Meningioma of the brain is a formation that grows from the hard membranes. This type accounts for a quarter of all primary tumors affecting the brain. Typically, meningiomas are benign, but in some cases they can become malignant. To prevent this, you need to diagnose the problem in time and begin its treatment.
General characteristics of the disease and its features
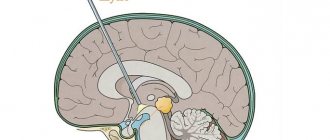
The neoplasm has a round shape and, as a rule, is fused to the dura mater of the brain. The size of the tumor can be small or, conversely, very large. Usually its dimensions start from a couple of millimeters and reach fifteen centimeters or more. The consistency of this formation is quite dense. It is characterized by the simultaneous appearance of cysts.
Basically, this form of the disease affects patients between the ages of forty and seventy years. In children, meningiomas of the brain practically do not occur. Most often, this type of tumor is diagnosed in women. The pathology is a benign formation and is characterized by a gradual increase along with multiple growths, which can significantly worsen the quality of life.
Given that the intracranial space is limited, the development of a tumor leads to compression of the most important nerve centers. If a malignant variant is observed, then the further prognosis for life is usually unfavorable.
In the presence of brain meningioma (according to ICD - D32), it does not always manifest itself, especially during the initial stages of development it is discovered completely by accident. This neoplasm is localized primarily on the surface of the brain. In the presence of such a tumor, surgery cannot always be performed, especially considering that relapses are likely. It is difficult to predict in which specific direction the meningioma will grow. In the most advanced cases, the tumor can grow in such a way that it can be noticed even without instrumental diagnostics. Treatment of brain meningioma without surgery will be discussed below.
Diagnostics
The following neuroimaging methods are used to diagnose meningiomas: MRI, CT, PET, selective and non-selective cerebral angiography, scintigraphy.
MRI
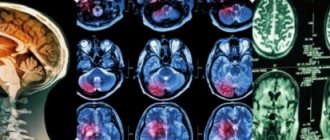
Currently, contrast-enhanced MRI is the leading method for diagnosing meningiomas of almost any location. MRI can visualize the vascularity of the tumor, the extent of damage to the arteries and venous sinuses, and the relationship between the tumor and surrounding structures. On native T1-weighted MRI, most meningiomas are indistinguishable in intensity from the cerebral cortex. Fibromatous meningiomas can be inferior in intensity to the cortex. On T2-weighted MRI, meningiomas are usually of increased intensity, and edema is also clearly visible on T2-weighted MRI. Intense contrast enhancement is detected in 85% of meningiomas. In meningiomas, the so-called “dural tail” is often found, an area of the adjacent dura mater that intensively accumulates CV. This dura mater can be either tumor or reactively altered. A dural tail occurs in 65% of meningiomas and only 15% of other tumors. Therefore, although it is not specific for meningioma, it allows us to more accurately speak in its favor. Among the disadvantages of this method, it is necessary to note the high frequency of false negative results in diagnosing the presence of calcifications and foci of hemorrhage.
CT
Contrast-enhanced CT is accompanied by moderate-to-severe homogeneous enhancement in most cases. About 90% of meningiomas are diagnosed using CT. The main role of CT is to demonstrate changes in bones and calcifications in the tumor.
PAT
Due to the high cost of the method and relatively low specificity, it is not widely used in the diagnosis of meningiomas.
Angiography
Allows you to visualize the blood supply to the tumor. Considering the invasiveness and radiation exposure, the value is mainly auxiliary. However, in combination with selective embolization of tumor vessels, it can be used as a method of preoperative preparation, and in some cases as an independent method of treatment.
Classification of pathology
The presented disease has different types. Everything directly depends on the benignity of the tumor, growth rate and overall prognosis of the disease. There are the following forms of brain meningioma:
- Typical type of disease. Such a tumor poses almost no danger to the patient’s life. It grows extremely slowly in the brain, and moreover, it can be completely removed. After surgery, examples of relapse of the disease are extremely rare. At the same time, the life prognosis is usually positive. This form of brain tumor occurs in ninety percent of cases.
- Atypical type of disease. This form of tumor cannot be considered a malignant variant, however, it grows much faster. Immediately after removal, brain meningioma can appear again. The prognosis in such situations is relatively favorable, since the sick person constantly has to be under the diagnostic supervision of specialists in order to avoid dangerous consequences.
- Malignant type of disease. This form of brain meningioma is the most dangerous, although it is recorded the least often. It develops very rapidly, severely destroying cells. The duration of human life in its presence is significantly reduced. You can only try to treat such a pathology surgically, but it’s worth saying right away that this method almost does not give any positive effect. The prognosis, unfortunately, in this situation is mostly unfavorable.
Of course, it is necessary to treat the pathology immediately after symptoms are detected, although quite a lot of time may pass before the first manifestations of the disease. In addition, people do not always attribute its symptoms to some dangerous disease.
Brain meningioma: prognosis for life without surgery, removal, rehabilitation, treatment
One of the most common brain tumors is meningioma.
It is formed from the tissue of the thin arachnoid membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Although this tumor does not directly affect the brain, it can press on nearby tissue, causing symptoms similar to those of brain tumors. In most cases, meningiomas grow slowly and do not always require urgent treatment.
Causes of the disease
The exact causes of meningioma in the head are unknown. Risk factors include:
- Heredity. A genetic predisposition to oncology can be inherited.
- Radiotherapy. A previous course of radiation, especially to the head, may increase the risk of developing a tumor.
- Female hormones. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in women over 30 years of age. It is believed that hormonal imbalances may increase the risk of tumors. Some studies have noted an association between breast cancer and the development of meningioma.
- Congenital neurofibromatosis. This rare nervous system disorder greatly increases the likelihood of developing brain tumors.
- Obesity. Research confirms that meningiomas are more common in overweight people. A high body mass index is a risk factor for many types of cancer.
A tumor of the arachnoid meninges can develop at any age and without any reason.
Classification of brain meningioma
Meningioma is formed from the arachnoid membrane, which covers the brain and spinal cord. Sometimes the tumor develops from the pia mater. It grows slowly, in 90% of cases it is a benign formation (not cancer). Most often found in the arachnoid membrane of the brain, less often in the spinal lining (spinal meningioma).
Tumors are classified according to location: for example, meningioma of the temporal region, tentorium cerebellum.
Malignant meningiomas are rare. As a rule, they grow quickly and metastasize to the brain, lungs and other internal organs. Some tumors are classified as atypical meningiomas. They can be called neither benign nor malignant, but they tend to malignize and develop into cancer.
Symptoms
In most cases, the tumor grows very slowly and may not cause clinical symptoms for years. Symptoms depend on the location and appear when the tumor begins to grow into neighboring tissues: the brain or spinal cord, nerves, and blood vessels of the brain. This process is accompanied by compression of nearby organs.
The main signs of meningioma:
- vision problems, especially double, upside-down, or blurry images;
- headache attacks that become more frequent and severe over time;
- ringing in the ears, hearing loss;
- memory problems;
- lack of smell;
- epileptic seizures;
- weakness in the limbs.
Most symptoms develop gradually, which is why patients with meningioma ignore them for a long time. If at least one of the listed signs is observed, you need to go to an appointment with a neurologist. Particularly alarming are the symptoms of visual impairment, memory and headaches, which are typical for meningioma of the frontal lobe of the brain.
Diagnostics
The slow growth of the tumor and vague symptoms significantly complicate the early diagnosis of meningioma. To make a diagnosis you will need:
- Neurologist's report. A complete neurological examination will reveal the slightest changes in the functioning of the nervous system. The doctor will carefully check all reflexes and, if necessary, refer you to other specialists for examination.
- Visualization of the tumor using CT or MRI with contrast. Tomography shows the presence of meningioma, the location and size of the tumor. MRI provides a more detailed picture and is more often used for diagnosis. In conclusion, the tomogram always clearly indicates the area of tumor localization. For example, “parasagittal meningioma” means that the tumor is visualized in the area of the sagittal sinus.
- Biopsy. Final confirmation of the diagnosis is possible only after histological examination of tumor tissue.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend additional tests (PET scan or angiography).
Treatment methods
Treatment tactics for meningioma are always developed individually and depend on many factors. Taken into account:
- size and location of the tumor;
- tumor growth dynamics and aggressiveness;
- patient age and concomitant diseases;
- neurological symptoms.
In the presence of small, slow-growing tumors, the doctor may advise postponing treatment and observing the dynamics of growth if there are no neurological disorders. Typically, such tumors are found by chance during other studies. You will need to undergo a routine MRI and see a doctor regularly.
If the tumor grows and/or neurological symptoms are observed, the most effective treatment is surgery. The earlier the operation is performed, the better the future prognosis.
Either the entire tumor or part of it is removed if the meningioma is located too close to the brain or spinal cord. Therapy after surgery depends on whether all tissues of the formation were removed and what the cell biopsy showed.
If the benign tumor has been completely removed, no further specific treatment is required. If the tumor was not completely removed, it is either monitored or stereotactic radiosurgery (gamma knife) is used.
If the tumor is malignant, radiotherapy will be needed. Chemotherapy is rarely used and is only used if other methods have failed. Atypical meningioma is treated in the same way as malignant one.
Traditional radiotherapy
Radiation therapy is indicated for atypical and malignant forms of meningioma. In the process of radiotherapy, neoplasm cells are destroyed under the influence of radiation rays. The more actively a cell divides, the more radiation affects it.
This is why the tumor cells die, and the healthy ones adjacent to it are not so damaged. Radiation is the standard treatment for anaplastic lesions, especially those with aggressive growth.
Radiation therapy is combined with surgery, although in some cases where surgery is not possible, this is the main method of treatment.
The course of radiation therapy takes several weeks, and several courses may be required. Side effects of radiotherapy include weakness, fatigue, hair loss, nausea, vomiting, and temporary suppression of bone marrow function.
Stereotactic (radiation) radiosurgery
Radiosurgery (gamma knife, cyber knife) is a type of radiation therapy, but the radiation occurs once in a very high dose. The use of radiosurgery allows you to irradiate tumor tissue directly without affecting healthy cells. The effectiveness of radiation is several times higher than the traditional method of radiotherapy.
Radiosurgical removal of meningioma is possible for tumors with a diameter of no more than 30 mm. Most often, radiosurgery is combined with classical surgery and, with the help of radiation, those tumor tissues that could not be excised are removed.
The disadvantages of the method include the high cost of the procedure and delayed effect. The tumor cells will gradually begin to self-destruct over the course of a year. This allows you to remove the effects of radiation exposure on the body, but at the same time, radiosurgery is not suitable for treating aggressive forms of meningioma.
Traditional methods
There are no folk remedies for treating meningioma. The tumor cannot resolve or stop growing if treated with traditional medicine. Treatment of meningioma of the brain or spinal cord without surgery is impossible.
The later surgical treatment is started, the worse the further prognosis. Alternative treatments can only be used to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Soothing teas, acupuncture and massage courses can help alleviate the patient's condition.
Before starting treatment at home, you should consult your doctor; there may be contraindications.
Consequences of the disease and life expectancy forecast
Possible consequences and prognosis depend on the benign quality of the process and the degree of development of meningioma.
If a benign tumor is surgically removed, the patient recovers completely, the possibility of relapse is only 3%. Neurological risks after surgery depend on the location and size of the tumor.
For example, after surgery to remove a brain meningioma that is compressing the optic nerve (such as petroclival meningioma), there is a risk of permanent vision loss. The deeper the tumor has grown, the more difficult it is to remove it without complications.
Such consequences are individual, and only a surgeon can predict them. If you have the slightest questions or doubts, you should voice them to your doctor.
The risk group for developing complications after surgery includes patients with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus and obesity.
Anaplastic meningioma is the most dangerous. The 5-year survival rate is about 30%. The earlier a tumor is detected and appropriate treatment is started, the more favorable the prognosis.
Rehabilitation
The need for rehabilitation after removal of meningioma arises after treatment of severe and advanced forms. If neurological symptoms remain after treatment or complications develop, physiotherapy courses are carried out to restore brain function and improve blood supply.
To restore motor skills and fine motor skills of the hands, exercise therapy, ergotherapy and mechanotherapy are used. Most patients also require psychotherapeutic help to return to their normal lifestyle.
Complications: why meningioma is dangerous
Malignant forms of the tumor metastasize to the brain, lungs and other internal organs. If not removed promptly, benign tumors can grow and compress brain tissue, causing irreversible neurological changes.
If there are suspicious symptoms, impaired vision, memory, or a constant headache, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Source: https://MedOnco.ru/rak-golovy/meningioma-golovnogo-mozga
Causes of the disease
Experts have not yet been able to accurately determine why meningioma develops. What is known today is that the risk category includes predominantly white women aged from forty to seventy years. This group also includes patients who have relatives with cancer. In addition to these categories of people, the risk group includes nuclear plant workers, that is, personnel who service nuclear reactors. HIV-infected people should be especially wary, and, in addition, those who have significantly reduced immunity. Persons who have undergone surgery related to organ transplantation are also at risk.
Among other things, the following predisposing factors can be identified:
- The presence of a genetic predisposition along with a defect of the 22nd chromosome.
- A person undergoing radiation therapy as part of the treatment of other malignant pathologies.
- Changes in hormonal levels in women, and, in addition, in men who have reached the age of forty.
- The presence of traumatic brain injury with the presence of damage to brain tissue.
- The appearance of disturbances in the functionality of the nervous system.
- Regular exposure to small doses of radiation on the body.
- Presence of breast cancer.
- The presence of harmful working conditions, for example, activities in the chemical or oil industry along with living in environmentally polluted areas.
- The appearance of inflammatory diseases of the brain, as well as its membranes in the form of encephalitis, meningitis, arachnoiditis.
- Regular consumption of foods that contain nitrates. Such substances can accumulate in the body.
Of course, in order to protect yourself from the appearance of a tumor, you must try to avoid the influence of the above factors. Regarding genetic defects, it should be noted that in such situations, qualified assistance from specialists is required.
The consequences of brain meningioma can be very serious.
Cost of treating meningioma on CyberKnife
| Service code | Name of medical service | Cost, rub. |
| 5.1.000 | Radiosurgery (single dose delivery) or stereotactic radiotherapy (hypofractionation technique - 2-7 fractions) of a malignant intracranial tumor using the CyberKnife installation (choice of treatment method and number of fractions as prescribed by the radiologist). | 210 000 |
| 5.1.001 | Repeated radiosurgery (single dose delivery) or stereotactic radiotherapy (hypofractionation technique - 2-7 fractions) of a malignant intracranial tumor using the CyberKnife installation (selection of treatment method and number of fractions as prescribed by the radiologist). | 195 000 |
| 5.1.004 | Radiosurgery (single dose delivery) or stereotactic radiotherapy (hypofractionation technique - 2-7 fractions) of two or more foci of malignant intracranial formation using the CyberKnife installation (choice of treatment method and number of fractions as prescribed by the radiologist). | 220 000 |
| 5.1.005 | Repeated radiosurgery (single dose delivery) or stereotactic radiotherapy (hypofractionation technique - 2-7 fractions) of two or more foci of malignant intracranial formation using the CyberKnife installation (choice of treatment method and number of fractions as prescribed by the radiologist). | 210 000 |
| 5.1.006 | Stereotactic radiosurgery (single dose delivery) of a benign intracranial tumor using the CyberKnife installation. | 210 000 |
| 5.1.007 | Stereotactic radiosurgery (single dose) of arteriovenous malformation or cavernous angioma using the CyberKnife installation | 210 000 |
| 5.1.008 | Stereotactic radiosurgery (single dose delivery) of functional impairment using the CyberKnife installation | 210 000 |
| 5.1.009 | Stereotactic radiotherapy of a benign intracranial tumor using the CyberKnife installation | 210 000 |
| 5.1.011 | Stereotactic radiotherapy of benign intracranial neoplasm of two or more lesions using the CyberKnife installation | 210 000 |
See the price list for prices for other services.
It is possible to undergo treatment on credit - the maximum loan amount is 200,000 rubles for a period of up to 24 months without a down payment. Read the terms and conditions
Symptoms of pathology
Initially, meningiomas do not appear, so a person may not even realize that he has a serious illness. Even after headaches appear, people do not assume that they are developing a tumor. But you should always listen to the body in order not to miss the emergence of pathological processes. This disease is characterized by the appearance of general and local symptoms. Common symptoms include the following:
- The appearance of a headache that is present almost constantly.
- The presence of drowsiness, which can overcome at any time of the day.
- The appearance of nausea and vomiting for no apparent reason.
- The presence of depression, lethargy, general weakness and depressed state in the state of health.
- Having problems with movement. Difficulties with mental operations and memory gaps.
- The appearance of epileptic seizures, convulsions, and paralysis of the limbs.
- Observing behavioral changes.
- Presence of muscle weakness.
- Observation of impaired consciousness.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
Depending on the position of the tumor, the following symptoms are distinguished:
- If the meningioma is located in the area of the sphenoid bone, and, in addition, on the surface of the hemispheres, the patient will experience epileptic seizures.
- If there are lesions of the cranial fossa, the patient will partially lose his sense of smell, and, in addition, his intracranial pressure will increase. Also, with this location of the tumor, people’s vision is disrupted and their psyche is disturbed. In addition, the development of hearing loss is possible.
- If a meningioma of the frontal lobe of the brain grows, the patient will experience a deterioration in thinking and memory. Such a tumor is characterized by the appearance of psycho-emotional disorders. It will be difficult for the patient to concentrate on anything, and it will also be difficult to make any specific decisions. As the tumor continues to grow further, the person begins to become irritable and becomes depressed.
- When a tumor appears in the cerebellum area, the patient may feel a loss of balance, it will be difficult for him to navigate in space, and there will be a disturbance of consciousness. Such patients cannot properly hold their body. People often experience seizures. If the tumor continues to grow further, complete paralysis of the limbs may develop.
- In situations where meningiomas grow in the temporal region, patients experience tremors with hearing and speech impairment.
Types of meningioma and their manifestations
It is also necessary to determine what local symptoms are present in a person with meningioma. The following types of disease with corresponding manifestations are distinguished:
- In the presence of falx meningioma, the tumor can grow from the falx process. Patients experience epileptic seizures. As the pathology develops, paralysis of the legs may occur with disruption of the internal organs.
- The appearance of anaplastic meningioma. This tumor is considered malignant and occurs predominantly among men. It is almost impossible to find through a routine doctor's examination or through symptoms. For accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to use instrumental research methods.
- Presence of petrified brain tumor. When it appears, a person gets tired very quickly and develops weakness in the limbs. He is unable to perform even the most simple actions. In this case, muscle tone is impaired and dizziness occurs.
- The appearance of parasagittal meningioma. Such a tumor is accompanied in patients by changes in pressure. Patients experience seizures along with epileptic seizures and loss of skin sensation. The lower limbs may become numb, making patients unable to move normally.
- Development of psammomatous meningioma of the brain. Such a tumor contains a significant number of spherical neoplasms. They arise in the connective membrane of brain tissue, as well as in the choroid plexuses.
- The appearance of convexital meningioma. This tumor is localized under the area of the temporal, frontal or occipital bone. After removal of such a tumor, serious and at the same time irreversible complications are likely.
If the tumor grows rapidly, then over time the patient becomes disabled, even despite successful treatment.
Prognosis for life with meningioma
Patient age at diagnosis is one of the most powerful factors for outcome. In general, the younger the patient, the better the prognosis. Typically, the best results are achieved with surgical removal of the entire tumor. However, this is not always possible due to the location of the tumor. The overall five-year survival rate for meningioma is 69%. In people with benign meningiomas, the overall five-year survival rate is 70%, while in patients with malignant ones it reaches 55%.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
just today
( 43 votes, average: 4.09 out of 5)
Postmastectomy syndrome: causes, symptoms, treatment
Hereditary breast cancer: causes, symptoms, treatment
Related Posts
Diagnosis of the disease
Only an experienced specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. The patient, first of all, will need a consultation with an ENT specialist, a neurologist, an ophthalmologist and a therapist. To determine the presence of a tumor in the brain, the patient must undergo the following studies:
- Carrying out computed tomography. This study is carried out using a contrast agent. Specialists have the opportunity to determine the nature of the neoplasm, while other diagnostic techniques do not need to be used. If the meningioma is malignant, then it will accumulate contrast in its tissues.
- Carrying out magnetic resonance imaging. This procedure is absolutely safe. It helps to find a brain tumor even when it is millimeter in size. In addition, with the help of such a study, relapse of pathology can be detected.
- Visual acuity examination and ophthalmoscopy.
- Carrying out a tissue biopsy of the formation. Histological examination is carried out immediately after removal of the meningioma, and, in addition, during surgery.
- The procedure for testing blood for the presence of tumor markers.
- Conducting angiography, which determines the condition of the blood vessels of the brain. This procedure is performed invasively using low radiation exposure. True, such research is not always required.
An accurate diagnosis is made by the attending physician: a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
How is meningioma treated with CyberKnife?
The treatment is virtually painless and does not require anesthesia or hospital stay. The radiation affects only the desired area. The procedure takes on average about 30-40 minutes, is carried out without special preparation, and after it the patient can immediately go home.
Before treatment, MRI and CT data are entered into the system, and the computer program calculates the depth and dose of radiation for maximum impact on the tumor. The radiation is directed precisely to the site of the lesion. The gentle effect allows most patients to tolerate CyberKnife treatment for meningioma well.
Patient, 58 years old, meningioma of the left cavernous sinus with spread to adjacent bone structures
Do you have any questions? Fill out the form and receive a response from an oncologist-neurosurgeon. Ask a Question
Features of treatment
Treatment of brain meningioma is carried out with the help of medications. In addition, radiation therapy and surgery are performed. Therapy depends on factors such as the general condition of the patient, the size of the tumor, location and symptoms.
In the treatment process, the following four approaches are mainly used:
- Monitoring the development of the tumor. Doctors regularly monitor tumor growth using magnetic resonance imaging. Diagnostics are carried out every six months. This method of treating brain meningioma without surgery is not used when the size of the tumor is too large and the symptoms are severe. Often, watchful waiting is used in the treatment of elderly patients, as well as those for whom surgery is contraindicated.
- Surgery to remove brain meningioma. If a benign tumor is completely excised, then the likelihood of its reoccurrence is reduced to zero. In addition, doctors receive enough material to perform histological analysis. Immediately after the operation, plastic surgery of the defects is performed using one’s own tissues or artificial materials. During the operation, doctors use very precise equipment. Doctors monitor the progress of the brain meningioma operation on monitors.
- Carrying out stereotactic radiosurgery. With its help, meningioma cells are destroyed, while healthy tissue is not damaged. The only disadvantage of this treatment is the limitation on tumor size. Radiosurgery can treat meningiomas whose size does not exceed three centimeters.
- Radiation therapy after removal of brain meningioma. It is required when there are many tumors, and their exact position cannot be determined. Most brain tumors cannot be cured with radiation therapy.
If the tumor is excessively fused with nerve fibers or blood vessels, then surgery to remove brain meningioma will be difficult and dangerous. Moreover, it will not be possible to completely remove it. Part of the tumor remains and may respond to radiation therapy in further treatment.
In addition to removing damaged tissue, the patient is prescribed symptomatic therapy. For example, it is necessary to remove cerebral edema with an inflammatory process. The disease is combated using traditional treatment. After the operation, the patient is prescribed corticosteroids in the form of Dexamethasone and Prednisolone. The use of anticonvulsant and antihypertensive drugs designed to lower intracranial pressure is also required.
Sometimes brain meningioma is treated without surgery and with folk remedies as part of complex therapy. For example, clover tincture helps. To prepare it, flowers and leaves of the plant are used. Requires 20 grams of raw materials and half a liter of vodka. Next, the product is infused for ten days, after which one spoon is taken before meals.
The prognosis for brain meningioma is presented below.
How to prepare for meningioma treatment on CyberKnife
Preparation for therapy includes two stages:
- Consultation with an oncologist at the PET center - if necessary, he can prescribe a PET/CT scan. For example, if a tumor is suspected of being malignant. Typically, most meningiomas are benign and are diagnosed using MRI.
- Drawing up a treatment plan - CT, MRI, PET/CT images are used for this. The doctor determines the size of the tumor, its localization and spread to different parts of the brain. The radiation trajectory is then modeled to maximize the effect on the tumor and minimize the effect on other tissues.
Consequences of the disease
Any tumors in the head are dangerous, as they can irreversibly impair the functionality of the brain. Treatment of benign neoplasms has a positive prognosis in most cases. But as for malignant tumors, they pose a great danger to the patient’s life. During operations, doctors may accidentally hit important parts of the brain. In this regard, it is never possible to predict the final outcome of an intervention. So, the brain meningioma was removed. After surgery, brain tissue needs time to recover. Rehabilitation of patients is carried out using the following methods:
- Carrying out acupuncture. This technique leads to activation of the endings of the brain nerves, and also restores sensation in the legs after paralysis.
- Carrying out drug treatment maintains the patient’s condition, preventing the recurrence of the tumor. For example, patients require medications that reduce intracranial pressure. Sometimes replacement therapy is relevant.
- Physical therapy classes, thanks to which patients can restore mobility along with other body functions. To avoid overwork, exercises should first be done in the pool.
What is the prognosis for brain meningioma?
A tumor that affects the brain is most often benign, however, certain negative factors can cause its unwanted degeneration. If a person is often bothered by headaches and other symptoms are present, there is no way to delay visiting a doctor.
Symptoms
A specialist can detect a tumor after identifying certain cerebral and local signs:
- General cerebral symptoms - impaired brain functionality, poor blood circulation and pressure on soft tissues. The patient can observe such signs of meningioma as dizziness, nausea with vomiting, forgetfulness and changes in the emotional background, indicating the appearance of a tumor.
- Local symptoms of brain meningioma - the tumor affects the patient’s well-being, affecting his mobility, partial loss of hearing and vision, pain at the site of formation.
Even if one symptom of a local nature occurs, it is worth undergoing an examination using all diagnostic methods. Timely medical intervention in the early stages will avoid complications and consequences of such pathology of the spinal cord and brain.
Forecast
The prognosis for life without surgery for brain meningioma can be different.
It depends directly on the type of tumor. In the presence of a benign tumor, the prognosis is favorable, and some patients can live with such a tumor for the rest of their lives, simply by regularly undergoing diagnostic tests.
In the presence of an atypical type, the prognosis for life with brain meningioma will be cautious and ambiguous. And directly with malignant forms, patients require urgent surgical intervention, otherwise death may occur.
Let's consider reviews about brain meningioma.
Rehabilitation
After surgery, rehabilitation takes no more than 7 weeks. The first week is gentle, so bed rest, short walks and avoidance of stress are necessary. Physical activity should be completely excluded; you can lift no more than 5 kilograms.
After removal of an atypical or malignant meningioma, the patient requires inpatient medical monitoring. Detection of relapse at an early stage allows stereotactic surgery to be performed, which increases the duration of remission.
Only complete removal of the tumor can increase the chances of a complete recovery. Surgical intervention can have the following consequences: disorders of speech, hearing, nervous system, vision, etc. Dysfunctions occur due to damage to a separate part of the brain that cannot be restored.
- stick to proper nutrition;
- exercise;
- ventilate the room and spend time in the fresh air more often;
- pay due attention to rest and sleep;
- Get a diagnostic examination several times a year.
You will learn more about rehabilitation in the following video:
Reviews
There are a large number of reviews about this disease. There are many positive comments.
Some patients are not particularly bothered by such tumors, sometimes they only have headaches. This does not affect the quality of life. Those people who underwent surgery to remove the tumor recovered quite quickly.
Of course, if the tumor is large, has an atypical structure, or is malignant, then you should not hesitate to visit a doctor and remove the tumor.
Advantages of CyberKnife treatment at the PET center
CyberKnife treatment is carried out at the PET center in Ufa. We use a treatment protocol for meningiomas based on diagnostic information about the size and location of the tumor. The interaction between radiologists and oncologists allows you to create a treatment plan that maximizes the preservation of healthy tissue and brain function.
| High-tech installation CyberKnife | Qualified radiologists | Affordable prices for high-level treatment | Programs for out-of-town patients | Repeated examination after 3-6 months |
Schedule a free consultation with a radiologist to find out if treatment is right for you. You can also read reviews from patients who were treated with CyberKnife for meningioma.