Symptoms
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, men experience symptoms of diseases of the digestive, nervous and cardiovascular systems. Patients often complain of:
- heartbeat;
- shortness of breath;
- tingling or burning in the heart area;
- bloating;
- diarrhea;
- tendency to constipation;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia in men are combined with increased anxiety and restlessness.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Clinical syndromes of VSD
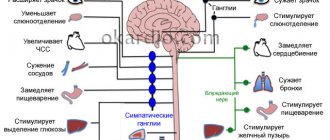
All signs of VSD in adult men are the result of an imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system . Depending on the dominant influence, two types of action of dystonia on smooth muscle tissue are distinguished: hypotonicity and hypertonicity.
More than 150 types of clinical signs and symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia have been described in medicine. Manifestations of dystonia are grouped into clinical syndromes:
- hypertensive;
- hypotonic;
- cardialgic;
- gastroenterological;
- mental disorder;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- syndrome of cerebral disorders;
- decreased trophism and metabolism in tissues.
According to the prevalence, dystonia can be local or generalized.
Among men, syndromes of vegetative-vascular dystonia with disorders of the cardiovascular system of the hypertensive type are often found. In rare cases, mental disorder, respiratory dysfunction and hypotonic signs of VSD are detected.
Hypertensive syndrome
The development of hypertension in vegetative-vascular dystonia is due to the influence of the sympathetic nervous system or hypersensitization of peripheral receptors to its humoral regulators. Hypertensive syndrome is manifested by the following symptoms:
- cardiopalmus;
- increased blood pressure;
- dilated pupils – mydriasis;
- chills, pale skin;
- panicky feeling of fear and anxiety;
- feeling of dry mouth.
Hypertensive, like other VSD syndromes, manifests itself in the form of panic attacks or seizures. During an attack, signs of hypertension develop in combination or in isolation . If an attack occurs with the appearance of one symptom, then it is customary to talk about the local nature of dystonia.
Sometimes, as symptoms worsen, symptoms worsen. In this case, they speak of a sympathoadrenal crisis.
All signs of a crisis are more pronounced. The duration of the crisis is up to 30 minutes. After the attack, a feeling of anxiety and restlessness remains, and the patient is unable to explain the cause of the anxiety.
Signs of sympathoadrenal crisis:
- increase in heart rate to 140 beats and above;
- increase in pressure to 170/100 or more mm Hg. Art.;
- the appearance of compensatory shortness of breath;
- cold sweat appears on the skin;
- dizziness and weakness;
- trembling of the limbs, feeling of muscle weakness.
All signs of a crisis are associated with the effect of adrenaline on the body. It maintains optimal smooth muscle tone and good blood supply to striated muscle tissue.
The physiological dominance of the sympathetic nervous system in men causes a high incidence of hypertensive syndrome in men.
Cardialgic syndrome
Cardialgia, or pain in the heart area , is the second most common VSD syndrome in men.
Clinically, cardialgia manifests itself as:
- local or point pain in the heart;
- arrhythmic contraction of the heart muscle;
- increased heart rate - tachycardia;
- development of physical inactivity or fear of “extra movements”;
- feeling of fluttering and interruptions in heart function.
Heart pain with VSD differs from pain with coronary heart disease. With ischemic heart disease, pain is associated with anxiety, physical activity, or occurs after going out into the frosty air.
- Pain during ischemia is associated with the appearance of zones of tissue hypoxia in the heart muscle due to disruption of their blood supply. Such changes are recorded on the electrocardiogram.
- With cardialgia, pain appears in the form of local uncomfortable tingling when moving and breathing. Sometimes the feeling of pain is so strong that a person is unable to move. There is a fear of “extra movements.”
The electrocardiogram does not reveal ischemic areas. Irritation of pain receptors occurs due to the influence of the nervous system, and not tissue hypoxia. The attack can go away on its own, without the use of drugs, and there is no threat to the patient’s life.
Gastroenterological syndrome
From the gastrointestinal tract, under the influence of predominantly the sympathetic nervous system, the smooth muscles of the intestinal wall contract.
- esophageal spasm;
- stomach spasm;
- development of spastic constipation;
- enzyme deficiency and bile deficiency due to spasm of the pancreatic ducts and gall bladder.
Spastic processes in the intestinal walls lead to a subjective feeling of discomfort in the form of nausea, a feeling of fullness, and heaviness in the stomach.
Sometimes patients associate the appearance of uncomfortable sensations with the action of provoking factors, for example, during stress or severe anxiety. Normally, such fleeting sensations occur in everyone. With vegetative-vascular dystonia, these phenomena become intrusive.
Cerebral syndrome
It is characterized by the appearance of signs of damage to the central nervous system. With the development of the dystonic process of cerebral vessels, unpleasant sensations arise:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- noise and ringing in the head and ears;
- loss of balance;
- gait disturbance;
- difficulty in performing coordination tasks;
- in severe cases of VSD, fainting conditions may develop.
All these signs are associated with the dominance of the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system in the regulation of impulses transmitted in brain tissue.
When the functioning of a certain area in the brain is disrupted, a clinical manifestation of the disorder of this area occurs. For example, when any pathology is localized in the vestibular apparatus, a loss of balance and difficulty in movement develops.
The variety of clinical signs of cerebral syndrome is due to the variety of brain functions.
Hypotensive syndrome
Hypotension with vegetative-vascular dystonia is very rare among men. Clinically the syndrome manifests itself:
- bradycardia;
- low blood pressure;
- redness of the skin and a feeling of heat on the face;
- constriction of the pupils;
- breathing disorder.
It is characterized by the development of a crisis state or vagoinsular crisis associated with a sharp activation of the parasympathetic part of the ANS. In this case, all the signs become pronounced and do not stop on their own.
Respiratory dysfunction
Breathing disorder often occurs with VSD in combination with other clinical signs. The main sign of breathing problems is the inability to breathe in or out deeply.
A respiratory disorder is distinguished from bronchial asthma when the main clinical sign is difficult prolonged exhalation and a decrease in the volume of exhaled air.
With dystonia, respiratory disorders go away on their own when the provoking factor is removed.
Mental disorder
Mental disorder with VSD is more often observed in women. It is rare among male patients. Mental disorder is manifested by a violation of motivational behavior. Signs:
- emotional lability;
- obsessive states;
- the appearance of phobias;
- night fears and worries.
Headache
In men, VSD with headaches mimics the symptoms of migraine, hypertension, and cluster pain. If you have a recurring headache, you need to undergo a full examination of the brain and blood vessels to rule out life-threatening diseases.
The head may hurt due to aneurysm of cerebral vessels or atherosclerotic damage to the arteries, tumors, and inflammatory processes. If cephalgia is one of the signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia in a man, therapy may be limited to lifestyle adjustments and sedatives.
What treatment is possible?
The objectives of treating vegetative-vascular dystonia in men include the following steps:
- normalization of physical activity;
- nutrition correction;
- normalization of sleep;
- eliminating anxiety.
Patients are recommended to consult with a psychotherapist to identify and eliminate the causes of anxiety.
Reduced stress levels
Complex treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in men includes reducing stress factors. They recommend taking a vacation and changing your surroundings. If internal restlessness and feelings of anxiety cause frequent exacerbations, weak sedatives are prescribed.
Daily physical activity
Sports, jogging, swimming improve overall well-being, normalize the regulation of vascular tone, and have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. In addition, muscle load increases the body's resistance to stress factors.
The need for comprehensive diagnostics
If symptoms of VSD occur in adult men, exclude diseases of the heart and blood vessels, endocrine and digestive systems:
- hypothyroidism;
- chronic viral infections;
- arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- hepatitis;
- pancreatitis.
The signs that patients complain about may hide diabetes mellitus, iron deficiency anemia, cancer, and systemic pathologies.
Treatment methods for VSD in men
The main goal of specialists is to eliminate the symptoms of VSD in men and prevent relapses. For this purpose, a step-by-step therapy complex has been developed, where treatment of vascular disease should be carried out at home. The main principle is a change in lifestyle, namely: adherence to a work schedule, proper sleep, adherence to a vitamin diet. It is important to exclude from the diet foods that affect the functioning of the central nervous system - alcohol, strong coffee, tea, spicy foods. According to the recommendations of doctors, the patient is obliged to avoid stressful situations and spend more time in the fresh air. Symptoms of VSD in men are easier to treat on vacation by the sea.
The main stages of treatment of VSD in men:
- Physical exercises, exercise therapy, sports, yoga, which are carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Active physical activity helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels, increases muscle tone, relieves tension, eliminates symptoms, improves mood, and gives confidence;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures are based on normalizing vascular tone and correcting autonomic functions. These include: electrophoresis, acupuncture, water treatments;
- Auto-trainings by the famous German psychotherapist Schultz I., suppressing the symptoms of VSD in men.
Drug treatment is prescribed individually, based on the main component and type of pathology.
The table shows examples of medicines recommended for use:
| Normalizing the cardiovascular system with symptoms of VSD in men | Soothing for symptoms of VSD in men | Normalizing the central nervous system for symptoms of VSD in men |
| Antihypertensives – normalizing blood pressure (calcium antagonists, diuretics). | Containing bromides - sodium bromide, valerian drops with sodium bromide. | Neuroleptics are psychotropic drugs. |
| Antiarrhythmic - asparkam, panangin, normalizing heart rhythms. | Containing barbiturates – valocordin, corvalol. | Antidepressants are drugs for treating depression. |
| Means that normalize blood circulation and metabolism. | Herbal medicines – glycine, valerian. | Sleeping pills – drugs to improve sleep (tranquilizers, antihistamines). |
All therapeutic methods are prescribed individually, depending on the form and clinical manifestations of the disease. Often, the doctor may not prescribe medications; for some, physical exercise and physiotherapeutic procedures may be sufficient. Symptoms of VSD in men are acutely manifested due to the natural restraint of character and reluctance to admit the existence of a problem. The task of the psychologist is to convince the patient of the benefits of timely implementation of medical recommendations, which help to avoid psychological and physical problems that pose a threat to life.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in other groups of patients
Symptoms of VSD do not only appear in men. More often, women who are more prone to emotional instability turn to doctors.
In childhood
The causes of dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system are hereditary. Psychotraumatic factors provoke an increase in symptoms. The causes of attacks can be:
- sudden climate change;
- unbalanced diet;
- passion for computer games.
After ruling out somatic pathologies, the doctor prescribes a consultation with a child psychologist and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Excessive passion for computer games can cause an attack of VSD
Among women
In women, symptoms of VSD arise against the background of an inability to deal with stress. Changes in hormonal levels in patients with increased anxiety provoke attacks of panic attacks. Therapy in such cases consists of a radical change in lifestyle, eliminating bad habits, and working with a psychologist.
How is vegetative-vascular dystonia diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosing this type of disease is quite difficult due to the very large number of symptoms, as well as the complete absence of any objective parameters. Here, only the so-called differential diagnosis is possible, which involves patients visiting medical specialists such as a neurologist, cardiologist, and endocrinologist.
After the history is established, it will be necessary to establish a family history of autonomic function of the body. In the vast majority of cases, family members of a person who is sick with vegetative-vascular dystonia suffer from diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and coronary artery disease.
In children who are sick with such a type of disease as vegetative-vascular dystonia, the anamnesis is very often aggravated by the unfavorable course of the so-called perinatal period, frequent relapses, as well as acute focal infection.
When carrying out the process of diagnosing such a type of disease as vegetative-vascular dystonia, special attention must be paid to autonomic tone, as well as indicators of autonomic activity. The initial state of the autonomic nervous system should be assessed exclusively when the patient is in an absolutely calm state. To assess it, patient complaints, ECG results, and brain EEG results can also be used. As for the so-called autonomic reactions of the nervous system, they must be determined using a pharmacological functional test, as well as using an orthostatic functional test.
The treatment process for people who suffer from this type of disease should take place under the close supervision of medical specialists such as an endocrinologist, psychiatrist, and neurologist. The treatment process for this type of disease involves long-term and complex therapy, which must be strictly individual in nature and take into account the general etymology.
Of all the treatment options for this type of disease, the most preferable is non-drug treatment. This approach involves the implementation of the process of normalizing the sleep of a person who is sick with vegetative-vascular dystonia, the implementation of the process of normalizing his work regime, eliminating physical inactivity, dosing physical activity, limiting the possibility of various kinds of stressful situations, individual psychological adjustment, family psychological adjustment. The nutrition of a person who is sick with vegetative-vascular dystonia should be regular and rational. Special therapeutic massage, reflexology, acupuncture, as well as various types of water procedures have a positive effect.