Acute cerebral circulatory disorders are becoming an increasingly pressing problem. The statistics are astonishing: more than 15 million cases of the disease are recorded annually throughout the planet, with a recurrent stroke diagnosed in a quarter of patients. What provokes the development of repeated disruption of blood flow in the brain tissue, how does it manifest itself, what are the methods of treatment and prevention of this condition?
In recent years, there has been a significant decrease in the average age of patients with repeated acute cerebrovascular accidents. The pathology increasingly affects the working population, while the incidence among older people is also growing. Severe consequences and an unfavorable prognosis turn the nosology into a real medical and social problem of our time. What is the danger of a recurrent stroke and how to avoid it are pressing questions for each of us.
Features of the structure of the prostate, functions performed
What is the prostate gland? What are the features of the anatomical structure and functions of the organ? The prostate is a purely male organ. It has the shape of an inverted trapezoid. As mentioned above, it covers the urethra and seminal ducts.
Male reproductive system
The prostate gland consists of two lobes, which are connected by an isthmus. The age factor provokes thickening of the isthmus, which contributes to compression of the canal. This leads to stagnation of urine and provokes inflammation of the bladder and kidneys.
The glandular organ performs the following functions:
- Secretory. Ensures the production of testosterone, stimulates secretions that are involved in the process of fertilization of the egg.
- Motor. The smooth muscle fibers of the organ are a sphincter that holds urine in the bladder.
- Barrier. Prevents the spread of infection from the urethra up the urinary tract.
The prostate produces hormones, ensures normal urination, and holds urine in the bladder when necessary. The adequacy of the prostate is an important aspect of men's health.
Healthy prostate and prostatitis
Explicit and hidden dangers
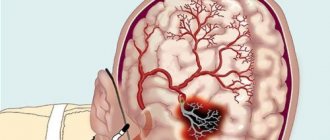
A secondary stroke is dangerous because it shortens the patient’s life to 2-3 years, occurs more extensively, affects more centers, depriving a person of the ability to think and move.
In almost all cases, a relapse ends with the patient receiving disabled status. The risk of death is significantly increased.
Depending on the location of the hemorrhage or ischemia, the patient risks losing certain functions of his body. Damage to the right hemisphere affects the functions of the left side of the body, and damage to the left hemisphere will affect the right side.
A person may experience the following disorders (sometimes several at once):
- loss of speech;
- loss of vision;
- loss of motor ability;
- loss of sensitivity.
The third and subsequent strokes, as a rule, are difficult for a person to survive. There is a significant risk of complete impairment of motor functions. Often, after the third attack, 65% of patients fall into a protracted coma, from which they rarely return to conscious life.
Malignant tumor formations
Malignant prostate pathology is the most common disease affecting men over fifty to sixty years of age. The causes of prostate cancer are heredity, progressive adenoma (benign tumor).
Symptoms and main manifestations of cancer can be divided into three groups:
- Impaired outflow of urine. Urination is frequent, in small portions. Nocturnal urination predominates. The urge to urinate is pronounced.
- Symptoms as a result of tumor growth. The appearance of blood in seminal fluid and urine. Erectile dysfunction. Palpable pain localized in the groin, perineum, and lower back.
- Symptoms as a result of metastases. Pain in the bones, swelling of the limbs, enlarged lymph nodes, sudden weight loss. Anemia develops as a result of a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells. Cancerous exhaustion, so-called cachexia, is also observed.
Malignant tumor
Diagnosis of cancer tumors and their treatment are mandatory steps on the path to recovery. Research methods such as prostate biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound scanning help establish an accurate diagnosis, characteristics, and location of the cancer tumor.
Prostate cancer is treated with surgery and minimally invasive interventions. Surgical means radical removal of the prostate while preserving erectile and urinary functions. An example of a minimally invasive intervention is targeted exposure to high-intensity ultrasound waves. Extreme temperature increases lead to the destruction of cancer cells. Radiation therapy is also carried out, targeting the tumor and lymph nodes.
Only 8% of stroke survivors are able to return to their previous jobs
Photo: iStockPhoto
October 29 is World Stroke Day, established by the World Stroke Organization in order to draw people's attention to this problem. Expert Dmitry Napalkov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, answers Gazeta.Ru’s questions. Professor, Department of Faculty Therapy No. 1, Faculty of Medicine, First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov.
According to the World Stroke Organization
.
One in six people will experience a stroke in their lifetime. The most common risk factors for stroke are hypertension, coronary heart disease, high cholesterol, and atrial fibrillation. And these risk factors are contributed by an unhealthy lifestyle: poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking and alcohol. According to experts, up to 80% of strokes can be prevented by preventive measures. Research has shown that even small steps toward a healthier lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk of stroke
.
And Swedish scientists have calculated that physical activity (which can also include working in the garden) reduces the risk of heart attack and stroke by 27%
.
— What is the trend in stroke incidence in recent years? Is it getting bigger?
— Over the past decade, the incidence and mortality from stroke have decreased in many Western European countries, but the number of patients with stroke is expected to increase due to demographic aging of the population and insufficient control of major risk factors.
According to the World Stroke Organization, 15 million people a year suffer a stroke.
Of these, 3 million are patients with atrial fibrillation. According to WHO, in 2002, about 5.5 million people died from stroke worldwide.
In Russia, stroke ranks third among the causes of death among Russians: about 200 thousand people die from it every year.
Stroke translated into numbers
About half of stroke survivors experience the problem again within the next five years.
— Is it true that stroke has made you younger recently? Is it possible to indicate the age groups in which it occurs most often? Are there differences between men and women?
— According to statistics, strokes equally often affect men and women. But for men, it is often accompanied by more severe consequences, mainly due to associated cardiovascular risk factors.
The main risk group for stroke is patients 65 years of age and older with additional problems - hypertension, atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation), and high cholesterol levels.
Cardiac arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, which increases the risk of stroke fivefold, can also occur in young people (20–30 years old) with a number of congenital defects of the conduction system of the heart and are most often provoked by excessive alcohol consumption. In addition, now more and more people aged 30–50 years are overweight, constantly live in a state of stress, and have high blood pressure, which, of course, leads to an increase in the incidence of stroke in this age group.
— What is the ratio of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes? How does the prognosis differ for these two types?
— According to recent studies, the ratio of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke is 5:1 (or 85 and 15%). Hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain) is more severe in its consequences; the risk of death when it occurs ranges from 60 to 90%. If we consider the different types of ischemic stroke, it is important to note the severe consequences of cardioembolic stroke, which most often occur with atrial fibrillation and claim the lives of about 20% of patients, and disability after it reaches 60%.
The patient's prognosis greatly depends on the time after which he seeks professional help.
“Hypertension has a bright future”
If adequate measures are taken up to 4.5 hours after a stroke, a person is more likely to regain full or partial body function.
— What are the current stroke outcome rates? What is the fatality rate? Disabilities? Is a full recovery possible?
- 50% of stroke patients become disabled, 30% of whom require outside care with the help of a nurse - these are people who become bedridden for life.
Of all deaths from cardiovascular diseases, 27% are due to cerebral stroke of ischemic origin.
And only 8% of stroke survivors are able to return to their previous jobs.
— Is there such a thing as a “micro-stroke”?
— There is such a concept, but in medical circles it is called lacunar stroke. And the big danger here is that a person may not notice it and not take the necessary measures to prevent a recurrent stroke. Those who suffer from sensitivity to geomagnetic storms and pressure changes may be susceptible to it. Both stress and excessive physical activity affect the likelihood of a mini-stroke. So no one can be completely protected from a mini-stroke.
— Are there any signs by which a non-specialist might suspect that a person is having a stroke so that they can immediately call for help? The following signs appear on the Internet: the inability to clearly answer a question, a lopsided smile, etc. This means that if this happened to a person in a public place, can others help and what should be done?
“Indeed, there are several techniques for recognizing stroke symptoms by others.
If you ask a person to smile, the smile may come out crooked; the corner of the lips on one side may be directed downward rather than upward. When speaking, pronunciation may be impaired. When you ask a person to raise both arms, and he cannot raise them at the same time, synchronously, this can also be a symptom of a stroke. It is necessary to ask the victim to show his tongue: during a stroke, it deviates from the center to one side. And if you ask a person to stretch his arms forward, palms up, and close his eyes, one arm involuntarily moves to the side and down.
Adenoma
Hyperplasia (excessive growth) of the prostate is an age-related pathology. Every second man over sixty years of age is susceptible to the disease. The essence of the pathology is the benign growth of prostate tissue, followed by blockage of the urethra.
The main reason for the development of adenoma is hormonal changes. Disruption of metabolic processes, an increase in the level of female hormones against the background of a decrease in male hormones leads to the formation of nodules, which over time increase to a significant size.
Prostate adenoma
Clinical manifestations are based on the main problem of adenoma - urinary disturbances. The main manifestations include:
- Difficulty urinating leads to the formation of residual urine. This contributes to the development of purulent-inflammatory processes, the accumulation of salts, with the subsequent formation of stones.
- Acute urinary retention. Promotes the development of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
Pain localized in the lumbar region, soreness accompanying the process of urination, small portions of urine are the main symptoms of adenoma.
Diagnostics includes: medical history, digital examination, gland biopsy, ultrasound examination, tumor marker (allowing to differentiate a benign tumor).
The optimal treatment option is surgery. Today, operations such as laparoscopic adenectomy, transurethral electroresection, and laser enucleation of hyperplasia are performed.
Consequences of a recurrent stroke
Why is a recurrent stroke dangerous? This question is often asked to doctors. And, unfortunately, the answer will not please you.
The consequences of a recurrent stroke are serious:
- Disability. After repeated disruption of cerebral circulation, almost all patients experienced a persistent loss of intellectual and motor activity. The patient does not orient himself in space and time, loses memory, cannot move independently—becomes disabled. A life-threatening prognosis and rehabilitation measures often do not bring positive changes in a person’s condition.
- Coma. Due to irreversible changes in the structures of the brain that occur during acute circulatory disorders, a person develops a pronounced inhibition of vital processes. Loss of consciousness, disappearance of reflexes, breathing problems and interruptions in heart function - these are the dangers of a stroke that develops again. The prognosis for life is unfavorable.
- Death. The five-year survival rate of such patients does not exceed 15%.
Signs of a recurrent stroke
The clinical picture of relapse of the disease resembles the debut episode of acute cerebrovascular accident with more severe symptoms. They often appear at night, suddenly. Typical symptoms include:
- Impaired motor activity. Weakness appears in the facial muscles and muscle groups of the limbs. It can be one-sided or two-sided. The first option is more common. In this case, a lesion on the left side of the brain is accompanied by impaired motor activity on the right side of the body, and an ischemic focus on the right side of the brain causes weakness on the left side of the body. This is explained by the peculiarities of innervation and is considered one of the key signs of the disease.
- Impaired sensitivity. This symptom is also more often one-sided. In this case, the cross principle remains the same: the right side of the brain is affected - sensitivity is lost in the left half of the body, and vice versa.
- Articulation impairment. A person is trying to tell something, but his speech is slurred, often on abstract topics. It is also difficult for him to understand the speech of others.
- Deterioration of vision. Loss of visual fields, “floaters” before the eyes, visual hallucinations are symptoms indicating hypoxia of the nervous tissue.
- Acute headache. This sign often appears at the peak of arterial hypertension.
Acute prostatitis
Modern medicine distinguishes such types of prostatitis in men as acute and chronic. The immediate cause of acute prostatitis is bacterial microflora. Getting from the source of infection to the prostate, bacteria contribute to the occurrence of the inflammatory process. Predisposing factors significantly accelerate the process: hormonal disorders, congestion in the pelvic organs.
Acute prostatitis is an acute inflammation of the prostate gland caused by infection
Medical classification distinguishes three forms of prostatitis:
- catarrhal There is inflammation of individual prostate ducts;
- follicular. Spread of the pathological process to the lobes of the prostate gland;
- parenchymal. Lack of treatment in the initial, mild stages leads to the spread of inflammation to both lobes of the glandular organ and the involvement of connective tissue. Abscess is the most severe form.
Symptoms of prostate inflammation are varied. There are local and general. Local symptoms include pain in the anal area, genitals, and perineum. The main symptom is impaired urination (frequent, small portions). General symptoms include a slight increase in temperature (rarely up to forty degrees), weakness, drowsiness, loss of appetite, dizziness.
Diagnosis of acute prostatitis includes medical history, rectal digital examination (palpation), laboratory tests (blood, urine).
Based on the results of the diagnosis, comprehensive treatment is prescribed, including drug therapy (antibiotics are required), adherence to a strict diet, cessation of smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Why is "HE" coming back?
According to statistics, age, gender and the nature of the cause that caused the primary stroke do not play a role in its recurrence. Having a stroke does not eliminate the risk factors for this disease.
On the contrary, the blow only aggravates the preconditions that existed before the hemorrhage, thereby forcing time to play against the patient, provoking the disease again. And the patient’s negligent attitude to the doctor’s instructions only increases the likelihood of another stroke.
Risk factors include:
- high (or low) blood pressure;
- visceral pathology;
- arterial hypertension;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- vascular stenosis;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- overweight;
- metabolic disease.
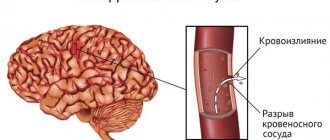
After identifying these factors in a patient, specialists identify the patient at risk for a recurrent stroke. The immediate physiological causes that initiate repeated hemorrhage (hemorrhagic stroke) are:
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombosis;
- artery aneurysm;
- vascular inflammation.
Chronic prostatitis
The medical classification distinguishes acute and chronic types of prostatitis and the main difference between them is the presence or absence of an inflammatory core.
In chronic prostatitis, there is no focus, however, the following symptoms appear:
- pain in the groin area;
- disturbance of urination (small portions of urine). Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- subsidence of sexual desire. Increased risk of developing impotence;
- aggressiveness, short temper, loss of strength, depression.
Congestive prostatitis occurs for two reasons. The first is stagnation of venous blood. The second is stagnation of the secret. Varicose veins, as well as a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and alcohol can provoke blood stagnation. Prolonged arousal, abstinence from sexual relations are the reasons that provoke stagnation of secretions.
Diagnostic measures, as well as for acute prostatitis, include anamnesis, palpation examination, urine and blood tests. Therapeutic measures other than bacterial inflammation of the prostate do not involve the use of antibiotics. Painful sensations and the inflammatory process are controlled with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The basis of treatment is massage and physiotherapy procedures.
Secondary prevention of brain stroke
As doctors assure, it is possible to avoid a recurrence of a brain stroke only if maximum efforts are made by the patient himself and the people around him. To do this, a victim of primary apoplexy must:
- Observe strict intake of all medications prescribed by doctors.
- Monitor and combat high blood pressure.
- Eat well.
- Do therapeutic exercises regularly.
- Monitor the reasonableness of your own physical activity.
- Unconditionally give up bad habits of smoking, alcohol and any other.
- Protect yourself from stress.
- Know and remember the first signs of relapse of the disease and regularly visit the doctor for prevention. If a patient experiences frequent dizziness, headaches and other symptoms, albeit remotely, that remind him of a brain stroke, he needs urgent consultation with a doctor.
Regular observation by a specialist
Let us note that for medical specialists it is quite obvious that it is important to begin secondary prevention of brain stroke from the moment of treatment of the primary cerebrovascular problem.
From the standpoint of evidence-based medicine, drug prevention of brain stroke recurrence must include three main areas. We are talking about the use of antihypertensive drugs, blood clot blockers and the use of so-called statins.
Every patient who has previously suffered an acute form of cerebrovascular accident should receive treatment according to a similar strategy, which can significantly reduce the risk of relapse, as well as radically reconsider their lifestyle, habits and diet. Such changes should be made in your daily life in the future.
Pressure control
To prevent another stroke, you need to control your blood pressure. Normally, it should not exceed 139/89 mmHg. The optimal blood pressure value is 120/80 mmHg. After a previous stroke, it is recommended to measure blood pressure twice a day. To do this you need to purchase a tonometer. If you have hypertension, you should consult a doctor immediately. In order to normalize blood pressure, it is necessary to take antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers or diuretics).