Respiratory neurosis reflects a dysfunction of breathing, interconnected with a disorder in the regulation of respiratory activity. A condition where it becomes difficult to breathe due to nerves leads to decreased ability to work and social maladjustment. During a panic attack, patients feel as if they are dying, which aggravates respiratory disorders. Pathology is more often detected among women.
Characteristic
Breathing is a vital function of the body. Respiratory dysfunction is accompanied by disruption of homeostasis and the development of concomitant syndromes and diseases. Shortness of breath during neurosis, also known as neurogenic hyperventilation, is excessively deep breathing caused by a feeling of lack of air and dissatisfaction with the respiratory process.
The patient needs to make several breathing movements - take a deep breath or several breaths to get enough air. Dyspnea during neuralgia occurs in a paroxysmal (symptoms appear during attacks) or permanent (manifestations are observed constantly) form.
Hyperventilation syndrome in clinical practice is considered separately from panic attacks. However, 50% of patients with diagnosed panic disorder experience hyperventilation syndrome, and 25% of patients with impaired respiratory function experience panic attacks. The pathology occurs in acute and chronic forms.
Breathing exercises for panic attacks
It is important to understand that exercises should not be started at the moment of an acute panic attack, but against the background of complete well-being.
When the adrenaline storm hits, there will be no time to learn breathing exercises, and good training the day before will provide a favorable way out of the situation. Breathing exercises during panic attacks during VSD will not only help relieve the disgusting symptoms of a crisis, but, with regular practice, will even begin to nip these attacks in the bud. Of course, not all exercises are suitable for public demonstration, but do not forget: in war, all means are fair.
By the way, the breathing exercises of yogis are based on the same principle: normalization of gas proportions in the body, getting rid of hyperventilation of the lungs. Here are the most effective and at the same time simple exercises that every VSD student should master.
» alt=»Proper breathing during panic attacks»>
Causes
In the pathogenesis of respiratory neurosis, the leading role is given to psychological factors. The causes of the condition, when breathing becomes difficult at rest or as a result of physical activity, are associated with mental disorders - anxiety (neuroses), anxiety-depressive, post-traumatic stress, less often hysterical.
Mental disorders disorganize respiratory function and provoke hyperventilation. The respiratory system is autonomous, but its work is affected by emotional states, especially increased anxiety. Metabolic disorders, especially calcium and magnesium metabolism disorders, are involved in the pathogenesis.
An imbalance of minerals causes disruptions in the production of respiratory enzymes, which is associated with breathing problems. Stress experienced in childhood and prolonged depression lead to a disorder in the breathing cycle. At the same time, the rhythm and frequency of respiratory movements are disrupted.
Increased pulmonary ventilation is associated with persistent biochemical changes associated with the accelerated removal of carbon dioxide from the body. Hypocapnia develops - a decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide against the background of an increase in the concentration of oxygen in the blood. In parallel, respiratory alkalosis develops - a shift in the acid-base balance towards increasing pH values (increasing the volume of alkaline fractions).
Alkalosis provokes the development of hypophosphatemia (low concentration of phosphate in the blood serum) and hypocalcemia (calcium deficiency), which triggers the mechanism of tetany (uncontrolled painful muscle contraction). Mental disorders are aggravated as a result of disruption of biochemical processes, accompanied by confusion, disruption of the autonomic system, allergic reactions and sensitivity disorders.
Associated symptoms
The causes of respiratory failure in adults are associated with emotional shocks suffered. Psychogenic shortness of breath is often detected in former participants in military operations. Related patient complaints include:
- Unmotivated fatigue.
- Night sleep disorder.
- Moderate pain of different localization.
- Muscle spasms.
- Paresthesia (sensitivity disorder manifested by a burning sensation, tingling, numbness).
- Dizziness, impaired motor coordination.
In the structure of the so-called “military syndromes,” respiratory distress occupies a leading position along with cardiac dysfunction. Increased respiratory activity is associated with muscular-tonic disorders. The severity of symptoms of respiratory neurosis correlates with physical effort and nervous tension.
Symptoms of shortness of breath developing due to nervousness include instability of breathing, changes in the frequency and duration of inhalations and exhalations, and a violation of the relationship between the periods of inhalation and exhalation. Neurosis, formed through physical and psycho-emotional overload against the background of an acute lack of rest, accompanied by impaired respiratory activity, is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Unfounded, groundless fears (uncertainty about the future, inability to concentrate, worries about possible future failures).
- Motor tension (agitation, fidgetiness, inability to relax, tension-related headaches).
- Hyperactivity of the autonomic nervous system (increased sweating, tachycardia - increased heart rate, discomfort in the epigastric zone, dry mouth, dizziness).
In 25-55% of patients, there is comorbidity (the presence of several diseases occurring simultaneously and associated with common pathogenetic mechanisms) of neuroses with attacks of depression, panic attacks, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and phobias. Lack of air during neurosis is combined with other symptoms of respiratory impairment:
- Difficulty in inhaling and exhaling.
- Violation of the automaticity of respiratory movements.
- Components of hyperventilation syndrome (sighs, yawning, dry coughing).
Neurogenic tetany is manifested by convulsive attacks (carpopedal spasms - involuntary contraction of muscles in the area of the feet and hands). Patients exhibit Chvostek syndrome, which reflects an increased level of neuromuscular excitation. The test is performed by irritating (tapping) the areas of the face that bear the projection of the facial nerve.
As a result, an uncontrolled contraction of the facial muscles occurs. Another sign is a positive result of the Trousseau test, which reflects a disorder of calcium metabolism. Tetanic syndrome, accompanying respiratory distress, correlates with alkalosis, which disrupts the functioning of the nervous system, which is manifested by increased transmission of impulses in the nervous and neuromuscular tissue. Procedure for performing the Trousseau test:
- Apply a pneumatic cuff or arterial tourniquet to the patient's shoulder for a period of 5-10 minutes.
- Maintaining pressure inside the cuff by 10 mm. rt. Art. higher than the patient's systolic pressure.
- The appearance of carpopedal spasms after removal of the cuff after the above period (stage after ischemia), which confirms a high level of neuromuscular excitation.
If the leading symptom is a feeling of lack of air, patients find it difficult to breathe. The condition is aggravated in situations of stress (public speaking, passing exams, family conflicts, problems related to professional activities). Patients find it difficult to breathe when they are nervous, and less often the symptoms persist in a state of mental balance. Patients, dissatisfied with inhalation, breathe frequently and deeply, try to open the window everywhere, and cannot stand being in a stuffy room.
A disorder of the automaticity of respiratory activity is accompanied by a feeling of respiratory arrest and asphyxia (suffocation). Patients suffocate when they are nervous and cannot take a breath. If a disorder of automatism occurs during neurosis, patients monitor the breathing process and actively participate in its regulation.
Difficulty breathing syndrome is manifested by a feeling of a “coma” stuck in the throat, breathing movements are performed tensely. When inhaling, there is a feeling that air is not passing into the lungs. The condition is called “atypical asthma.” Characteristic signs are disturbances in the rhythm of inhalation and exhalation, increased, intense movements of the chest during the inhalation phase. The patient looks restless and tense.
The shortness of breath that occurs as a result of neurosis is not associated with organic damage to the organs of the respiratory system. Instrumental diagnostics do not confirm the presence of lung pathology. Attacks of suffocation due to nervousness are aggravated during panic attacks, which leads to the development of a hyperventilation crisis.
During a hyperventilation crisis against the background of neurosis and concomitant disturbances in the functioning of the lungs, the patient is afraid of dying from lack of air, which can be associated with a feeling of fear of death, which initiates a panic attack. At the time of a panic attack, convulsive breathing is accompanied by symptoms reflecting malfunctions of the autonomic nervous system. Among them:
- Cardiopalmus.
- Increased sweating.
- Hyperemia or pallor of the skin.
- Painful sensations in the heart area.
- Disorientation in space, confusion.
- Nausea, sometimes gagging, increased peristalsis, bloating.
Fear of suffocation is associated with increased manifestations of neurosis. The patient begins to choke, his face turns red or pale, and profuse sweat appears on his face. At the same time, stiffness of the fingers is observed, and a pre-fainting state occurs.
Features of the course in children
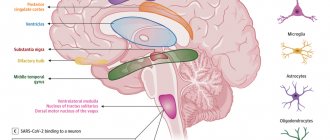
Breathing function is associated with emotions. Respiratory neurosis in children develops against the background of psychosomatic pathology. The respiratory center is located in the brain stem structures. The functioning of the respiratory apparatus is influenced by other parts of the brain, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, cortical structures, and limbic system. Inconsistency in the control of the respiratory muscles leads to the appearance of disorders - coughing, additional sighs, yawning.
If a child begins to experience shortness of breath, accompanying symptoms may appear - unsteadiness in a standing position, weakness, dizziness, muscle spasms in the arms and legs. Hyperventilation syndrome in children correlates with diseases such as vegetative-vascular dystonia, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and bronchial asthma. To identify the severity of mental disorders, testing is carried out and an anxiety scale (CMAS) is used.
Belly breathing
The simplest thing you can do is switch to belly breathing and increase your exhalation time. To do this, you do not need to know the principles of breathing exercises or count while inhaling and exhaling. But deep breathing with a long exhalation will help you calm down.
Place one hand on your stomach and the other on your chest to understand how you are breathing now. The task is to make it the stomach that moves, not the chest—it rounds as you inhale and retracts as you exhale.
With calm, deep breathing, oxygen is distributed evenly in the body, the nervous system relaxes, and the hormonal system sends safety signals. After a few minutes of deep breathing, the ability to think rationally returns.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on medical history and the results of instrumental examination. To make a diagnosis, uneven, intermittent breathing, as well as other typical signs, must be observed for at least 3 months. Other conditions:
- Absence of diseases - somatic, neurological, which can provoke respiratory disorders.
- Shift in blood pH values towards increasing alkaline fractions.
- Presence of signs of tetany.
The hyperventilation test shows breathing problems arising from nervousness. The patient is asked to breathe more frequently and deeply, which leads to the appearance or intensification of pathological symptoms. An instrumental examination in the format of MRI and CT is carried out to study the brain structures and determine the condition of the lungs in order to exclude other reasons that may make breathing difficult.
Electrocardiography shows the condition of the heart, electroencephalography shows the bioelectrical activity of the brain. X-rays of organs located in the chest area are carried out as part of differential diagnosis. Pulse oximetry shows the level of oxygen saturation in the blood. Saturation (saturation) of blood oxygen during hyperventilation syndrome reaches 100%.
Breathing 4-7-8
There are many breathing exercises. One of them that helps cope with anxiety is the “4-7-8” exercise. It has several useful properties:
- reduces anxiety, fear, aggression
- helps you sleep peacefully
- reduces cravings for emotional eating
To perform the exercise, sit in a comfortable position and relax your facial muscles. To do this, you need to press your tongue to the palate, and the tip to the upper front teeth, open your lips.
Procedure:
- Exhale completely, empty your lungs
- Inhale through your nose, counting to 4
- Hold your breath for 7 counts
- Exhale forcefully through your mouth for 8 counts (as if you are blowing out a fire or blowing on something hot)
Repeat at least 4 times. The effect of the exercise will be better if you close your eyes and imagine pictures that calm you down.
Treatment methods
Treatment of respiratory neurosis is aimed at eliminating nervous and physical stress, correcting mental disorders, and eliminating mineral imbalances. As part of complex therapy, the patient is taught proper breathing.
Treatment of children during exacerbation of pathology is aimed at eliminating manifestations of anxiety and fear, which is associated with a decrease in the severity of symptoms and improvement in the patient’s well-being. The therapy program includes therapeutic exercises, art therapy (visual creativity), and play therapy.
If severe shortness of breath, convulsive sighs appear against the background of symptoms of neurosis and a panic attack, treatment is reduced to providing emergency assistance to reduce the severity of the manifestations. The patient is asked to breathe inside a paper or plastic bag. The relief of the attack in this case is due to the blocking of the process of respiratory alkalosis.
The patient breathes his exhaled air with a high content of carbon dioxide, which leads to the equalization of the acid-base balance of the blood and the elimination of symptoms. To get rid of the manifestations of pathology, special exercises are done, which is interconnected with the need to regulate such characteristics as the frequency and depth of breaths. Basic principles of breathing exercises:
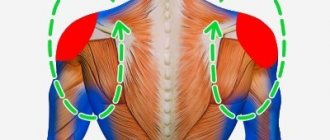
- Transition to diaphragmatic (involving the abdominal cavity) breathing, which leads to inhibition of the activity of the structures of the reticular pharmacy of the brain stem, responsible for the automatic regulation of inhalation-exhalation cycles. The result is muscle relaxation and mental relaxation.
- Maintaining a certain rhythm - short inhalation and extended exhalation (the duration of exhalation is 2 times longer than the duration of inhalation), reducing the number of inhalation-exhalation cycles (sparse breathing).
- Regularity of classes. The first classes last a few minutes. Gradually the duration of the workout increases. Against the background of regular training, a stable psychophysiological pattern of correct breathing is formed.
Gymnastics is done against a background of positive emotions and the absence of nervous and muscle tension. At the same time, the attending physician prescribes procedures such as autogenic training and psychological correction (psychotherapy). Instrumental treatment includes biofeedback (biological feedback). During the biofeedback procedure, patients develop self-regulation and self-control skills.
Drug therapy
Hyperventilation syndrome correlates with conditions when the patient is very worried or nervous, which confirms the participation of nervous regulation mechanisms (vegetative department) in the pathogenesis. The doctor conducts a diagnosis and, based on the results of the examination, helps the patient to return to a calm life; the main medications prescribed by the psychotherapist have a calming effect.
When correcting anxiety disorders, the first choice drugs are antidepressants, which, according to clinical studies, are more effective than anxiolytics (tranquilizers). Anxiolytics reduce feelings of emotional stress, anxiety, and restlessness. Main drugs: Amitriptyline, Fluvoxamine, Mirtazapine. Psychotropic therapy lasts for about 3-6 months.
In parallel, magnesium and calcium preparations are prescribed. Magnesium deficiency is aggravated as a consequence of stress, which leads to an increase in neuro-reflex excitability and deterioration of cognitive functions. Vitamins of group B are indicated. Drug therapy for pediatric patients involves the prescription of drugs based on plant extracts with a calming effect.