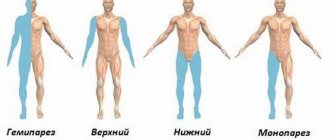
Peripheral paralysis is the result of damage to peripheral neurons responsible for motor functions. This results in loss of reflexes, degenerative muscle atrophy and hypotension.
In addition, it should be noted that the process of changing electrical excitability in the affected nerves, which is called degeneration, also starts. The severity of the disease is indicated by the depth of changes in electrical excitability.
Atony and loss of reflexes occurs due to a break in the functioning of the reflex arc, and at the same time the muscles lose tone. This factor prevents the corresponding reflex from being evoked. The disconnection of muscles from the neurons of the spinal cord causes their sudden weight loss and atrophy.
From neurons that are connected to muscles, impulses responsible for normal metabolism in the area of muscle tissue flow through the peripheral nerve.
When muscles are damaged, fibrillar twitching is observed, which looks like rapid contractions in the area of individual muscle fibers. Basically, such processes occur in the chronic form of the disease.
Peripheral paralysis occurs when a peripheral nerve is damaged. In this case, sensitivity may be lost, and as a result, autonomic disorders develop in the affected area.
Disease development process
The development of peripheral paralysis is associated with damage to the neuron responsible for movement and its axon.
If only the nuclei of the cranial nerves and anterior horns are affected, then spinal muscular atrophy may develop in parallel with flaccid paralysis. In addition, these two ailments are accompanied by characteristic fascicular twitching. When a peripheral nerve is deformed, there is a high chance that the innervated muscle will be paralyzed.
Peripheral and central paralysis are 2 pathologies that are often mistaken for one disease or even confused.
But these are different violations. With central paralysis, motor functions of the entire body are lost, the muscles are in constant tension. In addition, there are no signs of degeneration and the muscles do not atrophy. In the case of damage to the peripheral parts, the picture is different, or rather completely opposite.
Peripheral paralysis is a disease in which there is a decrease in muscle tone and paralysis of individual parts of the body.
Flaccid paralysis or what happens in the periphery of the nervous system
Peripheral paralysis is the result of damage to peripheral neurons responsible for motor functions. This results in loss of reflexes, degenerative muscle atrophy and hypotension.
In addition, it should be noted that the process of changing electrical excitability in the affected nerves, which is called degeneration, also starts. The severity of the disease is indicated by the depth of changes in electrical excitability.
Atony and loss of reflexes occurs due to a break in the functioning of the reflex arc, and at the same time the muscles lose tone. This factor prevents the corresponding reflex from being evoked. The disconnection of muscles from the neurons of the spinal cord causes their sudden weight loss and atrophy.
From neurons that are connected to muscles, impulses responsible for normal metabolism in the area of muscle tissue flow through the peripheral nerve.
When muscles are damaged, fibrillar twitching is observed, which looks like rapid contractions in the area of individual muscle fibers. Basically, such processes occur in the chronic form of the disease.
Peripheral paralysis occurs when a peripheral nerve is damaged. In this case, sensitivity may be lost, and as a result, autonomic disorders develop in the affected area.
Factors influencing the development of the disorder
Symptoms of flaccid paralysis, such as loss of motor function, are not an independent disease; they are often caused by concurrent illnesses.
Essentially, paralysis is a disorder in which a person makes involuntary movements. In some cases, patients cannot move part of the body or are completely immobilized.
Partial loss of motor functions indicates paresis. In any case, the disorder is evidence of damage to the nervous system, namely the centers that are responsible for movement and the peripheral parts. The following factors are noted as influencing the development of pathology:
- previous injuries;
- metabolic problems;
- infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, encephalitis, meningitis and polio);
- nutritional and toxic (pellagra, beriberi, heavy metal poisoning);
- oncological diseases;
- congenital and hereditary factor;
- intoxication;
- disruption of the nutrition system;
- diseases whose etiology remains unknown, for example, multiple sclerosis.
Drug therapy
Treatment of flaccid paralysis requires an integrated approach. The main goal of therapy is to restore the normal functioning of motor neurons. Patients are prescribed nootropic and antioxidant drugs in high doses:
- "Piracetam."
- "Actovegin".
- "Mexidol".
- "Trental."
- "Cerebrolysin".
These medications help normalize metabolism in damaged nerves and protect neurons from harmful effects.
A course of injections of the drug “Proserin” is shown. This remedy improves signal transmission from neurons to muscles and helps increase muscle tone.
Be sure to prescribe a course of vitamin therapy. It is necessary to take high doses of drugs, most often the drugs are administered intramuscularly. For treatment, vitamins B 1 and B 12 are used, which have a positive effect on the condition of the nervous tissue.
Characteristic manifestations
Signs of peripheral paralysis:
- complete or partial loss of motor functions;
- decreased muscle tone in the affected part;
- complete or partial absence of any reaction to sudden irritation of paralyzed muscles;
- denervation atrophy is observed, that is, loss of muscle mass;
- a reaction of degeneration or degeneration is also observed.
Over time, if a person does not receive proper treatment, peripheral paralysis can develop into another form, that is, an acute infectious disease. It is often found under the name polio. It is characterized by intoxication, while the nervous system also suffers, paralysis and acute flaccid peripheral paresis develop.
This infection is initiated under the influence of a filter virus, which is quite resistant and has increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, disinfectants and high temperature.
When the virus penetrates a neuron, a dystrophic-necrotic process is triggered, which is accompanied by the replacement of all dead neurons with glial tissue and subsequent scarring. In turn, the more neurons die, the faster paresis or paralysis occurs.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostic measures involve performing a whole range of examinations:
- examination by a specialist – neurologist;
- basic tests are taken (general blood test and toxic);
- instrumental diagnostics (electroneuromyography, computed tomography, electroencephalography and magnetic resonance angiography);
- an analysis of the patient’s complaints and medical history is carried out (the time of muscle inactivity is identified, the causes of complaints and the presence of these in other relatives and what caused such a reaction, that is, place of work, etc.);
- Often you are examined by a neurosurgeon.
In addition to the basic methods, specialists carry out differential diagnosis of the disease. At the same time, symptoms are identified that are very easily confused with signs of central paralysis.
In addition, do not forget that in some cases, the lack of motor functions can be caused by any kind of injury and such a symptom is not always a sign of peripheral paralysis. Therefore, a complete examination of the patient is carried out to identify such injuries.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of neuronal damage. If diagnosis and treatment were carried out in a timely manner, then it is quite possible to restore movement. However, this will require long-term complex therapy and rehabilitation. Typically, the process of restoring motor function takes about 2 years. After surgical treatment, movements return to normal after about 1 year.
In advanced cases, it is no longer possible to restore movement even with surgery. If a patient has lost more than 70% of neurons, then such changes are considered irreversible.
Health care
First of all, treatment is aimed at getting rid of the causes contributing to the development of the disease.
In some cases that are particularly complex, specialists resort to surgical intervention. In this case, only the part of the spinal cord on which the damaged muscles are located is affected. But we should not forget that peripheral paralysis may not be a consequence of some other disease, but it is quite likely that it will develop as an independent form of pathology.
A whole range of measures is used in treatment. In this case, both medications and more common methods such as physical therapy and massage are used.
The main task of specialists is to fully restore the patient’s motor functions. If this is done, the chance of developing other processes leading to deformation against this background is significantly reduced.
All this time, the patient must be under the supervision of a neurologist and follow all his instructions, including taking individually prescribed medications.
Among the medications that are often prescribed to patients suffering from flaccid paralysis are:
- Prozerin;
- Dibazol;
- Mellictin;
- thiamine chloride solution.
In addition, physiotherapeutic treatment is now actively used. This process takes quite a long time, but, nevertheless, this type of treatment is the most effective. If only this type of treatment is used, motor functions may not fully return, so a whole range of measures is required.
Acute flaccid paralysis in children and adults
With the development of flaccid paralysis, treatment procedures are aimed at restoring (if possible) the functioning of the peripheral neuron, and in addition to preventing the process of muscle tissue atrophy and the possible occurrence of contracture.
Medicines
To improve the functioning of nervous tissue, treatment with vasoactive and neurotropic drugs is necessary:
- nootropil or piracetam (tablet/capsule at a dosage of 0.4-0.8 g 3 times/day or 20% solution at a dosage of 5-10 ml IM or IV);
- Cerebrolysin (in a dosage of 3-5 ml IM or IV);
- Actovegin (in a dosage of 5-10 ml IM or IV through a dropper 1-2 times/day; 1 ml of the drug contains 40 mg of the active ingredient);
- trental (dragées in a dosage of 0.1 g 3 times / day or intravenously through a dropper 1 time / day in a dosage of 5 ml; 1 ml of medicine contains 0.02 g of the active ingredient).
Vitamins
Vitamins are also taken:
- vitamin B1 (solution 2.5% (thiamine chloride) or 5% (thiamine bromide), 3% or 6% at a dosage of 1 ml IM every day 1 time/day);
- vitamin B12 (dose 400 mcg 1 time/2 days IM, can be combined with vitamin B1, but they cannot be mixed in one syringe).
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Acute flaccid paralysis can be effectively treated with electrotherapy and other physical therapy methods. Basically, for this disease, balneotherapy and galvanization are prescribed.
Massage for flaccid paralysis
In the case of flaccid paralysis, massage is carried out to stimulate the muscular system, which is why deep kneading is used when performing it, and with it rubbing with high intensity, and in addition to this, the massage therapist actively influences the so-called segmental zones. But at the same time, you cannot massage paretic muscles with excessive force - the procedure should be short and moderate. It must be carried out over many months (short breaks should be taken between treatment courses). If you perform rough, painful techniques, the muscle, on the contrary, may begin to weaken.
In addition, acupressure is performed using a tonic technique. In this case, it is necessary to press the necessary points with the tip of your finger in order to cause quick short vibrating irritations that will stimulate the necessary movement.
Traditional and herbal treatment
There are several recipes for traditional treatment:
Roots of the evasive peony. You need to take 1 tsp. dry ingredients and pour boiling water (3 cups), then cover the container and leave for 1 hour, then strain. You need to drink the tincture three times a day. 1 tbsp each before meals (15 minutes before). Alcohol tincture should be taken in a dosage of 30-40 drops. 3 rubles/day before eating.
Dying or tanning sumac (fresh leaves are used). Take 1 tsp. ingredient and pour boiling water (1 cup), cover the container and leave for 1 hour, then strain. Drink 3-4 times a day. 1 tbsp each
Rosehip fruits and roots. A decoction of the roots is used externally - in case of paralysis, you need to bathe your feet in a bath with it.
Surgical treatment
In case of destruction of the anatomical integrity in the peripheral nerve system, the patient may be prescribed a neurosurgical operation.
Preventive actions
In order to avoid the development of disorders, experts recommend following the following instructions:
- Seeing a doctor at the slightest symptoms of the disease or any other problems;
- blood pressure should always remain under control;
- treating infectious diseases in their early stages, preventing them from causing more serious problems;
- It is best to eliminate all bad habits - alcohol and smoking contribute to the development of many health problems, not only peripheral paralysis;
- effective prevention is maintaining a healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, rest, adherence to a routine and physical activity).