Werdnig-Hoffmann disease is a spinal muscular atrophy characterized by degeneration of nerve cells within the lower region of the brain (brain stem) and some motor neurons in the spinal cord (anterior horn).
More than 80% of infants experience severe weakness before the age of 6 months and almost all of them will never achieve the ability to sit independently. Muscle weakness, lack of motor development and poor muscle tone are the main clinical manifestations of this disease. Most babies also have trouble sucking or swallowing. Some show signs of abdominal breathing during the first few months of life. Most children die before age 2 years, but survival may depend on the degree of respiratory function and respiratory support.
Werdnig-Hoffman disease is divided into five subtypes. This division is based on the age at which the first symptoms/manifestations appear, the course and progression of the disease. Subtype 0 is characterized by extreme weakness at birth, and all children require immediate mechanical ventilation almost from birth. These children will never be able to breathe on their own. Subtype 1 is characterized by acute spinal muscular atrophy, with symptoms and signs appearing around 6 months of age. In patients with subtype 2, symptoms and manifestations appear before the age of 1 year. Children with this subtype may learn to sit, but they will never be able to walk. Symptoms and manifestations of subtype 3 (Kugelberg-Welander disease) appear after the age of 1 year. This subtype progresses over a period of time to loss of motor ability. In individuals with the fourth subtype, the first symptoms and manifestations appear at the age of about 10 years.
Etiology of Werdnig-Hoffmann disease
Werdnig-Hoffman disease ( spinal muscular amyotrophy ) is characterized by pathology of the nerve cells of the spinal cord, resulting in the drying out of muscle fibers intertwined with healthy ones. This process is caused by an insufficient amount of protein responsible for the survival of motor neutrons. There are forms of the disease not associated with this pathology, caused by other modifying factors.
Disruption of the functioning of nerve cells leads to the proliferation of connective tissue, which replaces muscle tissue. The patient's swallowing process, musculoskeletal and respiratory functions are impaired. Mental development is not affected. The sensitivity of the parts of the body affected by the disease does not decrease.
Werdnig-Hoffman disease is hereditary, transmitted from two parents who are carriers of the pathological SMN gene, located on chromosome 5. However, they have no symptoms of the disease. Such a couple can give birth to healthy children or also carriers of the gene; the probability of giving birth to a sick baby is 25%.
Famous people with this disease: English astrophysicist Stephen Hawking and Russian IT specialist Valery Spiridonov from Vladimir.
Treatment methods
Treatment of spinal amyotrophy is symptomatic and aimed at stabilizing the patient's condition.
Medicines prescribed :
- improving metabolism - cerebrolysin, lipocerebin, aminalon;
- affecting the trophism of muscle tissue - potassium orotate, glutamic acid, methionine, tocopherol acetate;
- promoting neuromuscular conduction - prozerin, galantamine, dibazol;
- stimulating blood circulation in capillaries - complamin, nicotinic acid;
- supporting the viability of motor neurons - valproic acid, riluzole, L-carnitine.
Patients are prescribed orthopedic procedures in combination with warm baths, therapeutic exercises, gentle massage, oxygen therapy, and sulfide baths are indicated.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of the disease directly depend on its form; the study reveals the following clinical indicators:
- Malnutrition of muscle cells leads to their death. First, the muscles of the trunk are affected, primarily the back, then the process moves to the area of the shoulders, hips, and limbs;
- increasing pain;
- decreased muscle tone;
- muscle twitching;
- reduction in the diameter of long bones, detected by radiographs;
- curvature of the spine to one side and backward;
- established limitation of muscle function (does not bend or relax).
Symptoms indicating the presence of spinal muscular amyotrophy:
- muscle weakness, manifested in disruption of motor processes;
- due to thinning of the bones, the limbs become smaller;
- paucity of facial movements;
- swallowing and sucking reflexes are reduced or absent;
- if the intercostal muscles are damaged, breathing is impaired, and as a result, inflammatory and congestive processes in the bronchi and lungs;
- deformation of the skeletal system in the chest and spine;
- tremor of hands and feet;
- inhibition of physical development processes.
How is spinal amyotrophy treated?
Unfortunately, with early forms of the disease, the death of the child is inevitable. There are no means that could stop the progressive paralysis of vital centers. But, in the case of late development of symptoms, it becomes important to periodically take nootropic drugs, vitamins, and agents to improve the conductivity of neuromuscular impulses. Physiotherapeutic sessions, massage courses, exercise therapy are indicated, and if severe deformation of the chest has occurred or contractures have formed, then surgical orthopedic correction is indicated.
Forms and stages of the disease
Spinal muscular amyotrophy in most cases manifests itself in the first year of a child’s life. The earlier, the more severe its course. The mortality rate is high, most children die before the age of 4, rarely before the age of 20. It can also occur in adults. There are three main forms of the disease:
- Congenital Werdnig-Hoffman disease. The first symptoms appear immediately after birth or during the prenatal period. At the same time, fetal movements subside. The newborn has disturbances in the processes of breathing, sucking and swallowing. The child does not hold his head up, does not roll over, and screams weakly. The course of the disease is severe, acute, life expectancy is short, up to 2 – 2.5 years. However, in some cases, with the help of modern artificial lung ventilation devices and feeding not through a tube, but directly into the stomach, the patient’s life can be extended. The child develops mentally and emotionally without disturbances.
- The second form, early childhood. The child's development proceeds in accordance with the norms. He begins to hold his head up in time and roll over. Until six months, parents do not notice any symptoms. After an infection, the disease manifests itself in the form of peripheral paralysis of first the lower, then the upper extremities, and ultimately the entire torso; acquired skills are lost and muscle tone decreases. Tremors of the fingers and involuntary muscle contractions of the tongue occur. At a later stage, difficulty in the functioning of the respiratory system occurs. The course of the disease is not rapid, as with the congenital form; some children can live into adolescence. The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of damage to the muscles responsible for the respiratory process.
- Third form, late. The first symptoms appear after 2 years. By this time, the baby has already developed physically and psychologically according to age standards. The progression of the disease occurs slowly, gradually, and is characterized by lethargy and clumsiness of the child when walking and other motor processes. Paresis of the limbs develops, extinction of the swallowing and tendon reflex, signs of bulbar palsy, as well as deformation of bone tissue. The third form is milder than the first two, patients can live up to 30 years.
There are forms of spinal muscular amyotrophy that manifest themselves at a later age.
- Kuldberg-Welander disease is considered the mildest form of childhood atrophy. In most cases, the onset of the disease occurs during adolescence, but there are also earlier manifestations.
There are cases where patients do not lose the ability to walk and care for themselves, living a long life.
- Kennedy disease is associated with a gene mutation on the X chromosome and is transmitted to girls from two parents, and to boys from their mother. Appears in adulthood.
The malignant course of the congenital Werdnig-Hoffmann form gives little chance for planning the future of such children, however, with forms 2 and 3, it is possible to prolong the child’s life; it is important to respond in time to infectious diseases that sharply worsen the patient’s condition and lead to the appearance of new symptoms, the worst of which - respiratory dysfunction.
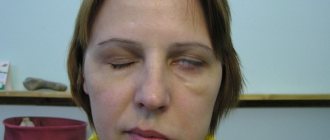
External manifestations of Werdnig-Hoffman disease
What is the danger of the disease?
Due to the fact that Werdnig-Hoffmann disease is incurable, the most important danger is death. With the congenital form, children live for a fairly short period of time, the disease progresses quickly and leaves no chance of survival.
With the help of modern research, it is possible to detect the presence of a disease in the fetus during pregnancy and prevent the birth of a seriously ill child.
In other forms, the disease shows its first signs after an intestinal or respiratory infection; subsequently, parents, under the guidance of attending physicians, limit the possibility of the child developing an infection, which will aggravate its course and pose a mortal danger. However, bronchitis, pneumonia and other diseases of the ENT organs are often found in patients with Werdnig-Hoffmann disease.
General information
So, spinal muscular atrophy includes diseases that differ somewhat in the type of occurrence and nature of the course of the disease. This type of disease was first described in 1891 by the scientist Verdingt. Subsequently, his research was supplemented by a description of the disease by another specialist, Hoffman. As a result, the most common muscle atrophy in children is called Werding-Hoffmann amyotrophy.
Neuron
Diagnosis and treatment of Werdnig-Hofmann disease
In the early stages of the disease, it can be difficult to differentiate the disease, since the symptoms may be similar to other diseases :
- acute poliomyelitis is characterized by the absence of disease progression and asymmetrical paralysis;
- myopathy – also of hereditary origin, has a progressive course, but the cause of muscle weakness is a violation of metabolic processes in them;
- congenital myatonia is most similar to Werdnig-Hoffmann disease; they can be distinguished quite easily using a biopsy of muscle tissue.
To diagnose the disease, a neurologist will need data on the first manifestation of symptoms, the nature of their development, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
A number of studies are carried out to make a diagnosis:
- Electroneuromyography reveals disturbances in the functioning of the neuromuscular system. Changes in the muscle type are observed, which indicates pathology of the motor neutron;
- Genetic analysis reveals a mutation in the SMN gene;
- Blood biochemistry for the level of creatine kinase, indicators within the normal range do not exclude the disease;
- Muscle biopsy for morphological examination, which reveals fascicular atrophy of muscle fibers alternating with healthy ones, as well as proliferation of connective tissue;
- MRI to rule out other diseases.
To diagnose the fetus in utero, chorionic villus biopsy, cordocentesis, and amniocentesis are used. Detection of the disease is an indication for termination of pregnancy. It is impossible to cure a patient with Werdnig-Hoffman disease. To prolong life and improve its quality, symptomatic treatment is used. The development of the disease and the worsening of symptoms are restrained by ensuring the functioning of metabolic processes in muscle tissue.
With the help of physical therapy and massage, blood circulation is improved, the risk of congestion is reduced, muscle performance is maintained, and joint immobility and loss of elasticity are prevented. Loads should be short and careful. Physiotherapy helps to maintain motor skills at the existing level and strengthen them. Special devices will help you move independently, use a computer, and even write. Portable ventilators enable patients to stay outside the hospital and live their lives more productively.
Causes
Werdnig-Hoffmann amyotrophy is a hereditary pathology encoded by a breakdown in the genetic apparatus at the level of the 5q13 locus of the 5th chromosome. The gene in which mutations occur is called the survival motor neuron gene (SMN) - the gene responsible for the survival of motor neurons. 95% of patients with Werdnig-Hoffmann disease have a deletion of the telomeric copy of this gene. The severity of SMA directly correlates with the length of the deletion site and the concomitant presence of changes (recombination) in the H4F5, NAIP, and GTF2H2 genes.
The result of aberration of the SMN gene is the underdevelopment of spinal cord motor neurons localized in its anterior horns. The consequence is insufficient innervation of the muscles, leading to their severe atrophy with loss of muscle strength and progressive decline in the ability to perform active motor acts. The main danger is weakness of the chest muscles, without which movements that ensure respiratory function are impossible. At the same time, the sensory sphere remains intact throughout the disease.