14.03.2017
It is not easy to classify brain cancer; the reason is the peculiarity of the behavior of intracranial tumors.
Primary lesions never metastasize; if a neoplasm grows rapidly and compresses healthy tissue and increases intracranial pressure, then it can be considered malignant.
In this situation, the malignancy of the tumor is determined not by cellular atypia, but by complications caused by cancer. There is a high risk of death.
In medicine, there is a certain classification of malignant tumors, which takes into account primary lesions, the presence of metastases in the lymphatic system, as well as the presence of distant secondary lesions. It is not used to determine the stage of tumors in the brain. The classification of the World Health Organization, which was adopted in 2000, is now used.
Classification of tumors
Difficulties in diagnosing this disease are manifested in the fact that it is simply impossible to perform a tissue biopsy for technical reasons. Doctors determine the presence of a disease solely by external signs, symptoms and complications, which are sometimes similar to other ailments. Stage 4 brain cancer gives a disappointing prognosis, and the risk of a sad outcome is very high. Today, doctors determine the stage of the disease according to the classification adopted in 2000 by the World Health Organization. Previously, the criterion was the presence of metastases, secondary and primary foci.
Prognosis and prevention
If at stages 1 and 2 the probability of successful treatment is quite high, then stage 3 poses a serious danger to human health and life: even after a successful operation, a person can live about 2-3 years. The difficulty of treating advanced oncology lies in the fact that surgical intervention does not completely remove metastases from the brain, which leads to their further development, which ultimately ends in damage to a large part of the brain tissue.
The following can be used as preventive measures for brain cancer:
- Regular physical activity.
- Minimum consumption or complete refusal of fried foods and fast food.
- Protection from UV radiation, which is especially important in the summer.
Varieties of 4 degrees
How can a stage 4 brain tumor manifest itself? How long do patients with this disease live?
The disease is divided into three types:
- malignant tumor with a classic course;
- malignant formation with uncharacteristic symptoms;
- malignant formation is rapidly growing.
The latter option almost always ends in death for the patient, since the rate of tumor spread is very high, and the disease is usually diagnosed in late stages.
What treatment measures are carried out at stage 4 cancer?
Treatment of the fourth stage of cancer of any location with extensive tumor damage and the presence of distant metastases is predominantly palliative and symptomatic. The main tasks of the doctor in treating such patients are as follows:
- Limiting the spread of the tumor.
- Reducing the rate of tumor growth, delaying the progression of the tumor process.
- Preservation of the functioning of organs and systems.
- Prevention of life-threatening complications - thromboembolism, strokes, heart attacks.
The main treatments for stage 4 cancer include palliative surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy and other methods used alone and in combination, depending on the type of malignant tumor.
Improvements in treatment methods for late-stage cancer have led to the introduction of procedures that can significantly improve the quality of life of patients, as well as extend life to a year or more. At the same time, some patients retain their ability to work and the ability to communicate with family and friends.
Individual antitumor vaccines are prepared in parallel with surgery, during which a large volume of the tumor is removed. A cell culture is grown from the removed tumor, and lymphatic dendritic cells are isolated from the patient’s blood leukocytes. In special laboratory conditions, immune cells are trained to respond to antigens from a removed tumor. The result is a personalized cancer vaccine that further protects the patient from recurrence and metastasis.
Monoclonal antibodies, including drugs such as imuteran, Erlotinib, prescribed for colon cancer, and SU11248, used to treat stomach cancer, selectively act on malignant cells and cause their isolated death after intravenous administration. The drugs Opdivo, Keytruda, and Tafinlar are used in the treatment of melanoma.
Radioembolization of liver metastases is performed for various oncological diseases in late stages. It includes intravascular selective catheterization of liver vessels under the control of an angiograph and the introduction of embolic particles with the radioactive isotope yttrium-90. The isotopes remain active and fight tumor cells for 64 hours.
Chemoembolization with microspheres is an endovascular operation during which microspheres with immobilized chemotherapy are injected directly into the artery feeding the metastasis. Chemoembolization is performed for inoperable neoplasms, with severe volumetric liver damage, and severe concomitant somatic diseases.
Radiofrequency RF ablation of liver tumors is performed for primary liver tumors and metastatic liver lesions up to 5 cm in diameter. It is the world standard in the complex treatment of late stages and metastases of colorectal cancer.
RFA is contraindicated when the tumor focus is located in close proximity to the portal vein, gallbladder, or large bile ducts.
- In percutaneous transhepatic radiofrequency ablation, under ultrasound guidance and general anesthesia, a hollow needle is inserted through the skin and liver parenchyma, through which a monopolar radio wave electrode is then inserted.
- The electrode locally heats up an area of the liver parenchyma, causing coagulation of tumor tissue and local necrosis.
- In some cases, radiofrequency RF ablation of liver tumors is performed during laparotomy, during the elimination of intestinal obstruction with anastomosis, or when removing the tumor infiltrate.
- Performing radiofrequency RF ablation of the liver significantly expands the indications for surgical treatment of patients with multiple polysegmental liver lesions.
In general, even palliative and symptomatic treatment of stage 4 cancer of any location prolongs the patient’s life and improves its quality.
Characteristics of varieties
Experts diagnose a grade 4 brain tumor and assign it to a specific subtype according to the following criteria:
- Initially, doctors study the characteristics of tumor cells.
- After this, special tests are used to calculate the rate of cell division.
- Next, specialists determine how quickly the cancer spreads in the blood vessels and lymph nodes.
- The last step is to count dead cells in the tumor tissues.
If, during a detailed study of cancer, doctors did not find any of the listed criteria, then the tumor is considered benign. The presence of the third or fourth sign in a patient indicates that he has stage 4 brain cancer. How long people with this diagnosis live depends on the characteristics of the disease and the specifics of its treatment.
Causes
According to the latest data, one of the main causes of this disease is age, as well as hereditary predisposition: if relatives have had large-scale processes in the brain, this significantly increases the risk of cancer in other family members. In addition, the tumor can be caused by direct contact with carcinogenic substances and radiation, which has an extremely detrimental effect on cells. Despite the assurances of many doctors, the harmful effects of using tobacco products and alcohol have not been proven.
Flow options
It also happens that the disease does not go through all stages of its development from the beginning, but immediately develops in its most severe form. This aggressive type is glioblastoma. The prognosis for this form of pathology is very disappointing. How long do people live with stage 4 brain cancer in the case of an aggressive course of the disease? Only a doctor can answer this question. As a rule, even with adequate treatment, this time does not exceed 1 year.
Photos of stage 4 brain cancer cannot but upset us. These are mainly tomograms of sick people, where it is clearly visible that a tumor can arise in completely different areas of the nervous system and always develops with its own characteristics. The stage of the tumor can be definitively determined only after removal of its primary focus and histological examination.
Types of tumors in stage 4
Some of them degenerate into others when the brain disease is already in its final stages. However, they should be distinguished.
Glioblastoma
A tumor, which in turn is divided into several according to the degree of benignity and localization (glioblastoma of the cerebellum, spinal cord, ventricle, etc.). At stage 4, multiform formations appear, glioblastoma grows into other tissues.
Tumor multiforme
It is scary because it acquires new features in each degree. The formation is closely related to the vascular system, has a dense plexus of capillaries and arteries, and therefore the possibility of surgery is associated with the risk of heavy hemorrhage.
Gliosarcoma
A malignant tumor that forms from connective tissue.
Sarcoma and glioma differ, for example, in the structure of cells: the first is formed from connective cells, the second from nerve cells. To date, several dozen types of brain cancer have been studied, but most, unfortunately, are still unknown or are under study.
How does the disease progress?
How long do patients with stage 4 brain cancer live?
This issue must be considered individually for each specific case. The disease is quite rare and occurs in only 1 person in a thousand. The tumor can be inherited or occur as a result of unfavorable environmental conditions. Even in the case of genetic transmission of the disease, tumor formation will never be the same. The outbreak can be localized in a completely different area than in relatives. If any signs, even the most insignificant, occur that hint at the presence of a neoplasm in the body, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is the difficulty of diagnosis that leads to such sad mortality statistics. The initial stages of cancer formation are rarely accompanied by any symptoms. Often, while the patient is undergoing all the necessary research, the tumor has already reached the last stage of development, when treatment by any means can no longer provide a 100% guarantee of recovery. Even with these statistics in mind, you shouldn’t give up. Of course, after treatment, a person’s life changes dramatically, but if cancer is detected in a timely manner, everyone has a chance of recovery.
Clinical picture of the disease
What are the signs of brain cancer?
- focal;
- general cerebral.
Focal symptoms occur due to an increase in tumor in the cranial cavity. The tumor puts pressure on the brain tissue, which can cause it to collapse. General cerebral symptoms occur when the disease begins to progress.
The symptoms and mechanism of development of the disease depend on the location of the tumor in the brain. Each part of the brain controls certain organs and systems of the body, so not all symptoms can be observed in the early stages of cancer development.
symptoms
Focal symptoms of the disease
- Decreased sensitivity (impossibility to determine body position, decreased pain and sensitivity threshold);
- Memory impairment (memory loss due to destruction of the cerebral cortex, absent-mindedness);
- Personality changes (social characteristics and intelligence);
- Hallucinations (visual and auditory);
- Impaired hearing and speech perception (if the tumor puts pressure on the auditory nerve, the patient is unable to distinguish human speech, he hears only noise);
- Visual impairment (damage to the optic nerve can cause complete or partial blindness, inability to recognize objects);
- Speech disorders (handwriting may change, speech becomes slurred);
- Paralysis (due to damage to the transmission pathways of motor impulses to the limbs);
- Dysfunction of the autonomic system (fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, dizziness);
- Deterioration of coordination (changes in gait, inability to make precise movements);
- Epileptic seizures and convulsions;
- Hormonal imbalance;
General cerebral symptoms of the disease
- Constant headaches (severe, not relieved by non-narcotic medications; the most common symptom of brain cancer);
- Nausea, vomiting (present constantly, the patient cannot drink or eat);
- Dizziness (disturbance of the vestibular apparatus, feeling of body movement at rest).
Principles of therapy
Basically, all treatment methods come down to relieving the patient of the symptoms accompanying the disease, since headaches in the final stages become simply unbearable. To relieve them, specialists prescribe strong narcotic drugs. Although the tumor is considered inoperable starting from stage 3, specialists still undertake treatment in more advanced cases.
There are three treatment methods:
- chemotherapy;
- surgery;
- radiation therapy.
How is the stage of cancer determined?
The stage of cancer shows how much the malignant tumor has grown into neighboring tissues, whether it has managed to metastasize to the lymph nodes and to various parts of the body. This is very important information, because it helps the doctor develop optimal treatment tactics and build a reliable prognosis.
To determine the stage of cancer, doctors rely on the generally accepted TNM classification. The letter T denotes the size and location of the primary tumor, N - metastases in nearby lymph nodes, M - distant metastases. A numerical index is indicated next to each letter.
Cancer stages are a set of signs that help describe the course of the tumor process. The following stages of cancer are distinguished:
- Zero stage. The so-called cancer in situ. The tumor is located within the tissues from which it developed and does not grow into neighboring structures. The tumor can be completely removed surgically.
- First stage. The tumor is relatively small and has not had time to grow deeply into the surrounding tissue.
- Second stage. The tumor still does not spread to neighboring tissues, but is larger in size. Single metastases may be detected in nearby lymph nodes.
- Third stage. Cancer cells have spread to surrounding tissues and nearby lymph nodes.
- Fourth stage. Metastatic cancer: Tumor cells have spread to different parts of the body.
Sometimes Latin letters are added to the numbers - A, B, C, if a substage needs to be distinguished in a stage.
Drug treatment
How long do patients with stage 4 brain cancer live? Only a specialist can answer this question accurately. You should know that cancer is not treated exclusively with drugs, and this technique is aimed only at relieving the patient of the symptoms associated with the disease. The main drug in treatment is Prednisolone, which relieves cerebral edema. It is a glucocorticoid substance. An additional symptom of the disease may be morning nausea and vomiting, which can be eliminated by taking antiemetics. Severe headaches are treated with morphine or non-steroidal painkillers, and possible mental disorders are treated with sedatives, tranquilizers, etc.
Surgery
Surgery is the most effective method to get rid of a tumor. Unfortunately, there is a high risk of damage to brain structures during the intervention. There are cases when surgical intervention is impossible in principle, because the tumor is located near an important part of the center of the nervous system or is too large. In this case, cryosurgery comes to the rescue. It makes it possible to freeze a tumor without removing it, without injuring neighboring healthy tissue at all. In the treatment of brain tumors, gamma knife, laser and other progressive techniques are actively used.
Chemotherapy and radiation
Very often, these techniques are used together with surgical treatment, since such a complex effect on malignant tumors gives the best result.
The drugs are administered intravenously along with antiemetics, since chemical effects on the body always provoke disorders of the digestive system. Irradiation of cancerous tissue is performed partially or completely on the entire brain, if the tumor has already grown to a large size and metastasis has begun. Radiation therapy is poorly tolerated by patients and must be accompanied by additional medications.
Forecasts for patients
With stage 4 brain cancer, how long do patients live? If the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner, patients always have a chance of recovery, but there are situations when the prognosis is disappointing. Such cases include glioblastoma, which manifests itself already in the last stage of development. This tumor cannot be treated, it is resistant to chemicals and radiation therapy, it grows very quickly and develops actively. Its outlines are unclear, so even surgery does not guarantee complete removal of cancerous tissue. A relapse often occurs several months after surgery.
Even modern medicine is not able to cure glioblastoma at the last stage. Patients with this diagnosis can live no more than 1 year, constantly undergoing courses of treatment. If therapy is completely ignored, death occurs within a few months.
Glioblastoma (grade 4 brain tumor): causes of development, symptoms, treatment, prognosis
One of the most aggressive and most common malignant brain tumors is glioblastoma.
Glioblastoma is diagnosed in half of the cases of detection of primary tumors and in every fifth case of detection of intracranial tumors.
While it does not metastasize, it still remains in a leading position among the most dangerous and aggressive tumors. Despite treatment, the prognosis for patients remains unfavorable.
Stage 4 brain tumor (glioblastoma)
Glioblastoma is a tumor resulting from the abnormal proliferation of astrocytes - stellate glial cells.
Glioblastomas are characterized by a chaotic accumulation of tumor cells with polymorphic nuclei, interspersed with areas of proliferative vessels and foci of necrotic lesions.
This type of tumor is very dangerous due to excessively active growth and the lack of a clear boundary between healthy and diseased tissues.
Causes of the disease
The exact reasons for the uncontrolled proliferation of glial cells and, as a consequence, the growth of glioblastoma, have not been identified to date.
There is an assumption that astrocytes may be influenced by harmful electromagnetic radiation due to the active use of mobile phones, but this theory could not be scientifically confirmed.
At-risk groups:
- Mature men According to statistics, men from 40 to 60 years old suffer from glioblastoma more often than at other ages. In women, this disease is also less common.
- presence of astrocytomas About 10% of pilocytic and fibrillary astrocytomas diagnosed in the early stages, which in themselves are not highly malignant, degenerate into glioblastomas.
- neurofibromatosis Neurofibromatosis increases the risk of developing glioblastoma due to the genetic disorders it causes.
- exposure to polyvinyl chloride , chemicals, especially polyvinyl chloride, have a sharply negative effect on glial cells. Long-term ionizing radiation has the same negative effects.
- viral diseases
- hereditary predisposition
- entry of already infected antibodies into the cerebral cortex during the natural blood flow.
Classification of tumors
Glioblastomas are primarily classified according to histological criteria .
Based on examination of a tissue sample, one of the tumor subtypes is diagnosed:
- Giant cell glioblastoma The sample taken will be filled with abnormally large cells, the nuclei of which will be polymorphic and easily distinguishable under a microscope.
- Glioblastoma multiforme In the case of glioblastoma multiforme, the drug will consist not only of malignant cells that are randomly located and do not have the same regular shape, but also of areas of proliferation of blood vessels. Also, focal necrotic lesions will be visible under the microscope. This subtype of tumor is the most dangerous and malignant and belongs to grade 4.
- Gliosarcoma This subtype of glioblastoma is characterized by bidermality - a mixture of glial cells and connective tissue cells (mesenchymal).
Among the listed tumor subtypes, the most dangerous and malignant type is glioblastoma multiforme.
Neurosurgeon on the problem of brain tumors:
Symptoms and diagnosis
The symptoms of glioblastoma of the brain stem are quite extensive.
Even at the earliest stage, if the tumor is located in close proximity to the centers of the brain responsible for speech or movement, fainting, sudden speech disturbances, and uncontrollable disruptions in motor coordination may occur.
With such complaints, it is possible to diagnose a tumor at the earliest stages.
In addition, warning signs may include:
- persistent headaches that cannot be relieved with analgesics;
- gagging in the morning after waking up;
- hallucinations of smell (substitution of odors);
- decreased visual acuity or memory.
Some localizations of small tumors do not give such signs at all, since they do not put pressure on the brain and active centers. In this case, only a random examination can detect the disease.
Diagnosis of glioblastoma involves the following procedures:
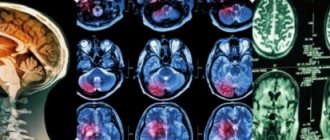
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain or computed tomography (CT) with contrast - allows you to assess the location of the tumor and its size;
- Biopsy (removal of part of the tumor to determine its type and subtype);
- Positron emission tomography (PET) can detect relapse of the disease.
To date, there are no other official methods for diagnosing glioblastoma.
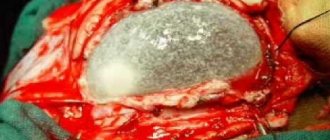
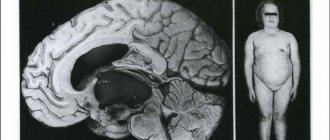
The photo shows the brain of a glioblastoma patient:
Tumor treatment methods
All methods of treating brain cancer are aimed at either removing the primary tumor or reducing its activity, since this type of malignant tumor does not metastasize at all.
The entire course of treatment is divided into three stages:
- Neurosurgical intervention.
- A combination of radiation and chemotherapy.
- Maintenance chemotherapy.
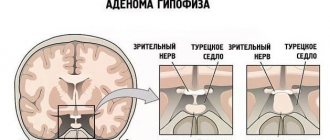
Symptoms of a pituitary tumor may be similar. It is less dangerous to humans, and in some cases it does not even need to be treated.
You can read about what will help you cope with headaches and anxiety in the article about anti-stress pills.
Neurosurgical intervention: complete surgical removal of the tumor
The longest life expectancy for patients is achieved if it is possible to completely remove the primary tumor, since further complex effects on glioblastoma bring tangible results only after neurosurgical intervention.
This is precisely the main goal of the first stage of treatment - to remove the tumor completely.
More recently, even the most experienced neurosurgeons could not efficiently remove glioblastoma due to its growth into the brain tissue and entangling the patient’s important centers of vital activity. It was necessary to leave pieces of the tumor and stop the operation without achieving the set goals.
Now, when carrying out neurosurgical operations to remove malignant tumors, a special substance is used - 5-aminolevulinic acid, which, under the influence of blue light, causes malignant cells to glow in a special way.
This way, during surgery, the surgeon can clearly see the boundary between healthy and diseased cells. The use of this method makes it possible to remove even those tumors that were previously considered completely inoperable.
Combination treatment: radiation therapy in combination with the drug Temodal
After surgery, the patient undergoes radiation therapy.
The stage is quite long - to achieve an optimal result, it is necessary to subject the patient to 6-week therapy (5 times a week, 2 g/day).
Thus, the total dose of rays will be about 60 gray. This dose is considered optimally acceptable, since it effectively affects malignant cells and does not cause unpleasant complications in the patient’s body.
Along with the radiation, the patient takes Temodal, a special antitumor drug, daily throughout the course of radiation.
Maintenance chemotherapy: Temodal
The antitumor drug Temodal is re-prescribed no less than 4 weeks after completion of the second stage of treatment. This stage of treatment is also quite long, since the drug is taken in courses lasting five days, between which there should be a break of 23 days. Usually 6 such courses are prescribed.
Targeted therapy: Avastin
Avastin is the newest drug that has a destructive effect on the tumor. Under its influence, tumor vessels are destroyed, and glial cells lose their ability to reproduce.
Avastin is not currently used to treat primary tumors as its ability to kill diseased glial cells is still being proven. But this drug has already proven effective in treating relapses.
Chances of recovery
When diagnosing brain cancer and assessing the general condition of the patient, doctors use the term “five-year survival rate.” The condition of absolutely all patients with a malignant tumor is assessed, regardless of what course of treatment was prescribed to them. With the right treatment program, some patients survive beyond the five-year threshold, but in most cases they require ongoing treatment.
Statistics show that only about 35% of brain cancer patients will continue to live normally after therapy. If the tumor causes complications, the prognosis is less comforting, since only 5% of patients survive.
Even if there is glioblastoma in the body, a person has a chance for a complete recovery, but only if the tumor is detected in the initial stages of development. Late diagnosis always has dire consequences, so patients and their relatives need to be provided with maximum psychological support. The tumor, growing, disrupts the functioning of the nervous system, provokes severe headaches and makes a person absolutely helpless.
How do patients die with stage 4 brain cancer? In fact, it is painful; it is very difficult for relatives to survive such a sight. Patients constantly suffer from unbearable headaches, which in recent days do not go away even after taking medications. Their mental activity is completely disrupted.
To avoid such a problem, especially if one of your relatives was previously diagnosed with cancer, it is necessary to periodically undergo a comprehensive examination. If severe headaches, nausea or other possible signs of a tumor appear, you should immediately go to the doctor. Always watch your health, because it cannot be bought for any money.
Stages and symptoms of a brain tumor
Since 2003, WHO has divided brain cancer into 4 stages, each of which differs in the size of the tumor, its spread and symptoms. Let's study each of them in detail.
Stage I. This stage is the least dangerous for human health, because not yet malignant cells appear in the brain, but cells with a broken genetic code. Among other things, their number is small, and the fission rate is low. True, identifying a tumor at this stage is extremely problematic, because its symptoms are either completely absent or weakly expressed, and the person simply does not suspect that a tumor has appeared in his head. Most often, a tumor that appears is discovered by chance, during a computed tomography scan during the treatment of a completely different disease.
Symptoms of the tumor include increased fatigue for no apparent reason, dizziness and headache. Rarely does a person associate such symptoms with brain cancer, and therefore, when faced with them, they attribute everything to extreme fatigue and lack of rest, and simply take painkillers for headaches. Naturally, in this case, a person only wastes precious time, because at the first stage of development of the pathogenic process, the tumor in question is 100% curable.
People over 45–50 years of age, as well as people who already have cancer patients in their family, should pay special attention to these symptoms. These complaints are a serious reason for performing a CT or MRI of the brain.
Stage II. As the tumor develops, it increases in size, thereby compressing neighboring areas of the brain and disrupting their function. Surgery is also possible in this case, although the chances of a cure are much less. The fact is that a tumor in the brain, as a rule, does not have clear boundaries, and in order to remove it completely, it is necessary to excise healthy brain tissue, which invariably affects a person’s health and well-being. However, in some cases, doctors manage to achieve stable remission of the tumor process.
If we talk about the symptoms of the disease at this stage, then headache and dizziness become more pronounced. At the same time, the patient begins to refuse food and rapidly loses weight, complains of nausea and vision problems. Often, a patient turns to an ophthalmologist with complaints of flickering in the eyes and the appearance of spots in front of the eyes. And in this case, a person wastes time, because attempts to normalize vision take him away from solving the main problem. The doctor will begin to suspect oncology only after attempts at unsuccessful treatment.
In this case, accurate diagnostic methods such as CT and MRI help to identify the disease. And if the dangerous diagnosis is confirmed, the patient will be scheduled for surgery. In approximately 75% of cases, such an intervention provides a good chance of 5-year survival.
Stage III. At this stage, cells with a disrupted genetic code become malignant, which means we can confidently talk about the appearance of a cancerous tumor in the brain. This stage is characterized by the rapid growth of the tumor, and the tumor itself begins to grow into neighboring structures and tissues, disrupting the functioning of the brain. Surgical treatment in this case does not bring positive results, and therefore doctors resort to drug treatment of the disease, in particular, radiation and chemotherapy.
Considering that malignant cells begin to penetrate into the deep structures of the brain, where the centers responsible for vision, hearing, motor activity, and sensory feelings are located, corresponding symptoms appear, namely:
- blurred vision with spots and flickering in the eyes;
- severe headaches that last a long time;
- poor coordination of movement (shaky gait);
- fatigue and constant lethargy;
- elevated temperature that is not relieved by medications;
- nausea and vomiting.
By the way, unlike a healthy person, vomiting does not bring relief to a patient with brain cancer, and headaches or fever are not eliminated by taking medications. Moreover, the patient feels constant weakness, which is why he does not have enough strength to get out of bed. But even after overpowering himself, the patient cannot move without assistance, and all because of impaired coordination of movement.
At the third stage, the lymph nodes and surrounding organs are involved in the pathological process. Already at this stage, metastases can penetrate into distant organs, which is clearly visible during CT or MRI. Even radiation therapy and chemotherapy provide a 5-year survival rate of no more than 30% of patients.
Stage IV. The fourth stage is the last stage of a malignant neoplasm in the brain, which inevitably leads the patient to death. In this case, doctors can no longer remove a malignant tumor that affects the entire brain and spreads through the bloodstream to the organs of the entire body. They can only use palliative techniques that can alleviate the patient’s condition by reducing the intensity of unpleasant symptoms. In this regard, both radiation therapy and drug treatment, including strong painkillers, are used. The extent of damage to the body is clarified using CT, MRI, and cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Symptoms of oncology at the last stage of the disease:
- severe headaches, accompanied by nausea;
- impaired visual function up to blindness;
- paresis and paralysis of the limbs;
- convulsive epileptic seizures;
- constant vomiting without subsequent relief;
- disturbance of consciousness. The patient ceases to understand the meaning of the appeal and cannot give an intelligible answer. As a result, the patient falls into a coma from which he never recovers.