The trigeminal nerve is one of the largest nerves of the facial region. This nerve has three main branches: the first (ophthalmic) is located above the eyebrows, the second (maxillary) is on both sides of the nose, and the third (mandibular) is in the lower jaw. Branching into smaller branches, the trigeminal nerve is responsible for the innervation of almost the entire face, providing sensitivity to the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth and eyes, facial skin and movement of some muscles.
With lesions of the trigeminal nerve, the patient experiences severe pain , which is localized in the area of the neck, jaws, chin, forehead, and brow ridges. Sometimes the inflammatory process can manifest itself in the form of toothache.
Characteristic features of inflammation of the nerve in the face are severe pain in the right region of the face and the fact that such neuralgia most often affects women aged fifty (and older).
Types of inflammation
There are two types of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on the face. These include:
- Primary. It is also known as "true". This type is considered a self-occurring pathology due to impaired blood circulation or nerve compression;
- Secondary. In other words, “symptomatic.” It is the result of another disease process in the body. Most often, the causes are serious infections or the development of a tumor.
Also, the difference may lie in the fact that one nerve branch or several may be affected at the same time.
A person has two trigeminal nerves located on both sides of the face. Each of them has three main branches. These are: maxillary, mandibular and ophthalmic nerves. The main branches are also subdivided into many smaller branches. If at least one of them is irritated or compressed, then the person begins to feel severe pain of an acute nature on the face.
The causes of this condition can be many factors. The main ones are:
- Congenital pathology in the form of narrowed openings and canals in which the nerves are located;
- Violation of the structure, development or location of blood vessels localized next to the trigeminal nerve;
- Diseases associated with metabolic disorders. Such as diabetes or gout;
- Inflammatory diseases of the teeth and sinuses. The cause may also be an incorrect bite;
- Infectious diseases, including syphilis and tuberculosis;
- Tumor processes;
- Hypothermia of the facial area;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Consequences of surgical interventions on the body. Most often this concerns maxillofacial operations;
- Mechanical injuries of the skull;
- Immune dysfunction;
- Strong physical and psycho-emotional stress.
When one of the two ternary nerves is irritated or compressed, a person begins to feel severe facial pain.
In some cases, pain is felt only with a certain type of irritation of the facial area.
Examples of such actions include:
- Physical touching of the face;
- Facial expressions, smile, conversation;
- Washing, shaving, brushing teeth.
Since the most ordinary things can provoke severe pain, the patient cannot lead a normal life. Therefore, he needs to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible.
Structure of the trigeminal nerve
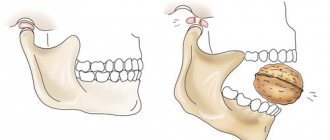
The trigeminal is the fifth and largest pair of cranial nerves. It belongs to the nerves of a mixed type, having motor and sensory fibers. Its name is due to the fact that the nerve is divided into three branches: orbital, maxillary and mandibular. They provide sensitivity to the face, soft tissues of the cranial vault, dura mater, oral and nasal mucosa, and teeth. The motor part provides nerves (innervates) some muscles of the head.
The trigeminal nerve has two motor nuclei and two sensory ones. Three of them are located in the hindbrain, and one is sensitive in the middle. The motor ones form the motor root of the entire nerve at the exit from the pons. Next to the motor fibers, they enter the medulla, forming a sensory root.
These roots form the nerve trunk, penetrating under the dura mater. Near the apex of the temporal bone, the fibers form the trigeminal ganglion, from which three branches emerge. The motor fibers do not enter the ganglion, but pass under it and connect with the mandibular branch. It turns out that the ophthalmic and maxillary branches are sensory, and the mandibular branch is mixed, since it includes both sensory and motor fibers.
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
The symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia can vary significantly between patients. As mentioned above, if some people experience pain for no apparent reason, then for others it is provoked by certain irritants.
The main signs of the disease are:
- Severe pain, covering one half of the face. The sensations, as a rule, are shooting in nature;
- Visible twitching of the facial muscles;
- Distortion of the affected part of the face. This is often indicated by distorted facial expressions that were previously not characteristic of the patient;
- Weakness, lethargy of the body, accompanied by aching pain in the muscles;
- Chills due to elevated body temperature;
- Migraine;
- Increased irritability, anxiety, and disturbed sleep;
- Small rash on the face, as well as reddened skin;
- Increased tearing and salivation.
In the vast majority of cases, pain is felt only on one side of the face, but in very rare cases, neuralgia can affect two trigeminal nerves at once. In 70% of cases, the nerve on the right side is affected. The unpleasant sensations are especially pronounced in the area of the lower jaw, nose and eyes. Often, when the first signs of neuralgia appear, patients confuse it with other diseases, for example, toothache.
Often the pain is felt only on one side of the face, less often on both
The nature of pain in trigeminal neuralgia is usually divided into 2 types:
- Typical. It occurs more often and feels like a small electric shock. It has a cyclical nature: it appears, then it subsides. The frequency of its occurrence varies; between attacks it can take several minutes, or maybe several hours. The pain is most pronounced in the lower jaw area.
- Atypical. This type of pain is much less common, but much more difficult to tolerate, since it is permanent. Painful sensations cover most of the face and do not subside.
The second type requires a special approach, as it is difficult to treat.
Causes of trigeminal neuritis
Trigeminal neuralgia is accompanied by severe pain as the trigeminal nerve is irritated. As a rule, the cause is the contact of an artery and vein with the trigeminal nerve at the base of the skull. The nerve is compressed, which causes severe pain. Other possible causes of trigeminal neuralgia include tumors that compress the nerve, multiple sclerosis, which leads to destruction of the myelin sheath of the nerve. In young people, the development of trigeminal neuralgia is usually associated with multiple sclerosis.
Despite the fact that the etiology of the disease is very wide, fortunately, it is not realized in all cases.
The main causes of the development of trigeminal neuritis are:
- Past viral infection. Almost any virus can cause neuritis. But the most important pathogen is considered to be representatives of the herpes family. In the first place among them is herpes zoster;
- Immune dysfunction of the body. Against this background, herpes viruses are able to become more active than in a healthy body;
- Local and general hypothermia. Most often, trigeminal neuritis occurs after exposure to a draft or other exposure to low temperatures on one of the halves of the ear and facial areas;
- Severe physical stress and psycho-emotional shocks, which lead to depletion of the body's defenses;
- Poor nutrition, and as a result, immune dysfunction;
- Severe infections of any localization, if they last a long time and require aggressive treatment.
The reasons that contribute to the onset of an attack of trigeminal neuralgia include:
- touching the skin of the face;
- washing;
- shaving;
- teeth cleaning;
- blow to the nose;
- light breeze;
- makeup;
- smile;
- talk.
How to treat the trigeminal nerve on the face
Depending on the degree of manifestation of the disease, as well as on the characteristics of the patient’s body, suitable therapeutic therapy is prescribed.
How to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve in each individual case is determined only by a doctor. Therapy may include both traditional drug treatment and more serious procedures.
Medication
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is treated with medications in the form of tablets and injections. They can have different effects on the body, so, as a rule, a whole range of medications is required.
The following drugs can be used to treat neuralgia:
- Anticonvulsants. They may also be known as anticonvulsants. Carbamazepine is one of the most popular representatives of this class. These drugs eliminate pain, increase muscle tone, and also have a positive effect on nerve patency. The appointment is made exclusively by a doctor, since there is a high risk of side effects in the form of poor condition, drowsiness, nausea;
- Painkillers. Their main role is pain relief. It is permissible to use even narcotic drugs;
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. Have a calming effect on the sore nerve;
- Glucocorticoids. Once in the body, they have an anti-inflammatory effect and also eliminate swelling that forms within the affected nerve;
- Antispasmodics. Aimed at eliminating spasmodic pain;
- Vitamins of group B. As a rule, they are used immediately as a complex: B1, B6, B12. They affect the cause of the disease, improving nerve conduction, and also enhance the body's immune system.
In addition, in one case or another, antihistamines, tranquilizers, vasotes, sedatives and other drugs may be prescribed.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine can help to quickly cope with the disease if it is used as a supplement to the main traditional treatment.
Popular remedies for eliminating pain in the facial area are:
- Buckwheat. The cereal is heated in a frying pan, after which it is transferred to a piece of clean cotton cloth, forming a closed bag. An improvised heating pad is applied to the sore part of the face and held in this position until it cools down completely. The procedure can be performed up to 3 times a day;
- Chamomile. The herb is brewed with boiling water. The resulting herbal tea is cooled to a warm state, after which it is taken into the mouth and held for as long as possible. This method can also be performed several times a day;
- Althea. 4 teaspoons of the crushed root of this herb are poured into 250 ml of warm boiled water, after which the solution is allowed to brew for 8 hours. Using this product, apply compresses to the sore side of the face. From above it is wrapped in a warm cloth, scarf or handkerchief. After 1.5 hours, the compress is removed, and the cheek is again wrapped in something warm.
Read also: Early teething in babies
Chamomile tea for neuralgia is kept in the mouth as much as possible and the procedure is repeated several times a day.
Before starting traditional medicine methods, you need to make sure that there is no allergic reaction to the components used.
The block is a minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting an anesthetic into the affected area of the face using a needle. The pain usually stops immediately, but the effect lasts temporarily, usually for 2 months. If necessary, the blockade is repeated.
In addition to it, there are various physiotherapeutic procedures, namely:
- Acupuncture for trigeminal neuralgia;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Electrophoresis;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Laser therapy.
Surgical method
If none of these methods is able to eliminate the cause of the inflammatory disease, the patient may be indicated for surgical intervention. Such radical treatment can be carried out in two ways:
- Microvascular decompression. During surgery, neurosurgeons move or completely remove blood vessels that are affecting the nerve trunk. In 80% of cases the operation has a positive result;
- Rhizotomy. This procedure involves the complete destruction of the trigeminal nerve or its nodes. To do this, the surgeon makes a small skin incision.
Another way to solve the problem is radiosurgery, namely the effect of high temperature frequencies on the affected nerve node. This is the most atraumatic procedure that does not require incisions, stitches or hospital stay.
Conservative treatment of neuralgia
Conservative and surgical treatment of the trigeminal nerve is possible. Almost always, conservative treatment is first used, and if it is ineffective, surgery is prescribed. Patients with this diagnosis are entitled to sick leave.
Drugs for treatment:
- Anticonvulsants (anticonvulsants). They are able to eliminate congestive excitation in neurons, which is similar to a convulsive discharge in the cerebral cortex during epilepsy. For these purposes, drugs with carbamazepine (Tegretol, Finlepsin) are prescribed at 200 mg per day with the dose increasing to 1200 mg.
- Centrally acting muscle relaxants. These are Mydocalm, Baclofen, Sirdalud, which eliminate muscle tension and spasms in neurons. Muscle relaxants relax the trigger zones.
- Analgesics for neuropathic pain. They are used if there is burning pain caused by a herpetic infection.
Physiotherapy for trigeminal neuralgia can relieve pain by increasing tissue nutrition and blood supply to the affected area. Thanks to this, accelerated nerve recovery occurs.
Physiotherapy for neuralgia:
- UHF (ultra-high frequency therapy) improves microcirculation to prevent atrophy of the masticatory muscles;
- UVR (ultraviolet irradiation) helps relieve pain due to nerve damage;
- electrophoresis with novocaine, diphenhydramine or platyphylline relaxes the muscles, and the use of B vitamins improves the nutrition of the myelin sheath of the nerves;
- laser therapy stops the passage of impulses through the fibers, relieving pain;
- electric currents (impulsive mode) can increase remission.
It should be remembered that antibiotics are not prescribed for neuralgia, and taking conventional painkillers does not have a significant effect. If conservative treatment does not help and the intervals between attacks become shorter, surgical intervention is required.
Prevention
It is quite difficult to predict the occurrence of neuralgia. But there are a number of measures that will help reduce the risk of inflammation of the facial nerve:
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases such as sinusitis, sinusitis, pulpitis and others;
- Avoiding drafts and hypothermia;
- Minimizing stressful situations;
- Avoiding facial injuries.
And an equally important criterion is supporting the immune system by leading a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and frequent walks in the fresh air.
Causes
The factors that provoke neuralgia differ in their nature of influence. Compression by adjacent blood vessels has been identified as the main cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. They compress it at the base of the skull, thereby causing nerve irritation and pain.
Photo: Trigeminal facial nerve
The following causes are also often diagnosed:
- tumor-like formation that pinches a nerve;
- multiple sclerosis with pronounced destruction of cell myelin . Most often, pathology caused by this reason is detected in people under 25 years of age;
- past viral infection . Herpes is considered the most dangerous virus. Neuralgia also occurs with other infections if the inflammation caused by them is long-lasting and progressive;
- hypothermia . It is not necessary to receive general cooling for pathology to occur. Sometimes it’s enough just to be in a draft without a hat;
- decreased protective properties of the immune system;
- stress , leading to sustained mental overstrain;
- excessive physical activity without adequate nutrition , which leads to depletion of muscle and nerve tissue.
Trigeminal neuralgia manifests itself with pronounced symptoms that make it possible to distinguish this disease from similar pathologies. At the initial stages, inflammation manifests itself as primary symptoms.
If the disease progresses, then secondary signs of neuralgia appear.
The main and most serious sign of neuralgia of this nerve is pain, which subsequently changes its frequency and intensity.
In addition, spasms of the affected area, numbness or increased sensitivity of the skin, and neurotization are noted. Let's look at all the symptoms in more detail.
An inflamed trigeminal nerve
is characterized by sudden and debilitating pain .
It has maximum intensity with sharp shooting. In this case, the pain permeates only one part of the face. Basically, the pain line through the passage originates in the area of the ears and spreads to the middle of the face. Such sensations accompany some similar pathologies, but in their case the location differs as follows:
- with tendinitis, pain manifestations are exactly the same as with trigeminal neuralgia, but are localized in the cervical region and are accompanied by headaches;
- with Ernest syndrome, pain is observed in the cervical region;
- with inflammation of the occipital nerve, pain is found in the occipital part of the head. In rare cases, it can spread to the upper part of the face.
In medicine, there are two types of pain that manifests itself with this inflammation:
- Typical . It is periodic in nature. It occurs due to mechanical impact on some facial areas and usually resembles sharp lumbago.
- Atypical . It is distinguished by its constancy. The area of inflammation includes most of the face. With such pain, treatment of this disease is much more difficult and longer than with the first option.
The location of painful manifestations depends on the order of damage to the nerve branches. Each of them has its own area of influence:
- with inflammation of the first branch, pain is observed in the forehead, eyes and temples;
- the second lesion is characterized by pain in the nasolabial triangle, cheekbones, and upper part of the jaw apparatus;
- the inflamed third branch gives pain to the chin, cheeks, lower jaw and tongue.
Most often, damage to the second or third branches is diagnosed. A paired inflammatory process is often observed.
As you know, toothpaste from Thailand is made exclusively from natural ingredients.
In this article we read about the treatment of gums with periodontal disease using folk remedies.
Changes in the frequency and duration of manifestations
You can determine whether the trigeminal nerve or another is inflamed by the frequency and duration of pain. For neuralgia of this type, these manifestations are clearly defined:
- duration does not exceed 3–5 seconds;
- the frequency can vary from single manifestations to several dozen per day. It is worth noting that in the cold season, attacks become more frequent;
- Without timely treatment, pain can last from a couple of days to several weeks. Basically, their intensity increases.
Changes in skin sensitivity
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, the tactile sensitivity of the facial skin in the affected area changes . It can decrease significantly or, conversely, increase.
In some cases, complete numbness of the skin is observed, which disappears after the underlying disease is relieved. The same thing can happen to the lips and soft tissues of the mouth.
In case of increased tactile sensations, a trigger zone is determined, where any impact causes an attack of pain. The most common actions of this kind are:
- washing;
- shaving;
- chewing;
- applying makeup;
- pronunciation of words.
During sleep, sensitivity usually normalizes.
This symptom leads to the fact that a person limits himself in movements that provoke an attack. For example, the chewing process is performed only on the healthy side of the jaw.
As a result, muscle compaction forms on the diseased half and dystrophic type changes occur, which are difficult to eliminate in the future.
Contraction of muscle tissue
With inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, along with pain, pronounced muscle contractions are noted. They, like the main manifestation, are observed only on one half of the face.
Read also: Temperature during pulpitis
With this disease, contractions of two types may be observed:
- tic-like – occur in a separate group of facial muscles. During attacks, it is almost impossible to notice tics visually. As a rule, they pass without discomfort;
- spasmodic . They are sudden and always accompanied by pain. Spasms often lead to persistent facial asymmetry.
Neurotization
Regular attacks accompanied by severe pain often lead to neuroticism. A person begins to refuse food, limits himself in communication and leaves himself alone with pain .
This leads to the development of persistent psychological discomfort. Neurotization is mainly observed in patients with advanced inflammatory processes.
But there have been situations when neuroticism was observed in people with inflammation for a period of less than three days. Most likely, in this case, the low natural sensitivity threshold plays a big role.
In addition to the main signs of this disease, secondary ones often appear, which are not very pronounced. Secondary symptoms include:
- increased salivation;
- lacrimation;
- severe hyperemia;
- chewing dysfunction;
- dryness in the nasopharynx;
- perversion or complete loss of taste.
Such manifestations are characteristic of a long-term inflammatory process with very pronounced main symptoms.
Irritants
If you experience occasional trigeminal pain, the first thing you can do is determine what is causing the pain.
Keep track of when and under what circumstances you experience these pains. Strong winds and eating spicy foods are the most common irritants that cause trigeminal pain. Try to avoid any, even slight, draft in the room you are in. Stop eating hot and spicy foods; in some cases it may be necessary to avoid specific foods, most often coffee, citrus fruits, bananas, etc. Trigeminal nerve pain forces a person to stop all physical activity. He is depressed and usually refuses to eat. However, you can use cold drinks to quell the pain. Try drinking them through a straw, this often helps reduce pain. How to Simply Recommend
Why the medicine does not work The key to successful treatment is, of course, following all the doctor’s recommendations and informing him of all significant changes during therapy. However, a specialist can talk as much as he wants about the regimen and duration of taking the drug, but most patients will still violate these rules. Read more
Treatment methods
If the process develops intensively, then it is necessary to seek help from a doctor as quickly as possible.
After a detailed diagnosis, the exact cause will be identified and appropriate therapy will be selected. For inflammation of this type, only complex treatment, which includes drug therapy, physiotherapy and traditional methods of treatment, .
Drug therapy
The effectiveness of treatment depends on properly selected drugs. The following drugs are mainly used:
- painkillers . Since attacks are associated with severe pain, both non-narcotic and narcotic drugs are used: “Ketanov”, “Ketalgin”, “Promedol”, “Morphine”;
- non-steroidal drugs with anti-inflammatory effects : Indomethacin, Dicloberl, Movalis, etc.;
- glucocorticoids . They are prescribed to relieve swelling and inflammation of nerve fibers. The most commonly used are Methylprednisolone, Hydrocortisone, and Dexamethasone;
- antispasmodics : “Sirdalud”, “Mydocalm”, “Carbamazepine”;
- antiviral agents : Lavomax, Acyclovir. Prescribed if the cause of inflammation is a virus.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with medications should only be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor who will correctly determine the drug and its dosage.
You will learn how to whiten teeth using tea tree oil in our article.
Well, here we’ll talk about the treatment of a fistula on the gum.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an effective remedy, especially if used in conjunction with drug treatment. To eliminate primary symptoms and relieve inflammation, the following are most often used:
- electrophoresis . Quickly restores the condition of the trigeminal nerve, even during an acute period;
- UHF . Particularly effective for infectious neuralgia;
- paraffin-ozokerite therapy . After such procedures, facial muscle tension decreases and swelling decreases;
- magnetotherapy . Helps relieve pain and eliminate inflammation;
- massage . Helps relieve excessive muscle tension and increases the tone of the atrophied group. Typically performed in a sitting position.
Use of folk remedies
Photo: fir essential oil
Treatment with such drugs is aimed at relieving the symptoms of inflammation. For this use:
- essential oils: fir, sage, etc. They are applied in the form of applications or rubbed with gentle movements into the affected area. Oils help eliminate pain and activate metabolic processes in the deep layers;
- infusions and teas from herbs with anti-inflammatory effects: chamomile, marshmallow . These products are used both for oral administration and for rubbing;
- vegetable juice . Black radishes are good for this. To relieve inflammation and swelling, wipe the sore spot with juice several times a day;
- Calcined buckwheat or boiled egg are used as warming agents , which are applied to the inflamed area.
There are a large number of folk recipes that are used for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. But do not forget that they are only an auxiliary means of the main therapy.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is not always a curable disease. It depends on the neglect of the condition. Therefore, the sooner you see a doctor, the greater the opportunity to stop the pathology completely.
In conclusion, a video where we will be told about the symptoms and treatment of the inflamed trigeminal nerve:
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Causes, symptoms and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
The trigeminal nerve is located in the face and has several branches that run around the nose, above the eyebrows and in the lower jaw area. Its main task is the innervation and control of the neurological condition of the facial part of the skull. If at least one branch is affected, it manifests itself very painfully and has a specific character. Trigeminal neuralgia requires long-term complex treatment.
In general, the disease can develop independently or as a result of another infectious (inflammatory) process. It is most often diagnosed in women over 50 years of age, although it can also affect men.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is severe and sharp shooting pain. Sometimes it is impossible to bear, and painkillers do not always help. An attack of neuralgia can last 10-15 seconds, sometimes longer, not exceeding 2 minutes. The localization of the pain syndrome does not change, but may radiate to other areas of the face.
At the peak of a painful attack, twitching of the facial and chewing muscles occurs. In some cases, secondary fascial prosopalgic syndrome develops. In this case, patients use only the healthy half of their mouth to chew food. As a result, the muscles become denser.
With exacerbation of facial neuralgia, facial redness may occur. Patients experience increased salivation and lacrimation, and mucous discharge from the nasal cavity.
The patient becomes irritable and has an increased feeling of fear and anxiety. In order not to cause increased pain, a person begins to remain silent and withdraws into himself. In severe cases, mental disorders develop against this background.
The affected side of the face becomes less sensitive, the patient may feel a tingling or dull aching pain, which is similar to the pain of caries, so often when the disease develops, patients first turn to the dentist.
If symptoms of illness occur, consult a doctor immediately. Do not use painkillers for a long time. Treatment is prescribed by a specialist after diagnosis.
Reasons for development
Trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminal) occurs due to exposure to negative internal or external factors. The following reasons can be identified:
- Hypothermia of the face. In this case, there is absolutely no need to be in the cold. Simply wash your face with cold water.
- Cranial injury, concussion.
- Oncological tumor or vascular aneurysm. These tumors compress the nerve endings, triggering the pathological process.
- Multiple sclerosis (incurable disease).
- Pulpitis, periodontal disease or other diseases of the oral cavity.
- Inflammation of the brain - meningitis.
- Malocclusion (misaligned bones can put pressure on nerves).
- Decreased immunity due to herpes.
- Disturbance of metabolic processes in the body.
- Acute viral or bacterial infections, respiratory pathologies.
- Atherosclerosis of blood vessels, which provokes “starvation” of the nerve.
- Stress, depression, neuroses, psychogenic disorders.
- Allergy.
Fayyad Akhmedovich Farhat, a neurosurgeon of the highest qualification category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Operative Surgery at Moscow State Medical University, talks about the disease:
Trigeminal neuralgia is a serious pathology that brings a lot of pain and discomfort. Inflammation can occur quite suddenly, so you need to know how to deal with it. Since the symptoms manifest themselves very clearly, it is necessary to act immediately.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The exact causes of trigeminal neuralgia are unknown. However, there are several factors that can trigger the disease:
- Viral nerve damage - neuro-AIDS, polio, herpetic infection;
- Odontogenic causes (due to problems with teeth) - dental flux, jaw injury, reaction to anesthesia, unsuccessful tooth filling;
- Diseases of the nervous system - cerebral palsy, meningitis, multiple sclerosis, meningoencephalitis (viral, tuberculosis), hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the brain), encephalopathy due to head injuries, epilepsy, infectious process, circulatory disorders and brain tumors;
- Compression of the trigeminal nerve - brain tumors, injuries and scars, excessive growth of connective tissue due to an infectious process, dilation of brain vessels (aneurysms, atherosclerosis, congenital pathologies of vascular development, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, increased intracranial pressure due to osteochondrosis).
In neurology, it is also common to identify a number of unfavorable factors that increase the risk of trigeminal neuralgia:
- the patient's age is over 50 years;
- stress;
- chronic fatigue;
- mental disorders;
- autoimmune and allergic diseases;
- avitaminosis;
- metabolic disease;
- infectious diseases (syphilis, botulism, tuberculosis);
- inflammation of the oral cavity (pulpitis, gingivitis).
In neurology, there are two mechanisms for the formation of trigeminal neuralgia. One of the mechanisms involves the destruction of the myelin sheath. This process is also called demyelination. As a result of damage, the nerve fiber becomes unprotected, and the nerve impulse spreads to the nearest nerve fibers. As a result, severe irritation of neurons occurs and pain occurs.
The second mechanism for the development of pathology involves a violation of the regulation of the functioning of the trigeminal nerve of the central nervous system. Due to damage to the nerve fibers, the nerve impulse is inhibited, which leads to irritation of the trigeminal nerve nuclei and, as a result, pain. There is an assumption that both of these mechanisms can sequentially follow each other.
Classification of pathology
Trigeminal neuralgia can occur in different parts of the face. The fact is that the main branch is divided into many small fibers. There are two types of inflammation:
- True. This type of neuralgia is the most common. It appears due to circulatory problems or nerve compression. Such inflammation often occurs independently. The pain in this case is strong, piercing, and appears periodically.
- Secondary. This inflammation develops as a complication of another pathology: a tumor, a severe infection. The symptoms are constant and burning. Pain occurs in any part of the face.
Inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve as a symptom of serious pathology
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve may indicate serious pathological processes occurring in the body. This:
- tumor neoplasms;
- viral infections. In most cases, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs when herpes viruses are activated;
- infectious diseases that provoke intoxication of the body and weakened immunity (tuberculosis, malaria);
- diseases of the hearing organs - otitis media, eustacheitis;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- multiple sclerosis;
- meningitis;
- encephalopathy;
- epilepsy;
- Cerebral palsy.
In the presence of provoking factors, damage to one or three branches of the trigeminal nerve may occur.
Symptoms
The pathology is characterized by vivid symptoms. Pain has its own characteristics:
- It usually starts on one side: from the temple, gums or teeth, edge of the nose, mouth.
- Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is characterized by boring, burning or piercing pain.
- The attack is short-lived but intense. Usually it does not exceed 2 minutes.
Doctor of Medical Sciences Alexander Leonidovich Myasnikov and neuropathologist Natalya Feliksovna Govorukhina will talk about what symptoms arise about the pathology and how it is treated:
- At the moment when the pain is expressed to the maximum, the person freezes with a grimace on his face. Short-term paralysis of facial muscles is possible.
- Attacks can be repeated over several hours, with short intervals between them.
- Sometimes pain is observed only in the area of the teeth, which complicates the diagnosis.
Read also: Tooth extraction in early pregnancy
The disease also has other signs: redness of the skin, increased lacrimation and salivation. The facial muscles begin to twitch. Subsequently, there is a deterioration in general health, sleep disturbance, fever, numbness of the cheeks and nose. If treatment is not started in time, facial asymmetry and other signs will remain forever.
Symptoms
The location of pain and other symptoms of neuralgia depends on which branch was affected. If several branches are affected at once, the symptoms may be combined. It is worth paying attention to the following signs; movement disorders with damage to the trigeminal nerve manifest themselves in this way.
- When the first branch is damaged, the sensitivity of the skin of the forehead and scalp in front is impaired, the sensitivity of the eyelid and eyeball on the affected side is impaired. The brow reflex decreases, facial expressions become less pronounced.
- When the second branch is damaged, the sensitivity of the skin of the side of the face, the lower eyelid and corner of the eye, the teeth of the upper jaw, and the mucous membrane in the lower part of the nasal cavity is impaired.
- When the third branch is damaged, sensory disturbances occur in the lower jaw, lower lip and skin of the chin, and disturbances in the functioning of the facial muscles. Paralysis of the masticatory muscles occurs, atrophy may develop, as a result of which the face may lose its usual contours.
Cramps in the jaw area and muscle paralysis may also be observed. If the sensitive part of the nerve is damaged, acute pain may occur, spreading along the affected branch.
When diagnosing the disease, sensitivity is checked, pressure is applied to the nodes of the facial nerves, checking whether pain is present. When examining disturbances in motor function, they look to see if the lower jaw moves when opening the mouth. Additional methods may be used to assess the condition of nerve branches and muscles.
It is also important to identify the cause of damage to the trigeminal nerve; the subtleties of treatment may depend on this. If there is no obvious cause for the pain, paralysis or numbness, further investigation is required. You may need a blood test, x-ray, MRI, and others.
Important! If you do not treat the lesion in time, it will be extremely difficult to restore muscle tone.
How to define a disease?
Diagnosis is carried out by a neurologist. For inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on the face, a specialist must conduct special tests. Basically, the diagnosis is established based on the patient's complaints. The specialist must determine the nature of the pain and the factors that provoke it. The location of the discomfort is also important. Trigeminal neuritis is determined using the following studies:
- Palpation of the face.
- Determining the presence of inflammatory diseases: sinusitis, sinusitis.
- MRI.
- CT.
- Angiography.
The pathology code according to ICD is G.50. It should also be noted that the diagnosis of the disease should be differential. The fact is that trigeminal neuritis in its symptoms is very similar to occipital neuralgia. Therefore, the root cause of discomfort should be identified as accurately as possible.
Types of inflammation
Depending on the mechanism of occurrence, primary (true) and secondary inflammation are distinguished:
- In the first case, the pathological process develops as a result of compression of the nerve roots or disruption of the blood supply in the absence of other pathologies, that is, an isolated lesion of the trigeminal nerve occurs. With primary inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, the pain is periodic and severe, piercing.
- In the second case, the nerve may become inflamed as a result of existing diseases or as a complication of the previous one. This type of pathology is expressed in constant, burning pain that occurs in any inflamed part of the face.
We suggest you read: Is it painful to remove a nerve from a tooth: with anesthesia, without anesthesia, video
What complications can the disease cause?
If treatment of the disease is not started on time, the consequences will be quite severe. Among them are:
- Hearing problems.
- Impaired sense of taste (and it can last a lifetime).
- Chronic pain that will recur under the influence of even the smallest factor.
- Atrophy or paresis of facial muscles.
- Serious damage to the nervous system.
- Sleep problems.
Traditional and physiotherapeutic treatment
This disease is difficult to treat. If the patient feels severe discomfort for more than a day, then further therapy is carried out in the inpatient neurological department. In this case, various methods are used: medications, physiotherapeutic, surgical. Often, folk remedies are used to eliminate pain, as well as the causes of its occurrence.
Among the drugs that are most often used for therapy, the following groups can be distinguished:
- Anticonvulsants: “Konvulex”, “Difenin”, “Finlepsin”. These drugs occupy a major place in drug treatment. They provide an anticonvulsant effect, inhibit neuronal activity, and eliminate pain. However, they are toxic, so they cannot always be used. In addition, the drugs presented have a negative effect on the liver and kidneys, causing mental disorders and drowsiness. They should only be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account all the characteristics of the body. Each tablet should be taken according to the instructions.
- Non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics: Analgin, Nise, Nurofen, Movalis. They must be taken strictly according to the instructions. The course of treatment usually does not exceed 7 days, but it can be extended according to doctor’s indications.
- Non-narcotic painkillers: “Ketalgin”, “Dexalgin”. They are necessary in the presence of severe pain. Trigeminal nerve blockade by injection may be necessary.
- Vitamin preparations, as well as neuroprotectors: “Milgamma”, “Neurorubin”. Thanks to them, you can reduce the risk of a recurrence of an attack.
- Glucocorticosteroids: Dexamethasone, Methylprednisolone.
- Antidepressants and sedatives: Amitriptyline.
Physiotherapy is no less useful. It can enhance the effect of any drug, as well as its effectiveness. Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is carried out using the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Electrophoresis
- Phonophoresis
- Ultrasound.
- Acupuncture.
Leonid Nikolaychuk, a patient who suffered from the disease, will talk about his treatment experience:
- Laser therapy. It relieves pain because it slows down the passage of nerve impulses through the fibers.
- Exposure to electromagnetic field.
- Irradiation with ultraviolet or infrared rays. Makes it possible to eliminate pain.
In addition, antiviral agents are used to combat the disease, as well as medications that promote the resorption of cholesterol plaques in the blood vessels. Drug therapy is selected for each patient individually, depending on the severity of the pathology, as well as the characteristics of his body.
Treatment of the disease is a serious campaign
You do not need to decide on your own how to treat the disease. Prescriptions should be made by a doctor, not friends on the forum, even if he is entirely devoted to this disease.
Conservative methods are used as therapeutic therapy, which include medication and physiotherapeutic procedures.
If radical action is needed, surgery is performed. There are many surgeries to treat the trigeminal nerve. The neurosurgeon will determine which method to choose.
Medicines
Drug treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is based on the use of drugs from the following groups:
- Non-steroidal and painkillers
tablets and other dosage forms of medications: Celebrex, Baralgin, Movalis, Analgin, Dikloberl. Therapy lasts from five to seven days, since these drugs negatively affect the intestines, stomach and liver. - Non-narcotic medications for severe pain : Ketanov, Dexalgin, Ketalgin.
- Narcotic analgesics : Morphine, Promedol, Nalbuphine, Tramadol.
- If neuralgia is caused by a virus, antibiotics : Lavomax, Acyclovir, Gerpevir.
- Anticonvulsants : Tegretol, Carbamazepine or Finlepsin. They quickly relieve cramps, spasms and pain.
Medication treatment cannot be carried out without a specialist’s prescription! The doctor must select not only the drug, but also indicate the dosage.
Physiotherapy
For trigeminal neuritis, the following physiotherapeutic manipulations are used:
- Ion therapy or electrophoresis - a medicinal substance is injected through the skin, pain and inflammation are eliminated.
- Laser radiation – relieves pain and swelling.
- Ultraphonophoresis - has a stimulating effect on tissues and cells.
- UT – vibration massage of tissues and acceleration of cell division are performed.
- DDT is an electrotherapeutic method that improves blood circulation, relieves headaches, and relieves swelling.
- Electromagnetic radiation – improves blood flow and muscle tone.
- UFO – improves the processes of nervous activity.
Surgical intervention
The operation is performed by an experienced neurosurgeon. Various types of operations are used, some of them:
- Microvascular decompression . During the operation, the vessel is removed or moved, as it creates excess pressure on the trigeminal root. In rare cases, facial numbness, stroke, double vision, and deafness may occur.
- Percutaneous rhizotomy . Glycerin is used as a medicinal substance. It is injected through the skin of the face into the area of the triple node of all branches.
- Air percutaneous compression . Using a needle, a balloon is placed near the nerve, which creates damage to the nerve ending. The disadvantage is that the pain may return after a while, sometimes the face goes numb.
- Radiosurgery using the Gamma Knife device. Thanks to ionizing radiation, the damaged process is eliminated. After 14 days, the patient's pain will begin to decrease.
Massage
The procedure is performed in a sitting position. The neck muscles should be relaxed, the head thrown back. The collarbone, chest and mastoid muscles are massaged. Then the parotid parts are rubbed and the injured and then the healthy part of the face is stroked.
The entire massage lasts no longer than 15 minutes, one course includes from 10 to 14 sessions.
Traditional methods
In alternative medicine, the following recipes are used to treat this disease:
- Geranium . The leaves of the plant are washed with running water, dried, kneaded in the hand and wrapped in a bandage or gauze. The bandage is adjusted to the painful area for 30 minutes. The manipulation is carried out 4 times a day.
- Horseradish root . The product must be ground to a paste. Gauze is placed into the prepared mixture for impregnation, then it is placed on the damaged area of the skin.
- Ice . You need to apply ice over your entire face and neck. Then the skin is warmed up with massaging movements and so on three times. After a while, the procedure is repeated.
- Vodka and raspberry tincture . The proportions are 3 to 1. The product is infused for 9 days and taken before meals for three months.
Folk remedies are an additional treatment, not a primary one; before using them, you should consult a doctor.
When is surgery necessary?
The operation is performed only if drug therapy has not given the desired effect for a long time. It can be used to eliminate the cause of the development of pathology, as well as to reduce the speed of impulses along the branch of the trigeminal nerve. In the first case, various brain tumors, aneurysms, and vasodilation are removed. It is also permissible to increase the exit point of the nerve itself from the skull. If the chosen surgical intervention is performed successfully, then trigeminal neuropathy goes away.
To reduce the conductivity of fibers, the following types of operations are used:
- Radiofrequency destruction. It destroys nerve roots that are pathologically altered.
- Balloon compression. Due to prolonged compression of the trigeminal ganglion with air, the pain fibers gradually die.
- Rhizotomy. It is carried out using the method of electrocoagulation, and involves dissection of pain fibers.
One intervention is not always enough. In some cases, multiple operations will be needed. Trigeminal neuropathy is a complex disease that is not easy to manage.
Traditional treatment of the disease
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can be treated even with the help of folk remedies. However, you must first consult a doctor. The following recipes will be useful:
- Chamomile decoction. To prepare 1 tsp. dried flowers must be poured with a glass of boiling water. Next, you need to cool the liquid a little, put it in your mouth and keep it there until the pain subsides.
- Fir oil. The product should be rubbed into the affected parts of the face throughout the day. It should be taken into account that it may cause redness of the skin, but the pain will go away. The course of treatment is 3 days.
You will learn more recipes by watching our video:
- Buckwheat compress. A glass of cereal should be fried, placed in a bag made of natural fabric, and applied to the affected areas until it cools down. The procedure is repeated up to 3 times a day.
- Clay. It should be mixed not with water, but with vinegar. After this, thin cakes are made from the pulp and applied to the affected area. The procedure must be repeated every evening.