Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a functional disorder of the autonomic nervous system, which is manifested by many pathological symptoms from the internal organs, but the organic substrate of the lesion is absent. Many experts do not consider VSD to be a separate disease, but rather include pathological symptoms in the clinical picture as neurosis, and in most countries there is no such diagnosis in official medicine. But domestic medicine recognizes the existence of VSD as a separate nosological form, although confirming the diagnosis can be quite difficult, since there are no objective criteria for pathology.
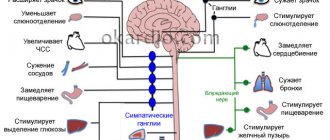
The development of VSD is based on dysfunction of the ANS, its parasympathetic and sympathetic parts, which regulate the activity of all systems and organs (respiration rate, heartbeat, gastrointestinal motility, gastric juice secretion, temperature, condition of the sweat glands, vascular lumen, etc.). Accordingly, when the normal functioning of the autonomic nerve centers and fibers is disrupted, pathological symptoms arise from various internal organs.
Young women are most often affected by VSD
In accordance with the predominance of certain symptoms in the clinical picture (changes in blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, cardialgia, respiratory pathology, digestive tract), types of pathology are also distinguished. Vegetative-vascular dystonia of the mixed type is characterized by a variety of signs that do not allow the disease to be classified as VSD of the cardiac, hypotonic or hypertensive type.
Let's consider a mixed version of VSD.
Symptoms
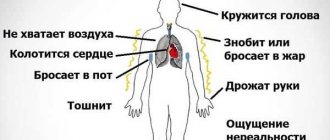
Each type of VSD has its own signs and symptoms; the symptoms are extensive and vary. Patients experience a deterioration in their health, and malfunctions in the functioning of various systems occur. The mixed type includes symptoms of other types of this condition:
- Periodic fluctuations in blood pressure, its sharp random increase and decrease;
- Dizziness and headaches;
- high fever or chills;
- Nausea;
- Fatigue, general weakness, morning sickness;
- Unreasonable irritability, inexplicable fear and even panic attacks;
- Unstable mood;
- Cardiac disturbances, tachycardia and arrhythmia;
- Unpleasant sensations in the chest area;
- Frequent shortness of breath and obsessive feeling of lack of air;
- Periodic fainting and pre-syncope;
- Increased sweating;
- Insomnia;
- Obvious weather dependence;
- Acceleration of metabolic processes;
- Tingling in the limbs, numbness.
Causes and mechanism of development of the disease
What exactly leads to the occurrence of VSD cannot be established. Considering that in this disease all tests are within normal limits, we can assume that the pathology refers to functional disorders. This means that there is no damage to the morphology of any organ. According to research and observations of doctors, there are factors that contribute to the development of VSD. These include:
- The presence of this pathology in relatives.
Often people suffering from symptoms of VSD have a family history. For the same reason, VSD is associated with the constitutional characteristics of each person. After all, they are also transmitted at the genetic level. Don't abuse bad habits - Instability of the psycho-emotional background. Mixed type vegetative-vascular dystonia most often occurs in people prone to depression and hysterical outbursts. As is known, female representatives are less resistant to stressful situations. This is associated with the high incidence of VSD in women, in particular in adolescents.
- Cerebral diseases. In the presence of organic lesions of the central nervous system, autonomic innervation also suffers. Manifestations of VSD can be observed after a stroke, in the presence of tumors in the spinal cord and brain, or hernias.
- Hormonal changes. An increased risk of developing VSD is observed in individuals suffering from endocrine diseases. There is a clear connection between this pathological condition and increased production of estrogen. VSD often occurs during puberty and menopause.
- Individual characteristics of the psyche and nervous system.
- Unfavorable climatic and environmental conditions.
- Abuse of bad habits.
The pathogenesis of VSD is to enhance the functioning of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation. This, in turn, leads to a change in vascular tone. Some of the small arteries spasm, causing hypoxia, while the other part expands. Vasodilation leads to slow blood flow and lower blood pressure. Due to functional disorders of the nervous and vascular systems, symptoms of dystonia develop.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of VSD of the mixed type is difficult to make; it does not have an exact scientific definition. The patient points to several symptoms characteristic of various diseases. For some reason, all systems begin to function incorrectly.
It is important to exclude pathologies of internal organs. It is also necessary to distinguish between hormonal imbalances, diseases of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract, infections, neurological and mental dysfunctions. To do this, you should contact doctors such as a therapist, neurologist, psychiatrist, endocrinologist, cardiologist and gastroenterologist, depending on the source of the ailment. In addition, you should undergo appropriate examinations - ultrasound, EEG, ECG, MRI, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, vascular Dopplerography, and laboratory blood tests.
When other causes of illness are excluded or the factors of their occurrence are eliminated, there are no organic and structural changes, and the symptoms do not fit into the picture of any disease from the International Classification, then a specialist can diagnose a vegetative disorder. This pathology is often considered a mild psychological disorder. Not every doctor can identify dystonia; the wrong therapy may be prescribed due to insufficient examination and similarity with many other diseases.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia: mixed type
Ecology of consumption. Health: The main symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the mixed type is jumps in blood pressure, both up and down...
Pressure surges as a symptom of VSD of mixed type
The main symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the mixed type is jumps in blood pressure, both up and down. Moreover, for some people, pressure changes occur unpredictably, while for others, patterns can be found. For example, in the morning the pressure is low, and in the evening it is high.
Similarly, with stress, emotional or physical overstrain: pressure can reach critical values, but in which direction depends on a host of additional factors, which sometimes remain a mystery to the patient himself.
In modern serious medical literature there is no such disease as vegetative-vascular (neurocirculatory dystonia) of a mixed type. And this is not accidental, because... the usual symptoms of VSD are not a disease of organs or systems, characterized by their organic damage (although very similar in its symptoms), but a functional disorder - neurosis. Those. the physical condition of the heart, blood vessels and other organs is normal, but symptoms, nevertheless, are present, mainly due to “malfunctions” in the nervous system, which controls the functioning of these organs.
Even among doctors who are adherents of the “old school”, there is no agreement on whether NCD of the mixed type should be classified as a separate category or whether the presented symptoms should be considered as a complex syndrome manifested in the alternation of VSD of the hypertonic and hypotonic type.
VSD of mixed type - what is it?
In the literature of past years, there are several classifications of NDC. However, the most popular is the one that was put forward, one might say, by the founding father of the diagnosis of VSD (as well as NCD) - Professor V.I. Makolkin. The cornerstone of this classification is the reaction of peripheral vessels and, consequently, the value of blood pressure - as the main objective indicator of the state of the cardiovascular system.
Thus, there are 3 types of vegetative-vascular dystonia:
1. VSD of the hypertensive type is accompanied by increased blood pressure, redness of the skin, a feeling of heat in the head, a characteristic headache, rapid breathing and heartbeat, as well as an increase in temperature.
2. With NCD of the hypotonic type, everything happens the other way around. Blood pressure decreases, bradycardia may be observed, as well as many unpleasant symptoms in the form of weakness and faintness, tingling throughout the body.
3. Vegetative-vascular dystonia of mixed type, in fact, is a combination of two previous dystonias, the symptoms of which successively change from one to another, and sometimes are present simultaneously.
At the same time, all subtypes of NCD are characterized by a “general maladaptation syndrome” in the form of increased fatigue, weather dependence, apathy and reduced performance.
And yet, in most cases, doctors deal with manifestations that are characteristic of VSD of the mixed type. Moreover, if you delay contacting a specialist, the symptoms tend to worsen. Additional fears appear, especially agoraphobia - a person begins to be afraid to leave the house unaccompanied: “What if it gets bad, and there is no one to help?” There is also a “fear of fear itself,” which only increases stress. And the worst thing is that the drug treatment usual for treating common diseases is not effective for treating this type of autonomic dysfunction.
Neurocirculatory dystonia of the mixed type, as we have already said, is accompanied by jumps in blood pressure, either upward or downward. There are also intervals when the pressure returns to normal. The patient, suspecting that he is faced with manifestations of a serious disease, undergoes a lot of tests, the results of which, however, do not go beyond the age norm. The heart, blood vessels, and thyroid gland are healthy, although the person continues to experience all the symptoms of NCD.
This diagnosis has already gained notoriety among doctors and patients, since it is made whenever they cannot determine the cause of ailments, or they find it difficult to choose an effective treatment that will allow the patient to regain health. And they often find it difficult because they work within the framework of an outdated paradigm that prescribes drug treatment for VSD of a mixed type.
The basis for making a diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia of mixed type” (in addition to problems with blood pressure) are also the following symptoms:
- weakness and fatigue;
- fainting, feeling of unreality of what is happening, dizziness, spots before the eyes;
- pain in the chest and heart - from momentary “pricks” to a feeling of pressure for several hours. In this case, the preceding factor is often neuropsychic or physical stress;
- changes in heart rate, extrasystoles. As a result, there may be a fear of cardiac arrest or heart attack/stroke.
NCD of the mixed type is in many ways reminiscent of the symptoms accompanying heart disease, although it is not:
- headache of a moderate, pressing or throbbing nature, usually occurring after physical or emotional stress;
- difficulty breathing - from the feeling that it is impossible to take a full breath, to shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air;
- restless, intermittent sleep , difficulty falling asleep and at the same time drowsiness during the day, feeling tired when waking up;
- increased sensitivity to weather changes , exacerbation of all symptoms during heat.
Since the test results indicate the absence of pathology, others may accuse the patient of “weakness,” laziness, and sometimes even accuse him of trying to feign an illness.
Damaged relationships with loved ones are not the main danger of VSD manifestations. What is especially unpleasant is that due to constant nervous unrest, anticipation of a panic attack, lack of sleep and other symptoms of mixed type vegetative-vascular dystonia, real somatic disorders may eventually appear, as well as serious mental disorders, in particular depression, OCD and others.
Also interesting: The key to healing: How the past is imprinted on a living organism
What is the ideal brain fuel?
So what to do with VSD of mixed type?
The first thing you should take into account is that vegetative-vascular dystonia of the mixed type is rarely treatable with drugs . A variety of symptoms, pressure surges, as well as the ever-increasing influence of emerging fears and concerns make it difficult to choose the right medicine correctly. But even if this was done, the symptoms return with renewed vigor when the medication is discontinued, since the “root of the neurosis” remained untouched.
Effective treatment of mixed type NCD usually does not contain pharmacotherapy at all or includes it to a small extent. Much more effective is the combination of physical therapy, massage, and other restorative procedures on the one hand, and learning skills to cope with stress, self-regulation, i.e. psychotherapy, on the other. published
PS And remember, just by changing your consumption, we are changing the world together! © econet
Treatment methods
If the cause is established, the underlying disease must first be eliminated. With a mixed type, there is no exact treatment regimen; the doctor decides how to treat VSD, focusing on the patient’s sensations and his individual characteristics. This can be either a medicinal method, or a non-medicinal or combined one. You should not self-medicate; often, haphazard use of drugs for temporary relief of well-being is fraught with adverse consequences and even greater health problems.
It is impossible to cope with a large number of manifestations if you take only one medicine, but prescribing a large number of tablets and injections means the doctor is incompetent. A good specialist approaches the problem in a comprehensive manner. Psychological therapy in combination treatment is necessary in addition to medication, because the state of the nervous system plays an important role.
Recommendations for eliminating dystonia:
- Healthy lifestyle;
- Moderate activity;
- Proper nutrition;
- Elimination of emotional and physical overload;
- Physiotherapy;
- Water procedures;
- Massage.
You should know that VSD is a disease without an organic basis, all organs are healthy, and medications only relieve symptoms, causing even more harm with side effects.
Causes of VSD of mixed type
Until now, the true reasons why this violation occurs are not known. Mostly children over 7 years of age, adolescents and young adults are affected; the pathology is more often observed in females. For some unknown reason (many believe that this is a genetic tendency to inferior autonomic regulation of body functions), after the triggering influence of provoking factors, a disease begins, which is characterized by a long course, but a benign prognosis. As a rule, all symptoms go away on their own with age, or this process can be accelerated by treatment and changes in risk factors.
Risk factors for VSD:
- hereditary predisposition;
- birth trauma, traumatic brain injury;
- living under chronic stress;
- unstable type of nervous system in the patient;
- unfavorable living conditions (social and economic);
- diseases of the central nervous system, for example, previous meningitis, encephalitis;
- periods of hormonal changes in the body;
- bad habits;
- unhealthy lifestyle, poor nutrition, physical inactivity;
- endocrine diseases;
- occupational hazards.
Important to remember! Determining risk factors for each individual patient is very important, since only this can effectively combat the disease, as well as prevent its recurrence.
The main provoking factor for VSD is stressful situations.
Drugs
The doctor prescribes medications based on the prevailing symptoms. In various situations, drugs with multidirectional effects are used, divided into several groups.
- Sedatives. They are selected according to the main component; preference is best given to plant-based products - Valerian or Motherwort. Stronger ones with the addition of a barbiturate are Corvalol or Valocardin.
- Tranquilizers. For nervous disorders, panic attacks and paranoia, Buspirone, Adaptol, Afobazol are used.
- Neuroleptics. Prescribed to reduce aggressiveness and nervousness - Sulpiride, Ridazine, Neurispin.
- Sleeping pills. To restore sleep patterns - Zopiclone, Dormikum.
- Antidepressants. Used for depression and apathy. Coaxil, Sindofen, Paroxetine.
- Nootropics. They help improve memory, promote better concentration, and help fight illness and weakness. This is Glycine, Piracetam or Actovegin, which is a neurometabolite.
- Cerebroangiocorrectors and antioxidants. Aimed at improving cerebral circulation. Of the former, Cavinton and Stugeron are popular, of the latter - Succinic acid and Mexidol.
- Medicines that increase or decrease blood pressure. Dystonia can cause hypertension or hypotension, and these conditions should be corrected immediately. To lower blood pressure, Anaprilin or Metoprolol are most often taken. To increase - Mezaton.
- Drugs affecting cardiac metabolism. Eliminate chest pain and normalize heartbeat - Riboxin, Mildronate, Concor, Barboval.
- Vegetotropes. They act on the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, eliminating various pains. Bellaspon, Platyfillin.
- Vitamins. Often included in therapy for general health. Complexes containing B vitamins, such as Neurorubin and Neurobex, are almost always used.
All appointments are made by the doctor. Some medications have double or even triple effects, which can lead to negative consequences. The treatment of mixed dystonia needs to be approached comprehensively in order to improve the quality of your life as soon as possible and forget about negative feelings.
Treatment
Treatment of mixed-type vegetative-vascular dystonia requires a lot of time and effort. Simply taking medications will not work here.
Treatment should include a whole range of measures:
- lifestyle correction;
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- hardening;
- massage;
- psychotherapy.
Read more about the treatment of VSD in this material at the link.
The basis for the treatment of VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia) of the mixed type is lifestyle changes.
The main thing is to reduce stress, neuropsychic stress, give up bad habits, normalize nutrition and exercise.
Sports help strengthen the body, proper rest and sleep, giving up bad habits and reducing stress - restore the health of the nervous system.
Proper nutrition allows you to saturate your body with the necessary vitamins and minerals, fatty acids and amino acids necessary for proper brain function.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment includes taking vitamins, vascular medications, sedatives and antidepressants. In addition to these medications, which help strengthen the body as a whole, antihypertensive drugs or substances that increase blood pressure are used symptomatically.
Typically, when treating VSD, herbal sedatives are prescribed: tincture of valerian, motherwort, peony; B vitamins, Actovegin, Nootropil, Vinpocetine and some others. Antidepressants are prescribed only for severe anxiety, fear or depression. The dose and duration of the course are calculated individually. Among the drugs, the latest generation drugs are popular: Fluoxetine, Sertraline or drugs with a minimum of side effects: Azafen, Nodepress, Valdoxan and others.
Other treatments
Physiotherapy, massage and hardening help strengthen blood vessels, normalize the functioning of the nervous system and get rid of hypertensive crises and sharp drops in blood pressure.
Psychotherapeutic treatment in VSD is of auxiliary importance; it helps to get rid of nervous tension, fear of a recurrence of the crisis or the occurrence of other symptoms of the disease. An experienced psychotherapist or psychologist teaches the patient to determine what exactly caused the stress, nervous fatigue or poor lifestyle that caused the development of the pathology and helps to cope not with the consequences, but with the cause of the disease.
Author of the article: psychiatrist Shaimerdenova Dana Serikovna
Course of therapeutic measures
Treatment of VSD is carried out in accordance with the severity of the disease identified in the patient during diagnosis. It is difficult to treat VSD, and it is almost impossible to completely rid the patient of the disease. Doctors focus their efforts on slowing the progression of the disease and eliminating relapses of crises.
Various methods are used comprehensively to treat VSD:
- Non-drug therapy.
- Medicines to stabilize blood pressure and eliminate other problems.
- Preventive measures.
The first type of therapy is often used for mild manifestations of the disease, when VSD syndrome can be eliminated by simple measures, for example, excluding stressful situations or stimulating effects on the patient of any factors. Most often, a person’s return to normal life is facilitated by the correct alternation of hours of work and rest.
To eliminate the syndrome, a diet for VSD is prescribed. Compliance with dietary nutrition is carried out to stabilize the condition. A person should give up foods such as coffee, alcoholic drinks, rich fish and meat broths.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of table salt - no more than 4-6 g per day. You are allowed to drink weak tea and cocoa. The patient's menu includes cottage cheese, baked potatoes, paprika, various fruits and vegetables. You can eat nuts, sprouted wheat, bran and other types of foods.
The patient must completely stop smoking. A psychologist and psychotherapist conduct treatment sessions for the patient to stabilize the person’s emotional state. It is recommended to choose the desired mode of changing physical and mental stress. The patient should engage in as much physical activity as possible or do exercises (prescribed by a doctor) to prevent physical inactivity. Physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, laser or magnetic therapy), acupuncture sessions and other techniques may be needed. They are chosen by the attending physician, focusing on the patient’s condition.