Causes of stroke
Stroke is not an independent disease, but a consequence, the result of problems associated with the vascular circulatory system.
It ranks second in popularity after heart disease. Typically, the causes of a violation are considered according to its two types, each of which has its own development path. But there is also a list of common causes leading to a stroke. Attention!
There is no such diagnosis as stroke in the medical dictionary. This term is considered to be “folk slang”. The diagnosis itself, as written above, is “Acute cerebrovascular accident.”
Obvious and common causes of stroke are:
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- nervous shock, stress;
- changes in atmospheric pressure.
It is necessary to dwell on each reason in more detail in order to explain the seriousness of its effect on the body.
Bad habits include not only alcohol, drugs and tobacco. Abuse of tea and coffee no less actively destroys the blood vessels of the hematopoietic system. It is very difficult to restore health after many years of its destruction. You should avoid becoming familiar with the causes of harmful effects on the body throughout your life.
Improper nutrition destroys the human body. Its negative impact weakens blood vessels, contributes to their clogging, and provokes impaired blood flow.
Foods and cooking methods that lead to vascular problems:
- meat products, fatty varieties;
- confectionery and flour products;
- spicy, canned and highly salted foods;
- fast food.
Mayonnaise or cheese sauces are very unhealthy foods. Proper nutrition is the key to strong blood vessels, which includes both the products themselves and the methods of preparation.
Conflicts, stress, and anxiety keep the blood vessels in constant tension. In such situations they say: “the blood boils,” which means that the blood flow puts strong pressure on the walls of the blood vessels. The more often such situations occur, the greater the risk of increased pressure, and, accordingly, ruptures in the vascular system.
Very little attention is paid to natural phenomena, but they play an important role in human health. This is especially true for the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Changes in atmospheric pressure provoke disruptions in blood pressure, which, in turn, leads to a stroke.
Attention! Recently, scientists have found that a cup of natural coffee a day prevents atherosclerosis, which can cause stroke.
The reasons can also include various diseases that lead to stroke.
Obesity is a disease that often leads to increased levels of “bad” cholesterol. Plaques form on the vessels, they become flabby, and blood flow slows down.
Hypertension is high blood pressure. Single surges in blood pressure (hypertensive crisis) will not cause a stroke, but they tend to be repeated, which leads to impaired blood flow.
Diabetes mellitus destroys the tissues of the vascular system that block the free flow of blood. Accompanied by high blood pressure.
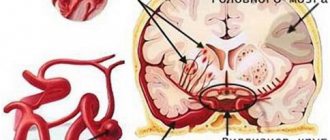
Aneurysm of cerebral vessels. With this disease, the walls of blood vessels are stretched, and in some places sacs form where blood accumulates. Such vessels are more vulnerable; with increased blood or atmospheric pressure, stress, and even climate change, they can rupture.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease that weakens the walls of blood vessels due to a failure of lipid metabolism. This is often caused by elevated levels of “bad” cholesterol.
Thrombosis is the formation of blood clots within the vascular system that interfere with normal blood flow. The narrowing of the lumen leads to partial oxygen starvation or complete deprivation of oxygen, and then to the death of some brain cells. Blood clots may not bother a person for a long time, but sooner or later they will make themselves known. Often a minor reason (stress, shock, changes in atmospheric pressure) provokes the detachment of a blood clot, which leads to the death of a person. An annual ultrasound examination of the hematopoietic system will help avoid this situation.
Blood clotting disorder. Thick blood weakens blood flow, the brain loses the ability to receive oxygen, and therefore, brain cells die.
Basic principles of treatment
Treatment of ischemic stroke should be timely and long-term. Only with this approach is it possible to partially or completely restore brain functionality and prevent consequences. Early consequences after an ischemic stroke of the brain include: cerebral edema, congestive pneumonia, inflammation of the urinary system, thromboembolism, bedsores.
Within the first 6 hours, patients are hospitalized in specialized wards of the neurological or intensive care unit. Treatment of ischemic stroke begins with the elimination of acute disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. If necessary, the patient is intubated and placed on artificial respiration. It is important to restore blood supply to the brain, normalize acid-base and water-electrolyte balance. 24-hour monitoring of respiratory function, cardiac and vascular activity, homeostasis is carried out - monitoring of blood pressure, ECG, heart rate, hemoglobin content in the blood, respiratory rate, blood sugar, body temperature. The main measures are aimed at reducing intracranial pressure and preventing cerebral edema. Prevention of pneumonia, pyelonephritis, thromboembolism, and bedsores is carried out.
Specific treatment for ischemic cerebral stroke consists of improving cerebral microcirculation and eliminating the causes that interfere with the delivery of nutrients to neurons.
Thrombolysis for ischemic stroke is the most effective technique if it is carried out in the first 5 hours after the onset of the stroke. It is based on the concept that during a stroke, only a part of the cells are irreversibly damaged - the ischemic core. Around it there is an area of cells that are turned off from functioning, but remain viable. When prescribing drugs that act on the blood clot, liquefy and dissolve it, blood flow is normalized and the function of these cells is restored. In this case, the drug used is Actilyse. It is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis of ischemic stroke intravenously, depending on the patient’s weight. Its use is contraindicated for hemorrhagic stroke, brain tumors, a tendency to bleeding, decreased blood clotting, and if the patient has recently undergone abdominal surgery.
The main drugs for the treatment of ischemic stroke are:
- Anticoagulants – heparin, fragmin, nadroparin.
- Blood thinners - aspirin, cardiomagnyl.
- Vasoactive drugs - pentoxifylline, vinpocetine, trental, sermion.
- Antiplatelet agents – Plavix, Tiklid.
- Angioprotectors – etamsylate, prodectin.
- Neurotrophics – piracetam, cerebrolysin, nootropin, glycine.
- Antioxidants – vitamin E, vitamin C, mildronate.
Treatment of ischemic stroke on the right side does not differ from the treatment of ischemic stroke on the left side, but therapy must have an individual approach and various combinations of medications that are prescribed only by a doctor.
Signs/symptoms of stroke
The symptoms of stroke often overlap with other, no less dangerous diagnoses, so many do not pay attention to the body’s signals. So-called “micro-strokes” are often suffered on the legs, but you should know that their repetition each time brings a person closer to the point of no return.
Symptoms that do not lead to serious consequences:
- a sharp headache in the occipital or temporal region, most often appearing during rest or sleep;
- nausea, vomiting;
- feeling of prostration, dizziness, loss of coordination;
- muscle weakness;
- hearing loss.
More serious symptoms will be:
- confusion in thoughts, loss of knowledge about the meaning of certain words, inability to collect oneself;
- memory impairment, memory loss, problems with awareness of reality;
- speech impairment, problems with writing;
- impaired speech understanding;
- difficulty swallowing;
- lack of sensations: gustatory, tactile, sometimes visual;
- problems with urinary retention;
- muscle weakness in the arms, legs, maxillofacial area (paralysis, immobility, usually on one side);
- aggression, nervousness;
- coma.
All of the above signs lead to a number of consequences and complications.
Signs of stroke in women
The reaction to stroke in men and women has some differences. They manifest themselves not in the symptoms themselves, but in their sequence and vividness of character:
- deterioration of vision, complete but temporary absence;
- lack of coordination of the body (in simple language you can often hear the phrase “the body moved”);
- weakness in the limbs;
- dysarthria;
- lack of understanding of what is happening;
- decreased physical sensitivity;
The signs do not replace each other, but increase smoothly. Because of their lethargy, very often it is the “female stroke” that is suffered on the legs until obvious health problems arise. In serious cases, muscle distortion of the face is visualized.
Signs of stroke in men
The male reaction is more specific; the force of the “blow” literally knocks the man off his feet. Very often the attack ends in death.
The signs will be:
- sharp and very severe headache, often occipital pain;
- vomiting, vertigo;
- clouding of consciousness, loss of reality;
- loss of perception of surrounding reality;
- dysarthria;
- muscle weakness in half of the body.
Problems in body movement appear in those places for which a certain part of the brain is responsible, affected by a stroke.
Attention! Previously, it was believed that strokes were mainly affected by representatives of the stronger sex. But today, due to heavy physical and mental stress, as well as poor lifestyle choices, women are increasingly facing this problem.
How to determine a stroke in a person
There are often cases when a person ignores the first signs of a stroke and even walks past the victim. Often this happens in the process of experiencing, during conflicts or quarrels between people, one of whom is the victim. You should take a close look at your opponent:
- the person bulges his eyes and tries to say something, but speech does not come out of his mouth, only mooing is heard;
- one side of the body stops moving;
- one side of the face weakens, stretches down, becomes motionless, the tongue is retracted to the side;
- loss of balance, fainting.
It is also possible that a person simply weakens before our eyes, but after resting a little, he gets back on his feet. More serious signs occur gradually over time. There are cases associated only with speech brain activity: loss of speech, misunderstanding of other people's words, memory.
Sometimes a person may simply fall and stop moving, with the eyes remaining open, slightly bulging, in an attempt to take on the full possibility of physical action. Any deviation from the norm, especially one that was accompanied by nervous tension, requires a quick reaction from the people around you. Time is often counted in minutes; delay will lead to death.
Symptoms of stroke in old age
Old age in itself is the cause of problems with the human vascular system. After 50 years, it is recommended to monitor your health more carefully, both for men and women. Often at this age, a stroke catches people “in full swing.”
The first signs of stroke in older women:
- a sharp “blow” in the occipital region, accompanied by nausea and sometimes vomiting;
- pressure surge;
- chills, cold sweat;
- loss of swallowing reflex;
- loss of visual focus, double vision;
- muscle tingling;
- visual distortion of facial muscles;
- numbness of the limbs;
- arrhythmia.
Male stroke is easier to identify, since its symptoms are more vivid and correspond to the classic description.
The first signs of stroke in older men:
- severe headache;
- facial redness;
- mooing instead of coherent speech;
- muscle distortion of one or another face;
- muscle weakness in half of the body;
- loss of consciousness.
In principle, one reason is enough to call an emergency ambulance, especially if it is loss of consciousness, speech or motor ability.
Stroke classification
Like any disease, stroke is subject to standard classification. There are two types of acute cerebrovascular accident: ischemic and hemorrhagic type.
Ischemic stroke
ACVA can develop according to the ischemic type (thrombosis, atherosclerosis);
Causes of ischemic type of development
Most often, doctors diagnose this type of stroke, which is caused by problems in the functioning of the vascular system: blood clots/clogging, atherosclerosis, weak, flabby vessels, and their narrowing. There is a violation of cerebral circulation, the possibility of supplying nutrients and oxygen to the cells of one or another part of the brain is limited and they are damaged.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
The person himself rarely has time to notice any deviations in himself; they are noticeable only to the people nearby.
First of all this:
- loss/reduction of pain sensitivity;
- problem with speech and hearing aids;
- problems with consciousness, disorientation, prostration;
- impaired sensitivity of facial muscles;
- paralysis of the limbs on one side of the body;
- body spasms.
The person himself may feel a sharp headache, pain in the eyeballs, and nausea.
Attention! With a right-sided stroke, speech may remain normal, since the left hemisphere is responsible for it. But numbness, loss of sensitivity and paralysis will affect the left side of the face and body. A left-sided stroke is primarily indicated by loss of speech.
Symptoms may come on quickly or increase gradually. This is due to the classification of strokes according to neurological characteristics.
A rapid and sharp onset of neurological symptoms is characteristic of heart rhythm disturbances.
Wave-like signs appear in healthier people and can quickly disappear from the overall picture. This is why immediate action is required.
The tumor-like course of ischemic stroke is characterized by a gradual but profound increase in symptoms. This move causes significant damage to brain cells, which are not known to repair themselves.
Types of ischemic stroke
Transient ischemic attacks (dysfunction of the central nervous system of the brain) are local, focally destructive. That is why the patient experiences certain symptoms, for which one or another part of the brain is responsible. Develops along a descending line.
Micro-stroke/small stroke – easily tolerated on the feet and allows a person to recover within a short period of time. Recovery can be complete or partial. This type of disorder is characterized by relapses, which entail more serious consequences.
Progressive appearance. The name speaks for itself, the disorder progresses very quickly, sometimes it actually takes an hour or two to save a person. Recovery may or may not be complete.
Complete stroke is a rarer type, which is dangerous due to traumatic consequences. Recovery from such a stroke is rare.
Hemorrhagic stroke
Acute cerebrovascular accident of the hemorrhagic type (rupture of a vessel due to a hypertensive crisis).
Causes of hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhage is hemorrhage of varying degrees and localization. Rupture of cerebral vessels is the cause of the hemorrhagic type. High pressure most often leads to this result: the walls of the vessels cannot withstand the load and rupture. The accumulation of blood puts heavy pressure on the brain tissue, which is the cause of stroke.
Reasons may also be:
- brain tumor;
- blood clotting disorder;
- vascular dystrophy;
- vasculitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- vascular aneurysm.
Attention! Often, acute cerebrovascular accidents are caused by long-term use of antitumor or hormonal drugs. The latter also include oral contraceptives, the use of which should be taken frequently and for long periods of time.
Types of hemorrhagic stroke
The types depend on the location in the brain and the dynamic development of the disease.
- Intraventricular hemorrhage. Blood in cavities of the brain called ventricles, which are filled with cerebrospinal fluid. With this type, a person either loses consciousness for a long time or falls into a coma.
- Sub- and epidural hemorrhage is a limited effusion of blood, often provoked by vascular injuries.
- Parenchymal or intracerebral, non-traumatic hemorrhage. The nature of this disorder depends on the location of the brain lesion responsible for certain neurological capabilities, areas of the body (paralysis of the body, facial paralysis on the right or left side, blindness, loss of speech).
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke
Symptoms of vascular rupture and cerebral hemorrhage are more obvious than with ischemic stroke.
Symptoms:
- sharp headache, sensation of a blow in the occipital region (pain may increase and cause vomiting);
- lack of tactile sensitivity;
- severe redness of the face;
- failure of one or both limbs at once;
- photophobia;
- paralysis of facial muscles;
- speech problems.
The disease regresses through several stages.
- Stage one. The man's incomprehensible gaze gives the impression of being stunned, completely lost.
- The stage of impaired consciousness is somnolence. The person resembles someone sleeping, but with their eyes open, without any reaction.
- Stage of deep depression of consciousness, stupor. Reminiscent of deep sleep with eyes open. The swallowing and blinking reflex is preserved. When touching the cornea.
- Coma - no reactions.
With each stage it will be more difficult for a person to recover, and from the last it is virtually impossible to do so.
Is there a mixed type of stroke?
As mentioned above, acute stroke is classified according to two types. A mixed type of stroke is diagnosed only when it cannot be accurately attributed to one or another classification. If a mixed type of stroke is diagnosed, the patient must have manifestations of both ischemic and hemorrhagic types. In other words: thrombosis, flabbiness and narrowing of blood vessels, as well as rupture and hemorrhage in the brain. In rare cases, this is possible, but most likely all symptoms will be attributed to the hemorrhagic type, since hemorrhage will be the dominant indicator in the diagnosis.
General characteristics of the pathology
A stroke is an episode of general or local vascular damage, which results in a permanent disruption of the blood supply. For the brain, such damage is especially dangerous: its work is the most complex and energy-consuming in the entire body. Thus, muscles and bones are able to withstand without oxygen and nutrients for more than an hour (for example, when a tourniquet is applied) without being harmed, while neurons die after several minutes of such a “hunger strike.”
A completed stroke is accompanied by softening or necrosis of tissue (infarction) in the affected area - this is the area closest to the blockage or narrowing of the vessel. At the same time, the activity of organs controlled by the affected part of the brain is disrupted.
A stroke can be caused by damage not only to the vessels inside the skull, but also to the arteries outside it. For example, almost a third of pathologies are associated with damage to the carotid arteries.
Ischemic stroke differs from hemorrhagic stroke both in the cause of its occurrence and in the course of the episode itself. Thus, with a hemorrhagic stroke, hemorrhage occurs due to damage to blood vessels, and with an ischemic stroke, a spasm or blockage of blood vessels occurs, causing insufficient blood supply. The following article will tell you more about the distinctive features of the course and methods of treating pathologies.
The normal blood volume is 60 ml per minute per 100 g of brain. When it decreases to 55 ml and below, the production of proteins in neurons is inhibited. When the volume is less than 35 ml, the breakdown of glucose is impaired. If the volume of blood flow continues to decrease, the cerebral cortex ceases to function.
If the total volume drops to 10 ml, a stroke nucleus forms in this area. Within 6-8 minutes, brain cells are capable of recovery, but if blood flow does not resume, they die.
During an attack, a number of processes occur. Firstly, intracranial pressure increases due to cerebral edema. Secondly, due to the fact that some parts of the brain have increased in volume, they shift and compress other parts. This is how the temporal lobe is displaced and the midbrain is pinched.
The mechanism of development of ischemic stroke is shown in this demonstration video:
Typically, the development of ischemic stroke occurs in four stages:
- At the first stage, the brain receives a signal about the decreasing level of oxygen in the brain tissue. Trying to compensate for this, the brain vessels dilate - this allows the volume of blood in the brain vessels to increase for some time.
- At the second stage , compensating for the lack of blood by dilating blood vessels is no longer enough. The volume of blood flow decreases, but this does not yet affect oxygen exchange - there is enough oxygen that came with the blood during the first stage.
- The third stage is called ischemic penumbra. Due to lack of blood, oxygen deficiency occurs, which leads to dysfunction of neurons. At this stage, damage to neurons can still be reversible. Sometimes at this stage everything returns to normal: blood supply is restored due to “bypass paths”, all neurological disorders are restored.
- If this does not happen, the fourth stage : hypoxia (lack of oxygen) worsens and changes in neurons become irreversible. This leads to some neurological disorders that do not recover on their own. The fourth stage is called total or complete stroke.
In addition to the stages, the course of a stroke is divided into periods:
- The first 3 hours are the so-called therapeutic window. If you take the victim to the clinic during this time and carry out the necessary procedures, you can protect the brain from the consequences and reduce the attack from a total stroke to a transient attack.
- The first 3 days are the most acute period, the patient is under medical supervision. However, already during this period, restorative procedures can be started as prescribed by a doctor.
- 4 weeks after the attack is the acute period.
- 6 months is an early recovery period.
- From one to two years is a late recovery period.
- After two years there is a period of residual manifestations.
How many years do people live after a stroke?
No doctor will give an exact answer to this question. It is worth saying that the mortality rate is high. In the first month, death occurs in 25%, and in the first year in 50% of sick people. To get as close as possible to the answer, you need to understand many aspects of the disease.
Firstly, everything will depend on the type of stroke. With the ischemic type, a person recovers much faster, which can prolong his life (with the exception of thrombosis).
Secondly, the healthier, stronger and younger a person is, the greater his chances of being rehabilitated and living to old age.
Third, after recovery, subsequent behavior is important. If the patient takes care of himself, leads a healthy lifestyle, avoids stressful situations, and sees doctors, then, accordingly, he will be able to extend the years of his life.
And finally, fourthly, in case of stroke, three aspects are very important: prompt access to a medical facility, treatment, and subsequent care for the patient.
If all points are observed, a long and happy life is possible, even if the violations occurred after 60 years.
With the hemorrhagic type, restoration, and sometimes even preservation of vital resources, will be a more difficult, sometimes impossible process.
How long does the recovery period take after an ischemic stroke?
The recovery period after an ischemic stroke is divided into 3 stages:
- early (up to 6 months from the moment of cerebrovascular disorder);
- late (6–12 months);
- residual effects (after a year).
For the most effective restoration of lost functions, rehabilitation measures should begin almost from the very first day of the patient’s stay in the hospital, immediately after stabilization of vital signs. Rehabilitation takes place with the greatest speed and effectiveness in the first year after an ischemic stroke. As for the neurological disorders observed during the period of persistent residual effects, they are practically not recoverable.
After recovery from the acute condition, the patient is sent to an outpatient rehabilitation facility or, if impossible, discharged home with further rehabilitation treatment.
Diagnosis and first aid for stroke
Providing first aid for a stroke at home is difficult, so if possible, it is worth preventing it. This is real, because, as a rule, it is a consequence of something: an incorrect lifestyle, an illness. If people know about the problem of their loved one (blood clots, high blood pressure, etc.), then they should not enter into conflicts with him, irritate him, take him to a country house, take him out into the sun. We must try to keep the patient in sight, measure the pressure, if it is high, remove it (water, chamomile tea, medications). But, often, a stroke occurs suddenly. In any case, the first step should be to call an ambulance - this applies to any situation, even before diagnosing the disease at home.
Before providing first aid, you should correctly assess the situation. There is an algorithm of actions that will help you understand whether this is really an acute disorder or not.
- You need to ask the person to smile. A stroke is characterized by a tilt of the mouth and tongue to one side, which makes it impossible to smile.
- The person must say his full name and repeat the phrase. Speech during a stroke is not very clear.
- You must ask to raise both hands. One of the limbs, of any half of the body, will be saggy and inactive.
If help has not yet been called, this should be done urgently. Doctors give no more than 3-5 hours between making a diagnosis at home and saving a person. Emergency medical care is the first step to saving him. Next, we must create all the conditions to support human life without panic.
What to do before seeking medical help with a patient who reacts to your words:
- help the person take a comfortable, horizontal position, if possible, transfer him to the bed;
- open the window to provide access to fresh air;
- bring a bucket, as vomiting may occur, at the same time turn the patient on his side and make sure that the vomit does not interfere with the respiratory process, clear the respiratory tract if necessary.
Attention! It is important to arrange assistance for transport to the hospital. Often there is no one to carry the stretcher; a lot of time is spent on organization, which is important for the patient. We need to find people before the carriage arrives. Of course, without leaving the person affected by a stroke without attention.
What to do before seeking medical help with a patient who does not respond to your words, is in a state of sleep with his eyes open, or is in a coma:
- carefully place him in a comfortable, horizontal position and check for associated bruises and wounds; this is possible when falling (the person may have hit his head and lost consciousness);
- check whether he is breathing, if there is no breathing, the heartbeat is weak, the pupils are dilated, provide resuscitation assistance: chest compressions, artificial respiration;
- organize a flow of fresh air, cover.
What to do in case of seizures during a stroke, first aid:
- push out the lower jaw, try to open it, but under no circumstances do this with your hands, but only with the help of a spoon wrapped in cloth;
- release the airways, stretch out the tongue, fix it by pressing it down between the jaws with the same spoon;
- help you take a comfortable position, try to unclench your limbs (this will require several people);
- put a pillow under your head and hold it in one position until the ambulance arrives.
The faster and more calmly the person nearby reacts, the greater the patient’s chances of surviving.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
Manifestations of an attack may vary depending on the size of the lesion and its location. Depending on the cause, they can appear abruptly (cardioembolic stroke) or stepwise (typical of atherothrombotic stroke). Hemodynamic stroke can begin both suddenly and in stages.
From the outside, the onset of an attack can be identified by the following signs:
- unnatural, asymmetrical change in the face;
- if you ask a person to smile, the smile will be crooked;
- a person cannot raise and hold both arms extended;
- speech impairment (for example, a person cannot say his name or repeat a simple word).
Even one of these symptoms serves as a recommendation to urgently call an ambulance.
This video explains how to recognize a stroke in a person:
Symptoms are divided into general cerebral and focal manifestations.
General cerebral signs include :
- deafness - for the patient, sounds come through as if through cotton wool, confusion may appear;
- agitation or drowsiness, sometimes panic;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
Focal manifestations depend on the location of the lesion. This may be a complex of two or more signs:
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- nausea;
- violation of coordination of movements;
- numbness of the limbs (one or both);
- weakening of the muscles on the side opposite to the lesion;
- loss of sensation in one half of the body,
- spasticity;
- inability to perform any actions even with awareness of what is happening;
- loss of ability to walk;
- loss or incoherence of speech;
- visual impairment (blindness in one eye, narrowing of visual fields);
- non-synchronous eye movements;
- rhythmic movements of the eyeballs;
- disorientation in space;
- unjustified repetition of the same word or action;
- urinary incontinence;
- lack of auditory, visual or tactile perception, despite preserved sensitivity.
Treatment and rehabilitation after stroke
In case of acute cerebrovascular accident, treatment should be provided strictly in a medical facility.
Treatment
To prevent the spread of the consequences of a stroke, medications are prescribed that will protect nerve cells from various effects. For this purpose, neuroprotectors are prescribed (“Actovigin”, “Cerebrolesin”, “Nootropil”, “Ceraxon”). These drugs preserve healthy cells as much as possible, which is important for human life.
Next, drugs are prescribed that relieve or reduce swelling in the radius of the affected cells. Usually these are diuretics (diuretics), which relieve swelling and remove fluid through the urinary system.
If the cause of the stroke was high blood pressure, intensive therapy to lower it is suggested. Angiotensin receptor blockers, Alpha-blockers, ß-blockers.
Further treatment will be focused on restorative measures, because after an acute disorder a person loses various physical and psychological abilities, for which certain parts of the affected brain are responsible.
Rehabilitation
Restorative actions must be carefully selected and distributed over a long period of time. The recovery period can last from one month to three years, it all depends on the patient’s condition and physical fitness.
Recovery algorithm
- Therapeutic physical education comes first, since motor and other physical abilities are lost.
- Therapeutic massage that helps restore muscle activity.
- Work on speech and memory. The patient is taught to speak, read, and understand speech; for this, a speech therapist works with him. A lot of time is devoted to gymnastics of the speech apparatus. Through various tasks and trainings, they work on memory restoration.
- Provide psychological support. Working with a psychologist to adapt to social life and social activities.
The patient will also be prescribed preventive measures to prevent relapses or complications of stroke.
Diagnostics
The purpose of diagnostic procedures is to make a diagnosis as soon as possible and differentiate ischemic stroke from other intracranial pathologies (hemorrhagic stroke, brain tumor, etc.)
The doctor first conducts a physical examination, assesses the functions of the lungs and heart, in order to immediately prescribe correction if necessary. These procedures in some cases suggest the cause of ischemia: for example, if there is a heart murmur and arrhythmia is present, most likely we are talking about a cardioembolic stroke, and a systolic murmur in the carotid artery indicates its narrowing.
Then the doctor assesses the patient's state of consciousness - clear, stupor, stupor or coma.
This article will tell you in more detail about how long a coma can last during a stroke, the stage of its development and what the prognosis for survival is.
To determine the cause of a stroke, a duplex (if necessary, triplex) ultrasound of the arteries supplying the brain is performed.
In the early stages, in the acute period, the most informative procedure is an MRI of the brain. On standard tomograms, the result of vessel occlusion becomes visible within 24 hours. If contrast agents are injected into a vessel, changes may be obvious even if several minutes have passed since the vessel was damaged.
In addition to examining the brain, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests, namely:
- general blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- coagulogram (blood viscosity test).
It is equally important to assess the condition of the heart using ultrasound to see if there are any pathological changes, because ischemic stroke and heart problems are often interrelated.
Folk remedies for restoring the body after a stroke
Folk remedies include not only herbal medicine, but also various oils, products and some physical manipulations. Traditional medicine pursues the same goals as conventional medicine: relieving swelling, preserving nerve cells, and recovery therapy.
Attention! Treatment with folk remedies should never be the only help for a person who has suffered a stroke. Traditional medicine is used after the provision of medical services, as restorative medicine. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate patients who have suffered such a serious illness.
Phytotherapy
The first effect of herbal medicine will be aimed at relieving swelling; any diuretic herbs and berries are suitable for this: lingonberries, bearberry, paralytic grass, dill, parsley, mint, horsetail, nettle. The steaming method is simple: one tablespoon of dry, crushed raw materials requires 200 ml of water. Steam in a water bath, cool, strain and take 1/3 cup on an empty stomach several times a day, no more than seven days. For restorative therapy, herbs are steamed: thyme, flax, chamomile, elecampane, licorice, ginger.
Restoration of speech function
An excellent remedy for restoring speech is sage. It can be taken either internally or as a relaxing bath.
Method for preparing the decoction: 2 tablespoons of dry, crushed leaves, pour two glasses of boiling water. Steam in a water bath, wrap in heat, and let brew for several hours. Strain and take 1/3 cup three times a day.
Method of preparing a bath: pour two glasses of dry raw materials in cold water, bring to a boil. Let it sit for 30 minutes, pour into a full bath.
Green pine cones are used for the same purpose: 2 cones per 0.5 liters of water, boil for 5 minutes, cool and strain. Take one teaspoon three times a day.
To develop speech, you can use foods that will irritate the oral cavity: onions, garlic, lemon, ginger, bitter radish. They can be chewed or sucked.
Fruits and vegetables will be an excellent addition to the healing process. Particular attention is paid to dates. Eating a handful of fruits daily promotes active recovery after paralysis.
Oils and salts
Essential oil therapy has been known since ancient times. Oils such as lemon balm, pine needles, and ylang-ylag are well suited for treating the body after a stroke. Salt: sage, pine concentrate, sea salt. Products can be added to the bathroom; the proportions are described in the instructions.
Diet and nutrition
Proper nutrition will be an excellent aid after a stroke. The diet should contain as much fiber as possible (fruits and vegetables), vitamin C, berry fruit drinks, vegetable soups and low-fat protein. You need to eat often, but in small portions. During the day you should drink as much clean water as possible; it will cleanse the body and help cope with swelling.
Attention! When using diuretics, it is recommended to take vitamins and minerals, since beneficial substances accumulated in the body are excreted in the urine.
Ischemic cerebral stroke: prognosis for life
The prognosis for life after a stroke depends on:
- age,
- timeliness of hospitalization,
- areas of brain damage
- effectiveness of treatment.
Several international methods are used to assess the patient's condition. The most common among them are the NIHSS and the Rankin scale. To assess the prognosis for life using the NIHSS scale, the patient is asked simple questions and required to perform simple operations. The correctness of reactions is assessed by points: 0 points - absolutely true, 2 points - not true. There are 15 questions in total.
With a total score of up to ten points, the patient has a 70 percent chance of fully recovering within a year. If the total score exceeds 35, this indicates unrestored blood supply. The patient needs repeated diagnostics and therapy to find and eliminate the cause of the impaired blood supply. The Rankin scale consists of six grades, one of which is assigned to the patient after examination and assessment of his functional capacity. The scale looks like this:
| Degree | Patient Assessment |
| Zero | There are no violations. |
| First | The loss of capacity is minimal, the patient practically does not feel the consequences of the stroke. |
| Second | The violations are mild. The patient can take care of himself throughout the week. |
| Third | Moderate loss of capacity. The patient retains the ability to move independently and take care of himself, but often he needs advice on complex matters: financial transactions, calculations of utility bills. |
| Fourth | The patient is mobile, but requires constant care and assistance. |
| Fifth | The patient has completely lost the ability to move and cannot care for himself. |
The lower the score on this scale, the better the prognosis for quality of life and the higher life expectancy.
Consequences of a stroke
The consequences of a stroke are painless, but unpleasant, and you should be psychologically prepared for them. Damaged brain cells are restored very slowly, and psychomotor functions dependent on the affected areas will be temporarily lost. After a stroke, a person may lose hearing, vision, and partially lose speech. Muscle paralysis most often does not recover or it requires a lot of strength, energy, patience and time.
It is also difficult for a person to recover his memory: he forgets not only fragments of life, but also the necessary words and even some physical actions. Careful work on yourself will help you cope with this illness.
More complex consequences will occur with a hemorrhagic stroke; the person may remain motionless or fall into a coma. With such consequences, restoration of physical and psychological functions is virtually impossible.
What it is
Ischemic stroke is a pathology that is an acute, critical for the body, severe deterioration of cerebral circulation. Another designation is cerebral infarction.
It occurs when blood clots or emboli narrow the lumen of the cerebral (brain) arteries or completely block them.
As a result of a sharp reduction or complete cessation of blood flow, brain cells die from lack of oxygen and vital nutrition, and tissue necrosis occurs. The brain stops working normally.
A person may lose speech, memory, motor activity, breathe independently, have problems with swallowing and vision. All this can result in paralysis, disability, and in case of serious, extensive lesions, death.
Stroke Prevention
Stroke prevention depends entirely on maintaining the cardiovascular system. The main actions will be: a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition. Bad habits prematurely wear out blood vessels, provoke the appearance of blood clots and cholesterol plaques, which impede the flow of blood.
The same can be said about food: the simpler the food, the stronger the blood vessels. You should definitely exclude from your diet what was mentioned at the beginning of the article. You can and should cook food: by steaming, in the oven, by boiling. Once a month, arrange fasting days. Replace strong black tea and coffee with ginger or green tea, water, compotes, fruit drinks. A couple of days a month you can simply switch to water alone to cleanse your blood vessels.
Sports are an integral part of a healthy lifestyle and the prevention of stroke. We are not talking about professional sports: daily gymnastics, gym or morning jogging, three times a week - this will be quite enough. Walking in the fresh air is useful, especially before bed: you should walk at least two kilometers within an hour. And, of course, be sure to avoid stressful situations and get rid of nervous tension with soothing teas or relaxing baths. Healthy nerves mean healthy blood vessels.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis depends greatly on how exactly the stroke occurred, which parts of the brain were affected, and how quickly the necessary help was provided.
For some, life itself will be a gift in the current circumstances, others will be able to move only with outside help, and still others suffer a stroke without serious consequences. In all cases, the main thing is timely assistance and a serious approach to rehabilitation.
The most serious, but also the most likely complication is a recurrent stroke, which, as a rule, has much more serious consequences.