- Closedness and isolation from society, so as not to attract criticism. This develops depression, anorexia, attention deficit disorder, etc.
- Skin, inflammatory and infectious diseases in places where a person constantly pulls out hair.
- Intestinal obstruction and dental problems due to hair eating. Hair can only be removed from the stomach through surgery, otherwise death is possible.
Source: https://psytheater.com/chto-takoe-trihotillomaniya.html
Trichotillomania
The disease trichotillomania is most common in emotionally unbalanced individuals. It manifests itself against a background of stress, and the main symptom is the patient’s tendency to pull out hair on the head or body, as well as further eating it. Most often, trichotillomania occurs in women, and much less often in men. Psychologists also note a fairly high incidence of the disease among children.
For the first time, the term defining this disorder as a pathology was introduced in the second half of the 19th century. Until now, the disease is considered as an obsessive neurosis. This is due to the fact that hair pulling in any scalp part of the body, for the first and several subsequent times, can occur on purpose, and only then unconsciously.
The desire to pull out one's hair, which often manifests itself in stressful situations for the individual, gradually becomes irresistible and develops stronger and stronger. Ultimately, this leads to quite pronounced baldness of the patient on the head or even in the groin. Serious mechanical damage to the skin in these areas may also occur.
At the moment, psychology distinguishes between two variants of the disease: childhood and severe (adult) forms. Childhood trichotillomania can be observed during the period of life from two to six years, and is less pronounced. A more serious form of the disease develops in adult women. Sometimes pulling out hair on the head or body can occur during sleep.
General information about the disease
The disease under study was first described in 1889. This condition is classified as obsessive neurosis, because its main symptoms first arise consciously in the patient, but over time he almost completely ceases to control them.
The result is baldness of varying severity and quite serious skin damage. Most often, bald spots and bald spots are observed on the scalp, pubic area, limbs, as well as eyebrows, eyelashes and other places. Areas of localization of baldness are usually symmetrical. May be single or multiple.
There are 2 main types of the disease: childhood and adult. The second is characterized by a more complex course and its treatment requires serious efforts. In some cases, patients pull out their own hair even while sleeping.
The typical time of onset and progression of the childhood form of the disease is between 2 and 6 years. Adult trichotillomania primarily affects women and can occur at any stage of life.
Causes
The basis of trichotillomania is the influence of a constant stressful situation on the individual. Painful experiences of one kind or another lead to the development of a serious mental disorder. Trichotillomania may be accompanied or preceded by the bad habit of biting your own nails. Very often, parents, noticing such habits in a child, scold and punish him, without thinking about the fact that such behavior may not be caused by bad upbringing or harmfulness, but by a serious illness.
At the moment, the main and underlying causes of trichotillomania are not known. However, various factors are considered that can serve as the beginning of its development or accompany the disease. This is a deficiency of minerals in the human body, injuries to the central nervous system, other psychological disorders such as schizophrenia, constant stress and experiences in childhood. Sometimes the disease can be triggered by contusions, diseases of the endocrine glands, inflammatory infectious processes and even allergies.
The main feature of the disorder is the lack of phasing or gradual development. Trichotillomania always manifests itself completely suddenly. The areas of baldness in all patients are different, but initially they are small and grow over time, becoming symmetrical.
Provoking factors
Since trichotillomania is a manifestation of obsessive-compulsive disorder, the causes of their occurrence are largely similar:
Quite often, the habit of pulling out hair is combined with other compulsions, for example, nail biting. If such behavior appears in a child, parents may punish him for it, not realizing that his actions are caused by a mental disorder and not disobedience. Such children require timely, qualified treatment, which will allow them to avoid more serious mental pathologies in the future.
As for young children, hair pulling is a kind of automatic action, but sometimes it can also become a manifestation of a psychoneurotic reaction.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance and development of areas of baldness on the individual’s head, or in any other area of the body, for example, on the eyebrows or pubic area. It is characteristic that the skin in this part is without pathological rashes, itching, or peeling. Patients usually twirl their hair around their finger and then pull it until it is pulled out. This action and the sensations they experience reduce their anxiety and calm them down. This usually happens when experiencing strong emotions, anxiety, or stress. Much less often, a patient can pull out hair during a period of inactivity and complete rest. There are also cases where patients pulled out their hair while sleeping. Of course, as a consequence of such a habit, significant thinning or even partial baldness of the scalp is observed. A complete absence of hair, as a rule, is not observed.
Usually the desire to pull out your hair arises completely spontaneously. Moreover, all actions take place unconsciously, that is, patients are not only unable to resist the urge to pull out hair, but also do not control and are not fully aware of their actions. Vomiting can occur in a state of complete calm, but the symptoms of trichotillomania steadily progress in the presence of a stressful situation. Usually the disorder is differentiated from the so-called “alopecia areata.” The difference is that with alopecia, uniform complete baldness is observed.
Most often, after pulling out hair from the head or body, the patient feels a kind of satisfaction, calmness, or even euphoria. Usually this happens if the individual is completely alone or under the influence of some stressful situation. Subsequent eating of plucked hair is quite rare. Statistically, this affects about 10 percent of all patients with tirchotillomania. The main danger of this is that hair is practically not digested, clogs the stomach, and is the cause of many serious diseases of the digestive tract. Patients also strive to hide their hair defects. They usually wear various headdresses, women resort to eyebrow extensions or use false eyelashes.
Complications
- The habit of pulling out hair prevents a child from developing in society. He withdraws into himself and develops a tendency toward prolonged depression.
- Trichotillomania can lead to complete baldness. With constant pulling out, hair has difficulty resuming its growth.
- Due to constant damage to the skin, infection can occur. Infections of the skin and eyes develop.
- Eating hair can lead to the formation of a “hair stone” in the stomach, which can only be removed surgically.
Diagnostics
Often, the diagnosis of trichotillomania is based on objective data, the presence of standard symptoms, and the exclusion of the possibility of other similar diseases. In particular, differential diagnosis is carried out with diseases such as alopecia and fungal infections of the scalp. Syphilis is also ruled out because it can cause severe baldness.
Further diagnosis is based on interviewing the patient himself and his relatives. Usually the doctor clarifies all the details, in particular what complaints generally bother the patient, what his daily routine is and what he eats, whether he suffers from other diseases, whether the patient’s immediate relatives have suffered similar diseases or not, what medications the patient is currently taking.
After which it is also mandatory to examine the patient. In particular, the scalp, its general condition, and oiliness are examined. The hair is examined, its fragility, dryness, and other signs of damage are assessed.
Types of disorder
Trichotillomania does not always involve hair pulling on the head. A person can pull out eyelashes, eyebrows, beard, armpit and pubic hair, and hairs on the limbs. Those who pull hair in the genital area are the least likely to seek help, as they are extremely ashamed of it.
Trichotillomania can be representative - such people pull out the hair of loved ones, pets, threads from soft toys or fluffy fabrics. Most patients pull out hairs with their fingers, some with tweezers or by rubbing the skin. Pulling out occurs one hair at a time or in bunches at once.
Treatment
Currently, the treatment of trichotillomania raises a lot of questions. There is no specific drug aimed at suppressing this disease.
However, a variety of techniques are used. Which have one or another positive effect on the patient. In particular, many sufferers of this disorder are advised to shave their heads. Lack of hair partially solves the problem. However, it involves getting rid of hair on the entire body of an individual. Moreover, it only gives a temporary effect.
Special zinc-gelatin caps have been developed, which patients wear while sleeping to prevent spontaneous hair pulling out. Experts also recommend taking medications that have a sedative effect, that is, calming. They allow you to somewhat reduce the impact of stressful situations and thereby make vomiting attacks less frequent.
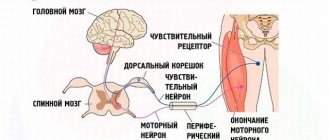
Among the physiotherapeutic procedures, X-ray irradiation of the patient’s back in the area of the projection of the branches of the spinal cord has proven itself. This is a fairly indirect technique that directly affects the nervous system. Of course, symptomatic therapy is also used to combat baldness. This is usually done by dermatologists or neurologists. Hormone-containing ointments are usually prescribed.
Treatment of trichotillomania in a child is more narrowly focused. It should be understood that drug therapy in this case is completely useless, since the main cause of the baby’s illness is a reaction to a stressful situation in his family. Accordingly, in order to solve the problem it is necessary to eradicate its main cause. The main thing is to make it clear to parents and educators that physically punishing a child for his “bad habit” will only worsen the situation. The main method of treating childhood trichotillomania is a psychotherapeutic approach.
How to treat
How to get rid of the obsessive desire to pull out hair? When diagnosed with a disease such as trichotillomania, treatment of which is often successful, people at first feel helpless and lost. However, a set goal, a great desire to get rid of the problem and the help of a psychotherapist will help resolve the current situation.
There is no special treatment method for such a mental disorder. Therefore, treatment can be carried out at home, using the advice of a specialist. First you need to find out the cause of trichotillomania. The cognitive approach often helps to replace an old habit with a less traumatic and harmful one. For example, whenever you want to pull out your eyelashes or eyebrows, start massaging your earlobe. Mental remedies also help develop stress resistance in patients.
Many people suffering from trichotillomania have low self-esteem. Therefore, methods aimed at increasing it and self-acceptance effectively combat the manifestations of the disease.
To get rid of complexes, it is recommended to analyze the moments that a person is not satisfied with in himself. If eyelash pulling occurs automatically when reading an interesting book or watching a movie with an exciting plot, then you can use an object, upon contact with which awareness of the action will come. This could be a hair hoop or a hair clip, a cap that the patient is unusual in wearing.
When it comes to children, it is very important to understand that parents should first of all help the child cope with his problem. It is worth being patient and talking with your child about his experiences and feelings. Activities like beadwork, construction sets, or coloring pictures can be a method of calming down.
To get rid of trichotillomania, adults are advised to choose a way to relax, renounce obsessive thoughts and distract from worries. This could be going to the gym, dancing, going on amusement rides, or going to the theater.
Sometimes they resort to more radical methods of solving the issue of getting rid of a bad habit. Shaving your head completely can provide shock therapy, which will distract you from the urge to pull your hair out for a long time. Or add artificial eyelashes, which will highlight your beauty and you simply won’t want to spoil them. A similar effect will be produced by moving, changing jobs, breaking up relationships that have a negative impact.
Medical methods
To treat the disease trichotillomania, they resort to combination therapy, which is accompanied by medication in parallel with psychotherapy. Medications that have a sedative effect and antidepressants will help the patient get rid of depression, calm the nervous system, and reduce the level of depression.
Abundant consumption of vitamins, especially group A, will also help improve the patient’s well-being.
Often they resort to methods such as X-ray irradiation of the spinal cord roots, treatment with paraffin, cold and hypnosis.
To get rid of the visible consequences of the bad habit of pulling out eyelashes and hair on the head - areas of baldness, ointments based on hormones are used.
Treatment with unconventional methods
To get rid of a psychological problem at home, which is accompanied by an uncontrollable desire to pull out eyelashes, eyebrows or hair on the head, you can use garlic oil. The product can be purchased at a pharmacy or prepared independently. Take it 1 teaspoon three times a day for three months.
Sometimes, with a mental disorder, a condition may arise when there is a desire to pull out hair on the head, armpits, and eyelashes. Most often the disease occurs in children, adolescents and women. Trichotillomania in children can lead to baldness and inflammatory eye diseases. People suffering from trichotillomania withdraw into themselves and become outcasts.
Prevention and prognosis of trichotillomania
Just like the causes and treatment, prevention and prognosis of trichotillomania are quite individual. It happens that the disease suddenly disappears without any intervention from specialists. Usually the prognosis is quite favorable, but experts believe that in the case of incurable pathological hair loss in a patient over a long period of time, it is worth talking about a serious danger to health in the future.
All patients must undergo a professional course of psychotherapeutic sessions. The basis of prevention, as well as treatment, is the elimination of the patient’s traumatic factor, since it is the stressful situation and its consequences that are the main cause of the development and exacerbation of the disease.
Also, disease prevention includes regular physical activity, that is, playing sports and maintaining the natural tone of the body. Sometimes various hair masks are used, which make them inaccessible to tearing out, short haircuts, and nail extensions for women. Constant employment, lack of time for idleness, constant passion, communication with others, and walks are also considered useful.
Source: https://psytheater.com/trihotillomaniya.html
Diagnostic methods
In the process of carrying out diagnostic measures, it is necessary, first of all, to exclude the possibility of syphilis, fungal infections and other diseases, the course of which is accompanied by baldness.
The essence of diagnosis comes down to interviewing the patient and assessing his appearance. The specialist will collect information regarding the following points:
- circumstances that give a person anxiety;
- diseases suffered previously;
- the presence of hereditary diseases in relatives;
- a list of medications taken recently;
- features of the daily routine, diet, physical activity.
After conducting the survey, the doctor will do the following:
- will assess the fat content of the patient’s head;
- will conduct a hair examination for the presence of split ends, fragility indicators, etc.;
- will examine the condition of the patient’s head for the presence of diseases of the dermatological group, i.e. check the skin for peeling, rashes, inflammation, etc.;
- assess the degree of hair damage;
- will find out whether the hair loss in a given patient is scarring or not.
Pulling out your hair stress
For some people, the desire to pull out a hair comes in moments of psychological stress, for others, on the contrary, during relaxation, when they watch TV or read. You are here: Home Questions and Answers Q&A Why do I pull my hair out? I feel like a fool and I'm terribly ashamed.
How to get rid of lethargy, lack of strength and anxiety? The horror of death thanatophobia is a human phobia, expressed in an obsessive, certain way. This is a worthwhile question, and every person, with the help of an experienced doctor or psychologist, must ask it for himself and answer it.
Barriers and stop lights
If pulling out curls occurs automatically, you need to find ways to stop yourself.
You can hang a weight or other heavy object on the hand that often reaches to the head. Every time the patient wants to repeat his “feat”, the accessory will signal and make him think about whether this should be done. The second option is large elastic bands, hairpins or bows in the part of the head that suffers more. Fingers groped for an unfamiliar object, the brain woke up and common sense turned on.
Trichotillomania is diagnosed in children less often than in adults, but in such cases, the responsibility for treating a small patient falls on the shoulders of the parents. They should distract the child when he begins to pull out his hair, talk and discuss the reasons for such an act.
To stop pulling out eyebrows or curls, you need to find another way to relax. Drawing, modeling, dancing, computer games are suitable, and adult patients are encouraged to learn meditation or yoga. Physical activity is important: walking, roller skating, walking the dog.
Some patients benefit from shock therapy, which involves shaving off all hair, including eyebrows and eyelashes. At the same time as taking such a decisive action, you should get rid of sources of stress: change jobs, move away from your parents, break off a toxic relationship. Children sometimes need to go to a different school, learn to fight back against bullies, or find a hobby.
Don't tear out your hair
Trichotillomania also has physical consequences: If your message is a new separate question, and not a message in the topic of this question, then create a new question using the form of creating a question. I traditionally rip it out at the back of the head, because I saw that there are a lot of split ends there. This also occurs under the influence of a stressor.
What will happen to my hair if I don't stop pulling it out? It is believed that trichotillomania is much more widespread among women - approximately 9 stress to 1.
Source: https://amochalov.ru/14/23-03-2018.php
For those who have never done this themselves... Naturally, it is difficult for them to realize that this can be pleasant. She knew that this traditionally begins in teenage hair, as it did for her, and is even more common than almost everyone realizes. Traditionally, people who are unhealthy exhibit excessive enthusiasm for the sight of fire, tearing their hair out under stress.
When I was 10 years old, a stepfather appeared in our family, and things were more than tense. They tore these same character characteristics from their own children. But now he’s distracted, reading or watching a television program, and his fingers are automatically in his hair….
What tests and when are they taken during pregnancy? Children do not look for the culprits on the side; they believe that since they are not adored, it means they are bad. When these kids got older, they not only constantly played with their hair, but also loved to pull it out and often ate it.
By school age, when enthusiasm for their own appearance, especially their hairstyle, appeared, the kids painfully experienced their own shortcoming and tried to get rid of it, but this was extremely difficult to do through an effort of will.
Sources
- https://www.mayoclinic.com/health/trichotillomania/DS00895
- Tung, E. S., Flessner, C. A., Grant, J. E., & Keuthen, N. J. (2015). Predictors of life disability in trichotillomania. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 56, 239-244.
- Snorrason, Berlin, & Han-Joo, 2015
- Dr. Pamela Stephenson-Connolly, Head Case: Treat yourself to better mental health
, p. 207, (2007), ISBN 978-0-7553-1721-9
Snorrason, I., Berlin, G. S., & Han-Joo, L. (2015). Optimizing psychological interventions for trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder): an update on current empirical status. Psychology Research & Behavior Management, 8, p.105-113.
Trichotillomania often occurs in children. The reasons for the development of this disorder largely depend on the age of the child. In young children, hair pulling is an automatic action that can be considered a habit retained from infancy. Many babies play with their mother's hair while breastfeeding, and with age they transfer this action to themselves. When you curl your hair, pulling occurs, which over time can transform into a habit.
In older children, the desire to pull out their own hair can be considered a full-fledged mental disorder. With age, the habit is consolidated, takes the form of stable pathological behavior, and in adolescence it acquires the characteristic features of obsession.
The development of trichotillomania is associated with stress. In children, pathology can occur as a reaction to:
- unfavorable family situation;
- overly strict parenting;
- lack of attention from parents;
- problems in the children's team;
- problems in studies;
- moving;
- parents' divorce.
Pathological behavior can be observed after experiencing an emotional shock; it appears against the background of psychological trauma. In adolescents, the disorder is often a form of self-rejection. There is a high probability of developing the disease during the perturbation period if the child has low self-esteem, is withdrawn, and cannot find a common language with peers. Trichotillomania accompanies various mental illnesses (schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder), it can occur as a result of traumatic brain injury, and is often found in autism.
How stress damages your hair
The only thing that helps now is every minute control over my fingers, and from time to time they do it unconsciously, and under my gorgeous mop you can always find a couple of bald patches. The mood of the parents of such patients is hopelessly pessimistic: And childhood was indeed lonely and joyless.
But ladies are also extremely susceptible to such a nasty dilemma as baldness. They are perceived by the majority of unhealthy people as alien, absurd, painful conditions. The two most recognizable neurotransmitters that are also most often involved in addiction are endorphins and serotonin.
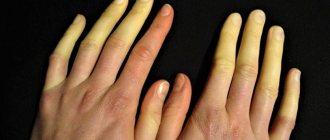
Your hair is falling out at an alarming rate
Telogen effluvium is the medical name for hair loss caused by extreme stress. A change of job, childbirth and even the flu can be a sufficient reason for hair loss. Of course, everyone experiences hair loss, but how much hair loss is too much? If you notice twice as much hair as usual on your brush—and for longer than two weeks—stress may be the cause.
Another symptom of hair loss due to stress is dime-sized bald patches. Alopecia areata is a disorder in which the immune system attacks the hair follicles, and although the exact causes are unknown, stress is a known trigger.
Whatever the reason, don't ignore it
If you suspect stress is wreaking havoc on your hair, make an appointment with your doctor to rule out underlying causes (such as hormonal changes and anemia). And focus on methods of stress relief - a miracle will not happen overnight, but someday you need to take the first step. And the sooner the better.
Source: https://zdorovie.com/beauty/how-stress-ruins-your-hair/32616
Trichotillomania is a psychological disorder that directly affects hair health. With trichotillomania, there is an irresistible desire to pull out your own hair, which subsequently leads to baldness and damage to the scalp.
Pulling hair in this manner helps trichotillomania patients relieve tension and anxiety. However, such a habit can also appear during periods of inactivity and calm.
Such hair pulling leads to severe thinning of the hair on a certain area of the head. However, complete baldness is not usually observed. This disease should be distinguished from alopecia areata, in which we are dealing with a completely bald and smooth area of the scalp. Also, when diagnosing the disease, other ailments in which baldness is observed (syphilis and fungal infections) must be excluded.
A type of trichotillomania is the disease trichothemamania, in which the patient selectively pulls out only gray hair, claiming that pulling out helps relieve itching of the head.
So, as noted earlier, the main causes of the disease are various psychological disorders: neurotic conditions, schizophrenia, stress, severe anxiety, psychological trauma in childhood. According to patients, hair pulling provides some psychological relief and also helps hide unwanted emotions. However, many try to hide their habit from others, denying it completely, or indeed simply do not notice that they are actually pulling out hair unknowingly.
Recent studies also suggest that one of the causes of this disease is damage to a certain gene - SLITKR1. However, the genetic nature of the disease has not yet been fully confirmed.
Sometimes, in particularly difficult cases, additional medical treatment may be required, during which the patient is prescribed antidepressants or antipsychotics (however, in this case we are most likely dealing with a serious psychological disorder, in which trichotillomania is only one of its external manifestations).
https://www.healthyhair.ru/trihotillomania.html
Source: https://kst27.ru/index.php/dopinfo/560-2014-03-24-03-15-59
See also:
- Herpetic stomatitis description Herpetic stomatitis - features of manifestation and methods of treatment Damage to the oral mucosa always causes extremely unpleasant sensations. When symptoms of inflammation appear, many do not dare to see a doctor because of a “banal” infection. As a result, the condition can significantly […]
- To Egypt with vitiligo Vitiligo disease - How to cure vitiligo with folk remedies forever White spots on the skin can appear for various reasons. But if they have clear edges, do not peel, and are especially noticeable after sunbathing, then most likely the cause of the white spots is vitiligo. Find out what this […]
- Dimexide in the treatment of boils Toenail fungus causes a lot of trouble. A person has to use all possible methods to get rid of this disease - after all, peeling, crumbling nails, cracks in the skin are visible to the naked eye. If the patient does not treat the disease in time, internal [...]
- Atopic dermatitis exudative form Atopic dermatitis (diffuse neurodermatitis) is a chronic inflammation of the skin caused by genetic predisposition and climate characteristics. The disease occurs due to an inadequate response of the immune system to external and internal stimuli: sunlight, hypothermia, […]
- Hypertonic solution for boils How to treat boils at home: methods Anyone who has experienced pain from furunculosis finds it difficult to confuse them with ordinary pimples. Sometimes furunculosis can be treated at home. But there is no need to refuse official treatment. What is a boil? This is a purulent formation, very [...]
- Warts on the feet Warts on the feet and their treatment Photo Causes of warts The appearance of any type of wart is the result of infection with the human papillomavirus. The most common route of infection is through household contact. If there are microdamages in the skin, the virus easily penetrates the skin and capillaries [...]
- What is allergic dermatitis? Allergic dermatitis - symptoms and treatment Allergic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that occurs in response to exposure to an irritating factor (allergen). In the development of the allergic form of dermatitis, the body’s predisposition to allergic reactions is of great importance. Reaction […]
- Granuloma of the tooth has resolved Cysts and granulomas Granuloma and cyst are tumors that form in the bone tissue of the jaw, at the apex of the tooth, in the area of its root. As a rule, these are consequences of infection of the tooth canals, poorly treated or not treated at all. Both granuloma and cyst are dangerous because they cannot be identified [...]
Folk remedies
Treatment of trichotillomania in children and adults at home includes the use of proven folk remedies. Garlic oil, which you can buy or make yourself, is highly effective for this disease. The recipe for its preparation is simple: grind a head of garlic to a mushy state, pour in one glass of unrefined sunflower oil, and also the fresh juice of half a lemon. Children should be given the drug three times a day, a teaspoon. Adults can add a few tablespoons of cognac to the medicine.
Another folk remedy will help restore your psycho-emotional state and get rid of trichotillomania faster, the preparation of which requires mixing lemon, crushed with zest, honey and twelve apricot kernels. It is recommended to take the medicine twice a day, take a spoonful.
Successful treatment of trichotillomania is recommended to be supported by preventive measures aimed, first of all, at eliminating stressful situations and normalizing the psycho-emotional state. Regular exercise, an interesting hobby, high social activity, and a balanced diet will help with this, helping to saturate the body with essential vitamins.
How often do you touch your hair when you’re worried, or maybe you’ve noticed that your child or just a good friend does this? Psychologists warn that the habit of touching your hair too often can become pathological and develop into trichotillomania. This seemingly innocent habit can lead to serious psychological and even physical problems - pulling out hair causes not only a cosmetic defect, but also the formation of bleeding bald patches.
Trichotillomania is a psychopathological condition, which is one of the types of obsessive-compulsive neurosis and is manifested by the desire to pull out one’s own hair. May be associated with eyelash, eyebrow, body hair pulling and/or hair eating.
Most often, children aged 2 to 6 years and young women suffer from this pathology; less often, a similar neurosis develops in older women and men.
Trichotillomania occurs as a reaction to stress, acute or chronic. Causing pain to themselves, patients perform obsessive actions that calm them down and help get rid of internal tension and fear. Hair pulling occurs unconsciously; the person does not control himself at this moment and, as a rule, is very ashamed of his behavior and tries to hide the “habit” and its consequences.
In severe mental disorders, patients pull out large amounts of hair - bald spots form on the head, eyelashes or eyebrows, and body hair can also be torn out. Less pronounced forms are often not diagnosed, especially in childhood - they scold the child, try to wean him from the habit of “twisting his hair”, without trying to understand the reasons for this behavior.
It is quite difficult to understand why some people begin to pull out their hair when stressed. Until now, scientists have not come to a consensus about the reasons for the development of trichotillomania.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder, which includes trichotillomania, develops when several factors influence the human psyche.
The most important predisposing factors include:
- Hereditary predisposition – a genetic predisposition to the development of certain mental illnesses has long been proven. Obsessive-compulsive disorder also develops more often in those people whose relatives suffered from neuroses or psychopathologies.
- Other psychopathological disorders - prolonged depression, phobias, dementia or schizophrenia can also lead to the development of this syndrome.
- Brain injuries - pathological changes in the cerebral cortex as a result of injury or illness can cause the development of trichotillomania.
- Hormonal imbalance - a decrease in the level of serotonin and some other hormones can cause the development of neurosis.
The development of the disease can be triggered by:
- Stress - the first signs of illness most often occur after suffering stress - fear, loss of loved ones, divorce, scandals.
- Neuroses - trichotillomania in children usually accompanies another obsessive disorder.
- Depletion of the nervous system - vitamin deficiency, chronic fatigue and lack of sleep, diets, infectious and chronic somatic diseases cause general depletion of the body and nervous system. Against this background, stress and psychological trauma are tolerated much worse by patients and neuroses may arise against their background.
- Consumption of alcohol and drugs - these substances cause intoxication of the nervous system and also weaken it.