Impaired consciousness
- a state of upset consciousness, syndromes of its switching off (coma, stupor, stupor) or stupefaction (oneiroid, delirium, twilight state of consciousness). Full functioning of consciousness presupposes a state of wakefulness, due to the full implementation of the cognitive function of the cerebral hemispheres and their relationship with the awakening mechanisms of the reticular formation, the distribution of nuclei and pathways of which are found in the diencephalic region, midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata.
The reticular activating system is a functional rather than a morphological concept and is located along the central axis of the diencephalic region and the upper brainstem. This system receives afferent impulses from many somatic, visceral, auditory, and visual sensory pathways, sends them to the reticular nucleus of the thalamus, from which, in turn, activation spreads throughout all parts of the cerebral cortex.
Content
- 1 Etiology
- 2 Types of disorders and disorders of consciousness 2.1 Syndromes of confusion in psychiatry
- 3.1 Supratentorial volumetric processes
Causes of the symptom
As mentioned earlier, the reasons for the appearance of such a symptom will not always indicate health problems. For example, in the event of a failure in the hormonal system, a person almost always develops fog in the head, a confused, cloudy consciousness. This condition often accompanies the pregnancy of women, and forgetfulness and irritability are also added. In addition, cloudy consciousness and fog in the head of the fair sex appear during menopause.
Etiology
Impaired consciousness is a manifestation of dysfunction of the hemispheres, the upper parts of the brain stem, or both areas simultaneously. Thus, local damage to supratentorial structures can be widespread, or, causing edema, it can displace brain structures, leading to transtentorial herniation, compression of the diencephalic parts of the brain and disruption of the function of the diencephalic activating system.
- Primary subtentorial processes (brainstem and cerebellum) can compress or directly damage the reticular activating system between the mid-portions of the pons and the diencephalic region.
- Metabolic or infectious diseases can have a depressing effect on the function of the hemispheres and brainstem through abnormal levels of blood components or direct toxic effects.
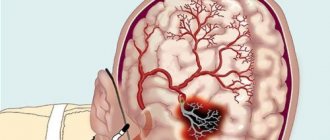
- Impaired consciousness can also be observed when there is a violation of cerebral circulation (syncope and heart attack) or when there is a change in the bioelectrical activity of the brain (epilepsy). Inadequate cerebral blood flow and chemical imbalances in the blood can also cause abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
- Concussions and psychological disorders cause impairment of consciousness without visible structural changes in the brain.
Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome
This disease can be cured using psychotherapeutic methods. However, provoking factors should also be excluded at the initial stage of therapy: lack of sleep, stress, mental stress and excessive physical activity. If you do not reduce the influence of these factors, then drug treatment and psychotherapy will not have the desired effect and will not eliminate the unpleasant symptom.
Medicines are used in severe cases. The most effective are sleeping pills, restoratives, antipsychotics, antidepressants and tranquilizers.
Types of disorders and disorders of consciousness
Impairment of consciousness can be short-term and long-term, superficial and deep.
- A short-term loss of consciousness is observed with syncope. With seizures, loss of consciousness may last longer, and with a concussion it can last up to 24 hours.
- Long-term impairment of consciousness is observed with intracranial pathology or metabolic disorders.
- Obtundation is manifested by decreased levels of wakefulness and is usually accompanied by hypersomnia. There are moderate and deep stunning with very arbitrary boundaries [1]. Obnubilation (“clouding of consciousness”, English) is a mild degree of deafness, slowed reactions and a “clouded” perception of reality.
- Moderate stun - partial disorientation, moderate drowsiness, compliance with all commands.
- Deep stun - disorientation, deep drowsiness, execution of only simple commands.
- Stupor (English stupor) is a concept in English literature, similar to stupor. In addition, the term is used in psychiatry to designate a symptom of catatonia and mania (catatonic stupor, manic stupor).
- Coma I - consciousness is lost, the patient does not open his eyes, in response to painful stimuli he responds with uncoordinated defensive movements without localizing the pain.
Syndromes of confusion in psychiatry
Main article: Syndromes of confusion
Confusion of consciousness, disorders of reflection of surrounding reality:
- Amentive syndrome
- Aura of consciousness
- Delirious syndrome
- Oneiric syndrome
- Twilight stupefaction
- Narrowing of consciousness (observed with affect, as well as with dissociative and conversion disorders)
How to deal with the effects of sugar
Choosing foods that raise blood sugar levels is important. To help make these choices, it helps to understand the glycemic index of foods. This is a rating given to foods that tells you how quickly that food will raise your blood sugar.
Low glycemic index foods penetrate your bloodstream slowly and efficiently. A high glycemic index puts you at risk for that quick, unwanted sugar spike I was talking about.
Eating healthy, low glycemic foods will help keep your blood sugar levels at moderate levels. You'll use it where it's needed for physical activity, but you won't overload your system so much that your insulin doesn't have time to process it properly.
People in Everyday Health explains some simple ways to maintain your blood sugar levels. First, you want to make sure you don't skip any meals. Always plan to have at least 3 meals and 2 snacks per day.
The most common causes of impaired consciousness
Supratentorial volumetric processes
- Epidural hematoma
- Subdural hematoma
- Cerebral infarction or intracerebral hemorrhage
- Brain tumor
- Brain abscess
Subtentorial damage
- Brainstem infarction
- Brain stem tumor
- Hemorrhage in the brain stem
- Hemorrhage into the cerebellum
- Brain stem injury
Diffuse and metabolic brain disorders
- Trauma (concussion, brain injury or bruises)
- Anoxia or ischemia (syncope, cardiac arrhythmia, pulmonary infarction, shock, pulmonary failure, carbon monoxide poisoning, collagen vascular disease)
- Epilepsy
- Condition after an epileptic seizure
- Infections (meningitis, encephalitis)
- Subarachnoid bleeding
- Exogenous toxins (alcohol, barbiturates, glutethimide, morphine, heroin, methyl alcohol, hypothermia)
- Endogenous toxins and metabolic disorders (uremia, hepatic coma, diabetic acidosis, hypoglycemia, hyponatremia)
- Psychomotor status epilepticus
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia
So, we figured out that the head is in a fog - this can be a symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia. To eliminate it, you need to seek help from a doctor. To relieve symptoms, various medications are used: sleeping pills, sedatives, drugs for dizziness, as well as medications to normalize blood pressure. In addition to drug treatment, experts also recommend adjusting your lifestyle: eating right, doing light sports, walking more often, eliminating stressful situations, waking up and going to bed at the same time, and giving up bad habits.
Also very effective in the fight against this disease are physical procedures, massage, and acupuncture.
Locked-in syndrome
Main article: Locked-in syndrome
Locked-in syndrome reflects a patient's condition in which consciousness is preserved, but contact with him is impossible due to bilateral paralysis of all parts of the body, with the exception of eye movements, with which the patient encodes his response.
Various diseases can lead to this condition, which results from bilateral damage to the corticospinal tract between the midbrain and the pons or from massive damage to the lower motor neurons (anterior horns of the spinal cord).
How to clear the fog in your head?
If negative symptoms appear due to lack of sleep, then you can simply get enough sleep and rest. Then the fog in your head will go away. But if this symptom occurs regularly, it is necessary to take measures to avoid possible complications.
But how can you remove the fog in your head and gain clarity of thought? First of all, you should seek help from a qualified doctor, who should find out the main reason for the appearance of such a symptom.
Brain death
The ability to provide mechanical ventilation to maintain lung and heart function over long periods of time despite impairment of other organ function has led to widespread legal and public recognition that human death is determined by the complete absence of brain activity, especially the brain stem. To establish this diagnosis, the doctor must be based on knowledge of the structural or metabolic causes of brain death, while excluding the possibility of the influence of anesthetic or paralyzing drugs, especially those taken by the patient independently. Correction of hypothermia (below 30 degrees C) is necessary.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome
If there is no clarity in the head, then this may indicate astheno-neurotic syndrome. This pathology, in addition to constant fog in the head, is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Problems falling asleep.
- Superficial sleep.
- Suspiciousness, irritability, hot temper.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Unreasonable anxiety.
- Daytime sleepiness.
- Decreased ability to work.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat.
- Memory problems.
- Stiffness of movements.
- Dizziness.
- Constrictive headaches.
- Tremor of the limbs.
In most cases, this syndrome affects people who are mentally stressed. In addition, this pathology often affects those who have an unstable psyche.
The main causes of astheno-neurotic syndrome are prolonged stress, prolonged nervous tension, anxiety, chronic lack of sleep, and overwork. In addition, pathology can occur in people who have the following diseases and ailments:
- Various chronic diseases.
- Hypertension.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Poisoning.
- Acute viral infection.
- Avitaminosis.
- Head injuries.
- Bad habits.
The syndrome develops over time. At the initial stage of its development, a person feels weak in the morning, restlessness and mild irritability. After this, in the absence of medical intervention, other symptoms appear in the form of sleep disturbances, loss of strength, memory problems, heaviness in the head, a feeling of futility, the appearance of fog in the eyes, as well as decreased ability to work.
After this, pain in the heart sets in, excessive irritability gives way to weakness, appetite disappears, mood and libido decrease, apathy appears, and the patient constantly thinks about the state of his health. As a rule, such people develop a fear of death. Ignoring such symptoms can lead to mental illness.
Causes of a heavy head feeling
Depending on the cause, the pathological manifestation may occur once a week or less, or become a constant companion.
The condition when the head is in a fog is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness and a feeling of lethargy, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the head;
- fatigue and weakness that are not associated with any type of activity or rest;
- a feeling of futility and dullness of consciousness - as if there is a vacuum in the head after drinking alcohol or drugs;
- headache, increased heart rate, and changes in blood pressure may be present. Often a person does not think well and cannot even move due to the fact that the muscles “do not work.”
Minor inflammations of the brain cause a distracted feeling, which makes it difficult to think clearly, the brain has difficulty thinking. The limbic system, which processes emotions and memories, is especially affected.
A person feels as if in a fog, as if a thousand bells are shimmering in his head. He has a feeling of wobbliness, a cloudy, vague state in his head. If an imbalance occurs due to oxidative stress or nutritional deficiencies, the following symptoms occur:
- concentration disorder;
- clouding of the head;
- memory problems;
- fatigue and weakness;
- mood swings;
- headache;
- feeling of heaviness;
- disorientation;
- anxiety.
These symptoms last for several minutes or weeks, months, or even years if the cause is not found or eliminated. Not all symptoms of brain fog occur simultaneously; they vary from person to person.
Brain fog is often preceded (or accompanied) by the following symptoms:
- extreme fatigue;
- dizziness;
- heartbeat;
- dyspnea;
- anxiety;
- nausea;
- blurred vision;
- inability to concentrate;
- tremor;
- excessive sweating.
For some people, these symptoms worsen during eating, heat, exercise, or strenuous activity. Increased symptoms are typical for women during menstruation.
Diagnostics
Due to the subjective nature of the main symptom of the pathological process, it is very difficult for the attending physician to create a reliable clinical picture. The same symptom is described differently by different patients. In such cases, specialists do not make a diagnosis, relying only on a detailed history, and resort to a number of other diagnostic procedures, including:
- Conducting laboratory tests of blood (general, biochemical), urine. The procedure allows you to record the presence of inflammatory processes in the body, assess the general condition of the patient and identify diabetes, which could be the cause of the appearance of fog;
- implementation of biomicroscopy. One of the most detailed methods for identifying pathologies of the organ of vision: diagnoses the formation of an inflammatory process, edema, detects the appearance of adhesions, cellular fluids, leukocytes and lymphocytes in the middle membrane of the eye, which indicates the development of uveitis;
- determination of the intraocular pressure parameter, an increased value of which may indicate the probable occurrence of glaucoma.
Constant dizziness and weakness during VSD, why feel dizzy
Each patient receives the symptoms of VSD in an original set. They are impossible to classify. Even panic attacks that the same person suffers from are strikingly different from each other.
And the patient is not even able to accurately formulate some types of poor, frightening well-being in simple words, in particular this concerns dizziness.
The head is either spinning, or losing weight, or refusing to think.
When words fail, the doctor is to blame!
“My legs are strangely wobbly, I have a helmet on my head, my heart floats in a vacuum, my hands don’t seem to be mine...”
Two different patients can describe an identical symptom with completely different metaphors. Sometimes it is impossible to convince the sufferer that his colorful sensations are not at all what he thinks.
For example, in the case when the patient experiences a condition that he calls “dizziness.” After conducting a few simple examinations, the paramedic announces to the patient that this is NOT dizziness. In gratitude, the patient calls the doctor incompetent and ruthless, unwilling to fulfill his duties.
“I have constant dizziness, and you think I’m a malingerer!”
In fact, doctors do not consider anyone to be malingerers; they know very well that with VSD it is difficult and scary. But they also know the symptoms and causes of true dizziness, which is fundamentally different from the “circling” with VSD.
How do you get dizzy with VSD?
There are usually only two reasons that cause the feeling of dizziness during VSD:
- Insufficient blood supply to the brain with oxygen, which can be a consequence of both high and low blood pressure. This occurs during panic attacks, with any irritants that provoke the release of adrenaline or internal tension: a sudden change in weather, stress, being in a frightening situation associated with a phobia (crowd, transport, confined space, darkness, forest).
- Chronic weakness caused by long-term stress. Sooner or later, being under stress, a person gradually spends his energy and weakness appears, which does not go away with time. This weakness can manifest itself in the form of dizziness, cloudy head, weak legs, unsteadiness and unsteadiness of gait.
When any of these reasons comes into force, the patient feels a certain weakness, lethargy, constriction, cloudiness in the head - the symptoms are very individual. But the patient is unable to describe them with a more suitable word than “dizziness”.
Especially if the symptoms of this headache are supported by low blood pressure, unsteadiness of gait, and a feeling that the ground is disappearing from under your feet.
A person may feel as if he is about to lose consciousness: his eyes become dark, spots appear, his balance is unstable, and there is no hope for his legs to support him.
How can anyone doubt that the patient has real dizziness?
But a VSD person who loves to read medical articles should know: true dizziness, which is caused by organic pathologies, is really very different from the imaginary one. In childhood, many people loved to have fun, spinning around themselves for a long, long time, and then walking around “like drunken people.”
Remember these games, they just caused a condition similar to pathological dizziness.
With severely narrowed blood vessels in the brain, due to some serious diseases, complicated osteochondrosis, thrombosis, or in a state of severe alcohol intoxication, the head may become dizzy so much that it will not seem easy. Then, indeed, without the help of another person, the patient will not be able to take even a couple of steps.
With VSD, the vessels do not narrow so much, and the patient stands quite level on his feet, although he imagines that he can faint at any second. The brain may lack oxygen, but not in such a critical volume to prepare for a fall.
And if the problem is only in the nervous system, then constant dizziness will occur even with normal blood pressure with a stable, even pulse.
Here the problem will be in the moral state of the patient, which only a psychotherapist can examine.
How to relieve dizziness during VSD
What to do with dizziness with VSD? All symptoms of VSD, such as a feeling of constant dizziness, weakness, cloudy head, staggering, unsteady gait, are simply caused by stress.
And thus, you need to fight not with these symptoms, but with stress or, in other words, with an anxiety disorder. This is a psychological problem and it needs to be solved by a psychologist.
If the condition is very serious and the symptoms are strong, then in addition to working with a psychologist, you need to add antidepressants, which will lower the level of anxiety and increase stress resistance.
It should be understood that dizziness will not go away quickly; it takes time for a person to recover from stress and recover. Until this happens, it is better to be as calm as possible about dizziness, unsteadiness and cloudiness. You won’t faint from this and nothing bad will happen to you. The calmer you are about these manifestations of VSD, the easier you will tolerate them.
If you think that you are experiencing true dizziness, you should undergo a full examination and identify the real cause of this condition.
Source: https://vsdshnik.com/postoyannoe-golovokruzhenie.html
Identifying the cause is a priority
It has already been emphasized that all of the above sensations are just symptoms that indicate the development of a particular disease.
To accurately determine which disease causes heaviness and fogginess in the head, you should contact an experienced specialist.
Also, for your own education, you should familiarize yourself with the most common reasons why the head becomes heavy, and lead and weakness spread throughout the body.
Stress - stress - neurasthenia
In addition to feeling leaden, some patients experience fatigue, trouble sleeping, and loss of appetite. The person becomes irritable. All this is a sign of neurasthenia - a common phenomenon in our time.
Although the technological progress characteristic of the 21st century has made it possible to facilitate human physical activity, it has contributed to the development of stress on its mental component. Every day, a modern city resident experiences severe stress, both at work and on the way home.
The patient does not immediately detect a nervous breakdown. As a rule, it develops gradually. As stress accumulates, it reduces physical and mental activity. A person begins to experience difficulties in performing seemingly the simplest everyday tasks. He suffers from headaches and dizziness. The head feels like cotton wool, there is fog and cloudiness in the eyes. It becomes difficult to think and do something.
Osteochondrosis of the neck
It would seem that lead in the skull and compression in the temples are a direct indicator of brain disease, but this is a misconception.
It turns out that these and similar symptoms occur with degenerative disease of the discs located between the vertebrae.
Cervical osteochondrosis negatively affects not only the head, but also the upper internal organs. With this disease, the spinal cord receives more damage, and it, in turn, sends painful impulses to other parts of the body with which it is connected by nerve endings (in other words, throughout the body).
In addition to cloudiness and heaviness with osteochondrosis, the patient experiences ringing in the ears, which can either subside or intensify. This phenomenon is facilitated by pinching of the vessels supplying the brain. Disruption of neuron nutrition provokes auditory hallucinations, as well as:
- drowsiness;
- painful sensations in the back of the head and temples;
- visual impairment;
- memory losses.
Due to compression of the vertebrae, causing disruption of circulation in the brain, the patient feels not only heaviness and cloudiness, but also periodic dizziness. This, in turn, may be accompanied by sweating, burning in the face, and pain in the neck.
Allergic reaction
Unfortunately, not everyone is aware of all the pathogens that can cause this phenomenon in the body. An allergy is a malfunction of the immune system when a person interacts with something or someone. And it can happen at any time.
Swelling, swelling, nasal and mucous congestion are not the only symptoms of allergies. Often this reaction in the body begins with the appearance of congestion and fogginess in the brain.
Infectious lesions
The penetration of infection contributes to the deterioration of well-being. Often this process manifests itself through headaches and deterioration of visual function. The infection spreads very quickly in the body, which emphasizes the need for prompt medical intervention.
Injuries as a risk factor
Athletes and people whose work activities involve constant health risks are most susceptible to this phenomenon. Bruise, concussion and fracture - all this causes unpleasant sensations. Moreover, a varying period of time may pass before these signs appear from the moment of injury.
You don't have to be in an accident to get injured. One sudden movement is enough for the discs in the vertebra to shift. This can happen both during training and in public transport (during sudden braking). A person will not immediately feel a deterioration in health. Only a gradually heavier crown and growing fog in the eyes will indicate a deterioration in blood flow.
Oxygen starvation
The reasons for this phenomenon can be many factors:
- alcohol consumption;
- smoking;
- past injury;
- increase/decrease in pressure;
- displacement of discs in the spine;
- and much more.
The bottom line is this: due to the compression of the channels that supply the brain with oxygen, a gradual deterioration in well-being occurs. Fog appears in the eyes, the body is overcome by weakness, and the head becomes like a stone. A person feels better only in a supine position. Possible loss of consciousness.
Prevention
Cloudiness in your head will no longer bother you if you follow preventive measures. First of all, this symptom manifests itself in people in case of an incorrect lifestyle. If you eat poorly, don't get enough outdoor exercise, smoke, drink alcohol, don't exercise, take drugs, don't sleep well, or are constantly stressed, then you shouldn't even think about feeling good.
That is why, in order to improve the condition, experts recommend normalizing your rest and sleep patterns, and sleeping at least 8 hours every day. It will be very important to avoid frequent stressful situations. In addition, experts recommend increasing physical activity and exercising regularly. The best option would be swimming, cycling or jogging. In parallel with all this, you will have to adhere to the correct diet and nutrition regimen, as well as give up bad habits.
Now you know how to deal with brain fog. If you completely change your life, you can not only get rid of brain fog, but also strengthen your immune system and improve your overall health.
Source: fb.ru