25-year-old Muscovite Alina had been bothered by headaches for about two months, so much so that they even radiated to her eyes. In addition, her stomach hurt, she slept poorly, and she often broke into a sweat. She decided to undergo a full examination. The therapist gave a referral to a neurologist, who sent the girl for a magnetic resonance imaging scan of the head.
In the conclusion that she was given after the examination, Alina saw many incomprehensible terms: a picture of moderate external replacement hydrocephalus (that is, a violation of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid), signs of hypoplasia of the left vertebral artery (narrowing of a vessel in the bony canal of the spine), signs of subluxation in the atlanto-actial joint (cervical spine). Alina and her family were seriously worried.
The neurologist diagnosed: vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). The reason for his poor condition, he said, is stress. Medicines - antidepressants.
“I don’t see any pathologies in your head.” Sweating and nausea, plus your general condition - all signs of VSD are obvious. You need to be in a comfortable environment, less nervous. Don’t forget to take antidepressants and nootropics (drugs that improve mental performance. - Note by Life). And sleep more,” the doctor recommended.
But other experts believe that everything is not so simple here.
“The attending physician is obliged to exclude all other possible causes of the disease before diagnosing VSD,” says neurologist Mikhail Moiseev. “It is likely that the symptoms shown by the MRI of this girl are a congenital phenomenon and do not require special treatment (medication). But this could also be a consequence of a recent injury (Alina had a concussion six months ago. - Note by Life), and then you should definitely seek advice from a traumatologist. It would be a good idea to refer her for a consultation with a neurosurgeon to be sure that the features diagnosed on the MRI are not dangerous.
Introduction
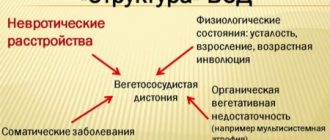
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a combination of functional disorders caused by disturbances in the regulation of vascular tone (their tension and relaxation) by the autonomic nervous system.
Click on photo to enlarge
The harmonious and coordinated work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system ensures autonomous (independent of the central nervous system) tension and relaxation of blood vessels. The process is influenced by changes in external and internal factors (adrenaline release, heat, cold, emotional stress).
With VSD for various reasons (chronic diseases, birth injuries, nervous stress, poor nutrition), the work of departments is not coordinated, failures provoke a pathological reaction of the vascular system and impaired blood supply to the departments. The result is increased heart rate, headache, dizziness, fainting and other symptoms caused by hypertonicity or relaxation of blood vessels at the wrong time.
In pathology, disorders depend on the localization of the process, so the symptoms of VSD appear in isolation (if only one system or organ is involved in the process, for example, the gastrointestinal tract or intestines) or in combination with each other (when several organs and systems are involved in the process).
In children, VSD is characterized by a sharp deterioration in condition during puberty (against the background of hormonal changes and nervous stress associated with workload and increased demands from parents); in adults, it progresses over time and is combined with concomitant diseases, which causes complications of vascular pathologies. In fact, in children and adults the pathology proceeds and is treated in the same way.
In 90% of cases, the disease is not dangerous; timely treatment can completely eliminate or reduce the severity of symptoms and manifestations of VSD. In 10%, the pathology can become complicated to the point of vegetative-vascular crises, contributes to the development of serious disorders (neuroses, arrhythmias, etc.), and when a complex of symptoms is combined, it worsens the quality of life and negatively affects the ability to work.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
The appointment for VSD is made by a general practitioner. If the pathology is accompanied by severe symptoms of cardiovascular, neurological, endocrine disorders, contact the appropriate specialist (endocrinologist, neurologist, cardiologist, etc.).
Symptoms
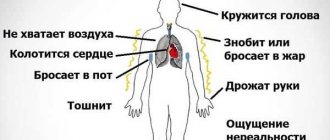
The disease in question can manifest itself in different ways - medicine has identified and described several syndromes, which are considered signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Hyperventilation is characterized by the appearance of rapid breathing, its retention and a feeling of lack of air. Patients demonstrate the so-called “false shortness of breath”, in which an imaginary spasm of the larynx occurs when inhaling - the patient thinks that he is suffocating. This fear provokes the formation of a panic attack with fear of death. The oxygen content in the blood decreases, and the patient’s respiratory activity is inhibited.
With vegetative-vascular dystonia, the oxygen content in the blood decreases
. In this case:
- the sensitivity of the skin around the lips and in the nose area is impaired;
- the sensitivity of the skin of the hands and feet decreases;
- muscle spasms occur without a specific localization;
- my head is spinning.
- Syndrome of impaired thermoregulation.
We are talking about a violation of the function of maintaining normal body temperature - the patient periodically feels chilly, even if he is warm.
Sometimes a patient may consult a doctor complaining of a sudden increase in temperature. This variant of the development of VSD is easier to tolerate and is not accompanied by headaches, weakness and other symptoms of ARVI. In some cases, different temperatures may be recorded when measuring it in the right and left armpits (more often in children).
- Sweating – this complaint is presented by almost all patients diagnosed with VSD. Increased sweating occurs during attacks. The face (especially the forehead) is mainly affected; beads of sweat appear on the forehead and all over the face; during periods without attacks, the process of sweating is not disturbed.
- Cardiovascular syndrome (cardiovascular) manifests itself with different intensity in different patients. Common complaints are heart rate disturbances (fast or slow), sudden and rapid changes in blood pressure. Often, with cardiovascular syndrome, the patient feels cold in the bones (chills from the inside) and feet, he is very pale, and sometimes hot flashes occur (as in women during menopause).
- Cardiac syndrome is expressed in:
- Pain that occurs in the area of the heart - both aching and sharp or pulsating;
- A feeling of discomfort that occurs in the area of the heart, which can be difficult for the patient to describe in words.
Important! This symptomatology is also present with angina pectoris, however, with angina pectoris, the described symptoms arise in connection with physical activity and are relieved within a few minutes with the help of nitroglycerin. With VSD, cardialgia syndrome can develop even at rest, and there will be no effect from nitroglycerin.
If you have pain in the heart area, you must consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
- A panic attack during VSD manifests itself in the form of severe fear, increased anxiety, but the wave-like “covering” of fear is not resolved productively; the patient is overcome by a feeling of hopelessness, the intractability of the problem, and the fear of death. It seems to the patient that his heart has stopped (or is about to stop), and his breathing becomes difficult (“intercepts”). The attack can last about 15 minutes and disappear without a trace. But such attacks can be repeated very often.
During VSD, feelings of anxiety and panic attacks may occur
- Cystalgia manifests itself in patients in the form of frequent urination - and even if the patient has not consumed a large amount of liquid. Pathologies of the urinary system cannot be identified.
- Irritable bowel syndrome is expressed in aching or cramping pain and a feeling of discomfort in the abdomen, as well as frequent bowel movements along with a false urge to defecate.
Important! Differentiate this syndrome as a manifestation of VSD with gastrointestinal diseases.
In addition, it may be accompanied by:
- disturbances of appetite - from complete loss of interest in eating, to real “gluttony”;
- vomiting or feeling sick after eating;
- violations of the act of swallowing - even drinking liquids causes difficulty;
- slight pain in the epigastric region or “in the pit of the stomach.”
- Sexual disorders in men are expressed in decreased or absent potency; women complain of anorgasmia and decreased sexual activity. However, these symptoms are not accompanied by a loss of attraction to the opposite sex.
In general, all of the listed symptoms characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia cannot occur simultaneously and in any type of disease.
How does VSD develop and proceed?
With VSD, numerous disorders can develop in three types, depending on which part of the autonomic nervous system most actively provokes the failure:
- The parasympathetic department is responsible for constricting the pupils, lowering blood pressure, slowing breathing, increasing the tone of smooth muscle muscles, and slowing down the heart rate. Changes in the body are caused by its increased activity and cause the development of VSD of the parasympathicotonic (vagotonic) type (hypotension, headaches, vascular spasm, suffocation).
- The sympathetic department is responsible for relaxing the pupils, increasing blood pressure and increasing heart rate, relaxing the rectum and bladder, and decreasing the tone of smooth muscle muscles. Its increased activity provokes the development of VSD of the sympathicotonic type with corresponding symptoms (headaches, hypertension, sudden urge to urinate or defecate).
- Approximately equal pathological activity of the parts of the autonomic nervous system ensures the development of VSD of a mixed type, without a predominance of symptoms of one type or another.
Several organs and systems of the body can be involved in the process at the same time (respiratory, cardiovascular and digestive); in this case, the pathology is accompanied by numerous symptoms that worsen the quality of life and temporarily reduce ability to work (during an attack of headache or pressure surge).
Classification of symptoms
VSD causes a variety of symptoms in adults. Depending on their prevalence, the following may be diagnosed:
- Generalized form of dystonia. Pathological manifestations arise from several organ systems at once.
- System form. Symptoms from one system predominate.
- Local form.
Types of dystonia, depending on the intensity of clinical manifestations:
- Hidden dystonia. The symptoms are mild.
- Paroxysmal or paroxysmal dystonia. Violation manifests itself in crises.
- Persistent dystonia. Its symptoms bother people all the time.
Depending on the severity of the course, dystonia can be:
- Easy.
- Medium-heavy.
- Heavy.
Crises with dystonia are divided into:
- Sympathoadrenal.
- Vagoinsular.
- Mixed.
Some doctors deny the existence of VSD as a syndrome. They indicate that the symptoms that characterize this disorder occur in every adult during his life. All people cannot suffer from VSD. This is what an alternative point of view looks like.
Asthenic syndrome with VSD
Asthenia develops in most people suffering from VSD. Its main manifestations:
- Fatigue. The person begins to get tired quickly. After rest, fatigue does not go away.
- General weakness, lack of desire to perform one’s work and daily duties.
- Sleep disorders. The patient has difficulty falling asleep at night, and during the daytime he will experience drowsiness. In the morning, people complain of feeling tired.
- Apathy.
With a pronounced asthenic symptom, the patient develops depression. It leads to the fact that a person simply does not have enough strength to leave the house.
Nervous system symptoms
If nervous system disorders come to the fore during VSD, the person will present the following complaints:
- Headaches, chronic migraine.
- Dizziness.
- Fainting.
- Feeling of heaviness in the head.
- Increased sweating of the palms, soles and armpits.
- Poor tolerance to heat and cold.
Vegetative thermoregulation disorders manifest themselves in instability of body temperature. It can be stably reduced to 35 degrees, or increased to 37-38 degrees. Sometimes temperature fluctuations are fast and sharp, which is manifested by hot flashes and a feeling of chilliness.
Disorders of the cardiovascular system
Failure in the functioning of the autonomic system leads to disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Manifestations of cardiac syndrome:
- Heartache.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Feeling of heart sinking.
- Interruptions in his work.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Impaired blood circulation in tissues.
Hypertensive syndrome manifests itself in an increase in blood pressure, and hypotonic syndrome manifests itself in a fall. If these are the symptoms that come to the fore, diagnosis becomes difficult. Before making a conclusion about VSD, it is necessary to exclude other cardiovascular pathologies.
Disorders of the respiratory and digestive system with VSD
On the part of the gastrointestinal tract with VSD, the following signs may be observed:
- Abdominal pain.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Bloating.
- Belching.
- Increased salivation.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Changes in appetite.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
When vagotonia predominates, appetite is reduced, but the person gains weight. If VSD proceeds according to the sympathicotonic type, appetite, on the contrary, increases, and the person is constantly haunted by thirst.
The following disorders are observed in the respiratory system:
- Rapid breathing.
- Chest congestion.
- Feeling of lack of air.
- Dyspnea.
In severe cases of VSD, the patient experiences attacks of suffocation, reminiscent of asthma.
Disorders in the genitourinary system
VSD can cause the following disorders of the genitourinary system:
- Decreased potency in men.
- Increased volume of urine excreted at night.
- Frequent and painful urination.
- Neurogenic bladder.
These symptoms lead to a deterioration in the quality of sleep and cause a person to experience some discomfort during the day. The true cause of disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary system can be identified only after excluding its organic damage.
Causes of pathology
Vegetative-vascular dystonia can appear immediately after birth (due to developmental pathologies or birth injuries) or during life (due to a combination of negative factors).
| Main causes of VSD | Main risk factors |
| Hereditary predisposition | Excitable psyche |
Intrauterine fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation)Click on photo to enlarge | Nervous, stressful work |
| Traumatic brain injuries (including those received during childbirth) | Age range from 20 to 40 years |
| CNS diseases (congenital and acquired) | Gender (in men, vegetative-vascular dystonia develops 3 times less often than in women) |
| Hormonal disruption or changes in the body (puberty, pregnancy, menopause) | |
| Chronic diseases (gastrointestinal tract, endocrine, cardiovascular, nervous, infectious, allergic, connective tissue diseases) | |
Cervical osteochondrosisClick on photo to enlarge | |
| Anomalies of the constitution (body structure) | |
| Psycho-emotional tension and nervous stress | |
| Bad habits (drinking alcohol and smoking) | |
| Physical inactivity | |
| Unbalanced, monotonous diet | |
| Hypovitaminosis, lack of microelements | |
| Toxic effects (including drugs) | |
| Climate change |
Causes of VSD
Tocopherol
Vitamin E is necessary for the human body for the normal functioning of the brain. Under its influence, the walls of cerebral vessels are strengthened and the risk of cholesterol plaques forming in them is reduced.
Most tocopherol is found in:
- egg yolks;
- nuts
When treating VSD, the body needs all vitamins in combination. If there is no deficiency, the likelihood of developing vegetative crises is reduced.
It is common to take vitamins prophylactically just like that, without taking into account the symptoms of their deficiency. But the body is not a dump, and you shouldn’t drink vitamin complexes simply because “the time has come.” If you don’t want to consult a doctor, then open the reference book and read about the symptoms of vitamin deficiency (which is rare) and hypovitaminosis, which develops under certain conditions. It is much safer to try to diversify your diet than to buy expensive drugs.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing VSD is quite difficult due to the combination of numerous symptoms that resemble other pathologies. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, organic diseases (gastritis, glomerulonephritis, mental disorders, infective endocarditis, bronchial asthma) are gradually excluded in consultation with relevant specialists.
Help to establish a diagnosis:
- analysis of the patient's symptoms and complaints;
- ECG of the heart;
- Holter monitoring (daily ECG);
- electroencephalography of the brain;
- functional tests (orthostatic, pharmacological), with their help the reactions of the autonomic nervous system are assessed.
Vitamin complexes and minerals
To treat VSD, balanced vitamin complexes containing B vitamins and magnesium are often used:
- Supradin;
- Centrum;
- Berocca Plus;
- Complivit;
- Vitrum;
- Magnesium Plus;
- Multi-tabs.
Vitamin complexes with zinc (Stressstabs-zinc) can also be used.
Vitamin complexes improve the functioning of the nervous system, increase the body's adaptive reserves, eliminate the effects of prolonged stress, normalize sleep and improve metabolic processes in tissues.
Treatment methods
With timely treatment, in 90% of cases it is possible to completely cure or significantly improve the patient’s condition, reducing the main disturbing symptoms to a minimum.
In adults, treatment of VSD is carried out using a complex of physiotherapeutic methods and a healthy and active lifestyle. Only 1/3 of patients require medication.
Drug treatment of VSD
Medicines are prescribed for severe VSD, severe symptoms of disorders, and the appearance of vegetative-vascular crises.
| Group of drugs | Name of the drug | What is it prescribed for? |
| Adrenergic blockers | Anaprilin | Eliminate symptoms of heaviness and pain in the heart, normalize rhythm |
| ACE inhibitors | Captopril | Normalizes high blood pressure |
| Stimulating herbal remedies | Tincture of hawthorn, eleutherococcus, lemongrass | Normalizes low blood pressure |
| Vasodilators | Cinnarizine, Vinpocetine | Improves blood supply to the brain |
| Neurometabolic stimulants | Nootropil | Improves metabolism in nerve cells |
| Sedatives | Phytosed | Gently calm the nervous system, normalize general condition, eliminate feelings of depression and anxiety |
| Antidepressants and tranquilizers | Phenazepam, elenium, seduxen, gidazepam | Improves mood, relieves all pronounced neurological symptoms in adults with VSD (lethargy, apathy, restlessness, anxiety, irritability, melancholy, etc.) |
| Neuroleptics | Haloperidol | Designed for the treatment of severe mental disorders |
| Multivitamin complexes | Supradin | Imbalance of vitamins and minerals is one of the reasons for the development of VSD |
VSD with severe symptoms must be treated over a long period of time, regularly repeating the course (twice a year, in spring and autumn, during seasonal exacerbations).
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapeutic methods are effective for the treatment of moderate and mild forms of vegetative-vascular dystonia. In case of severe VSD, they are combined with a course of medication:
- water treatments (carbon dioxide, sulfur, pine baths, Charcot shower, swimming in the pool);
- electrophoresis (administration of drugs through the surface of the skin under the influence of direct electric current);
- galvanization (exposure to constant power electric currents);
- massage of the collar area (neck and shoulders) and general (whole body);
- reflexology (stimulation of biologically active points);
- phototherapy (bright light treatment);
- physical therapy classes.
Lifestyle
In the early stages of VSD, doctors strongly recommend changing your lifestyle; in most cases, this helps to stop or completely eliminate the manifestations of the disease.
What is needed to get rid of pathology:
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals and amino acids (plant and animal protein) beneficial for the functioning of nerve cells.
- Regular physical activity (yoga, swimming, walks in the fresh air);
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- A daily routine that excludes rush jobs, brainstorming, sleepless nights working or reading books.
- Climate change, positive emotions and lack of stress.
If you have severe neurological symptoms of VSD (apathy, anxiety, suspiciousness, tearfulness), you can undergo several sessions of psychocorrection with a psychologist or get a consultation with a psychiatrist, this will help cope with stress and depression.
Vitamin B complexes for dystonia
Neuromultivit is a complex preparation containing cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine and thiamine. They:
- necessary for normal operation of the NS;
- stimulate metabolism;
- improve regeneration processes;
- help the smooth transmission of nerve impulses.
Neuromultivitis for adults is prescribed from 1 to 3 tablets per day, take the drug after meals. The course of treatment for VSD is from 2 to 4 weeks. Improvement in well-being occurs within 7–10 days of taking a multivitamin complex.
Vitamins from group B are also contained in the following preparations:
- Neurobex;
- Neurorubin;
- Neurovitan.
The drug Milgamma is used in the treatment of VSD and other neurological diseases; it contains therapeutic doses of B vitamins. In the acute stage of vegetoneurosis, the medicine is prescribed in the form of injections.
After the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia have decreased, treatment can be continued using the tablet form. Milgamma:
- restores nerve conduction;
- improves metabolic processes;
- promotes the formation of hemoglobin.
Prognosis for recovery
VSD in adults is a complex, multicomponent pathology. At stages when most organs and systems are involved, the disease can be treated for years. Patients with a tendency to vegetative-vascular crises are registered at the dispensary, should be examined and repeat the course of prevention 1-2 times a year.
In the early stages, in 90% of cases, the disease can be cured completely, although more often, due to the difficulties of diagnosis, patients with severe symptoms and complications of the pathology (vegetative-vascular crises) turn to doctors.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia affects 80% of the population; it is diagnosed in women 3 times more often than in men. The first obvious symptoms of VSD in adults appear between the ages of 20 and 40; the risk group includes people with an unstable psyche and subject to constant nervous stress.
The prognosis depends entirely on the patient’s desire to improve his own condition through feasible physical activity, a balanced diet and giving up bad habits. Uncontrolled VSD over time greatly worsens the quality of life and affects mental and physical performance.
Ascorutin for VSD
The pharmaceutical drug Ascorutin contains two vitamins - ascorbic acid and rutin, they complement each other's action (synergistic effect). Application of the drug:
- reduces the permeability and fragility of capillaries, making them more elastic;
- improves redox processes;
- leads to the formation of hormones;
- increases tissue regeneration.
- increases immunity.
In the treatment of VSD, Ascorutin is often prescribed as part of complex therapy. Adults are recommended to take the drug for 2-3 weeks, one tablet three times a day with meals.