Confirmation of diagnosis and initiation of treatment
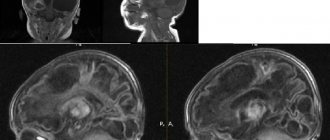
Treatment begins only after the diagnosis is completed. The diagnosis can be confirmed using magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and ultrasound. A cyst is a bubble filled with a liquid mass that can appear in any area of the skull.
- The symptoms that arise may indicate exactly where the pathology occurred. But often a neoplasm in the left or right temporal lobe, in the region of the posterior cranial fossa, does not manifest itself in any way in the early stages of development. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, you must strictly follow the doctor’s instructions and agree to surgical treatment.
- There are times when there is no need for therapy. In such a situation, a wait-and-see approach is chosen, the dynamics of the pathology is monitored, and if it progresses, urgent surgical intervention is prescribed.
- Surgical treatment can be performed using various methods: endoscopy, cystocystrenostomy, excision and bypass surgery. Such radical methods are necessary only when the cystic neoplasm increases in size or provokes painful symptoms.
What is a bypass procedure?
Shunt surgery is indicated when complete sclerosis of the cyst is impossible and the cells are actively producing intracapsular fluid (CSF).
It is carried out using specialized shunts in the form of hollow tubes that facilitate the outflow of accumulated contents and reduce pressure inside the skull.
Depending on the choice of the cavity where the cerebrospinal fluid will be diverted, it is divided into:
- peritoneal;
- pleural;
- atrial.
The procedure is dangerous when removing retention cysts or abscess cavities due to the high risk of infection.
Sometimes the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid by installing a shunt is necessary for
brain tumors , which are accompanied by hypertension - increased intracranial pressure.
The bypass operation consists of three important stages:
- Installation of catheter and valve;
- Providing a reservoir;
- Installation of a subcutaneous invisible outflow shunt.
The valve “determines” the moment when it is necessary to discharge excess liquid. It can be fixed or programmable. When shunting hydrocephalus of the brain in newborns, a fixed intensity of the valve operation is used, and for adults, a programmable one is used.
Preparation for the procedure
The success of removing a brain cyst directly depends on the quality of preparation for the operation and the studies completed.
Required examinations:
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging - for precise determination of the location, size and structural features of the cyst.
- Administration of a contrast agent during CT and MRI to assess blood supply and circulatory collaterals.
- Duplex ultrasound examination - to assess the condition of the vessels of the head and neck. Selection of a vessel as a shunt.
- Standard mandatory procedures include blood and urine tests, fluorography, electrocardiography.
- Balloon occlusion of blood vessels - to test the body's response to the cessation of blood circulation in certain arterial vessels.
In addition to hardware and laboratory preparation methods, individual organization before surgery is important.
Preparation algorithm:
- refusal to drink alcoholic beverages and smoke tobacco for 10–14 days;
- medications (corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and others) are discontinued at the discretion of the doctor;
- the day before, meals no later than 18:00–19:00, fermented milk products are allowed, still mineral water is allowed in the morning;
- shave the hair on the head completely or partially;
- taking a shower and washing your hair;
- foreign objects are removed: earrings, piercings, glasses, contact lenses.
Once the patient is ready, consent for surgery is written. The patient is informed about possible postoperative risks and complications. They talk about the need for rehabilitation measures after brain bypass surgery.
If the operation is to be performed on a child, consent is given by the parents or legal guardian.
The average operation time is 2–3 hours, with complications developing or other anomalies being detected up to 6–7 hours.
Scheme of implementation
The neurosurgical operation is performed under general anesthesia. The patient is placed on the operating table so that there is access to the necessary part of the brain. Medicines are administered intravenously, and after achieving a sleepy state, they are intubated.
At the same time, the patient’s body is covered with sterile sheets, leaving a so-called window for prompt access. And in compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics, tissue excision and trepanation are performed using special instruments. A shunt and a method for fluid outflow are created. Connect to a pre-selected cavity.
Treatment of arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) cyst of the brain
- Tumors of this type are benign cavities formed as a result of splitting of the membrane containing fluid similar to cerebrospinal fluid. As a rule, an arachnoid cyst forms against the background of other pathologies, that is, it is a secondary disease or complication.
- The disease can be congenital or acquired. Most often it occurs in male children and adolescents. Most often, arachnoid cysts are diagnosed in the temporal lobe (right or left) and posterior cranial fossa. Usually the cause is injury or inflammation.
When the pressure inside the cyst exceeds the intracranial pressure, it begins to compress the cerebral cortex, which provokes unpleasant symptoms:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- convulsions;
- hallucinations.
The size of the tumor becomes larger due to an increase in the amount of fluid in it or due to the ongoing inflammatory process that caused it.
Arachnoid cerebrospinal fluid cyst is treated through surgery. The doctor chooses one of the following methods:
- endoscopy;
- excision;
- shunting.
The main indication for radical treatment is the progression of symptoms: convulsive paroxysms, development of focal signs, hemorrhages, impaired cerebrospinal fluid circulation, etc.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the area occupied by the tumor. The larger the cyst, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease. Sometimes it is accidentally found during a CT scan or MRI.
ATTENTION! The patient may not even be aware of the presence of pathology, since the disease is asymptomatic. But more often, signs of the disease appear before the age of 20.
One of the following signs may indicate a problem:
- Headache;
- Sensation as if brain were pressing on skull;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Fainting;
- Balance imbalance;
- Hallucinations;
- Hearing or vision impairment;
- Limited motor ability of an arm or leg.
As the tumor grows, the patient's vision and hearing deteriorate. When located in the right temporal region, a person may not understand other people, even if they address him in their native language.
In complex cases, the following may develop:
- Brain herniation;
- Hydrocephalus (accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain);
- Epileptic seizures appear.
All these signs are taken into account when collecting anamnesis.
Retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst: removal from the brain
This type, unlike arachnoid, is formed not outside, but inside the organ as a result of the death of gray matter cells. The cause may be a stroke or poor blood circulation in this area; surgical interventions on the skull; injuries; inflammatory processes (eg encephalitis). The growth can be triggered by new foci of infections and micro-strokes.
Treatment of this type of neoplasm begins after diagnosis and study of symptoms. As a rule, with an asymptomatic course of the disease, there is no need for any medical measures. The patient should periodically visit a neurologist to monitor the size of the tumor, as in the presence of pathology of the right or left temporal lobe. If its increase is observed, the symptoms become more pronounced, and surgical intervention is resorted to.
If you have any kind of cyst, you must undergo a full examination. A complete diagnosis allows you to establish the causes of the disease, choose the optimal treatment method (surgery, medications), assess the risks and make a prognosis for the future.
A retrocerebellar cyst can be removed using one of three methods:
- Endoscopy is one of the modern and safest options. During the operation, an endoscope is inserted into the skull to remove fluid. However, endoscopy should not be used in the presence of tumors inside the brain;
- Shunting is a procedure that allows you to distribute fluid from a neoplasm to other body cavities for which its presence is a normal condition;
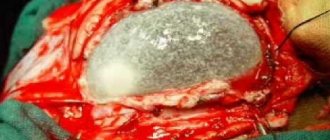
- Craniotomy is one of the methods of neurosurgery. This option is associated with great risks, but this is the only way to remove not only the fluid from the cyst, but also its walls, resulting in a complete recovery.
Types of operations
Removal of a brain cyst, depending on the purpose, is divided into radical and palliative:
Radical - performed to completely eliminate the pathological focus: hematomas, tumors, abscesses, cysts.
Palliative surgery is aimed at improving the general condition of the patient, due to the inaccessibility of the site. The cyst may be partially removed or a shunt may be formed.
Depending on the urgency of brain cyst removal, they are classified into planned and emergency. Emergency - performed for vital reasons, when the threat is compression of vital structures, blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid ducts, or dislocation of the brain.
According to the operational access method, the following are used:
- Brain shunting is often indicated for closed hydrocephalus, when there is no outflow of the fluid component, as well as for stroke, a tumor, or a large cyst. A natural or artificial shunt is created.
- Laser cyst removal - treatment with a dosed stream of light energy. Advantages include no swelling, low risk of relapse and postoperative complications.
- Trepanation with the formation of burr holes - can be diagnostic or therapeutic. Necessary for removing an intracranial cyst, obtaining biological material (biopsy) or fluid from the ventricle of the brain.
- Resection craniotomy is caused by the removal of part of the bone tissue without further plastic surgery. Used for cysts in the occipital part of the brain. After suturing, a thick layer of occipital muscles prevents injury to brain structures.
- Osteoplastic craniotomy involves the preparation of a bone flap, which subsequently closes surgical access. It is used for surgery on the parietal and temporal lobes. The tissue incision is horseshoe-shaped, facing the base of the skull.
- Stereotactic - a stereotaxic atlas is created with the most precise indication of brain structures down to the millimeter. Thanks to spatial orientation, you can adjust the immersion depth, determine the position of the tool and guide it.
- Endoscopy - rigid and flexible probes are widely used, mainly for surgery on the ventricles of the brain. Can be performed in combination with a stereotactic apparatus.
- Radiosurgery is a focused radiation treatment of a pathological focus (Gamma Knife, Cyber Knife), based on the principle of spatial and stereotactic orientation.
Undoubtedly, removal of a brain cyst requires careful preparation, examinations, premedication and individual selection of surgical techniques.
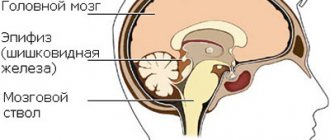
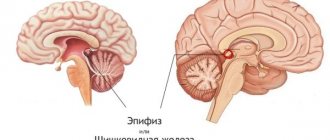
Epiphysis cysts
This type of disease is accompanied by:
- pain in the head;
- disorientation;
- drowsiness;
- double vision;
- difficulty walking.
In the absence of these symptoms, there is a possibility that the formation will not increase in size.
It is worth noting that in most cases this pathology is discovered completely by chance during the diagnosis of other diseases.
At the first stage, drug therapy is used. It is necessary to constantly monitor the dynamics of tumor development. If the course is severe, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Signs of the disease
What are the signs for diagnosing a cyst?
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- coordination is impaired;
- headache;
- mental disorders;
- complete paralysis of the limbs;
- violation of muscle tone in one direction or the other;
- loss of consciousness accompanied by convulsions;
- noise in ears;
- sensation of pulsation in the head, nausea and vomiting;
- feeling of squeezing of the brain;
- lameness;
- Infants have pulsation of the fontanelle and vomiting.
What symptoms the patient will have depends on the location of the tumor and the area of the brain being compressed.
Perineural cyst occurs in the spine. To clarify its localization, designation using letters of the Latin alphabet is used. For example, at level s3 means that it is located at the level of the third vertebra of the sacral region. The lumbar vertebrae are designated by the letter L.
Arachnoid, also known as spinal cerebrospinal fluid cyst, also known as perineural cyst, is formed in the lower parts of the spine, in its lumen. If the tumor is large, it can compress the spinal nerves. It is formed as a result of expansion of the spinal nerve. A perineural cyst gives symptoms of other diseases and to clarify the diagnosis, you should undergo diagnostics.
How is a cerebrospinal fluid cyst treated?
In this case, drug therapy may be involved. The causes of formation can be inflammatory processes, hemorrhages in the meninges, strokes, and surgical interventions.
Indications for the use of surgical treatment: the appearance of arachnoid formations, progression of convulsive paroxysms, disorders of the blood circulation.
Methods for removing cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the temporal lobe:
- Drainage of its cavity using needle aspiration. This method is one of the simplest, but often after such treatment there is a relapse of the disease;
- Trepanation and open removal of a tumor of the posterior fossa or temporal lobe. The positive point is that the cyst cavity can be examined, but postoperative scars remain, which can lead to the re-development of tumors;
- Brain shunting can be internal (flow of contents into the subdural space) or external (into the abdominal cavity). This method, like drainage, is simple, but the patient becomes dependent on the shunt. A significant disadvantage of this method is the high risk of complications;
- Endoscopy, including laser;
- Symptomatic treatment, which consists of relieving pain, cramps and other manifestations of the disease.
Briefly about the anomaly
Brain cysts are considered to be the most dangerous and pathogenic. Many areas and areas of the brain are responsible for the production of hormones and control the most important processes in the body. If an anomaly affects any part of the brain, the damage is immediately reflected in the body. For example, an arachnoid cyst of the brain can lead to the development of many complications, adverse reactions, pathologies and stimulate the development of all kinds of somatic abnormalities.
A choroid plexus cyst is a congenital type of tumor that forms in the brain cells of a child during the stage of his embryonic growth. Such choroid plexus cysts in infants, according to many statistical studies, tend to be removed independently before the end of pregnancy and the onset of childbirth. Because of this feature, choroid plexus cysts are not considered pathogenic or dangerous to human health or brain development.
Pseudocysts of the choroid plexus can become dangerous and harm the baby’s health only if the mother:
- suffered a serious infectious disease during pregnancy;
- has chronic ailments and inflammation;
- if pregnancy proceeds with complications and threatens miscarriage.
Causes of the anomaly
Due to the fact that tumors of subependymal choroid plexus cysts are extremely rarely diagnosed and identified, the exact causes and features of their formation have not yet been studied. The overwhelming majority of such choroid plexus cyst tumors in a child are formed in the early period of development in the womb without identifying any distinctive symptoms.
Such a tumor can be detected using ultrasound scanning or intrauterine diagnostics. However, usually the tumor of the choroid plexus cyst of the brain disappears even before the birth of the child, which makes it difficult to perform a qualitative analysis of the disease and determine its main features and characteristics. The main cause of the appearance of such cystic bodies known today is the herpes virus, which is transmitted through the mother’s blood to the child.
It is important to note that in some cases, choroid plexus cyst tumors on the right can form after the child is born. However, even such forms of the disease are not considered pathogenic and life-threatening. As a rule, such abnormal bodies do not grow to large sizes, do not affect adjacent tissues and fibers, and self-destruct after a couple of months. Physicians, as a rule, do not carry out additional diagnostics of such anomalies of the left choroid plexus cyst, nor do they provide medicinal effects on the foreign body.
Consequences without treatment
The choroid plexus, from the tissues of which the choroid plexus cyst on the left is formed, is intended to nourish the brain tissue with the fluid produced in the vascular cavities. In some cases, due to congenital disorders, a cavity forms between the vessels in the child’s brain, which is filled with a viscous tumor substance. It is almost impossible to prevent such a process, since it is still unclear why such a failure occurs and a foreign body is formed.
Due to its specific location, a 5 mm subependymal cyst of the left choroid plexus has exactly zero impact on other areas and functions of the organ. It does not interfere with the natural pace of development and does not put pressure on vital departments.
Cystic manifestations in the choroid plexus area as such do not cause any harm to a person. However, in combination with other inflammations and diseases of the brain, they can become pathogenic tumors that cause enormous damage to tissues and provoke many complications.
Choroid plexus cysts - what are the causes? When, during the initial diagnosis, the doctor discovers a cystic formation of the above type in the brain tissue, he, as a rule, prescribes repeated diagnostics and scanning of the problem area in order to promptly identify the presence of collateral inflammations and lesions, as well as analyze the growth rate of the cyst and its size.