Causes of drug addiction
Drug dependence occurs for the following reasons:
- psychological;
- situational;
- biochemical;
- social.
But the main mechanism for the formation of addiction is conditioned reflex processes, in which drugs cause euphoria, calm, harmony, and activity. The need to constantly take medications develops. A characteristic sign of drug addiction is a constant desire to increase the dosage. When symptoms of drug withdrawal occur, the patient experiences:
- mental disorders;
- discomfort;
- withdrawal (panic fear of drug withdrawal).
There are the following types of drug addiction:
- physical;
- mental;
During the physical stage, the patient develops neurological, autonomic, and somatic disorders. When mental dependence occurs, emotional instability and psychological discomfort, an uncontrollable desire to take the drug, as well as:
- euphoria;
- reduction of anxiety;
- elimination of nervous tension;
- changes in thought processes, attitudes towards others.
Drugs that cause drug dependence and other serious conditions include:
- tranquilizers;
- psychostimulants;
- sleeping pills;
- steroids;
- alcohol-containing products;
- analgesics (pentalgin);
- some antiarrhythmic drugs.
Drug dependence symptoms are characterized by a constant desire to take the drug, irritability, anxiety during its absence, insomnia, pain, discomfort, an increase in the amount of the drug, since the old dosage is no longer enough.
If you are addicted to drugs, treatment can be difficult because there is a paradoxical reaction to the drug and brain damage.
The clinical picture of drug dependence is manifested by fluctuations in blood pressure, poor health, and general weakness.
In addition, a number of syndromes develop that negatively affect human health:
- The psychological syndrome is characterized by a constant craving to take medicine due to discomfort, to experience a feeling of euphoria. Taking the medicine becomes the dominant idea for the patient;
- Physical syndrome is characterized by decreased sensitivity to the drug and the desire to increase the dose;
- Withdrawal syndrome is characterized by a sharp deterioration in health
.
Drug dependence and its treatment is a very difficult task, requiring the use of many methods, highly qualified doctors, and accurate diagnosis.
An individual approach, complex therapy, rehabilitation, and prevention are necessary steps in the treatment of drug addiction.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease. This is difficult, because many, especially mental patients, have the same diagnosis for years, take the same drugs according to standard regimens, without taking into account individual genetic characteristics, without monitoring the concentration of the drug and its metabolites in the blood, without preventing addiction.
Treatment of drug addiction is an “art”, and the use of modern equipment and methods is not available in all medical centers.
Drug addiction is difficult to treat. To do this, you need to combine the efforts of the doctor, the patient, and your immediate environment. Sometimes this requires hospital treatment.
The sincere desire of the patient is the key to recovery.
What it is?
Pharmaceutical dependence is a condition that occurs with prolonged or repeated use of drugs. Accompanied by a sharp deterioration in well-being physically and psychologically. Interruption of medications provokes an exacerbation of symptoms of the disease. It is often formed when a group of antidepressants, painkillers, sleeping pills, and tranquilizers is prescribed. Treatment is carried out according to an individual scheme for each patient, this reduces the likelihood of dependence syndrome. After diagnosing the disease, the doctor prescribes short-term medications and selects the most effective combinations of pharmaceuticals. It is important not to self-medicate, as this is dangerous for relapse and the appearance of new symptoms.
Useful advertising. We recommend that you pay attention to insurance against the COVID-19 coronavirus. The cost of the policy is from 1,690 rubles, there are tariffs for the whole family. Together with Zetta Insurance.
Advantages of treatment at the Minutko clinic
At the clinic of Doctor of Medical Sciences V.L. Just a minute, methods of getting rid of drug addiction are 30-40 years ahead of the methods practiced in budgetary institutions:
- drug withdrawal occurs only with the use of objective criteria - monitoring the concentration of the drug in the blood and its metabolites.
- replacing the drug with a less potent drug with gradual withdrawal;
- psychotherapy sessions;
- physiotherapy;
- occupational therapy.
Treatment of drug addiction is a difficult process, but with the high qualifications of the doctor, the desire of the patient, and the impeccable execution of prescriptions, everything is possible.
Drug addiction can be overcome! Medicines are the same as crutches. Get rid of them with the help of the clinic of Doctor of Medical Sciences V.L. Just a minute!
Drug dependence manifests itself in the fact that a person who has been taking medications for a long time, for one reason or another, cannot give them up. When the drug is discontinued or even a small dose reduction, the condition of such patients sharply worsens, and symptoms of the disease reappear or intensify.
Diagnosis and treatment
Pharmaceutical drug addiction requires a comprehensive approach to treatment. At the first stage, the patient turns to a therapist to identify organic pathology that has affected the deterioration of psychological and physical condition. Diagnostics includes a comprehensive examination:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound or MRI of systems and organs.
If no therapeutic pathologies are identified, a consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist is prescribed. Treatment requires an integrated approach, coordinated work of the doctor, the patient and his environment. Most often a hospital stay is required. During the rehabilitation period, the support of family and friends is important. Drug therapy is also prescribed to reduce physical dependence. Physical therapy and psychotherapeutic correction sessions are used to restore the patient’s psycho-emotional state.
Causes and types of drug addiction
There are two main types of drug addiction. The first of these occurs if the patient takes medications that effectively cope with the symptoms of certain diseases, but do not eliminate their cause. Such drugs are often used for insomnia, headaches, panic attacks, anxiety, autonomic disorders, joint and muscle pain. The drugs that most often cause this type of addiction are painkillers, antidepressants, tranquilizers and antipsychotics.
Dependence on these drugs usually occurs when treatment is not completed. Almost all of the diseases and symptoms listed above require long-term treatment, which should be aimed at eliminating the cause of these unpleasant conditions. Symptomatic treatment should be only the first part of therapy. It is necessary because it relieves acute symptoms, normalizes the patient’s condition and allows one to proceed to a systematic search for the root cause of the disease and its elimination. But that alone is absolutely not enough!
But very often, many patients do not have enough patience, and after their condition improves and acute symptoms disappear, they stop examination and treatment, believing that the disease has been defeated. Naturally, after some time, all the unpleasant symptoms return, and often appear even stronger than the last time. The patient again suppresses them with the same drugs that helped him before, often without even consulting a doctor. But the cause of the disease is not eliminated! And the person walks and walks in this vicious circle, or rather, a spiral leading down...
Treatment of drug addiction in this case usually does not present any big problems, although it is often quite lengthy and requires scrupulous adherence to all the doctor’s recommendations. The main thing here is to move from symptomatic treatment to finding and eliminating the root cause of the disease. In the vast majority of cases, this is possible, provided, we repeat, that all necessary examinations are completed and the patient carefully follows all the doctor’s prescriptions.
The second case is much more complicated. It occurs when the drug is included in the processes of metabolism and nervous regulation. And when you stop taking this drug, serious disruptions in the body’s functioning occur. Damage to the brain and peripheral nervous system may occur.
This type of drug dependence can occur when taken for a long time and in large doses of tranquilizers, psychotropic drugs, codeine-containing drugs, and narcotic analgesics. By the way, very similar processes in the body occur in people suffering from alcohol or drug addiction.
The prognosis for treatment in this case is not always favorable and largely depends on the drug to which addiction has arisen, and on the degree of damage to the brain and nerve cells at the time of treatment.
What is addiction?
What is addiction? Let's read the definition: An urgent need to achieve a certain desire or perform a specific activity is called addiction. In ordinary life, this is often called addiction. Previously, it was believed that only those who use chemical substances become addicted: alcohol, drugs, etc. Today, non-chemical addiction is distinguished: shopaholism, food and Internet addiction, etc.
In the process of constant consumption of a particular substance or satisfaction of one’s need, an increasing need arises to increase the dose. A person becomes not enough of what he had. Now we need to get even more. This is called tolerance, which is also accompanied by psychophysiological changes in the body.
In psychology, this concept is characterized by the desire to escape from reality by clouding consciousness. A person can resort to socially acceptable forms of addiction:
- Creation.
- Workaholism.
- Sport.
- Meditation.
- Spiritual practices.
Unacceptable forms of addiction in society are:
- Drug addict.
- Kleptomania.
- Substance abuse.
- Alcoholism.
Modern forms of addiction, which arose only with the technological progress of society, are:
- Gambling addiction.
- Computer addiction.
- Shopaholism.
- TV addiction.
- Internet addiction.
- Addiction to social networks and virtual communication.
- Food addiction, etc.
Addiction always develops against the background of dissatisfaction with some part or whole life. Sometimes this is a form of self-regulation, self-soothing. A person is forced to resort to some dependent form, because this helps him quickly recover and come to his senses. If we remember the “Anchoring” exercise, then it becomes clear that once a person found a quick way to achieve a certain state, after which he began to constantly use it.
Symptoms of drug addiction
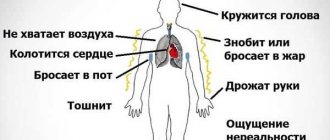
A sure sign that a person has developed drug dependence is the occurrence of ailments after stopping taking medications or reducing their dosage. The following manifestations are usually observed:
- pain (both minor and severe);
- vegetative crises;
- increased arousal;
- lethargy;
- blood pressure disorders;
- general malaise;
- changes in blood biochemistry.
Many of us take various medications every day. The above signs of drug dependence, all or some, appear in such people immediately as soon as the “regime” is broken. In these cases, you should not delay contacting a doctor.
Causes
The formation of drug dependence syndrome is influenced by a number of factors:
- Psychological characteristics of the patient. Thus, people with unstable psyches and prone to impulsive behavior often fall into the risk group.
- The biochemical reactions that occur when taking medications give a feeling of calm and security. The inability to independently cope with stressful situations leads to the need to use medications.
- The development of mental illness is accompanied by changes in the emotional state. Drugs can temporarily stop clinical symptoms, returning you to your usual comfortable reality.
- Drug dependence develops in patients with severe pain syndrome; drugs help to significantly alleviate the condition.
- Self-medication is one of the common causes of the syndrome; after completing the course, the patient does not feel an improvement in the quality of health, but, on the contrary, an exacerbation of symptoms.
Treatment methods for drug addiction
Treatment for drug addiction depends on the type of disease and the drug to which the addiction has arisen. The following therapy methods can be used in various cases:
- Replacement, complete or gradual, of addictive drugs with analogues that do not have such properties.
- Regularly reduce the daily dose of the drug until you completely stop using it.
- Psychotherapy that helps accelerate the recovery of the patient from depression. When you are cured of neuropsychiatric diseases, the need to use psychotropic drugs will disappear by itself.
- Treatment of diseases whose symptoms are associated with the recurrence of the patient’s anxiety-depressive state: postpartum trauma, rehabilitation period after an accident, problems with cerebral vessels, ICH (intracranial hypertension).
- Detoxification of the body in case of chemical dependence on the drug. The use of the method helps to cleanse toxins and other remnants of the addictive drug.
- Treatment of internal organs (liver, kidneys, nervous system) in which secondary changes have occurred in patients suffering from chemical dependence.
The most important thing to avoid is manifestations of excessive anxiety, nervousness, and depression. Then the desire to suppress them with the help of drugs will disappear, therefore, the likelihood of “picking up” drug addiction will disappear.
Drug dependence is a pathological condition, often mental, but sometimes even physical, which was formed as a result of the influence of pharmacological drugs on the human body, characterized by various reactions, mainly of a behavioral type, including the desire to constantly or periodically take a certain substance in order to prevent discomfort caused by breaks. while taking this medication.
Dependence can be on one drug or on several at the same time. Its development is based on tolerance
, - a decrease in sensitivity to the influence of a drug, requiring an increase in its dose to achieve the same effect that previously occurred from lower doses.
Biological mechanisms
Research data shows that there are certain biological mechanisms responsible for addiction. However, this area remains a subject of controversy. As discussed in the discussion “Sociogenetism or Biogenetism,” the biological nature of innate qualities can influence decision-making and actions. Certain factors related to genetics, DNA, mental disorders may be latently present, and then activated at a certain moment [21].
On the other hand, addictive behavior can be caused by environmental influences that lead to behavioral modification of the individual. Favorable relationships, abuse, social interaction, exposure to toxic substances - all of this can change a person's behavior. Some researchers recognize the influence of both social and biological factors, which together shape behavior patterns.
The biological mechanism of addiction may involve certain areas of the brain. Most notable is the dopamine release mechanism in the Nucleus accumbens, which is triggered by many drugs of abuse, thereby reinforcing addiction[22]. The release of dopamine is a natural process of stimulating action, characteristic, for example, of nutrition or sex. Drugs act similarly. In particular, some drugs increase the production and release of dopamine in the brain by 5-10 times, allowing users to experience feelings of pleasure in an artificial way[23][24][25]. Thus, amphetamine directly stimulates the release of dopamine, affecting its transport mechanism [26]. Other drugs, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, block natural dopamine reuptake mechanisms, increasing its concentration in the synaptic space[27]. Morphine and nicotine mimic the action of natural neurotransmitters[27], and alcohol blocks the action of dopamine antagonists[28]. Starting in the limbic dopaminergic system, the process then modifies other parts of the brain, such as the ventral tegmental area[29].
The mechanisms by which this process occurs include the penetration of additional AMPA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane of dopaminergic neurons. Studies in mice show that cocaine exposure for two weeks causes long-term changes in the ventral tegmental area. Moreover, the pleasure effect of a drug increases the behavior associated with obtaining and taking it until it becomes a habit. Initially, the process takes place in the ventral part of the striatum, mainly in the reinforcement center (English Nucleus accumbens), but then changes develop in the upper part of the striatum ( dorsal striatum
). Presumably, addiction-related neuronal modifications follow a dorsally cascading sequence of reciprocal connections between the two aforementioned regions[30].
The predisposition to drug addiction is influenced by several factors. It may be connected to the prefrontal cortex of the brain, which is responsible for judgment, risk decisions, and impulse control. This would explain why children are more prone to drug addiction. Some studies show that children aged 10 to 12 years, those who show the least inhibition in behavior, are at the greatest risk for developing drug addiction[31].
Symptoms characteristic of drug addiction
It can manifest itself in several syndromes that characterize the phases of its development:
- Mental dependence syndrome;
- Physical dependence syndrome;
- Withdrawal syndrome.
Mental dependence
This is a human condition that is characterized by an unhealthy need to take various kinds of psychotropic drugs in order to prevent the appearance of discomfort and mental disorders that develop if they stop using them. and other drugs, which is in such a phase does not manifest itself in the form
Physical dependence
In this phase of its development, the pathology is characterized by the possibility of developing abstinence in the event of a break in taking the medication or the administration of antagonist substances. An addiction that has gone so deep is characterized by tolerance; it is characteristic of taking opiates.
Withdrawal syndrome
This condition develops when the addictive medication is abruptly stopped. For example, if clonidine is suddenly discontinued, a hypertensive crisis may occur, quinidine withdrawal may provoke the development of severe arrhythmia, antianginal medications may cause angina pectoris, and anticoagulants may cause thromboembolism.
Relationship addiction
In its pure form, it is characterized by a person’s habit of a certain type of relationship. Relationship addicts create an “interest group.” Members of this group meet regularly and with pleasure, go to visit each other, where they spend a lot of time. Life between meetings is accompanied by constant thoughts about the upcoming date with friends.
It should be noted that a person’s attachment to a certain group can turn into relationship addiction. Rehabilitation therapeutic communities, such as AA (Alcoholics Anonymous), NA (Drug Addicts Anonymous), AK (Cocaine Addicts Anonymous), etc., with all the unconditional benefits in terms of abstaining from taking psychoactive substances, make their members communication addicts in this community. Leaving the community usually ends in relapse. Life, including even spending leisure time and vacations, becomes unthinkable without constant communication with others like you. We see something similar in a number of rehabilitation centers, especially religious ones, outside of which former chemical addicts practically cannot exist. In them one can state the emergence of relationship addiction along with religious addiction. The thoughts expressed do not in any way detract from the need for rehabilitation measures for those addicted to psychoactive substances. This is just another reminder that “recovery” from chemical addiction in most cases is accompanied by the emergence of a replacement non-chemical addiction, which, at best, is as socially acceptable as possible (Egorov A. Yu., 2004).
Drug dependence – drug addiction or addiction
Experts from the expert committee of the World Health Organization decided to combine both of these concepts, and now this dependence, both mental and physical, is considered both drug addiction and addiction.
However, all forms of this pathological phenomenon also have common symptoms.
Important components of the development of the disease are the special characteristics of a person’s personality, his socio-economic status, as well as the extent to which drugs that cause drug dependence are available. This condition is not primarily a pharmacological problem, since people suffering from it may substitute one drug of choice for another. WHO recommended differentiating this pathology based on the drug taken. The following types
:
- Morphine;
- Barbiturate;
- Cocaine;
- Nicotinic;
- Alcoholic;
- Mixed.
Treatment
How to get rid of this deviation? Treatment depends on the type of drug that caused the pathology. For example, in the case of the development of barbituromania, extended hypnotic sessions (from one to one and a half hours) are recommended. Autogenic training may also be useful for such patients.
.
They have a tranquilizing effect, normalize sleep, and are able to “replace” the hypnotic effect of barbiturates. Treatment of any type of addiction involves increasing attention to the patient’s personality, the role of addictive substances in his life, and solving his personal problems. It is important to use psychotherapeutic, and especially group, treatment methods
. After all, a constant feeling of discomfort in the mental state, as well as the presence of symptoms directly related to the withdrawal state, make contact with the patient difficult. This is especially due to the silencing of the very fact of pathological attachment by the patient, due to his fear of being deprived of access to the drug. In a group, patients, seeing people around them who have exactly the same problems and are trying to get rid of them, can open up and share with the doctor all the information that he had previously hidden. However, other patients, on the contrary, may need individual psychiatric sessions before undergoing group sessions.
Video: Drug addiction
Drug addiction is a mental, sometimes physical, well-being that occurs as a result of the influence of drugs on the human body. A distinctive feature is the manifestation of different reflexes. Dependence manifests itself in the desire to continuously or occasionally take a particular drug, so as not to experience discomfort caused by the intervals between taking a particular drug.
Drug dependence is predominantly psychological in nature
Other non-chemical addictions
Urgent add-on.
It manifests itself in the habit of being in a state of constant lack of time. Being in some other state contributes to the development of a person’s feelings of discomfort and despair (Korolenko, Dmitrieva, 2000).
Fun driving addiction
(joy riding dependence, or Toad's syndrome) was described by E. McBride (2000) as a variant of dependent behavior in British schoolchildren, who, since the mid-1990s, Cars and motorcycles were stolen en masse for the purpose of “fun driving”, enjoying risk and riding. The second name - Toad syndrome - comes from the literary character Mr. Toad from the popular novel among young people by K. Grahame “The Wind in the Willows”. Toad leads an antisocial lifestyle, has a special attachment to cars, and at the same time is quite likable personally. E. McBride analyzed Toad’s behavior from the point of view of addictionology and came to the conclusion that teenagers who repeat his behavior are addicts, and Toad syndrome is a type of technological addiction, since the car belongs to the achievements of high technology of the 20th century. In our opinion, Toad syndrome is the implementation of an adolescent behavioral reaction of imitation, and not addiction itself. The addictive component of Toad's syndrome can be considered as a variant of sports addiction (passion for extreme sports).
Spiritual search.
This form of non-chemical addiction was described by V.V. Postnov and V.A. Derechey (2004) based on observations of 9 patients with alcoholism who were in remission and, in the process of psychotherapeutic sessions, tried to master various spiritual practices. However, none of the patients connected these classes with the rehabilitation program, considering their problems with alcoholism “already solved.” All patients managed to change the direction of their “spiritual quest” several times before their alcoholic breakdown. Another feature of these patients was the inevitable failure of remission after a stage of severe adaptation disorders in the form of an increase in interpersonal conflicts, nervousness, irritability and outbursts of unmotivated aggression.
“Socially acceptable” forms of non-chemical addictions
The directions of spiritual search were very different: participation in personal growth groups, holotropic breathing, body-oriented therapy, meeting groups, esoteric and religious knowledge.
In our opinion, spiritual search is an option, sometimes a combination of religious addiction and relationship addiction, and should hardly be singled out as an independent form of addictive behavior. An alternative would be to call all variants of addictive behavior associated with spiritual growth and self-improvement “spiritual search.” In this regard, it will overlap with various forms of fanaticism.
A state of permanent war.
This form of addictive behavior was described by the same authors (Postnov et al., 2004) in alcoholic combat veterans who were in remission. Being in remission, these individuals sought to create dangerous situations and take unjustified risks: “I wanted to shake myself up, I haven’t fought in a long time.” In these situations, patients often committed antisocial and criminal acts. The state of permanent war, in our opinion, is close in its genesis to addictive extreme sports and, of course, is a variant of self-destructive behavior (see: Lichko, Popov, 1990).
Technological addictions
To designate new forms of non-chemical (behavioural) addiction associated with high technology, M. Griffiths (1995) proposed the term “technological addiction”, which he divided into passive (for example, addiction to TV) and active (Internet games). Subsequently, addictions to various electronic devices (electronic diaries, Tamagotchi-type toys, and especially mobile phones) were added here, referred to in Western literature as gadget addictions (from the English gadjet - trinket, technical novelty).
We believe that the separation of technological addictions into a separate group is justified for the reason that, despite their widespread distribution, from the point of view of addiction, all of them are controversial in terms of phenomenological independence. The peculiarity of technological addiction, in our opinion, is that the object of addiction (computer, mobile phone) is actually an object of addiction, a means of implementing other behavioral forms of addictive behavior. Below we will try to substantiate this point of view.
Internet addiction
The last two decades have been marked by the widespread spread of the Internet in both the professional and everyday lives of tens of millions of people. Through the Internet, purchases are made, communication takes place, information is obtained about all aspects of life, sexual and gaming preferences are realized, and much more. As Israeli psychologists Y. Amichai-Hamburger and E. Ben-Artzi (2003) rightly note, “there seems to be no aspect of life that is not affected by the Internet.”
In connection with the increasing computerization and “internetization” of Russian society, the problem of pathological use of the Internet, which arose abroad in the late 1980s, has become relevant. We are talking about the so-called. Internet addiction (synonyms: Internet addiction, nontagolism, virtual addiction, Internet behavioral addiction, excessive/pathological use of the Internet).
Technological addictions
Psychotherapists were the first to encounter Internet addiction, as well as companies that use the Internet in their activities and suffer losses if employees develop a pathological attraction to being online. Two Americans can be considered the founders of the psychological study of the phenomena of Internet addiction: clinical psychologist K. Young and psychiatrist I. Goldberg. In 1994, K. Young (2000) developed and posted a special questionnaire on the website. As a result, almost 500 completed questionnaires were received, about 400 of which were sent, according to her chosen criterion, by addicts. In the mid-1990s. To denote this phenomenon, I. Goldberg (1996) proposed the term “Internet addiction”, as well as a set of diagnostic criteria for determining Internet addiction, based on signs of pathological addiction to gambling (gambling).
M. Orzack (Orzack, 1998) identified the following psychological and physical symptoms characteristic of Internet addiction:
Psychological symptoms:
• feeling good or euphoric at the computer;
• inability to stop;
• increasing the amount of time spent at the computer;
• neglect of family and friends;
• feelings of emptiness, depression, irritation when not at the computer;
• lying to employers or family members about your activities;
• problems with work or study. Physical symptoms:
• carpal tunnel syndrome (tunnel damage to the nerve trunks of the hand associated with prolonged muscle strain);
• dry eyes;
• migraine-type headaches;
• back pain;
• irregular eating, skipping meals;
• neglect of personal hygiene;
• sleep disorders, changes in sleep patterns.
According to research by K. Young (Young, 1998), dangerous signals (harbingers of Internet addiction) are:
• obsessive desire to constantly check email;
• anticipation of the next online session;
• increase in time spent online;
• increasing the amount of money spent on the Internet.
According to K. Young (2000), the following criteria serve as signs of the onset of Internet addiction:
• preoccupation with the Internet;
• the need to spend more and more time online;
• repeated attempts to reduce Internet use;
• when you stop using the Internet, withdrawal symptoms occur that cause anxiety;
• time control problems;
• problems with the environment (family, school, work, friends);
• lying about time spent online;
• changing mood through the use of the Internet.
“Socially acceptable” forms of non-chemical addictions
The prevalence of this disorder ranges from 1 to 5% of the population (Griffiths, 2000; Young, 1998), with humanities and non-college-educated people more susceptible to it than computer network specialists. According to Korean researchers, among high school students, possible Internet addiction is registered in 38% (Kim et al., 2005). As data from monitoring the audience of Internet users show (www.monitoring.ru), in Russia from 1992 to 2004 the proportion of teenagers increased from 2 to 25%, i.e. teenagers are becoming more and more active users of the Internet, and therefore Cases of Internet addiction among young people are increasing.
In a pilot study conducted by Young and Rodgers (1998), 259 people, 130 men (mean age 31 years) and 129 women (mean age 33 years), completed an online mode, the 16-factor personality questionnaire (16PF) by R. Cattell and the Internet addiction questionnaire compiled by Young. In accordance with the data obtained, addicts were characterized as having a high level of abstract thinking and self-confident individualists, sensitive and emotionally responsive to other people, wary and not showing conformist behavior. According to researchers, being individualists, addicts easily adapt to long periods of relative isolation and are able to be content with only indirect contacts with other people; some of them tend to react exaggeratedly (sharply negatively or, conversely, with ardent approval) to the words of distant interlocutors - with such intensity of emotions that is not encouraged or taboo in more traditional forms of communication (“face to face”),
M. Shotton (1989) developed a typology of computer addiction, including three types of such addiction. Firstly, these are “networkers”
(networkers): they are optimistic, to the greatest extent - compared to other types of addiction - they are socially active and have a positive attitude towards other people, have friends, including those of the opposite sex, and maintain normal relationships with their parents. For them, the computer is something of a hobby: they may be interested in searching remote databases or, for example, playing role-playing group games like MUD, but they are less likely than other identified types of computer-dependent people to program on their own, to a lesser extent interested in applications, particularly computer graphics or hardware.
Secondly, these are “workers”
(workers) - the smallest group. They own the most modern and expensive computers. Their programming process is clearly planned; they write programs to achieve the desired result. As a rule, representatives of this group have studied or are studying well, and they are not satisfied with the standard training program, and they attend additional training courses. They are characterized by a very strict “work ethic”: for example, any kind of “computer piracy” is unacceptable.
Thirdly, these are “researchers”
(explorers) is the largest group. For them, programming is akin to an intellectual challenge and at the same time entertainment. They write extremely complex programs, often without even finishing them and starting new, even more complex ones. Representatives of this group enjoy debugging programs; They accept computer piracy and hacking, considering them “fair game” against other programmers (program developers) and/or computer system administrators. From a formal point of view, their level of education is lower than, say, that of “workers”, while they not only do not lag behind their colleagues with more significant diplomas, but often surpass them in the amount of knowledge. There are also few ambitions: neither high positions nor large salaries are important for
Technological addictions
them a dominant role. Thus, they are rather indifferent to the social criteria of success in life. For “researchers,” the computer is a kind of partner and friend, it is animated, and it is easier to interact with it than with people.
Among Internet addicts, there is a higher level of affective disorders with a predominance of depression and obsessive-compulsive disorders (Kraut et al., 1998; Shapira et al., 2000), as well as masked depression within the framework of low-progressive schizophrenia (Dzholdygulov et al., 2005). Korean researchers found that high school students with Internet addiction were more likely to experience depression with an increased risk of suicide (Kim et al., 2005). Studying personality traits using the Eysenck questionnaire in Internet addicts, Y. Hamburger and E. Ben-Artzi (2000) found that introverts and extroverts use different Internet resources. Moreover, in men, extraversion is positively correlated with the use of the Internet “for entertainment,” and neuroticism is negatively associated with the use of information sites. In women, extraversion was negatively correlated, and neuroticism was positively correlated with the use of Internet information resources. Later, the same authors found that predominantly female Internet addicts are characterized by a feeling of loneliness, which they try to reduce by spending time chatting (Amichai-Hamburger, Ben-Artzi, 2003). American researcher S. Caplan (2002) identifies the following personality traits of Internet addicts: depression, loneliness, modesty and self-esteem.
Summarizing the results of various studies, N.V. Chudova (2002) provides the following list of traits of an Internet addict: difficulties in accepting one’s physical “I” (one’s body); difficulties in direct communication (closedness); tendency to intellectualize; a feeling of loneliness and lack of mutual understanding (possibly associated with difficulties in communicating with the opposite sex); low aggressiveness; emotional tension and some tendency towards negativism; the presence of at least one frustrated need; independence acts as a special value; ideas about the ideal “I” are undifferentiated, inflated or even unrealistic; self-esteem is low; tendency to avoid problems and responsibility.
A study of the personal characteristics of 75 young males with signs of Internet addiction, conducted by A. Yu. Egorov and colleagues (Egorov et al., 2005), showed that according to V. Dvorshchenko’s test of personal accentuations, among Internet addicts, teenagers with schizoid ( 29.8%), hysterical (19.3%), labile and epileptoid (12.3% each) types of accentuation. Less common were unstable and psychasthenic accentuants (7% each), and in isolated cases - astheno-neurotic (5.3%) and hyperthymic (3.5%). In the control group (healthy subjects), hyperthymic (22.2%), cycloid (19.4%), psychasthenic (16.7%) and sensitive (13.8%) types of personality accentuation predominated. In contrast to the group of addicts, hysterical (11.1%), epileptoid (8.3%) and schizoid (5.6%) types of accentuations were significantly less common. Among Internet addicts, there was a significantly higher risk of possible personality disorders (psychopathy) and social maladjustment. Among the examined Internet addicts, the risk of alcoholism was 7 times higher than in controls, and the pronounced and moderate risk of drug addiction was 6.8 times higher.
The relative predominance of schizoid accentuators among Internet addicts is apparently associated with the characteristics of online activity: this is a certain withdrawal from reality, which is characteristic of schizoids. It may seem unexpected that there is a fairly large number of people with hysterical accentuation, who, in theory, should strive to constantly be “in sight”, where they could show their demonstrative
“Socially acceptable” forms of non-chemical addictions
new features. We believe that this is that part of hysterical teenagers whose needs are frustrated in the real world, and they strive to realize their hysteroidal traits in the virtual world (for example, this could be dating and chatting, which has elements of pseudology regarding hysteroids). Related to the frustration of needs in the real world is the so-called addiction to reincarnation in cyberspace, which has been observed among teenagers in recent years (Lee, Shin, 2004).
In terms of character traits, Internet addicts also differ from adolescents with chemical dependence. In the latter, hyperthymic, unstable, epileptoid and hysteroid types of accentuations predominate and schizoids are extremely rare (Lichko, Bitensky, 1991; Egorov, 2003). At the same time, the increased tendency to alcoholism and drug addiction, found among Internet addicts, indicates the presence of common psychological traits of individuals prone to various forms of addictive behavior.
A study of the sphere of needs using R. Cattell's 16-factor personality questionnaire showed that in the control and experimental groups there is a clear qualitative difference in the communication needs of young people. In the control group, a predominance of the “social” type of communication was revealed. Among Internet addicts, it turned out that teenagers, having a high, dominant need for close, heart-to-heart communication (high scores on factor A and Q2), do not have sufficient social courage (factor H) to establish relationships with people around them in real world. Internet addicts are low adaptive and shy, which prevents them from looking for people close to them and establishing close, trusting relationships with both peers and adults. Perhaps the satisfaction of their needs for support, approval, and communication is shifting from everyday life to virtual life. In general, adolescents with addiction have a frustrated need for communication, which is replaced by the Internet.
The self-esteem of Internet addicts turned out to be significantly lower than in the control group (40.1 versus adequate 62.6, according to the Dembo-Rubinstein method). It is known that such low self-esteem can hide two psychological aspects: genuine self-doubt (which is often a feeling of inferiority) and “defensive”, when declaring to oneself one’s own inability, lack of abilities, etc. allows one not to make any efforts in this regard. case, to adapt the “adulting self” to new social conditions.
Self-attitude was studied using the “Self-attitude” test by V. Stolin and S. Patileev (1993), which allows us to identify three levels of self-attitude, differing in the degree of generalization: 1) global self-attitude as an integral feeling “for” or “against” one’s “I”; 2) self-attitude, differentiated by self-esteem, auto-sympathy, self-interest and expectations of attitude towards oneself; 3) the level of specific actions (readiness for them) in relation to one’s “I” (self-leadership, self-consistency, self-acceptance). It was found that: 1) there are significant differences in the expression of the integral feeling “for”/“against” one’s “I” between Internet-addicted and Internet-independent teenagers. The indicators of Internet-addicted adolescents are lower than those of Internet-independent adolescents; 2) significant differences were found in self-interest as a modality of self-attitude between Internet-addicted and Internet-independent teenagers. Self-interest among Internet-addicted adolescents is less pronounced than among Internet-independent adolescents; 3) between Internet-addicted and Internet-independent teenagers, statistically significant differences were revealed in the severity of self-blame as a level of specific actions to avoid
Technological addictions
carrying to yourself. Internet addicts have higher scores on the self-blame scale, in contrast to Internet independent adolescents; 4) significant differences were noted between groups in the severity of self-interest as the level of specific actions towards oneself. In Internet-independent adolescents, this level is much more pronounced than in Internet-addicted ones.
Correlation analysis of the data revealed the following features of self-attitude among Internet addicted adolescents:
• lack of correlations between the integral feeling in relation to one’s “I” with other factors of self-attitude;
• lack of significant connections with the factors of self-understanding and self-interest;
• factors of self-acceptance, expectations of positive attitudes from others, self-confidence, auto-sympathy and attention to others are of great functional importance in the system of self-attitude among Internet-addicted adolescents, but the self-attitude of this group does not have a single system-forming factor;
• the leading level in self-assessment is emotional;
• the leading level of specific actions is self-acceptance.
It can be assumed that for an Internet addict, such an altered self-perception is desirable and approved by him and the virtual community with which he actively interacts. Accordingly, with the help of the Internet, escape from the present self is realized (Egorov et al., 2005).
Internet addicts exhibit hidden forms of other addictions: sexual addiction turns into “cybersex”; communicative dependencies, such as pseudology and crusade (Mendelevich, 2003) manifest themselves in “cybernet relationships”; Gambling addictions find a way out in a kind of Internet gambling. D. Greenfield (Greenfield, 1999) emphasizes that Internet addiction is very often (in 20% of cases, according to his data) accompanied by sexual addiction. The monitor screen, he writes, has a hypnotic effect and puts users into a trance-like state, which makes, say, love messages especially effective: a side effect is the fixation of Internet addiction.
K. Young (Young, 1998) described five main types of Internet addiction:
1) obsessive addiction to working with a computer (games, programming or other activities);
2) compulsive navigation on the WWW, searching in remote databases;
3) pathological addiction to Internet-mediated gambling, online auctions or electronic shopping;
4) dependence on social applications of the Internet, i.e., on communication in chats, group games and teleconferences, which can ultimately lead to the replacement of family and friends in real life with virtual ones;
5) dependence on “cybersex”, i.e. on pornographic sites on the Internet, discussion of sexual topics in chat rooms or closed groups “for adults”.
M. Griffiths (1998) hypothesized that Internet addiction can be formed on the basis of various forms of Internet use: a possible means of communication in the absence of face-to-face contact, interest in the direct content of the site (for example, porn sites), online social activity (for example , chatting or playing games with several people). Polemicizing with K. Young, M. Griffiths (1999) argues that many intensive Internet users are not Internet addicts themselves, but use the network to realize other addictions. In contrast
17 Zak. 3806
“Socially acceptable” forms of non-chemical addictions
which is from M. Griffiths, J. Kandell (1998) defined Internet addiction as a pathological dependence on the Internet without regard to the form of activity on the network.
Expanding the definitions of Internet addiction proposed by K. Yash; R. Davis (2001) proposed a cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internet use. He identified two forms of Internet addiction, which he designated as Specific Pathological Internet Use and Generalized Pathological Internet Use. The first form is dependence on a specific function of the Internet (online sexual services, online auctions, online stock sales, online gambling). The theme of addiction remains the same; it can also be implemented outside the Internet. The second form is non-specialized, multi-purpose excessive use of the Internet and involves spending a lot of time online without a clear purpose (chatting, email addiction), i.e., it is largely associated with the social aspects of the Internet.
Agreeing with K. Young about the ambiguity of the phenomenon of Internet addiction and supporting the point of view of M. Griffiths, we believe that Internet addiction is a combined group of different behavioral addictions, where the computer is only a means of their implementation, and not an object. Thus, we consider it possible to distinguish the following types of Internet addicted people:
Internet gamblers
use a variety of Internet games, sweepstakes, auctions, lotteries, etc.;
Internet workaholics
realize their workaholism through the network (searching databases, creating programs, etc.);
Internet sexaholics
visit various porn sites, engage in virtual sex;
Internet eroticaholics
— love addicts who meet each other and have affairs via the Internet;
online shoppers,
those who are addicted to spending money through endless online shopping;
Internet addicts
relationships spend hours chatting, endlessly checking email, etc., i.e., they replace the real relationship addiction with a virtual one.
Like other chemical and non-chemical addictions, different forms of Internet addiction can transform into one another and coexist in various combinations.
One more important aspect should be highlighted, related to Internet addiction and influencing the development of other forms of deviant behavior. These are serious dangers that children and adolescents can encounter while online:
• exploitation of children's trust: they may be tempted to commit indecent acts;
• Access to pornography: Children may be exposed to pornography due to its widespread availability online. Software that restricts children’s access to such sites does not always work, and is often absent altogether; it may not be available at school or in the library;
• inappropriate content sites with destructive content, such as instructions for making a bomb or drugs. Parents should be interested in the sites their children visit and be attentive to any changes in the child’s behavior;
Technological addictions
• passion for games like DOOM, QUAKE, and online games with violence increases the aggressiveness of children. Parents need to know what games their child plays and be ready to offer a constructive alternative. It is quite obvious that with the growth of computerization in the CIS countries, the number of Internet addicts will steadily increase, especially among young people.
Previous90Next
Features of the disorder
In psychology and sociology, this condition is called addictive. Addiction is a strong addiction that a person experiences when he has an obsessive desire in a specific area.
This syndrome is expressed in the form that a person takes medications for a long period and cannot abstain from it. If you cancel or reduce the dosage, the state of health of such a person will change for the worse, and signs of the disease may appear or worsen.
Drug dependence is manifested by the inability to give up medications
Types of addiction
A person can become addicted to almost anything. It all depends only on whether this method helps a person satisfy his need or not. Conventionally, addiction can be divided into the following types:
- Chemical (physical). It is characterized by the effect on the body of certain substances that help in changing consciousness or state. Often these substances cause harm and destroy the body. The most common and well-known forms of addiction of this type are:
- Alcoholic – when a person is unable to control the internal craving for alcohol, hangover, or achieving internal comfort by drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Narcotic (drug addiction) is an irresistible craving for drug use. This also includes substance abuse. The body is destroyed so much under the influence of these substances that a person almost always dies early.
- Behavioral (psychological). Characterized by the performance of such actions that allow a person to get what he wants. He attaches super-valuable importance to a certain type of activity, which is why he cannot refuse it. These include the following forms:
- Gaming – when a person cannot see life without roulette, slot machines, casinos and other gambling games. It is revealed by changes in qualities in a person: irritability, a change in social circle, an increase in the amount of time spent on the game, an increase in bets, an inability not to play or refuse to play, etc.
- Love – increased interest in a partner. I constantly want to be close to him and limit his social circle.
- Avoidance – when a person is susceptible to fear of abandonment, therefore he avoids too close relationships and attachment.
- Intimate – increased desire for intimate caresses, even if they lead to negative consequences.
- Workaholism is a form of escape from reality. A person, by completely devoting himself to work, avoids relationships, friendships, and close contacts with people. There is no goal here to earn a lot. The goal of workaholism is to achieve success and approval. A workaholic wants to be better than others, but if he is fired from his job, then he takes it hard. Often in such cases, the workaholic will eliminate his stress with chemicals, that is, the behavioral addiction will become chemical. However, there are cases when a person gets rid of chemical dependence through workaholism.
- Computer - using computer capabilities to escape reality. The most progressive is Internet addiction, when a person goes into the virtual world and refuses real communication with people.
- Sports – when a person exercises excessively. This type of addiction is socially acceptable. However, a person often exposes his body to danger: he wears it out, overstresses it, and quickly ages it. Often former athletes become chemically dependent: alcoholics, drug addicts, substance abusers, etc.
- Shopaholism is an uncontrollable desire to make purchases. A person almost never can quench his thirst for acquiring things. Moreover, people often buy things that a person does not need at all. Thus, it briefly replaces the feeling of happiness, which passes very quickly. Here problems arise in work life, since a person spends a lot of time in stores, in monetary terms, since a lot of money is spent, with the law and debts. Relationships with relatives and loved ones also deteriorate, since they are not able to understand the impulses of a shopaholic who spends a lot of money on unnecessary things.
- Food – when a person becomes fixated on food: he either overeats or starves. Anorexia, bulimia, and compulsive overeating are discussed here.
Factors and main types
There are two types of drug addiction. The first type is formed on the basis that a person takes medications that effectively prevent the manifestations of diseases, but do not exclude the cause of their occurrence. In this case, antidepressants, antipsychotics, tranquilizers, and painkillers are used.
This drug dependence is formed due to the fact that the treatment was not carried out in full or was not completed.
When treating such a pathology, it is important to have patience so that even with the slightest improvement in the condition you do not interrupt therapy. If the treatment was violated, then after a while all the unpleasant manifestations will resume and intensify. The patient will again suppress them with the same drugs he took before. Treatment of such a pathology is not problematic, but it can be quite lengthy and requires strict compliance with all the doctor’s instructions.
The second version of addiction is more severe. It is formed as a result of the fact that the drug is involved in metabolic processes and the functions of the nervous system.
If you stop taking the medicine, severe disruptions to the body's performance appear, and the brain and part of the nervous system may be affected. This type of drug dependence can appear as a result of long-term use and large dosages of narcotic drugs, analgesics, tranquilizers, and psychotropic substances. Similar processes occur in the body in people who are addicted to alcohol and drugs. Monitoring treatment in such a situation may not always be positive and is determined by the drug on which the dependence has developed, depending on the stage of damage to the brain and nerve cells.
Symptoms
Expressed by combinations of symptoms caused by a single pathogenesis:
- Mental attack syndrome. It is caused by a painful need to take psychotropic medications, trying to eliminate discomfort and mental disorders that arise as a result of interrupting medication. Drug dependence in this case is not yet expressed in the form of withdrawal symptoms.
- Physical craving syndrome. Addiction is caused by tolerance and is characteristic of those who use opiates. In this case, addiction is determined by the likelihood of the formation of withdrawal syndrome due to a pause in taking medications or the introduction of antagonist substances.
- Withdrawal syndrome. Caused by sudden cessation of taking drugs that are addictive.
A clear symptom of the formation of drug dependence in a person is the appearance of a painful state as a result of stopping medication or reducing the dosage. The following signs are noted:
- pain;
- mental disorders that are accompanied by panic attacks;
- increased agitation, agitation;
- lethargy, slowness;
- pressure failures;
- blood composition disorder.
Most people use medications daily. All symptoms of drug cravings appear immediately after stopping or disrupting the intake of the medicine on which the person is dependent. If there is a drug dependence of a mental or physical nature, you must immediately visit a doctor.
Forms
Pathological addiction to drugs manifests itself in psychological and physical forms. A number of medications do not lead to the development of mental dependence at all, characterized by an irresistible craving for taking the drug and the development of serious emotional discomfort upon its withdrawal, but only cause psychological attachment.
In patients with psychological dependence, when the drug is discontinued, a pronounced decrease in the emotional background occurs, and an irresistible craving for taking the substance is observed.
In case of physiological dependence, the patient develops a state of abstinence during drug withdrawal. The body reacts to the absence of medication with negative manifestations from various organs and systems, neurological and mental disorders.
In simple speech, this condition is called “breaking”.
Not only a break in taking the drug, but also the administration of antagonists of the active substance to the patient can provoke the development of withdrawal syndrome. The withdrawal symptoms depend on the type of drug that provoked the addiction, the doses used and the duration of use.
Habit or drug problem
Today, drug dependence and drug addiction are combined. Both mental and physical passion for drugs can relate to both drug addiction and drug addiction.
Personal qualities of a person, social and financial status, and the availability of drugs that cause drug addiction also play a role in the formation of pathology.
This disease is differentiated depending on the drugs that are taken. There are these types of addiction:
- from morphine;
- from barbiturates;
- from cocaine;
- nicotine;
- alcoholic;
- combined.
Morphine addiction
Ways to overcome
Overcoming and eliminating drug addiction is determined by the nature of the disease and the drug to which the addiction has developed. Main methods of treatment:
- Replacing addictive medications with similar ones, but with a gentler composition.
- Systematic reduction of the dosage of tablets until complete cessation.
- Psychological treatment that helps the patient recover from a stressful state. Having cured diseases associated with nervous and mental disorders, the need to use psychotropic drugs is eliminated.
- Overcoming and treating diseases caused by repeated stress in the patient (intracranial pressure, recovery period after an accident, postpartum depression or injury).
- Natural and artificial removal of toxins from the body as a result of drug addiction of a chemical nature. This method cleanses the body of toxic substances of the drug, which contributes to addiction.
- Treatment and restoration of the body.
The main thing to be wary of is the severity of excessive anxiety, irritability, and nervous tension. In this case, the urge and desire to weaken them with the help of drugs disappears, and the possibility of contracting a drug addiction disappears.
If you are faced with a similar problem, do not waste time: seek help from specialists, such a habit is detrimental to your health.