Overdose and side effects
For adults and children over 12 years of age, when taken orally, the daily dose is 4-80 mg of the drug
. In the chronic course of the disease and in resistant cases, the daily dose can be increased to 150-400 mg. The frequency of administration and duration of treatment are determined individually.
For adults and children over 12 years of age, with intramuscular administration, a single dose is 5-10 mg. For intravenous administration, a single dose is 1 mg.
Maximum doses: adults and children over 12 years of age with intramuscular administration - 15-30 mg/day, with intravenous administration - 5 mg/day.
Overdose symptoms
a sharp increase in side effects from the central nervous system, an increase in body temperature, severe depression of consciousness, even to the point of coma, should alert you to the development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Treatment in intensive care unit or intensive care unit, diazepam and dextrose solution are administered, symptomatic therapy is carried out, and the activity of organs and systems is supported.
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are ineffective.
One of the drugs widely used to treat certain conditions is Etaperazine. Instructions for its use are mandatory for both doctors and patients. It covers cases of drug overdose, both accidental and intentional. The consequences can be quite serious: from the appearance of acute neuroleptic symptoms and fever to impaired consciousness and coma.
The initial dosage of the drug is 0.012 g. Instructions for use of Etaperazine indicate that the daily dosage can be increased to 0.06 g, and for some patients up to 0.12-0.18 g. A dose of 0.002-0.004 g is prescribed as an antiemetic in obstetrics , therapeutic and surgical practice. Instructions for use of Etaperazine recommend taking the product 3-4 times every day.
When using the drug in high doses, acute neuroleptic symptoms may occur. In such cases, the temperature often rises. In severe situations, impaired consciousness may occur, and coma is also possible.
The drug should be stopped immediately. Intravenous administration of Diazepam, nootropic drugs, dextrose solution, vitamins B and C is indicated. Treatment is symptomatic.
An overdose is fraught with exacerbation of neuroleptic manifestations. This is most often indicated by hyperthermia, impaired consciousness and coma. To prevent undesirable consequences, you should stop taking the medicine and administer nootropic medications, Diazepam, ascorbic acid or ampoule B vitamins intravenously.
At the beginning of therapy, the use of Etaperazine may be accompanied by adverse reactions from the skin, gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system:
- arrhythmia;
- intestinal atony;
- diarrhea;
- photosensitivity;
- disturbances of accommodation;
- decreased appetite;
- epigastric pain;
- decreased blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- angioedema;
- difficulty urinating.
Very rarely, an antipsychotic provokes extrapyramidal disorders: tremors of the limbs, impaired coordination of movement, dizziness, etc. If they occur, you should stop taking the medication and consult a doctor.
Side effects of antipsychotics are as follows:
- neuroleptic syndrome is an increase in muscle tone, but the patient experiences a slowdown in movements and other responses;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- excessive sleepiness;
- changes in standard appetite and body weight (increase or decrease in these indicators).
In case of an overdose of antipsychotics, extrapyramidal disorders develop, blood pressure drops, drowsiness, lethargy occurs, and a coma with suppression of respiratory function is possible. In this case, symptomatic treatment is carried out with the possible connection of the patient to mechanical ventilation.
If something went wrong
The drug "Etaperazine" and analogues of this medicine can cause side effects when used even in recommended dosages.
Most often, extrapyramidal disorders occur, manifested in changes in muscle tone, disturbances in motor activity, as well as the appearance of twitching (hyperkinesis) or immobility (hypokinesia). But this is not the only side effect that can occur as a result of taking Etaperazine. The following problems may also occur:
- agranulocytosis;
- hemolytic anemia;
- amenorrhea;
- arrhythmia;
- asthma;
- atony of the intestines and bladder;
- anxiety;
- pallor;
- abdominal pain;
- bradycardia;
- lethargy;
- gynecomastia in men;
- hyperactivity;
- glaucoma;
- dizziness;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- lethargy;
- itching;
- change in libido;
- change in heart rate;
- insomnia;
- perspiration;
- skin rash;
- leukopenia;
- lethargy;
- fever;
- mydriasis;
- miosis;
- muscle weakness;
- menstrual irregularities;
- nighttime confusion;
- fainting;
- orthostatic hypotension;
- paradoxical reactions - exacerbation of psychotic symptoms;
- pigmentary retinopathy;
- increased appetite and body weight;
- decrease/increase in blood pressure;
- hives;
- skin pigmentation,
- increased intraocular pressure;
- vomit;
- dry mouth;
- bile stasis and cholestatic hepatitis;
- tachycardia;
- nausea;
- thrombopenic purpura;
- enlarged mammary glands and galactorrhea in women;
- skin photosensitivity;
- photophobia;
- eczema;
- exfoliative dermatitis;
- eosinophilia;
- erythema
Such an abundance of possible undesirable health problems makes taking the drug “Etaperazine” extremely careful; only in case of an established diagnosis is it possible to prescribe it for use.
Contraindications
The following contraindications to the use of this drug are known: progressive systemic diseases of the brain and spinal cord, cirrhosis, hemolytic jaundice, hematopoietic disorders, thromboembolic diseases, pregnancy, breastfeeding, hepatitis, nephritis, myxedema, decompensated heart disease, hypersensitivity to the active substance, late stages of bronchiectasis .
Contraindications to the use of the drug
are: hypersensitivity, coma or severe depression of the central nervous system, incl. against the background of the prescription of high doses of drugs that depress the central nervous system (barbiturates, alcohol, narcotics, analgesics, antihistamines), blood dyscrasia, inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis, liver disease, suspected or established subcortical brain damage with or without hypothalamic injury, heart pathology, organic diseases CNS.
Antipsychotic drugs are not recommended for people with severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Contraindications to prescribing the medication are:
- chronic alcoholism;
- Parkinson's disease;
- stomach ulcer;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- breast carcinoma;
- cachexia;
- liver failure;
- violation of intracardiac conduction;
- pathologies of bone marrow hematopoiesis.
It is undesirable to use antipsychotic medications for pathologies of the brain and spinal cord, as well as decompensated hypothyroidism.
It is recommended to take antipsychotics for the following neurological and psychological disorders:
- schizophrenia;
- neuralgia;
- psychosis;
- bipolar disorder;
- depression;
- anxiety, panic, restlessness.
Contraindications:
- individual intolerance to drugs of this group;
- presence of glaucoma;
- defective liver and/or kidney function;
- pregnancy and active lactation period;
- chronic heart disease;
- coma;
- fever.
If the drug cannot be taken
The medicine “Etaperazine”, analogues of this drug, like all medical substances, have their contraindications for use. It should not be prescribed or taken in the following cases:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- bronchiectasis in late stages;
- hemolytic jaundice;
- hepatitis;
- myxedema;
- hematopoietic disorders;
- nephritis;
- heart disease in the stage of decompensation;
- progressive systemic diseases of the brain and spinal cord;
- thromboembolic diseases;
- cirrhosis.
Also, this medical drug is not prescribed in case of hypersensitivity to the active substance perphenazine. "Etaperazine" is prescribed with extreme caution in the following cases:
- prostate adenomas;
- Parkinson's disease;
- glaucoma;
- depression;
- during alcohol withdrawal;
- for convulsive disorders;
- renal failure;
- breathing disorders of various etiologies;
- epilepsy.
The drug is not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age. You should especially remember about pregnant and breastfeeding women - the substance penetrates the placental barrier and into breast milk and can cause significant harm to the health of the fetus or newborn baby.
Pharmacological properties
Etaperazine has antipsychotic, muscle relaxant, hypotensive, antiallergic and sedative effects. The effectiveness of the drug is due to inhibition of the activity of D2 receptors, which are localized in the mesolimbic and mesocortical systems.
By blocking adrenergic receptors in the reticular region of the brain, perphenazine has a calming effect on the central nervous system. In the usual amount, the antipsychotic does not increase the hypnotic effect and muscle fatigue.
The active components of the antipsychotic drug inhibit dopamine receptors in the vomiting center, which is located in the brain. This ensures the antiemetic and hypothermic activity of the tablets.
The drug is antipsychotic. It has a sedative and antiemetic effect.
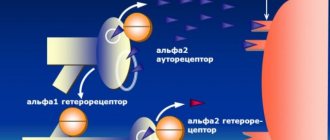
How does the drug work?
All the necessary information about the drug “Etaperazine” is contained in the instructions for use. Analogs of this substance should have a similar effect, although they may differ in specific purposes, possible side effects, and dosage of the drug. The decision about which remedy needs to be taken in a particular situation is made by the attending physician. Once in the human body, the active substance primarily affects the central nervous system (CNS). Thanks to its ability to block alpha-adrenergic, dopamine, histamine, m-cholinergic, serotonin receptors, the drug has a blocking effect on the occurrence of delusions and hallucinations, lethargy and lethargy syndromes. This substance also affects the occurrence of extrapyramidal syndromes and an increase in the level of the hormone prolactin in the blood (hyperprolactinemia), produced by the pituitary gland. This drug has a strong antiemetic effect due to the inhibition of D2-dopamine receptors in the area of the vomiting center and by reducing the secretion and motility of the gastrointestinal tract as a result of blockade of m-cholinergic receptors.
Interaction with medications
The drug of the neuroleptic group “Etaperazine” and its analogs should be prescribed for use with extreme caution, since their interaction with other drugs can lead to serious adverse consequences. Alcohol, as well as drugs that depress the nervous system, in combination with Etaperazine or its analogues will increase the adverse effects on the nervous and respiratory systems, causing disruption in their functioning.
Substances of the neuroleptic group in combination with perphenazine activate the manifestation of extrapyramidal disorders. Treatment of hyperthyroidism with appropriate medications and taking Etaperazine can cause the development of agranulocytosis. Taking this medicine with drugs such as Guanethidine, Levodopa, Clonidine, Epinephrine, or drugs with amphetamine reduces their effectiveness.
The active components of Etaperazine enhance the pharmacological activity of anxiolytics, anesthetics, hepatotoxic and hypnotic drugs.
Suppression of the nervous and respiratory systems increases when combined with drugs that depress the nervous system, as well as ethanol-containing drugs and ethanol.
Combination with drugs that provoke extrapyramidal reactions increases the number and frequency of extrapyramidal disorders. Fluoxetine can also cause extrapyramidal symptoms and dystonia.
Anticonvulsants may lower the seizure threshold, and medications to treat hyperthyroidism may increase the likelihood of agranulocytosis.
Interaction with drugs that provoke arterial hypotension can cause orthostatic hypotension.
Combination with drugs that have anticholinergic effects may lead to increased anticholinergic effects, and the antipsychotic effect of the antipsychotic may be reduced.
READ MORE: Treatment of ulcerative colitis with folk remedies
Concomitant use of Etaperazine with MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants and Maprotiline increases the likelihood of developing NMS. And combination with antacids, lithium salts and antiparkinsonian drugs interferes with the absorption of phenothiazines.
Interactions with amphetamines, Clonidine, Epinephrine, Levodopa and Guanethidine may reduce their effect.
Combination with Ephedrine may weaken its vasoconstrictor effect.
When used simultaneously
with drugs that have a depressant effect on the central nervous system, with ethanol, ethanol-containing drugs, it is possible to increase the depression of the central nervous system and respiratory function.
When used simultaneously with anticonvulsants, the threshold for convulsive readiness may be lowered; with drugs for the treatment of hyperthyroidism - the risk of developing agranulocytosis increases.
When used simultaneously with drugs that cause extrapyramidal reactions, an increase in the frequency and severity of extrapyramidal disorders is possible.
When used simultaneously with drugs that cause arterial hypotension, severe orthostatic hypotension is possible.
When used simultaneously with drugs that have anticholinergic effects, their anticholinergic effects may be enhanced, while the antipsychotic effect of the antipsychotic may decrease.
When used simultaneously with tricyclic antidepressants, maprotiline, and MAO inhibitors, the risk of developing NMS increases.
With the simultaneous use of antacids, antiparkinsonian drugs, lithium salts, the absorption of phenothiazines is impaired.
With simultaneous use, it is possible to reduce the effect of amphetamines, levodopa, clonidine, guanethidine, epinephrine.
When used simultaneously with fluoxetine, the development of extrapyramidal symptoms and dystonia is possible.
With simultaneous use, the vasoconstrictor effect of ephedrine may be weakened.
Notes[ | ]
- Danilov D. S.
Modern classifications of antipsychotic drugs and their significance for clinical practice (the current state of the issue and its prospects) // Review of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology named after. V. M. Betkhereva. - 2010. - P. 36-42. - ↑ 1 2 Mashkovsky M.D.
Medicines. — 16th ed., revised, corrected. and additional - Moscow: New Wave, 2012. - 1216 p. — 5000 copies. — ISBN 978-5-7864-0218-7. - ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6
Guide to the rational use of medicines (formulary) / Ed. A. G. Chuchalina, Yu. B. Belousova, R. U. Khabrieva, L. E. Ziganshina. — GEOTAR-Media. - M., 2006. - 768 p. — ISBN 5-9704-0220-6. - Yurieva L.N.
Clinical suicidology: Monograph. - Dnepropetrovsk: Thresholds, 2006. - 472 p. — ISBN 9665257404. - Drobizhev M. Yu.
Truxal (chlorprothixene) in the treatment of patients in the general somatic network // Psychiatry and psychopharmacotherapy. - 2001. - T. 3, No. 6.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The drug affects the central nervous system. This is an antipsychotic drug that has a wide spectrum of action. It has antipsychotic, antiemetic and cataleptogenic effects. In addition, the drug has alpha-adrenolytic activity. Anticholinergic and sedative effects are weak or moderate. The hypotensive and muscle-relaxing effects are weakly expressed. The neuroleptic effect is combined with a stimulating one.
The drug is also characterized by a selective effect on deficiency symptoms. Significant extrapyramidal abnormalities are possible.
Etaperazine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Significant fluctuations in maximum plasma concentration are possible. Strong binding to plasma proteins. The drug is intensively broken down, mainly in the liver. Excreted through the kidneys and with bile.
General information about the drug Etaperazine
Etaperazine is produced by domestic pharmaceutical companies and is effective in the treatment of psychoses, psychopathological syndromes, and other mental abnormalities.
Drug group, INN, scope of application
The drug belongs to typical antipsychotic drugs. International nonproprietary name (INN) is Etaperazin.
Scope of application: treatment of acute and transient psychotic disorders characterized by depression, delusions, hallucinations, and other constantly changing symptoms.
Release forms and prices for Etaperazine, average in Russia
Available in the form of film-coated tablets, their color depends on the dosage of the drug:
- 4 mg – yellow, light yellow;
- 6 mg – white;
- 10 mg – green, yellowish-green color.
The contour blister pack contains 50 round biconvex tablets. The average price of a blister pack of Etaperazine is shown in the table.
Composition and pharmacoaction
The dosage form contains active and auxiliary components. The active substance is perphenazine dihydrochloride - perphenazine.
Auxiliary ingredients:
- lactose monohydrate – filler, optimizes calcium metabolism, normalizes the composition of intestinal microflora;
- potato starch – has enveloping, anti-inflammatory properties, lowers cholesterol levels;
- calcium stearate – food stabilizer.
The components of the film shell are sucrose, povidone, silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, beeswax, etc.
The drug is a piperazine derivative of phenothiazine and belongs to the group of antipsychotic drugs. The antipsychotic effect of phenothiazine is caused by inhibition of postsynaptic dopamine neurons in the mesolimbic systems of the brain. The piperazine derivative has a strong antiemetic effect. The central action is exerted through blockade of dopamine D2 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the cerebellum. Peripheral – associated with blocking of the pulmonary gastric nerve in the digestive tract. It has an alpha-adrenergic blocking effect, the calming effect is mild to moderate, the hypotensive effect is weak. The antiemetic effect is enhanced by anticholinergic and sedative properties, and also has a muscle-relaxing property.
The active substance of the drug intensively binds to the proteins of the liquid part of the blood. Etaperazine is excreted in bile and partially in urine.
See also:
Instructions for use and reviews of the drug Fibro-Vayne
Storage conditions
This product is sold in pharmacies only by prescription.
Store in a dark place.
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 5–25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
The antipsychotic drug is sold in pharmacy chains with a written prescription from a doctor. Its shelf life is 36 months from the date of issue. The tablets should be stored in a dark place inaccessible to small children at a temperature of 20-25 degrees Celsius.
Etaperazine
Active substance:
Perphenazine*
Pharmgroup:
Neuroleptics
Average price in pharmacies
| Name | Manufacturer | average price |
| Etaperazine 0.004 n50 tablet po | Tatkhimpharmpreparaty OJSC | 351.00 |
| Etaperazine 0.01 n50 tablet po | Tatkhimpharmpreparaty OJSC | 396.00 |
Analogs for the active substance:No data on synonyms |
Additionally
Extrapyramidal disorders occur more often when taking high doses. Tardive dyskinesia occurs more often in older patients, especially women, while dystonia occurs more often in younger people. If signs or symptoms of tardive dyskinesia occur, consider discontinuing antipsychotic treatment (however, some patients may require continued treatment despite the presence of the syndrome). The likelihood of liver damage, deposits in the lens and cornea, and irreversible dyskinesia is higher with long-term therapy.
The antiemetic effect of perphenazine can mask the symptoms of toxicity caused by an overdose of other drugs, and also complicate the diagnosis of diseases such as brain tumors and intestinal obstruction.
Perphenazine may lower the seizure threshold in predisposed patients and should be used with caution in seizure disorders and alcohol withdrawal. With simultaneous treatment with perphenazine and anticonvulsants, an increase in the dose of the latter may be required.
Alcohol intake is excluded, because Additive effects and hypotension may occur. The risk of suicide and the risk of antipsychotic overdose may be increased in patients who abuse alcohol during treatment.
Perphenazine should be used with caution in patients with a history of serious side effects from other phenothiazines. Some of the adverse reactions of perphenazine occur more often when taking high doses.
Use with caution in patients working in conditions of elevated temperature, as well as in those who have contact with phosphorus-containing insecticides.
Use with caution in patients receiving atropine or similar drugs (an additive anticholinergic effect is possible).
During treatment, it is necessary to monitor the function of the liver, kidneys (with long-term therapy), and the picture of peripheral blood. If signs or symptoms of blood dyscrasia occur, treatment should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Treatment should also be stopped if there are abnormalities in liver tests or if the blood urea nitrogen level is abnormal.
Most cases of agranulocytosis were observed between 4 and 10 weeks of therapy. During this period, patients should be especially careful to monitor for sore throat or symptoms of infection. If the number of leukocytes decreases significantly, the drug should be discontinued and appropriate therapy should be started.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from engaging in potentially hazardous activities, working with machinery, or driving a car, because perphenazine may impair mental and/or physical performance and also cause drowsiness (especially in the first 2 weeks of treatment).
A significant increase in body temperature can be caused by individual hypersensitivity. If hyperthermia occurs, treatment should be discontinued immediately.
Jaundice that develops (rarely) during treatment (between 2 and 4 weeks of therapy) is usually considered a hypersensitivity reaction. In this case, the clinical picture is similar to that of infectious hepatitis, but the results of liver function tests are characteristic of obstructive jaundice. It is usually reversible, but cases of chronic jaundice have been reported.
Sudden death has been rarely reported in patients receiving phenothiazines. In some cases, the cause of death was cardiac arrest, in others it was asphyxia due to a deficiency of the cough reflex.
Contraindications for the use of Etaperazine
The instructions for use indicate that Etaperazine, like most antipsychotics, has a fairly impressive list of contraindications. Among them:
- endocarditis (inflammatory processes in the internal cavity of the heart);
- some diseases of the heart and blood vessels (heart failure, arterial hypotension);
- diseases of the brain, both brain and spinal, especially progressive ones;
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- coma.
- brain injuries;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- children's age up to 12 years.
In addition to categorical contraindications, there are cases when the drug can be used, but only under the supervision of a doctor and with extreme caution:
- peptic ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disorders of the kidneys and liver, including liver and kidney failure;
- Parkinson's disease;
- disorders of hematopoietic processes;
- the patient has alcohol dependence;
- mammary cancer;
- epilepsy;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- The drug should also be used with caution in elderly patients.
Treatment of migraines at home using modern folk remedies - recipes and techniques.
How to distinguish signs of nervous exhaustion from symptoms of other diseases of the nervous system. Methods of treating neuroses and neurasthenia.
About opening a group and starting to use it
As mentioned above, the first antipsychotic was developed back in the 50s, but it was discovered by accident, since Aminazine was originally invented for surgical anesthesia, but after seeing the effect it has on the human body, it was decided to change the scope of its application and in 1952, Aminazine was first used in psychiatry as a potent sedative.
The main merit of this remedy should be attributed to the abolition of lobotomy, since a similar effect from this procedure could be obtained using medication without surgery.
A few years later, Aminazine was replaced by the more improved drug Alkaloid, but it did not stay long on the pharmaceutical market and already in the early 60s, second-generation antipsychotics began to appear, which had fewer side effects. This group includes Triftazin and Haloperidol, which are still used today.
Today, powerful tranquilizers are also considered neuroleptic drugs, since they have a similar effect.
The main active ingredients on which almost all antipsychotic drugs are based are:
- Phenothiazine;
- Aminazine;
- Tizercin;
- Magentil;
- Nuleptil;
- Sonapax;
- Thioxanthene;
- Clopixol;
- Butyrophenone;
- Trisedyl;
- Leponex;
- Eglonil.
READ MORE: Folk remedies for rectal cancer
One of the medications in demand in psychiatric practice is Etaperazine. The indications for its use are quite extensive - from calming long-term hiccups to relieving superidea syndrome. This drug has the chemical component perphenazine as an active substance. It is a derivative of the first neuroleptic, aminazine, and is similar in structure to prochlorperazine.
Special instructions for use and precautions
The instructions for use indicate that during treatment with Etaperazine, doctors recommend monitoring the functioning of the liver and kidneys, as well as the condition of the blood.
When the first deviations from the norm appear, you should contact your treating specialist, as it may be necessary to adjust the course of treatment or discontinue the drug.
If treatment lasts more than 4 weeks, the patient should pay attention to whether he or she exhibits symptoms of infectious diseases, as this may be a sign of agranulocytosis, a disease in which the number of granulocytes in the peripheral blood decreases.
who have previously been treated with Etaperazine or other drugs with a similar active ingredient should be especially careful
Doctors recommend avoiding work that involves driving , operating machinery, or requiring significant concentration and mental activity, as well as work in high-temperature environments.
It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol during treatment, since in addition to the listed side effects, the patient may increase the risk of suicide.
Before using Etaperazine as an antiemetic, it is worth finding out the causes of vomiting, since the effect of the drug can mask a more serious disease (intestinal obstruction, brain tumor) and thereby aggravate the patient's condition.
Article on the topic: Folk remedies for menopause from hot flashes
The drug is available with a doctor's prescription.
New generation neuroleptics without side effects
Thanks to the active development of researchers, the list of antipsychotics is annually replenished with a new generation of antipsychotics, which can now be differentiated according to the duration and severity of the clinical effect, mechanism of action and chemical structure.
Modern drugs have less effect on the brain, do not cause addiction or side effects, but are more likely to be antidepressants that eliminate symptoms rather than a means of treatment.
These include: Abilify, Quetiapine, Clozasten, Levomepromazine, Triftazine, Fluphenazine, Fluanxol.
Advantages:
- There are no disturbances in psychomotor reactions
- safe for treating children
- the risk of developing pathologies is reduced
- easy tolerability
- One dose of the drug is enough to achieve a positive result
- help with skin diseases (recent studies have shown that treating dry skin with antipsychotics produces positive results in older people whose diseases are associated with neuralgia)
Antipsychotics are potent drugs for the treatment of neuralgic, psychological disorders and psychosis (schizophrenia, delusions, hallucinations, etc.).
There are 2 generations of antipsychotics: the first was discovered in the 50s (Aminazine and others) and was used to treat schizophrenia, thought disorders and bipolar deviation. But, this group of drugs had many side effects.
The second, more advanced group was introduced in the 60s (it began to be used in psychiatry only 10 years later) and was used for the same purposes, but at the same time, brain activity did not suffer and every year the drugs belonging to this group were improved and improved.
Analogues of Etaperazine
The drug “Etaperazine” is quite often prescribed in many clinical cases of manifestations of psychotic disorders. Analogs and synonyms of this drug either have the same active substance or have a similar effect. Synonyms for “Etaperazine” are drugs that are exactly the same in composition, active component and, accordingly, the effect.
These include, first of all, the generic Perphenazine. Also in this group you can include the drug from America “Trilafon”. It is extremely rare to find advertised synonymous drugs under other names in the pharmacy chain. Similar drugs have a similar effect based on other active ingredients. These include drugs with the active substance fluphenazine or trifluoperazine, which have a similar effect on the human body.
Moditen
Triftazin
Analogues of Etaperazine are practically not found. The drug can be replaced with Perphenazine, as well as phenothiazine derivatives.
You can replace Etaperazine with drugs that have neuroleptic, muscle relaxant and sedative activity:
- Trilifan;
- Chlorpiprozine;
- Perphenazine;
- Decentan.
When using medications, you need to monitor the correct functioning of the detoxification organs, as well as monitor the biochemical parameters of the blood.
How the drug works
As already mentioned, Etaperazine has an antipsychotic effect. This effect of the drug on the body is achieved by blocking certain categories of receptors of the mesocortical and mesolimbic systems with perphenazine.
The antiemetic properties of the drug are due to the fact that the active component acts on the vagus nerve of the gastrointestinal tract.
As for the sedative properties of Etaperazine, the drug has this effect due to the effect of the active substance on the receptors of the brain stem.
Pharmaceutical properties and mechanism of action of antipsychotics
Most antipsychotic drugs have one antipsychological effect, but this is achieved in different ways, since each drug affects a specific part of the brain:
- The mesolimbic method reduces the transmission of nerve impulses when taking drugs and relieves such pronounced symptoms as hallucinations and delusions.
- A mesocortical method aimed at reducing the transmission of brain impulses that lead to schizophrenia. Although this method is effective, it is used in exceptional cases, since affecting the brain in this way leads to disruption of its functioning. In addition, it should be taken into account that this process is irreversible and the abolition of antipsychotics will not affect the situation in any way.
- The nigrostriate method blocks some receptors to prevent or stop dystonia and akathisia.
- The tuberoinfundibular method leads to the activation of impulses through the limbic pathway, which, in turn, can unblock some receptors for the treatment of sexual dysfunction, neuralgia and pathological infertility caused by nervousness.
As for the pharmacological action, most antipsychotics have an irritating effect on brain tissue. Also, taking antipsychotics of various groups has a negative effect on the skin and manifests itself externally, causing skin dermatitis in the patient.
When taking antipsychotics, the doctor and the patient expect significant relief, there is a decrease in the manifestations of mental or neuralgic disease, but at the same time the patient is exposed to many side effects that should be taken into account.
Reviews of Etaperazine
One of the most popular drugs in psychiatric practice is Etaperazine. Patient reviews about it can be found radically opposite. For some, this medicine helped overcome mental conditions - fear and anxiety - and cope with obsessions. But for some, this drug turned out to be ineffective, causing not an improvement in the health situation, but only a lot of side effects, many of which were very difficult for patients to tolerate. In any case, this medicine still remains in demand, bringing a therapeutic effect.
“Etaperazine,” although it belongs to the list of vital medications, cannot be simply bought at a pharmacy. Its dispensing is strictly controlled, and you can purchase this medicine only by presenting to the pharmacist a prescribed prescription with the signature and seal of the attending physician and the stamp of the institution.
You can find very different reviews about Etaperazine on forums. Basically, people write that the drug helps. However, there are also reports of side effects. They especially often write about drowsiness. Based on reviews, we can conclude that the medicine helps with a correct diagnosis and a well-developed treatment regimen.
Indications for use
It should be noted that Etaperazine is successfully used in several areas of medical practice.
Of course, the main branch remains psychiatry. Etaperazine is indicated for the treatment of:
- schizophrenia;
- manic and obsessive states;
- psychosis;
- depressive states;
- delusional and hallucinatory states;
- neuroses, including states of fear and tension;
- emotional disorders.
In addition, the drug is used in obstetric practice as an antiemetic.
Dermatologists prescribe Etaperazine to neutralize itchy skin .
Etaperazine is used as a sedative in therapy and surgery. In addition, after operations on the gastrointestinal tract, chemotherapy and radiotherapy sessions, this drug can be used to treat vomiting.
In some cases, Etaperazine is used to relieve hiccups.
Etaperazine price, where to buy
Tablets of 10 mg (50 pieces in a package) cost approximately 300 rubles. And the price of Etaperazine in 4 mg tablets (50 pieces in a package) is about 270 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
ZdravCity
- Etaperazine tab. p.o 4mg n50AO Tatkhimpharmpreparaty
- Etaperazine tab. p.o 10 mg n50AO Tatkhimpharmpreparaty
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Etaperazine (tablet p/o 10 mg No. 50)
- Etaperazine (tablet p/o 4 mg No. 50)
show more
Method of administration of Etaperazine and dosage
It is recommended to take the tablets after meals with plenty of water.
The dosage should be determined solely by the doctor, depending on the disease and general condition of the patient.
In psychiatry, treatment with Etaperazine begins with a dose of 4-10 mg 1-2 times a day . If the patient has previously taken this drug or in cases where the disease is rapidly progressing, the initial dosage may be increased to 40 mg per day.
Article on the topic: Hiccups - causes and treatment methods
In the future, the amount of the drug taken can be increased to 80 mg per day, divided into 2-3 doses.
For patients whose disease is chronic, a course of treatment lasting up to 4 months is prescribed, during which the daily dose of Etaperazine is 100-150 mg.
In surgery, therapy and obstetric practice, when the drug is used as an antiemetic, as a rule, no more than 8 mg of the drug is prescribed 4 times a day.
TOP 20 famous antipsychotics
Neuroleptics are represented by a very broad group of drugs; we have selected a list of twenty drugs that are mentioned most often (not to be confused with the best and most popular, they are discussed below!):
- Aminazine is the main antipsychotic that has a calming effect on the central nervous system.
- Tizercin is an antipsychotic that can slow down brain activity during violent behavior of the patient.
- Leponex is an antipsychotic drug that is somewhat different from standard antidepressants and is used in the treatment of schizophrenia.
- Melleril is one of the few sedatives that acts gently and does not cause much harm to the nervous system.
- Truxal - due to blocking some receptors, the substance has an analgesic effect.
- Neuleptil - by inhibiting the reticular formation, this antipsychotic has a sedative effect.
- Clopixol is a substance that blocks most nerve endings and can fight schizophrenia.
- Seroquel – thanks to the quetiapene contained in this antipsychotic, the drug is able to relieve the symptoms of bipolar disorder.
- Etaperazine is a neuroleptic drug that has an inhibitory effect on the patient’s nervous system.
- Triftazin is a substance that has an active effect and can have a strong sedative effect.
- Haloperidol is one of the first antipsychotics, which is a derivative of butyrophenone.
- Fluanxol is a drug that has an antipsychotic effect on the patient’s body (prescribed for schizophrenia and hallucinations).
- Olanzapine is a drug similar in action to Fluanxol.
- Ziprasidone - this drug has a calming effect on particularly violent patients.
- Rispolept is an atypical antipsychotic, a derivative of benzisoxazole, which has a sedative effect.
- Moditene is a drug that is characterized by antipsychotic effects.
- Pipothiazine is a neuroleptic substance in its structure and effect on the human body similar to Triftazine.
- Majeptil is a drug with a weak sedative effect.
- Eglonil is a drug with a moderate antipsychotic effect that can act as an antidepressant. Eglonil also has a moderate sedative effect.
- Amisulpride is an antipsychotic similar in action to Aminazine.
READ MORE: How to quickly remove worms at home using folk remedies
There are also additional antipsychotics that are not included in the main classification due to the fact that they are an addition to a particular drug. So, for example, Propazine is a drug intended to eliminate the mental depressing effect of Aminazine (a similar effect is achieved by eliminating the chlorine atom).
Well, taking Tizercin increases the anti-inflammatory effect of Aminazine. This medicinal tandem is suitable for the treatment of delusional disorders obtained in a state of passion and in small doses, and has a sedative and hypnotic effect.
It is important to know: the maximum permitted dosage of all these drugs (from the TOP-20) is 300 milligrams per day.
In addition, there are Russian-made antipsychotic drugs on the pharmaceutical market. Tizercin (aka Levomepromazine) has a mild sedative and vegetative effect. Designed to block causeless fear, anxiety and neuralgic disorders.
The drug is not able to reduce the manifestation of delirium and psychosis.
Side effects
The greater the dosage and course of antipsychotic therapy, the higher the likelihood of unpleasant consequences for the body.
Side effects of antipsychotics are also associated with age, health status and interactions with other drugs.
They can cause:
- disruption of the endocrine system (prolacthymenia, amenorrhea, erectile dysfunction)
- disorders of the central nervous system (akatasia, muscular dystonia, parkinsonism)
- neuroleptic syndrome (inhibition of actions, slurred speech, oculogyric crisis, in which the head is thrown back and the eyes roll back)
- loss of appetite, drowsiness, weight loss or gain
In 10% of cases, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular and genitourinary systems occur, and akathisia caused by antipsychotics occurs in 26%. But the main thing that makes them dangerous for humans is the “withdrawal syndrome” caused by a sudden cessation of taking antipsychotics. The patient becomes so accustomed to the daily dose of medication that, without receiving it again, he falls into a state of depression or constant discomfort. “Withdrawal syndrome” has several varieties and can lead to psychosis and tardive dyskinesia.
Some patients, not waiting for improvements after treatment, the effect of which does not occur immediately, try to cope with depression with the help of alcoholic beverages. But combining antipsychotics and alcohol is strictly prohibited, since when interacting they can cause poisoning and even a stroke.
Indications
Main indications of the drug Etaperazine:
- schizophrenia;
- psychotic disorders, especially with agitation and hyperactivity;
- neuroses with the presence of fear, tension;
- skin itching;
- hiccups;
- nausea and vomiting (various genesis);
- uncontrollable vomiting in pregnant women;
- senile and exogenous-organic psychoses, accompanied by hallucinatory phenomena.
It should be taken with extreme caution when:
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- alcoholism;
- pathological changes regarding the hematopoietic system;
- prostatic hyperplasia;
- peptic ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract;
- breast cancer;
- Parkinson's disease;
- renal or liver failure;
- cachexia;
- vomiting, the cause of which is an overdose of other drugs;
- advanced age;
- Reye's syndrome.
Atypical antipsychotics
Typical antipsychotics include drugs with a fairly wide spectrum of action that can affect the structure of the brain responsible for the production of adrenaline and dopamine. Typical antipsychotics were first used in the 50s and had the following effects:
- relief of neuroses of various origins;
- sedative;
- sleeping pills (in small doses).
Atypical antipsychotics appeared in the early 70s and were characterized by having far fewer side effects than typical antipsychotics.
Atypicals have the following effects:
- antipsychotic effect;
- positive effect on neuroses;
- improvement of cognitive functions;
- hypnotic;
- reduction of relapses;
- increased prolactin production;
- fight obesity and digestive disorders.
The most popular atypical neuroleptics of the new generation, which have virtually no side effects:
- Flupenthixol;
- Fluphenazine;
- Clozapine;
- Olanzapine;
- Zyprexa;
- Risperidone;
- Quetiapine;
- Seroquel;
- Ketilept;
- Lakvel;
- Nantharid;
- Quentiax;
- Sertindole;
- Serdolect;
- ziprasidone;
- Zeldox;
- Aripiprazole;
- Abilify;
- Amisulpride;
- Solian;
- Limipranil;
- Sulpiride;
- Betamax;
- Deprall;
- Dogmatil;
- Prosulpin.
Reviews from patients and doctors
Today, it is impossible to imagine the treatment of mental disorders without antipsychotics, since they have the necessary medicinal effect (sedative, relaxing, etc.).
I would also like to note that you should not be afraid that such drugs will negatively affect brain activity, since these times have passed, after all, typical antipsychotics have been replaced by atypical ones of a new generation, which are easy to use and have no side effects.
Alina Ulakhly, neurologist, 30 years old