - physical or mental, stress (physiological or mental) usually occurs, and it is stress
becomes the first stage in the development of a particular
functional disorder
.
Stress, first of all, causes disruption of the electrical conductivity of nerve fibers, i.e.
conductivity of nerve structures, and hence
functional impairment of the nervous system.
It follows that the restoration of a functional disorder of the nervous system and health in general should begin with the restoration of the conductivity of nerve fibers, i.e., their electrical conductivity.
And the first thing you need to start with is eliminating the stressful state of the body, relieving physiological and mental stress.
“Turn on” self-regulation.
Today, there are a huge number of methods for relieving physiological and mental stress. Starting from ordinary massage to in-depth psychoanalysis. One of the methods of relieving physiological and mental stress, and therefore restoring the conductivity of nerve fibers, i.e. The “electrical network” of our body is my author’s technique —
Since the nervous system regulates all physiological processes in the unity of the whole organism, when the conductivity of nerve fibers is restored, the stress state of the body is eliminated
– relieving physiological and mental stress.
As a result of the restoration of the conductivity of the nervous structures of our body, blood circulation and respiration improve, the supply of oxygen and nutrition to the cells of our body is activated, metabolic processes are improved, waste waste is removed more quickly, and stagnation is eliminated. At the same time, the physiological activity of not only muscle tissues and organs, but also the nervous system itself and its metabolic processes improves. A self-healing process of nervous activity occurs, i.e., self-regulation.
Polyneuropathy of the lower extremities is a common pathology associated with damage to peripheral nerves. The disease is characterized by trophic and vegetative-vascular disorders affecting the lower extremities, manifested by sensory disturbances and flaccid paralysis.
The danger of the pathology is that over time its manifestations worsen, problems with movement arise, which affects the ability to work and interferes with a full life. Today we will talk about the symptoms and treatment of polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, and also consider methods aimed at preventing further progression of the pathology.
Drugs that improve the conduction of nerve impulses
To improve neuromuscular conduction in the treatment of PNC, anticholinesterase drugs are successfully used, which provide a pronounced effect on impulse transmission in peripheral synapses.
Even with damaged myelin sheaths of the nerves of the lower extremities, these agents guarantee the conduction of motor signals along the surviving sections of the nerve fibers.
The use of anticholinesterase drugs helps restore lost muscle strength and increases the level of sensitivity.
In addition to standard anticholinesterase agents (proserin), modern methods of treating PNC use ipidacrine, which has a dual effect on peripheral nerves . It helps stimulate neuromuscular transmission and at the same time improves conduction along the peripheral nerve.
The drug is highly effective and has no side effects. It is well tolerated when administered long-term in combination with antioxidants and neurotropic medications.
Several drugs from this group, used in injection and tablet forms, have an identical effect:
- neuromidin;
- axamon;
- amiridine;
- ipidacrine.
The arsenal of modern means of treating PNC, which modern medicine is armed with, when used in a complex manner, can effectively influence the symptoms of PNC.
With individual selection of medications by the attending physician and sufficient patience on the part of the patient, the disease gradually but steadily recedes.
People who work in production and are constantly exposed to vibration can eventually develop an occupational disease - vibration disease. It is important to observe preventive measures at work and receive timely treatment in the presence of risk factors and at the first symptoms of this disease.
Read all about the dangers of a ruptured brain aneurysm on this page.
Polyneuropathy of the lower extremities - why does it occur?
Polyneuropathy of the lower extremities is not an independent disease. According to ICD 10, this condition is considered a neurological syndrome that accompanies a variety of diseases:
- (diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities);
- chronic alcohol intoxication (alcoholic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities);
- vitamin deficiencies (especially with a lack of vitamin B);
- severe poisoning with drugs, arsenic, lead carbon monoxide, methyl alcohol (acute axonal polyneuropathy);
- systemic diseases - biliary cirrhosis, malignant tumors, lymphoma, blood diseases (chronic axonal polyneuropathies);
- infectious diseases (diphtheria polyneuropathy);
- hereditary and autoimmune pathologies (demyelinating polyneuropathies).
The cause of the disease can be a wide variety of health disorders and chronic diseases. Cancerous tumors can disrupt the functioning of the peripheral nervous system. In addition, signs of polyneuropathy may appear after a course of chemotherapy.
Infectious and inflammatory processes in the joints and any types of intoxication of the body (drugs, alcohol, chemicals) can cause problems with impaired sensitivity and damage to nerve fibers. In children, this disease is most often hereditary; for example, symptoms of porphyritic polyneuropathy appear in a child immediately after birth.
Thus, doctors divide all the factors that provoke the development of a pathological condition into several groups:
- metabolic (associated with metabolic disorders);
- hereditary;
- autoimmune;
- infectious-toxic;
- toxic;
- nutritional (caused by dietary errors).
Polyneuropathy never occurs as an independent disease; damage to nerve fibers is always associated with an etiological factor that negatively affects the state of the peripheral nervous system.
Clinical picture
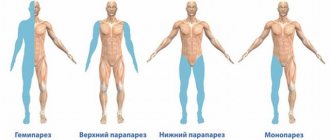
Polyneuropathy of the upper and lower extremities begins with increasing muscle weakness, which is associated with developing damage to the nerve fibers. The distal parts of the limbs are damaged first. In this case, a feeling of numbness occurs in the area of the feet and gradually spreads to the entire leg.
Patients with polyneuropathy complain of a burning sensation, crawling, tingling, and numbness of the limbs. Various types of paresthesia are complicated by muscle pain. As symptoms increase, patients experience severe discomfort even when accidentally touching the problem area. In the later stages of the disease, there is unsteadiness of gait, loss of coordination of movements, and a complete lack of sensitivity in the area of damage to nerve fibers.
Muscular atrophy is expressed in weakness of the arms and legs and in severe cases can result in paresis or paralysis. Sometimes unpleasant sensations in the limbs occur at rest, causing reflex movements. Doctors characterize such manifestations as “restless legs syndrome.”
The pathology is accompanied by autonomic disorders, which are manifested by vascular disorders (a feeling of cold in the affected limbs, marbled pallor of the skin) or trophic lesions (ulcers and cracks, peeling and dry skin, the appearance of pigmentation).
Manifestations of polyneuropathy are difficult to miss; as the pathology progresses, they become obvious not only to the patient, but also to the people around him. The gait changes and becomes heavier, as the legs become “wobbly”, difficulties arise with movement, the person has difficulty covering even short distances that he previously covered in a few minutes. As the pathology progresses, the feeling of numbness in the limbs increases. A pain syndrome arises, which manifests itself in different ways; some patients feel only minor discomfort, while others complain of aching or sharp, burning pain.
Patients experience swelling of the extremities, impaired knee reflexes, and lack of response to stimuli. In this case, only one or several characteristic symptoms may appear, it all depends on the severity of the damage to a particular nerve trunk.
Classification
According to the nature of the course, polyneuropathy of the lower extremities can be:
- Spicy
. It develops within 2-3 days most often against the background of severe poisoning with medications, methyl alcohol, mercury salts, and lead. Treatment takes on average 10 days. - Subacute
. Symptoms of the lesion increase gradually over a couple of weeks. Pathology usually occurs against the background of toxicosis or metabolic disorders and requires long-term treatment. - Chronic
. This form of the disease progresses against the background of diabetes, alcoholism, hypovitaminosis, blood diseases or oncology. It develops gradually over a long period of time (from six months or longer).
Taking into account the damage to nerve fibers, polyneuropathy is divided into several types:
- Motor
(motor). The neurons responsible for movement are damaged, as a result of which motor functions become difficult or completely lost. - Sensory
polyneuropathy of the lower extremities. Nerve fibers directly related to sensitivity are damaged. As a result, painful, stabbing sensations occur even with a light touch to the problem area. - Vegetative
. There is a violation of regulatory functions, which is accompanied by such manifestations as hypothermia, severe weakness, and profuse sweating. - Mixed neuropathy of the lower extremities
. This form includes a variety of symptoms from all of the above conditions.
Depending on the damage to cellular nerve structures, polyneuropathy can be:
- Axonal. The axial cylinder of nerve fibers is affected, which leads to decreased sensitivity and impaired motor functions.
- Demyelinating. Myelin, which forms the sheath of the nerves, is destroyed, resulting in a pain syndrome accompanied by inflammation of the nerve roots and weakness of the muscles of the proximal and distal parts of the extremities.
The demyelinating form of polyneuropathy is the most severe form of the disease, the mechanism of development of which is still not fully understood. However, as a result of a number of studies, scientists have put forward a theory about the autoimmune nature of the pathology. In this case, the human immune system perceives its own cells as foreign and produces specific antibodies that attack the roots of nerve cells, destroying their myelin sheaths. As a result, nerve fibers lose their functions and provoke innervation and muscle weakness.
Good to know
Since almost all autoimmune pathologies are associated with heredity, it is assumed that the cause of the development of this form of pathology may be a genetic factor.
Diagnostics
If polyneuropathy is suspected, the patient will have to undergo a series of diagnostic procedures, including laboratory and instrumental studies. After collecting an anamnesis, the doctor will conduct an external examination, examine reflexes, and then send the patient to the laboratory to donate blood for a general and biochemical analysis.
In addition, the patient will undergo an ultrasound of the internal organs, x-rays of the affected areas, and cerebrospinal fluid will be collected. If necessary, a biopsy of nerve fibers will be taken for examination. The choice of treatment regimen begins only after a full examination and diagnosis.
Treatment
The basis of therapeutic measures for polyneuropathy is a combination of medication and physiotherapeutic methods aimed at preventing the progression of pathology and restoring impaired innervation of nerve fibers. Treatment methods will largely depend on the cause contributing to the development of the pathology.
If severe chronic diseases are to blame, first of all they treat the underlying disease. Thus, for diabetic polyneuropathy, drugs are selected that will not affect the level of the glycemic index, and the therapy itself is carried out in stages. First, the diet is adjusted, body weight is normalized, and a complex of therapeutic exercises is developed for the patient. Subsequently, the treatment regimen includes neurotropic and alpha-lipoic acid injections, immunosuppressive drugs and glucocorticoids are prescribed.
If the disease is of a toxic nature, detoxification measures are carried out first, after which the necessary medications are prescribed. If the pathology develops against the background of dysfunction of the thyroid gland, hormonal drugs are used in the treatment process. Malignant neoplasms are treated surgically, removing the tumor that compresses the nerve roots.
To develop limbs and eliminate movement disorders, methods of physical therapy (physical therapy) are used. B vitamins help restore sensitivity; to relieve pain, analgesics are prescribed in the form of ointments, tablets or injections.
Main groups of drugs for the treatment of polyneuropathy
Metabolic agents
These are the drugs of first choice in the treatment of polyneuropathy; their therapeutic effect is aimed at improving blood circulation in the area of damage, improving tissue trophism and regeneration of nerve fibers. Most often, medications from this list are included in the treatment regimen:
- Cerebrolysin;
- Mexidol;
- Alpha lipoic acid;
- Instenon;
- Cytochrome C;
- Trental.
The action of the drugs is aimed at improving neuromuscular conduction, accelerating metabolism, and improving the supply of tissues with blood and oxygen. Metabolic agents can have an antioxidant effect, fight free radicals, stop the processes of destruction of nervous tissue and help restore impaired functions.
Metabolic and blood flow influencing agents
These drugs play a major role in the treatment of PNC. In addition to the main metabolic effect, they usually have a number of other therapeutic effects: they improve the regeneration of nervous tissue, have antioxidant properties, and improve trophism and blood circulation of damaged tissues.
The drugs of choice in the treatment of PNC are:
- Cerebrolysin;
- alpha lipoic acid preparations;
- Mexidol;
- Actovegin;
- cytochrome C;
- instenon;
- pantothenate Ca.
The principle of monotherapy and long courses of treatment (over 1 month) make it possible to achieve maximum effect in the treatment of various types of neuropathy. Thus, the symptoms of diabetic PNK are better relieved by alpha-lipoic acid, and Actovegin is prescribed for obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the legs.
Thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid preparations have a powerful antioxidant effect, reducing the content of free radicals, normalizing metabolic processes and blood circulation in nervous tissue. The result of its use is a significant regression of the neurological clinic in patients with polyneuritis. The effectiveness of the drug thiogamma in the treatment of PNC has been confirmed by large-scale international studies. The course of treatment usually begins with intravenous administration of the drug, and after 2-3 weeks they switch to tablet dosage forms. Alcohol is contraindicated during treatment.
Actovegin (solcoseryl) is a hemoderivative from calf serum with a pronounced stimulating effect on regenerative processes and an antihypoxic effect. Its administration for PNC combines intravenous and oral administration. The complex action of Actovegin is simultaneously aimed at processes in the peripheral and central nervous systems.
Instenon is a multicomponent drug with vasodilating, metabolic and antispasmodic activity. The complex effect during PNK provides improved neuromuscular conduction and improved blood supply to tissues depleted of oxygen. By restoring trophism, it is possible to quickly restore impaired functions. The course of treatment consists of intramuscular injections and internal use.
Cerebrolysin is generally recognized as one of the best neurometabolites, capable of stopping degenerative processes in nervous tissue, accelerating its metabolism and protecting it from harmful factors. The drug minimizes the risk of neuronal death during hypoxia and ischemia and has a strong neurotrophic effect. It is used for PNC in courses both intramuscularly and intravenously.