Author of the article:
Rybitskaya Marina
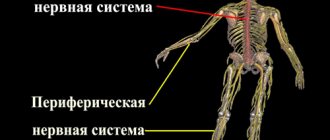
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is represented by structures located outside the brain: cranial and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses and formations. Their function is to “deliver” impulses from the central nervous system to muscle fibers and back. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, diseases of the peripheral nervous system occupy third place in the ranking of overall morbidity.
Causes and symptoms of damage to the peripheral nervous system
The most common diseases of the peripheral nervous system are neuritis and radiculitis. In the first case we are talking about the inflammatory process of nerve tissues, in the second – about the consequences of osteochondrosis and extensive damage to the roots of the spinal cord.
Possible causes of neuritis and radiculitis:
- injuries (bruises, fractures, cracks);
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- a consequence of a cold, acute respiratory viral infection, flu;
- inflammation of the middle ear (otitis);
- hypothermia/dehydration;
- hypovitaminosis;
- emotional shock, stress;
- intoxication;
- tumor processes;
- age-related changes in vertebral discs;
- somatic diseases.
Symptoms of damage to the peripheral nervous system gradually increase, and the pain seems to paralyze the person and turn him into a disabled person.
Characteristic symptoms of a progressive pathological process:
- decreased sensitivity of individual parts of the body;
- paresis, muscle atrophy;
- increased sweating;
- myalgia, arthralgia;
- pain in the limbs;
- change in skin color;
- increased nervousness;
- increased body temperature;
- decline in performance.
Causes and types of neuropathy
In 30% of cases, neuropathy is considered idiopathic (that is, arising from unknown causes).
Otherwise, the causes of the disease can be divided into internal and external.
Causes associated with various internal pathologies:
- endocrine diseases, of which diabetes mellitus accounts for about a third of all neuropathies;
- vitamin deficiency, especially deficiency of B vitamins;
- autoimmune diseases;
- multiple sclerosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
External factors that provoke the development of neuropathy include:
- alcoholism (a common consequence is neuropathy of the lower extremities);
- injuries;
- intoxication;
- infections.
Often the cause of nerve damage is a hereditary factor. In such cases, the disease can develop independently, without any additional harmful effects.
Neuropathy is a very serious illness that requires qualified diagnosis and adequate treatment. If you are concerned about any of the symptoms listed below, consult a neurologist immediately!
Depending on the location of the disease, neuropathies of the upper, lower extremities and cranial nerves are distinguished, for example:
Facial nerve neuropathy
It can develop as a result of a traumatic brain injury, a viral infection, hypothermia, unsuccessful dental surgery, depression, pregnancy and childbirth, as well as due to a neoplasm. Signs of the disease are: weakening of the muscles on the side of the affected nerve, salivation and lacrimation, inability to completely close the eyelids.
Trigeminal neuropathy
Caused by various reasons (maxillofacial surgery, dentures, difficult childbirth, heredity) damage to the nerve endings of the gums, upper and lower lips, and chin. Patients complain of severe facial pain from the affected nerve, radiating to the upper and lower jaws, not relieved by analgesics. There is also discharge from one nostril, lacrimation and redness of the eye.
Radial nerve neuropathy
It often occurs against the background of so-called “sleep paralysis,” i.e. compression of the nerve due to incorrect position of the hand. Occurs in people who use drugs or alcohol. It also progresses with wrist fractures, bursitis or arthritis. It manifests itself as a violation of the dorsiflexion of the hand (the hand hangs), numbness of the thumb and index fingers, pain can occur on the outer surface of the forearm.
Median nerve neuropathy
Damage to this area of the upper limb can occur due to sprains, fractures, diabetes mellitus, rheumatism, gout, neoplasms, as well as in the event of nerve compression. It manifests itself as severe pain (as well as numbness and burning) in the forearm, shoulder, hand, thumb, index and middle fingers.
Ulnar nerve neuropathy
The cause of this disease may be traumatic (sprain, tear and rupture) or other damage to the ulnar nerve (for example, caused by bursitis, arthritis). It manifests itself as numbness of the first and half of the fourth fingers, a decrease in the volume of the hand, and a decrease in the range of movement.
Sciatic nerve neuropathy
It usually results from a serious injury or illness (knife or gunshot wound, fracture of the hip or pelvic bones, intervertebral hernia, oncology). It manifests itself as pain along the back of the thigh, lower leg, buttock from the side of the nerve lesion.
Neuropathy of the lower extremities
It can develop due to excessive physical overload, tumors in the pelvic area, hypothermia, and also due to the use of certain drugs. Symptoms: inability to bend forward, pain in the back of the thigh, numbness in the lower leg.
Peroneal nerve neuropathy
It occurs due to bruises, dislocations and other injuries, as well as due to curvature of the spine, carpal tunnel syndrome, and wearing narrow, uncomfortable shoes. Manifestations: inability to dorsiflex the foot, cock-like gait (the patient cannot bend the foot towards himself).
1 Massage
2 Massage
3 Acupuncture
Complex treatment of diseases of the peripheral nervous system
Damage to the peripheral nervous system is not a diagnosis, but a set of pathological processes. To establish a diagnosis, differential diagnosis is performed.
General recommendations that are important to follow during complex therapy:
- reduce physical activity, avoid stress and emotional stress;
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- reduce salt intake in the daily diet;
- enrich the daily menu with fresh vegetables and fruits;
- undergo a course of physiotherapy (electrophoresis, exercise therapy, massage, UHF, etc.);
- take medications if pain increases;
- do therapeutic exercises;
- take multivitamin complexes.
If complex therapy does not produce positive results, and the pain does not subside even in a passive state, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment followed by rehabilitation.
Causes
Peripheral neuropathy may be caused
- Diabetes
- Traumatic or positional compression of nerves
- Traumatic rupture
- Tumor (including tumors of surrounding tissues such as fat, muscle, blood vessels that can compress the nerve)
- Intraneural hemorrhage
- Prolonged exposure to cold or radiation
- Certain medications or toxic substances
- Vascular or collagen diseases such as atherosclerosis, lupus, scleroderma, sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis
- In some cases, neuropathy may be due to heredity, vitamin deficiencies, infections and kidney disease
Recommended treatment regimen
Taking dietary supplements is no less effective than taking full-course official medications. Herbal components are also able to quickly stop an attack, prolong remission and restore the functions of the peripheral nervous system without complications or side effects. Treatment regimen:
| Name of dietary supplements | Treatment regimen | Recommended course, week |
| Esobel granules | electrophoresis | 8-12 procedures |
| Flavigran | 1 teaspoon three times a day. | 4 |
| Florenta cream or Cream Esobel with cinquefoil extract | Treat the source of pathology 2-3 times a day. | 2-3 |
| Esobel with cinquefoil or Esobel-Art | 1 teaspoon three times a day with meals; 2 capsules three times a day. | 3-4 |
| Turpentine baths | every two days on the third, take mixed baths. | 12-15 procedures |
The basis of complex therapy is the Esobel series of the indicated release forms. The use of other herbal preparations is discussed individually with a consultant, taking into account the characteristics of the disease.
Peripheral nerve injuries
Peripheral nerve injuries
— different mechanisms of damage to the nerve trunks of the peripheral nervous system. They manifest as pain and symptoms of decrease or loss of motor, sensory, autonomic and trophic functions of the nerve distal to the site of injury.
Peripheral nerve injury is diagnosed based on the results of a neurological examination and electrophysiological studies of the neuromuscular system.
Treatment can be conservative (painkillers, vitamins, physiotherapy, neostigmine, vasoactive drugs, exercise therapy) and surgical (neurolysis, nerve autoplasty, nerve suture, neurotization).
Peripheral nerve injuries, according to various data, account for 1-10% of the total number of injuries. Wounds of the extremities are accompanied by damage to the nerve trunks in 1.5% of cases, and fractures in 20% of cases.
The most common areas for nerve injury are the upper third of the shoulder, the armpit, the lower thigh, and the upper leg.
The last two account for up to 65% of all injuries to peripheral nerve trunks.
Every year in Russia, up to 7 thousand people need surgical treatment, the indication for which is peripheral nerve injury. Many patients are discharged from trauma or general surgical clinics with existing neuromotor deficits.
The lack of timely qualified assistance from specialists in the field of neurology and neurosurgery leads to disability of patients, most of whom are of working age.
According to some data, permanent loss of ability to work is observed in 60% of victims.
Peripheral nerve injuries
According to the nature of the damage, peripheral nerve injury is classified as compression (compression), concussion, contusion (bruise) and anatomical break. The latter can be partial (incomplete), complete and intra-barrel.
With a partial and intra-trunk break, the possibility of spontaneous regeneration of the nerve remains due to the ingrowth of the axons of the terminal sections of its central segment into the peripheral section. The rate of this process is 1 mm per day.
Significant nerve damage leads to scar formation and conduction disturbances distal to the injury site.
A complete anatomical break with divergence of the ends or the presence of an obstacle between the formed segments of the nerve in the form of a bone fragment, scar, or foreign body causes the development of neuroma. A neuroma can also result from a bruise of the nerve trunk or hemorrhage into it.
On the other hand, all nerve injuries are divided into open, which most often leads to an anatomical break of the nerve, and closed, in which concussion, compression or bruise of the nerve is possible. Open injuries include various wounds: stabs, lacerations, cuts, chopped, gunshots.
In this case, there is a danger of direct infection of the wound tissue. Closed injury to the peripheral nerve is possible due to bruise, blow with a blunt object, compression of a limb, or excessive traction.
Closed include damage to the nerve during dislocation and closed fracture, its compression by post-traumatic scars, hematoma, callus, etc.
In some cases, combined injuries occur, in which open injury to the nerve is combined with its closed damage. A special group consists of iatrogenic injuries of peripheral nerve trunks that occur as a complication of a number of surgical operations or various medical procedures.
How many drugs are needed per course?
To complete 1 course, it is recommended to purchase dietary supplements in the following quantities and not violate the prescribed dosages:
- Flavigran (120 g) – 2 packs;
- Turpentine baths No. 1 and 2 – 1 bottle each;
- Esobel granules (50 g) – 1 pack;
- Esobel cream (50 g) – 2 packs;
- Florenta cream (30 ml) – 2 packs;
- Esobel with cinquefoil (120 g) – 2 packs;
- Esobel-Art (90 caps.) – 2 packs.
One course is enough to experience sustainable positive dynamics and solve a number of serious health problems.