Vegetative-vascular dystonia, according to the latest data from the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, is one of the most common diseases in our country. The syndrome of this disease manifests itself in almost 70% of the adult population of our country and in 20% of children. It is interesting to note that the disease occurs 3 times more often in women than in men. This is due to the fact that women are more emotional than the representatives of the stronger half of humanity and manifestations of feelings are a normal phenomenon for them.
However, in many countries, VSD is simply not considered a disease, so debate still arises whether vegetative-vascular dystonia should be considered a disease or not. In Western countries they believe that this is simply a syndrome of other diseases. Also, scientists cannot come to a single name for this disease. Another term is often used to refer to it: neurocirculatory dystonia. Sometimes VSD is also called vegetative-vascular asthenia or cardiac neurosis. If you come across one of these definitions on a card, you should not be alarmed, since this disease can be effectively treated. Yes, and, apart from feeling unwell, it does not manifest itself in anything else.
General characteristics of the syndrome
Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD) is a complex of functional disorders. Currently, this concept is outdated and is not reflected in ICD-10. However, this classification includes somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the nervous system, a concept that can be used as a more modern analogue of VSD. Despite this, the term VSD is still actively used by some specialists - more often in general therapy, cardiology, and neurology.
The autonomic nervous system is a department of the nervous system and is responsible for regulating the activity of internal organs. Its centers are located in the spinal cord and subcortical structures of the brain; there is no control from consciousness.
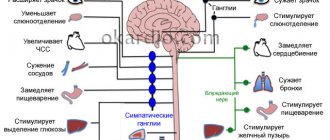
The autonomic nervous system is represented by the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. The first is necessary to control stress and the fight-flight response, the second is responsible for rest and restoration of the body.
The development of vegetative-vascular dystonia is based on low resistance to stress factors. The autonomic nervous system is poorly adapted, therefore, under unfavorable conditions, there is a loss of its balance, which disrupts the normal functioning of various organs, in particular the cardiovascular system.
VSD is quite widespread. It occurs in 80% of people, and in approximately 30% of cases therapeutic and neurological assistance is required. In most cases, the first manifestations of the syndrome occur in childhood or adolescence, but become pronounced after 20-30 years.
Personality types, or who is susceptible to psychosomatic illnesses like VSD?
First of all, people who are unable to control their ambitions are susceptible to vegetative-vascular dystonia. These individuals crave success, constantly going ahead. But when they fail to achieve their plans, even against the backdrop of ordinary little things, they experience a state of great nervousness, and at the same time irritation. They can often be very aggressive. People with a coronary personality type often have pathologies of blood vessels and the heart.
If a person regularly experiences some kind of negative emotions, then his body seems to remember the physical manifestation of this state. Next, the body instantly begins to react violently to any similar circumstances, causing an identical wave of disorder.
Those who have an excessive need for care and love are also susceptible to VSD. This makes a person attached to close relatives and family. They are emotionally very dependent, and, in addition, they are prone to self-doubt. Frequent companions of these types of personalities are depression along with anxiety states.
Some patients who are prone to VSD are pedantic with constant anxiety. They usually take on more responsibility. And they cannot always bear the burden of responsibility they have taken on. Like representatives of the first type, they exhibit a sense of purpose along with the belief that they deserve more than they actually have at the moment. They may often have a tendency to be vindictive. In people with such psychosomatics, diseases of the digestive system prevail.
If a person regularly tries to control himself and hardly expresses his feelings, then he may also develop vegetative-vascular dystonia. This approach to life often leads to periodic emotional outbursts. In such conditions, vegetative-vascular dystonia has everything it needs for active development. Therefore, if people have VSD, they first need to undergo treatment with a psychotherapist. Now let’s find out how people suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia manifest the symptoms of this disease.
Let's take a closer look at the symptoms of VSD and psychosomatics.
Classification
Currently, there is no single official classification of vegetative-vascular dystonia, therefore it is divided into types according to several criteria:
- Depending on which part of the autonomic nervous system is affected to a greater extent, the following forms of VSD are distinguished:
- sympathicotonic;
- parasympathicotonic (vagotonic);
- sympathetic-parasympathetic (mixed).
- Depending on the nature of the course of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the following varieties are distinguished:
- latent (hidden);
- paroxysmal (paroxysmal);
- permanent (permanent).
- The course of the pathology also differs in severity:
- light;
- medium-heavy;
- heavy.
- The prevalence of autonomic disorders may vary. Based on this sign, the following forms of pathology exist:
- localized (only one organ is involved; this form of VSD is also called local);
- systemic (only one organ system is affected);
- generalized (several systems are simultaneously involved).
- Depending on the etiology of vegetative-vascular dystonia, its primary and secondary forms are distinguished.
- The course of the pathology is complicated by various attacks, which can be of a different nature:
- sympathoadrenal crisis;
- vagoinsular crisis;
- mixed crisis.
Get to the truth
Despite the fact that psychotherapeutic techniques are actively combined with traditional treatment, it is psychotherapists who help to get to the bottom of the true cause of the disease. In fact, it is worth noting that the psychosomatics of VSD can be corrected without any difficulties; this ailment is an excellent example of how the final successes of treatment depend on the patient’s desire.
But the main condition is that you need to contact specialists directly for help as early as possible. You cannot limit yourself only to folk remedies or any medications. The maximum that can be achieved in this case is to stop the attacks, but the problem may not only remain with the person, but will also develop further.
Causes
Various factors can provoke vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In young children, this pathology can develop for the following reasons:
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- birth injury;
- diseases in newborns.
Under the influence of one of these factors, the formation of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted, so it may not perform its full functions.
During puberty, there is a discrepancy between the growth rates of the body and the development of internal organs in relation to the formation of neuroendocrine regulation. As a result, autonomic dysfunction worsens, which negatively affects the cardiovascular system.
In adulthood, vegetative-vascular dystonia can occur for the following reasons:
- chronic diseases;
- stress;
- depression;
- neurosis;
- trauma: craniocerebral, cervical;
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, disorders of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands, pheochromocytoma);
- diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract;
- hormonal changes in the body (typical for women during pregnancy and menopause).
Regardless of a person’s age, vegetative-vascular dystonia can develop against the background of constitutional heredity. This may be a lack of development of connective tissue, belonging to the asthenic type.
risk factors are also identified :
- socio-cultural environment;
- features of psychology (often the cause of VSD lies in the inability to verbally express one’s thoughts);
- emotional instability;
- hypochondria;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse;
- allergy;
- occupational diseases: radiation, vibration.
Women are at risk of developing vegetative-vascular dystonia. In men, this pathology occurs 3 times less often.
Why is psychotherapy needed?
Conducting psychotherapy for this pathology should minimize the total number of nervous strains that aggravate the patient’s condition. This is the main key to normalizing the condition. Psychosomatic VSD, as a rule, manifests itself after any traumatic events. In addition, it can occur as a result of a person’s prolonged stay in a state of stress. Next, we will try to understand the causes of this disease, as well as the psychosomatics of cardiovascular failure.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia
The clinical manifestations of the syndrome are very diverse. In total, there are about 150 of them, not counting clinical ones (more than 30).
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, symptoms are divided into 2 types. Some are general, while others express a disorder of one organ or system. The second option usually involves entire sets of symptoms combined into syndromes.
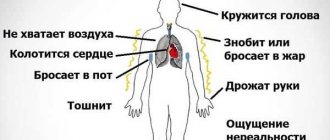
Possible general manifestations of VSD include:
- fast fatiguability;
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- weather sensitivity;
- sleep disorder;
- cardiopalmus;
- breathing problems, asthma attacks, lack of air (can be triggered by emotional stress, large crowds of people, temperature changes);
- muscle and joint pain;
- nausea;
- flatulence;
- urinary disturbance;
- bowel disorder.
The most common syndromes associated with VSD are:
- Psychoneurological syndrome, which is expressed by the following symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- general weakness, lethargy;
- decreased performance;
- increased irritability;
- tearfulness;
- headache;
- weather dependence;
- sleep disorders: insomnia, shallow and restless sleep.
- Cardiovascular syndrome. This symptom complex is also called cardiovascular. It is characterized by the following manifestations:
- heart rhythm disturbances: tachycardia, bradycardia, extrasystole;
- changes in blood pressure;
- vascular reactions: blanching or marbling of the skin, hot flashes, chilliness of the hands and feet.
- Cardialgic syndrome. It manifests itself as discomfort in the heart area or pain of aching, stabbing or pulsating nature. Such symptoms are not associated with physical activity and are relieved by nitroglycerin.
- Genitourinary disorders:
- anorgasmia (no orgasm) with preserved sexual desire;
- increased urination;
- painful sensations when urinating.
- Hyperventilation syndrome:
- rapid breathing;
- lack of air;
- incomplete or difficult inspiration;
- dizziness;
- development of muscle spasms;
- impaired sensitivity in the area around the mouth, hands, feet.
- Irritable bowel syndrome:
- pain in the lower abdomen - aching, spastic;
- bloating;
- stool instability;
- increased urge to defecate;
- digestive disorders: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dysphagia.
- Sexual disorders:
- in men – erectile dysfunction, ejaculation;
- in women – vaginismus, anorgasmia;
- libido may decrease or remain at the same level.
- Impaired thermoregulation:
- persistent but slight increase in temperature;
- chills;
- an asymmetrical increase in temperature in the armpits is possible.
- Impaired sweating. More often, this disorder involves hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), which mostly affects the palms and soles.
- Cystalgia. This term refers to painful urination, the frequency of which increases.
The clinical picture of vegetative-vascular dystonia also includes various crises . Their manifestations are related to the degree of severity:
- Mild crises are characterized by a short duration - 10-15 minutes. They manifest themselves as one symptom.
- Crises of moderate severity are characterized by a duration of 15-20 minutes and polysymptomatic manifestations.
- Severe crises can last more than an hour. Polysymptoms, hyperkinesia, and convulsions are observed. Post-crisis asthenia develops and persists for several days.
Psychosomatics of high blood pressure from Louise Hay, Liz Burbo, Vladimir Zhikarentsev and Luule Viilme
In her book Heal Yourself, Louise Hay explains that blood is an expression of joy, freely circulating in the body.
And unresolved long-standing emotional problems are the main metaphysical causes of high blood pressure in a patient.
Repeated repetition of harmonizing statements: “I joyfully consign the past to oblivion. There is peace in my soul” - according to Louise Hay, it helps to heal high blood pressure and the psychosomatics of hypertension.
Liz Burbo in her work “Your body says: “Love Yourself!” indicates the following metaphysical sources of hypertension:
- over-emotionality of the patient;
- endless reliving of the same situations, reminiscent of old, unhealed emotional wounds;
- dramatization of what is happening;
- intense mental activity, initiating many different feelings and emotions;
- excessive sensitivity of the victim.
The researcher recommends that her patients change their perception of the concept of “responsibility.” This will allow them to get rid of meaningless stress, enjoy life and live in the present.
Vladimir Zhikarentsev, like Louise Hay, connects the psychosomatics of pressure with a long-existing insoluble emotional problem.
A possible solution that, in his opinion, will contribute to healing, would be to repeatedly utter positive attitudes: “I am happy and easily freed from the past. I have peace inside."
Luule Viilma in his book “The Warmth of Hope” calls the habit of judging others and finding their mistakes as a metaphysical source of high blood pressure.
To heal hypertension, the healer advises her patients to learn to consciously forgive themselves and others.
Diagnostics
Vegetative-vascular dystonia does not have a clear characteristic, and its manifestations are very diverse, so diagnosing the syndrome is difficult.
Typically it consists of the following methods:
- Collecting a life history. It is important for a specialist to find out the family history of VSD. In childhood, such a diagnosis usually implies an unfavorable course of the perinatal period, relapses of acute and chronic focal infections.
- Assessment of autonomic tone using the Kerdo index. For calculations, you need to measure your blood pressure and find out your heart rate.
- Assessment of autonomic reactivity. To do this, they resort to the Valsalva maneuver, deep breathing tests, isometric stress, cold and heat tests.
- Study of vegetative support of activity. For these purposes, they resort to dosed physical activity and evaluate vegetative indicators.
- Electroencephalography.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Echocardiography.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia may involve damage to various organs and systems, so the range of studies necessary in a particular case is selected on an individual basis. An important point is differential diagnosis, which allows you to exclude certain diseases and make a diagnosis of VSD.
A therapist, endocrinologist, neurologist, or psychiatrist can participate in the diagnosis of VSD. If various organs and systems are affected, it may also be necessary to involve specialized specialists.
Symptoms of VSD
Among the main symptoms that accompany this disease are the following:
- The presence of often high blood pressure.
- As a rule, vegetative-vascular dystonia is extremely difficult to treat with medications.
- Presence of headaches.
- The presence of uncomfortable pain in the chest and heart.
- The appearance of dizziness.
- Having difficulty breathing.
- Periodic loss of consciousness.
The causes of VSD, as well as the symptoms of this disease, mainly arise from the prolonged stay of patients in a stressful state. It is for this reason that psychological treatment methods are always the most effective.
Next, let's move directly to the methods used to treat such an ailment as vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia
VSD therapy involves a conservative approach. Drug therapy is prescribed and physiotherapeutic procedures are performed. It is also necessary to make certain adjustments to the patient’s lifestyle and diet. In addition to the main treatment, traditional medicine methods can be used.
General recommendations, diet
Patients diagnosed with VSD should adhere to a certain lifestyle, including proper nutrition. This approach should be the basis of conservative therapy. It consists of the following rules:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- adherence to daily routine;
- proper alternation of work and rest;
- proper nutrition;
- avoiding stress;
- moderate physical activity;
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- limit emotional impact (TV, Internet, nervous work).
For vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is useful to master various relaxation techniques. For this purpose, you can practice yoga, which can also be an excellent alternative to many sports.
It is important for people diagnosed with VSD to pay attention to their diet. Food must meet the following rules:
- eat more legumes, nuts, dried fruits (dried apricots, raisins), eggplant;
- increase consumption of foods rich in ascorbic acid;
- exclude foods with large amounts of bad cholesterol, as they negatively affect the state of the cardiovascular system;
- sufficient fiber intake;
- maintaining the balance of BZHU;
- intake of sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals from food;
- eat fractionally and in small portions;
- do not overeat, do not overeat at night;
- if necessary, normalize your weight, but do it gradually and using gentle methods;
- exclude black coffee, strong tea, chocolate, spices;
- completely give up alcohol;
- Before going to bed, it is useful to drink warm milk, adding honey to it.
Drug therapy
The use of various medications is the basis for the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia. The features of drug therapy depend on many factors, including the form of the pathology, the characteristics and severity of its manifestations.
The specialist may prescribe the following medications:
- Sedative medications. For minor violations, it is recommended to use herbal preparations: tincture of motherwort or valerian, Persen, Novo-Passit, Dormiplan.
- Antidepressants. With the help of such medications they fight depression, improve mood, and indirectly normalize sleep. Sertraline, Paroxetine, Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine may be prescribed.
- Neuroleptics. These drugs reduce nervousness, aggressiveness, irritability, and anxiety. At the same time, they normalize blood pressure and vascular tone. Among such medications, they resort to Thioril, Sonapax, Sulpiride, Neurispin, Rispolept.
- Tranquilizers. Such medications are prescribed to patients with severe emotional disorders and anxiety disorders. More often they resort to Gidazepam, Afobazole, Buspirone. For severe disorders, Phenazepam and Diazepam are prescribed.
- Sleeping pills. These medications are prescribed for sleep disorders. They are used in short courses. The doctor may prescribe Andante, Ivadal, Somnol, Zolpidem.
- Nootropic drugs. They are also called neurometabolic stimulants. These medications stimulate mental activity, improve memory, and increase the brain's resistance to the harmful effects of various factors. Among such drugs they resort to Glycine, Piracetam, Pantogam, Noofen, Aminalon.
- Vegetotropic medicines. They have a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state, relieve pain, and relieve sweating. For this purpose, they resort to Bellaspon, Bellataminal, Platyfillin.
- Adaptogens. Such medications are prescribed to increase the body's resistance to stress due to its antiasthenic effect, increasing vascular tone and nonspecific immunity. Among such drugs, they resort to Rhodiola rosea, ginseng, Eleutherococcus, and Schisandra.
- Antihypertensive drugs. They are used to lower blood pressure. Metoprolol, Bisoprolol, Anaprilin are most often prescribed. For minor violations, it is recommended to use herbal preparations based on valerian, lemon balm, St. John's wort, hawthorn, and viburnum.
- To increase blood pressure, they resort to medications based on caffeine and mesatone.
- Drugs to improve blood circulation: Pentoxifylline, Trental, Cavinton.
- When the heart rate increases, they resort to Asparkam, Barboval, Concor.
- For increased intracranial pressure, Furosemide or Diacarb are included in the therapy, and herbs with a diuretic effect are also used.
Only a doctor should select drugs for drug therapy after a comprehensive diagnosis. Some medications are sold strictly according to prescription. It is important to follow the recommended duration of treatment and prescribed dosages.
Physiotherapy
Various physiotherapeutic methods can be included in the conservative treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia. They are selected individually.
The following procedures may be prescribed:
- electrophoresis with drugs (for vagotonia, calcium, caffeine, Mezaton are used; for sympathicotonia - Papaverine, bromine, magnesium, Eufillin);
- acupuncture;
- exposure to currents – sinusoidal, modulated;
- electrosleep;
- ultrasound therapy;
- inductothermy;
- photochromotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- darsonvalization;
- galvanization;
- paraffin applications;
- laser therapy;
- ozokerite therapy;
- acupressure;
In the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia, good results are provided by water procedures. They resort to contrast baths, circular and fan showers. Swimming is useful. To treat sympathicotonia, they resort to sulfide and carbon dioxide baths, and for vagotonia, radon and salt-coniferous baths.
Various methods of physiotherapy have contraindications. You should resort to them only as prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Physiotherapy is usually carried out in a course. Its duration, duration of sessions and breaks between them are calculated individually. All doctor's instructions must be strictly followed.
ethnoscience
In the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the use of traditional medicine is appropriate. You can use the following recipes:
- Take one part each of hop cones, motherwort, hawthorn, mint, lemon balm, oregano and thyme. Add St. John's wort, sweet clover, valerian, dill seeds, chamomile flowers, wormwood, calendula, mistletoe and yarrow in 4 parts. Brew a tablespoon of the collection with half a liter of boiling water, leave for half an hour, then strain. Take a glass three times a day. Continue treatment for 3 weeks, then repeat after a week break. In total you need to take 4 courses.
- Take one part each of black currant, lungwort and nettle leaves, barberry, add 2 parts of rose hips. Brew 2 tbsp. l. of this collection in 0.4 liters of boiling water and leave for 4 hours under the lid. Afterwards, strain the mixture and take half a glass three times a day before meals.
- Place 2 tbsp in a thermos. l. valerian root and a glass of dry dill seeds, brew with a liter of boiling water and leave for 24 hours. Dissolve 2 cups of honey in the strained infusion and mix thoroughly. You can store this mixture in the refrigerator. Take a tablespoon three times a day, half an hour before meals. The resulting volume of product is designed for one course of use. It is used to cleanse blood vessels.
- If vegetative-vascular dystonia affects the heart, it is recommended to mix several herbal tinctures - 25 ml of peppermint, 50 ml of eucalyptus, 100 ml of valerian, motherwort, hawthorn and evading peony. Add cloves (10 buds) to this mixture and leave for half a month in the dark, shaking occasionally. Strain the prepared tincture and take three times a day before meals. For one dose, 25 drops of the product are enough, which should be dropped onto sugar or diluted in a small amount of water.
- If you are overweight and have atherosclerosis, it is recommended to make a collection of chamomile, St. John's wort, birch buds and immortelle. Brew a tablespoon of the mixture in half a liter of boiling water, leave in a thermos for 4 hours, then filter. Drink a glass of the product at night, adding a teaspoon of honey. In the morning, heat the rest of the infusion, add honey and drink half an hour before meals. For one course of treatment you need to take 100 g of each herb.
- To improve immunity, it is useful to drink tea from pine needles. Take fresh raw materials and finely chop them. Place 5 tbsp in a thermos. l. prepared needles, add 2 tbsp. l. onion peels, brew 0.7 liters of boiling water and leave overnight. In the morning, strain and drink in equal portions throughout the day, replacing water with this tea. Continue treatment for 4 months.
- For hypertension and intracranial pressure, you need to take juniper fruits and calamus rhizomes in one part, chicory flowers, veronica herb, St. John's wort and strawberry leaf in 2 parts. Add yarrow herb and rose hips in 4 parts. Brew 2 tbsp in half a liter of boiling water. l. such collection and leave in a thermos overnight. In the morning, filter and take half an hour before meals warm, dividing the resulting volume into 3 servings.
Even natural remedies have contraindications and side effects. Before using traditional medicine recipes, you should consult your doctor about this possibility. For the first time, any drug should be taken with caution due to the risk of individual intolerance to the components.
Non-drug therapy
It consists of following the recommendations below:
- adequate sleep, normalization of work and rest schedules;
- moderate physical and mental stress;
- avoiding overwork;
- limiting TV viewing and computer use;
- nutrition adjustments;
- eliminating bad habits;
- walks in the open air;
- elimination of stress factors - unloved work, scandals in the family, annoying person;
- When playing sports, it is worth giving up cardio for a while.
The following also help to cope with the signs of VSD:
- electrophoresis;
- phototherapy;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- swimming;
- balneotherapy;
- massage of the collar area.
All of the above treatment methods are aimed at generally strengthening the body and relaxing the nervous system. If they do not bring the long-awaited effect, medications are prescribed. This type of treatment is selected strictly individually, taking into account the presence of third-party diseases. Medicines are started with a minimum dose, with its gradual increase.
Prognosis, complications
With timely detection and proper treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the prognosis is favorable - in approximately 85% of cases, the pathology goes away completely, or most of its manifestations are significantly reduced, and the body’s adaptive capabilities are restored. The effectiveness of results and their maintenance also depend on compliance with secondary prevention measures.
Lack of treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia or the wrong approach to it is fraught with the following complications:
- psychosomatic disorders;
- physical and psychological maladjustment;
- decreased quality of life;
- vegetative crises (in half of the cases).
Psychologist Pavel Zhavnerov talks about somatomorphic dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system:
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a fairly broad concept. Making such a diagnosis may imply damage not only to the autonomic nervous system, but also to other organs and systems. Regardless of the characteristics of the pathology, it cannot be left without treatment - any deviations from the norm require a timely and competent approach.
Psychotherapy methods
Modern methods, which many psychotherapists now have, are primarily aimed at quick treatment. After completing such a course, patients feel very comfortable, and their pathological symptoms gradually decrease. So, Ericksonian hypnosis can be used along with cognitive behavioral therapy and so on. All this will help relieve the exacerbation of VSD.
It is very important to correct psychosomatics, but it does not give the full effect if the necessary attention is not paid to physical health. This primarily concerns healthy eating, and, in addition, physical activity.
How can you heal yourself?
You won’t be able to completely recover on your own; to do this, you need to see a psychotherapist. Often thoughts or emotions that lead to the development of diseases are not realized. They exist somewhere in the unconscious. Only full-fledged work with a psychotherapist will give a healing effect.
However, you can carry out prevention yourself. Psychohygiene and psychoprophylaxis are the only things that can help a person prevent the development of psychosomatic diseases. Psychohygiene includes the following subsections:
- Psychohygiene of the family and sexual activity.
- Psychohygiene of education, training at school and university.
- Psychohygiene of work and rest.
Ultimately, psychological hygiene is aimed at satisfying the basic needs of life:
- love and care;
- safety;
- self respect;
- feeling of happiness;
- freedom of thought and creativity;
- presence of positive memories.