After which it all begins
First of all, this condition is due to the fact that the nerve lies in a canal formed by hard tissues, this helps protect it from external influences. But if the canal wall is deformed, compression of the nerve occurs. The causes of deformation may be overstrain of the ligaments or tendons, resulting in thickening. With permanent damage, changes in the canal become permanent, and the tissue surrounding the nerve itself changes. As a result of this, characteristic symptoms develop.
In rare cases, the causes lie in swelling of the nerve; this may be as a result of poisoning, for example, with salts of heavy metals, arsenic, or mercury. However, that's not all, this pathology of the upper limb can appear as a result of a long-term disease that requires the use of antibiotics, diuretics, and vasodilators.
Anatomy of the ulnar nerve and cubital tunnel
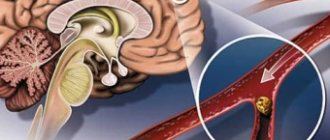
The ulnar nerve originates in the cervical plexus, being one of the three main nerves of the upper limb. It runs along the inner surface of the shoulder, then lies in the canal formed by the olecranon process, the internal epicondyle and the ligament that connects these two bone formations, forming a rather narrow cubital canal.
Next, the nerve passes through the intermuscular space of the forearm, flowing into another channel, this time on the wrist. This canal is called the Guyon Canal. It is at the level of this canal that the ulnar nerve begins to divide into 3, sometimes 4 branches, ending with the sensory branches of the 5th and inner half of the 4th fingers, as well as the motor branches of the 3-4-5 lumbrical muscles of the hand.
It is difficult to understand the uniqueness of lesions of the ulnar nerve at various levels without basic knowledge of its anatomy and topography, so we will dwell on the basic information on the course of the ulnar nerve fibers.
We suggest you read: Heel hurts and it’s painful to step in the morning after sleep, causes of pain when walking
The ulnar nerve is a long nerve of the brachial plexus. It consists of fibers from the CVII-CVIII (7th and 8th cervical) roots, which exit the spinal cord. The nerve enters the arm from the axillary fossa, then pierces the medial intermuscular septum in the middle of the shoulder, lies in the osteo-fibrous canal formed by the internal epicondyle of the shoulder, the olecranon process of the ulna and the supracondylar ligament, the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris.
This canal is called cubital (Mouchet canal). It turns out that in this place the nerve is located quite superficially and at the same time close to the bone formations. This circumstance causes a high frequency of compression of nerve fibers in this place. Anyone who has hit their elbow at least once has experienced this peculiarity of the superficial location of the ulnar nerve. You can even feel it in this place.
After leaving the canal, the ulnar nerve follows between the muscles of the forearm (at the same time giving part of the branches to the muscles). At the border of the lower and middle third of the forearm, the nerve is divided into the dorsal branch of the hand (which innervates the skin of the dorsal part of the fourth, fifth and ulnar part of the third fingers) and the palmar branch, which passes from the forearm to the hand through Guyon’s canal.
Knowledge of the topographical features of the nerve course helps in diagnosing its lesions. For example, if weakness of the muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve is detected in the area of the hand and forearm, this means that the level of nerve damage is located above the middle third of the forearm, and if muscle weakness is detected only in the area of the fingers, then the nerve damage is located at the level of Guyon’s canal . The level of involvement is important if surgical treatment becomes necessary.
Risk factors
Although risk is a noble cause, there are some factors that can cause disease if they appear systematically. First of all, narrowing of the canal and compression of the nerve occurs in those places where there is constant stress as a result of monotonous movements repeated with the same frequency. This mainly happens in the joint area, but there are other factors.
There are certain categories of the population that can be safely classified as at risk for narrowing of the canal and the appearance of nerve compression.
This pathology of the upper limb can appear in:
- People whose work involves monotonous movements of flexion and extension. Thus, hairdressers, text editors, tennis players, sign language interpreters have their hands constantly tense; among the musicians at risk are violinists and guitarists.
- This also includes people with age-related changes in the hand and the whole body. Such symptoms are typical for people over 50 years of age.
- Persons suffering from endocrine pathology, often diabetes mellitus, pathologists of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland. With these diseases, the restoration of hand tissue is impaired.
- Genetic predisposition to pathology of the musculoskeletal system or the presence of this pathology. The list consists of arthritis or osteochondrosis.
- Microtraumas of the joints and ligaments of the hand, which are often found among loaders, bodybuilders, and masons.
- Persons with autoimmune diseases.
Causes of the disease
Systematic movements associated with flexion and extension of the elbow in professional or sports activities (working at a machine, behind a conveyor, lifting a barbell, throwing a shot, and the like).
Direct long-term pressure on the elbow in the area of the cubital (ulnar) canal with:
— Long-term (several days) use of the armrest while traveling;
— Elbow hanging down while working with a computer mouse, keyboard, or laptop;
— Severe bruise of the elbow;
— Fractures of the shoulder or forearm;
— Formation of bone spurs, cysts, osteophytes inside the elbow joint, narrowing the lumen of the cubital canal and, as a result, compressing nerve and muscle fibers;
Types of tunnel syndrome
The most common type of carpal tunnel syndrome is narrowing of the carpal tunnel. The condition develops when not just one nerve is compressed, but an entire group:
- narrowing of the canal of the suprascapular nerve occurs in people involved in athletics, athletes in javelin throwing and shot put, tennis players, volleyball players; the development of narrowing of the canal occurs on the side that is more amenable to work;
- compression of the ulnar nerve;
- median and radial nerves;
- peroneal and tibial nerve;
- nerves of the sole and fingers.
If any nerve is compressed in the canal cavity, symptoms that are very similar develop. It is worth further understanding them in more detail, and only then starting full-fledged treatment.
Symptoms
Compression of the nerve in the canal cavity develops gradually; as the compression progresses, symptoms progress. At the initial stage, the disease does not manifest itself in any way in the area of the joint and from it; minor discomfort occurs with prolonged stress on the hands. As the canal narrows in any part of the canal of the upper limb, nerve function is impaired. Symptoms in this case appear:
- pain that gets worse after exercise;
- pain at rest, often at night;
- beyond the pressure point on the upper limb, numbness and tingling appear;
- when you try to stretch the joint and tap, the pain becomes stronger;
- in case of significant narrowing, pain in the joint and limb area becomes stronger;
- joint mobility is limited;
- Muscle tone and strength decrease.
It is not difficult to check the strength of symmetrically located muscles; you can simply ask a person to clench his fists. You can also try to “say hello”; if muscle strength decreases, you can judge their atrophy.
There is also another distinctive feature if a nerve is pinched in a large joint, for example, in the area of the hip, scapula, or elbow joint. Symptoms in such a case will make themselves felt at a considerable distance from the site of the lesion. As a result, the diagnostic process may require additional effort or time. For example, symptoms that manifest as numbness in the arm or upper back may indicate pressure on a nerve in the scapula or elbow joint.
Symptoms in the wrist joint area
Symptoms occur due to compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. The first symptom that appears with this variant of the disease is numbness of the hands, paresthesia that occurs at night. If the pathology progresses, the symptoms become disturbing during the day, and sensitivity in the area from 1 to 4 fingers decreases. If you raise your arm and hold it above your head for some time, paresthesia and pain become stronger due to impaired blood circulation.
The pain becomes stronger when the hand is strongly flexed or the shoulder is pressed with a device for measuring pressure until the pulsation disappears. If movement disorders occur, difficulties arise when fastening buttons, it becomes difficult to lift an object with the index finger and thumb at the same time.
With compression of the ulnar nerve
Most often, this happens in the area of the elbow joint, more precisely, in the area of the cubital fossa, where the nerve is surrounded by a fibrous arch; the second place is Guyon’s canal, located in the area of the wrist joint. A similar condition develops with compression if a person is unconscious.
It happens that the disease occurs if you sleep on your arm, it is compressed by the body and the bed. A long conversation during which you have to hold the telephone receiver can cause compression, as the nerve trunk is compressed.
The main symptoms for this condition are paresthesia, pain, itching on the side of the ulnar edge of the hand, this is the area of the fifth finger and half of the fourth. The symptoms become stronger if you tap on the nerve from the elbow joint. With the development of neuropathy in the area of Guyon's canal, the abduction of the fourth and fifth fingers of the hand is impaired.
Damage to the external (lateral) cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Symptoms occur when the nerve of the same name is compressed, passing under the inguinal ligament or in the area located in the area of the anterior superior spine, located on the ilium. The reason for this is often excess weight, sometimes it appears when wearing a tight belt. Paresthesias along with pain are located along the anterolateral surface of the skin of the thigh. Symptoms may be supplemented by impaired hair growth and decreased sweat production.
Manifestations and symptoms
Often the very first symptom of carpal tunnel syndrome is partial numbness of the inner side of the forearm, wrist and hand, 4th and 5th fingers.
If the first symptoms are not eliminated, the numbness is accompanied by a nagging pain on the inside of the forearm, continuing to the hand.
Subsequently, finger movements become inaccurate or difficult, pain and numbness become more severe with prolonged bending of the arm at the elbow, for example, during a telephone conversation or sleep.
Painful sensations when gripping with the hand and extending the fingers, especially after sleep, since the elbow was in a stationary and/or bent position for a long time.
Complication of the syndrome
Basically, the process becomes chronic; this happens if you get carried away with folk remedies and ignore going to the doctor. The disease has a period of exacerbation and remission, when symptoms do not manifest themselves.
The disease rarely spreads beyond the affected area. But the pain can intensify at any moment. In this regard, the disease does not pose a threat to the life of the person who developed it. But pathology may well disrupt the usual way of life.
The pain becomes more pronounced and severe as time passes. A person’s sleep and appetite become poor, and irritability occurs. As a result, other diseases develop, such as anorexia, insomnia and others.
Folk remedies
It is immediately worth noting that folk remedies should be used only in combination with other types of therapy. In some cases, as the only method of treatment, they may not give the desired effect, and at the same time the disease will only get worse.
Sea buckthorn compresses have shown some effectiveness. For these purposes, only fresh berries are taken, which are ground in a mortar until a homogeneous mass is formed. The pulp must be heated in a water bath and applied to the affected area of the joint.
Pumpkin compresses turned out to be no less effective. To do this, the pulp is slightly warmed up, after which it is applied to the joint and tightly fixed with cling film.
For oral administration, decoctions of white rose leaves, bearberry herb and parsley root are used. These plants have a full range of beneficial properties that can act comprehensively, relieving swelling.
Diagnosis of the disease
Before any disease is treated, it must be diagnosed, first of all, diseases similar to tunnel neuropathies are excluded. These can be: arthritis, arthrosis, neuralgia, myalgia and much more.
Special neurological tests can complement the diagnosis; they can identify various types of disorders in the area of the nerve trunk. Most often, Tinel's symptom is used for diagnostic purposes; it is carried out by tapping over the canal in which the damaged nerve is located. If there is tunnel syndrome, then the person notices numbness, a tingling sensation, itching, which is also called the feeling of “crawling goosebumps”.
If the disease develops in a place that is not suitable for the Tinel test, electroneuromyography is indicated. With its help, the ability of the nerve to conduct the sent impulse is established.
How is diagnosis carried out?
In case of tunnel syndrome, the diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a neurologist, whose task includes:
- Questioning the patient about the possible causes of this pathology: whether there have been injuries in the past, what nature of the pain, what movements cause it.
- Examination of a sore elbow joint.
- Determining the most painful areas.
- Identification of the paths of the pain impulse and its intensity.
- Carrying out tests for the functionality of the radial nerve.
Usually this is enough for an experienced and qualified doctor to diagnose ulnar nerve tunnel syndrome.
In complex or advanced forms of the disease, the doctor may additionally prescribe an examination using special devices: EMG - electromyography, ENMG - electroneuromyography.
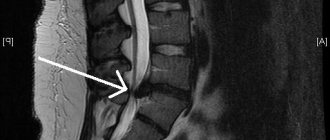
X-rays, MRI, ultrasound can be prescribed only if the nerve has been pinched by bone growths: spurs, osteophytes, deformed cartilage that were formed after fractures, arthritis, gout and other joint diseases.
Treatment process
The main treatment of the pathology is aimed at relieving the inflammatory process and eliminating swelling at the site of compression. As a result, the person is completely relieved of pain; treatment also involves pinching the nerve to a greater extent.
Use of medications
There are many medications used for treatment. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used first. In addition to the fact that they have an anti-inflammatory effect, they help relieve pain. If the drugs of the previous group are ineffective, treatment can be supplemented with hormonal drugs. They can be injected into the affected area as an injection or topically using an ointment.
Calcium chloride complements the anti-inflammatory effect; it is administered intravenously to relieve inflammation. The drug can also stabilize the immune system response. Vitamins complement the treatment and improve tissue conductivity; in the area of nerve compression, they help restore blood circulation.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy can complement any traditional treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. To more effectively treat the disease using physical methods, anti-inflammatory drugs and ointments are used. Examples of such techniques are iontophoresis, electrophoresis; reflexology allows normalizing the functioning of the nervous system and impulse conductivity.
You can use exercises at home, they are selected by the doctor strictly individually, independent use will not bring any effect, and may cause harm. Prolonged and intense physical activity is completely excluded. Some exercises are indicated in the period when the active inflammation phase has passed. There are some exercises that can help you get rid of pain at home.
For the first option, you will need a deep container, which is filled with water at a pleasant temperature; it should not exceed 36-37 degrees. Hands are immersed in the water. The hands are clenched into a fist and rotated slowly for 10 to 15 minutes. Then the hands are placed in a towel, where they remain at rest for the same period of time.
You can also use other means, for example, massage, which does not require skill or experience. You should start with the fingers, as well as the outer side of the palm, gradually moving up the center of the inner side of the forearm 2 to 3 times. When the procedure is completed, rest the limb in a warm place for half an hour.
Operation
In cases where conservative methods do not bring any effect, and the condition gradually worsens, surgery is indicated. Surgical treatment is performed under general anesthesia and lasts an hour, but there are always options. The doctor uses a scalpel to remove thickened tissues that put pressure on the nerve, thereby restoring its function.
But any treatment has its certain disadvantages, and surgery is no exception to this list, because no one can say in advance how effective its outcome will be. There is a small percentage, which is approximately 2-3%, in which the symptoms increase.
Who is at risk: prevention
In principle, anyone can encounter this problem, but physical activity and some professions lead to this more often than other reasons. To avoid problems, we must not forget about therapeutic exercises, especially for those who are at risk due to professional activities. Thanks to this, it will be possible to restore the normal functioning of tendons and muscles.
To avoid being at risk, you need to try to control your posture while sleeping. Arms must be extended at the elbows. It is also necessary to avoid potentially traumatic movements. In cases where professional activities or sports cannot be put on the “altar of health,” you can protect yourself by using elastic fixators, which may not limit movement, but slightly relieve the load from the joint.
We invite you to read: Treatment and prevention of gout with folk remedies
Among other things, as a preventive measure it is necessary to do therapeutic exercises. Naturally, exercises should be selected individually for each person, but there are general exercises:
- you need to straighten your back while sitting on a chair, in a position where both arms are extended forward. Now you need to start squeezing and unclenching your hands one by one. 10-15 repetitions are enough;
- then, without changing position, with clenched fists, begin to rotate them at the wrists. 10-15 repetitions are enough;
- change position and rest your shoulder on the back of the chair so that your arm hangs unhindered to the floor. Now you need to start moving the pendulum with your hand. The elbow joint should flex and extend as much as possible. 10-15 repetitions are enough.
Exercises are effective both as prevention and during the recovery period after surgery.
It is very important to go to a specialist as quickly as possible, already at the first manifestation of symptoms. Only in this case can we hope for quick treatment and restoration of all functions of the joint.
Search for a doctor based on the topic of the article
Right way of life
It is not enough to simply treat any disease; after recovery, you will need to lead a certain lifestyle to prevent the disease from reoccurring. Do not assume that after taking the pills you do not need to make any effort. In the treatment of tunnel neuropathy, the patient himself takes an active part, actively trying to get rid of the disease.
To prevent the disease from making itself felt, it is necessary to completely eliminate stereotypic movements, which largely lead to the fact that the nerve is compressed. In many cases, it is this approach that allows a person to forget about carpal tunnel syndrome.
In case of compression of the nerve in the area of the shoulder, elbow, or wrist joints, make movements with your healthy hand. If it is impossible to comply with the rule, the load should be reduced or performed if necessary. To a greater extent, the load is placed on the healthy arm, the opposite while at this time in a state of rest, which will prevent irritation of the nerve.
The habit of sleeping on your side, which is located on the opposite side of the sore arm, leg or shoulder blade, will be useful. Due to this, the diseased area will be able to rest during sleep, and the loads that occurred during the daytime will be compensated.