A pineal cyst can pose a certain danger to human health. This pathology often occurs with certain clinical symptoms. If the first signs of this disease occur, you should visit a doctor. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe a rational course of treatment.
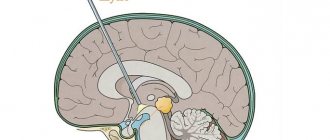
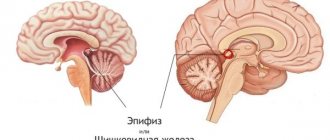
The pineal gland is one of the deep centers of the brain
general information
The pineal gland (pineal gland) is one of the most important structures of the human brain, performing an endocrine function. Active substances such as melatonin and adrenoglomerulotropin are produced here.
The main functions of the pineal gland are the following:
- decreased rate of sexual development;
- decreased level of sexual desire;
- control of the volume of growth hormone production;
- control of the body's circadian rhythms;
- inhibition of tumor cell growth.
One of the most important roles of melatonin is to control the body's circadian cycles.
In children, the pineal gland is relatively large. Over the years, its tissues become somewhat hypotrophied, since with age a person’s need for melatonin production decreases.
A pineal gland cyst in the brain is a benign tumor. This pathology is currently quite common.
Note. An epiphyseal cyst is also called a pineal mass.
Pineal cyst: risks and prognosis
The main risk in the formation of a pineal cyst in a person is the high probability of developing hydrocephalus - dropsy of the brain due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular parts of the brain. However, pineal cysts are usually non-dynamic. That is, the resulting cyst does not in any way affect the functioning of parts of the brain. Constant monitoring of cystic formation will prevent its further development.
The greatest risk when diagnosing cystic formations of the pineal gland is making a false diagnosis and prescribing ineffective treatment or unnecessary surgery.
Reasons for development
Today, some reasons for the formation of such pathology are known. The main ones among them are the following:
- parasitic diseases of the pineal gland;
- blockage of the excretory channel.
Parasitic cysts in the pineal gland can form as a result of the activity of echinococcus. This parasite is carried by dogs and some farm animals. This type of cyst is quite rare. Its size is constantly increasing, which can lead to compression and damage to surrounding brain tissue.
Advice! If previously, before the development of the disease, you had frequent contact with farm animals or dogs (especially hunting dogs), then you should mention this at an appointment with a specialist.
Echinococcal cyst can be much more dangerous than usual
Blockage of the pineal gland can occur in the following cases:
- Too viscous secretion of the pineal gland;
- The excretory channel is too tortuous.
When the pineal gland's excretory canal is blocked, the cyst almost never reaches a large size.
Types of epiphysis formation
Depending on the morphological (structural) characteristics and mechanism of appearance, several types of pineal cysts have been identified.
If the cavity has a diameter of up to 0.5-0.9 mm, then its course is asymptomatic in most cases. During MRI, such formations are found by chance, their prevalence reaches about 5-7% of all studies. A large cyst is considered to be a structure larger than 1 cm. It causes compression of blood vessels, epiphysis tissue, and outflow tracts of intracerebral fluid. Its course resembles a tumor process.
When neuroglia (non-functioning tissue) grows in patients with severe hypertension, rheumatism, or renal hypertension, a false cyst is formed.
In the depths of such accumulations, cells are destroyed, and a cavity appears in their place. Unlike a simple cyst, it does not have a lining layer inside. False formations also occur with drowning, rabies, tetanus infection, acute inflammation, acute swelling of the epiphysis.
Simple true cysts are covered with cells on the inside and have a well-defined outer shell of connective tissue fibers. Between these layers there is a middle one, formed by the tissue of the epiphysis. It may also contain calcium deposits.
The formation of a cyst in the fetus is associated with maternal infections, alcohol, smoking, and lack of blood flow through the placenta due to circulatory disorders. Oxygen starvation of the child’s brain also occurs with diabetes mellitus or its gestational form in a pregnant woman.
Main manifestations
A pineal cyst of the brain can occur without any clinical symptoms. In this case, it can only be detected by chance during a computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain for another pathology.
A cystic tumor of the epiphysis can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- severe headaches;
- decreased visual acuity;
- deterioration in coordination of movements;
- nausea leading to vomiting.
The severity of headaches with a pineal cyst usually correlates with the size of the formation
With large cystic formations (usually with hydatid cysts), mental disorders, as well as epileptic seizures, can occur.
Note. Pineal cysts rarely manifest themselves. More often than not, they do not bother the patient throughout his life.
Types of surgical operations
To remove brain tumors, 3 types of interventions are used:
- Endoscopic removal of stagnant CSF in the skull through an opening using a special device (endoscope) and installation of a drainage tube to ensure the outflow of cerebral secretion. Contraindicated in cancer.
- Complete removal of the microcyst with complete opening of the skull (trepanation), prognosis – complete cure.
- Fluid outflow by shunting, in which, after the release of stagnant CSF, the healing process of the affected areas of the meninges begins.
- Bypass surgery is a procedure performed using a drainage tube.
It is important to know that contraindications to the operation are: pregnancy, old age, weakened immunity.
Main indications for surgery:
- suspicion of the development of cerebral hydrocele;
- intense manifestations of the disease (headaches, blurred vision, etc.);
- has a damaging effect on the cardiovascular system;
- an overgrown cyst puts pressure on nearby tissues;
- nausea and vomiting are indications for urgent surgery, since these signs indicate the accumulation of melatonin and can cause the patient to fall into a comatose or lethargic state;
- the beneficial effect of surgical removal of the cyst outweighs the risk.
Diagnostic Basics
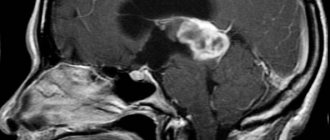
If this type of pineal formation does not bother the patient, its detection becomes incidental during brain imaging studies. We are talking about magnetic resonance and computed tomography. The same diagnostic measures are applied in cases where the patient is bothered by the above symptoms. Typically, the more pronounced the clinical picture, the larger the volume of the cystic formation.
MRI of the brain is the “gold” standard in the diagnosis of pineal cysts
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safer research technique since it does not involve radiation exposure. In addition, it allows for much better visualization of brain formations.
Based on the results of an MRI, if a cyst is present, the following picture will be obtained:
- the presence of a cavity of one size or another in the epiphysis;
- the cyst is limited by a thin wall;
- the cavity is filled with liquid.
If we are talking about a parasitic cyst, then areas of microhemorrhages, softening of tissues and an inflammatory process around the formation of the epiphysis are identified.
If the doctor suspects the presence of a parasitic cyst, then he will refer the patient for further examination. He will have to undergo allergy and immunological tests.
Immunological and allergy tests will help clarify the presence of a parasitic cyst
Advice! If you have symptoms of the pineal gland and the queue for an MRI of the brain is too long, it is better to undergo this examination on a paid basis.
Which specialist should I contact?
Most people do not know what it is - a pineal cyst, and which doctor should be contacted if the main symptoms of this disease occur. Currently, the first link in the diagnosis of pineal cystic formation is a neurologist. This specialist will order a brain imaging test.
If signs of a common cyst are detected, he may refer you for a consultation with a neurosurgeon. As for suspicions of an hydatid cyst, if they arise, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist is prescribed. It is this specialist who subsequently prescribes immunological and allergy tests.
About therapeutic measures
If a microcyst of the pineal gland has been identified, treatment is usually not prescribed. An exception may be those small formations of the pineal gland that cause the development of a different clinical picture.
Those cysts that do not manifest themselves in any way and were discovered by chance should not be treated. The patient is prescribed periodic magnetic resonance imaging (usually once a year) to monitor the size of the formation.
Taking medications for brain cysts is symptomatic therapy
In cases where the symptoms of the disease still bother the patient, the following treatment can be carried out:
- therapeutic;
- surgical.
The use of medications may be a sufficient measure only in cases where the clinical manifestations of the cyst are mild. For example, with a slight headache due to the presence of a benign tumor of the pineal gland, diuretics may be prescribed. They reduce the amount of fluid in the cystic cavity. In addition, drug therapy is necessary for those patients for whom surgical treatment is contraindicated. Most often these are people of an older age group with a large number of concomitant diseases. In this situation, the following medications may be prescribed:
- diuretics;
- antiepileptics;
- sedatives;
- painkillers.
Note. Usually, medications help to completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease, but only for a certain time.
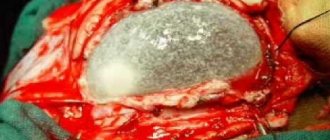
Surgical treatment is used when the cyst reaches a large size and can threaten the surrounding tissues with compression. In addition, surgery is necessary if a parasitic cyst is detected. The pineal gland suffers not only from compression, but also from a constantly occurring inflammatory process.
Surgery is the only way to get rid of a pineal cyst forever
Surgical treatment allows you to quickly relieve all symptoms of the disease.
Important! After the operation, the contents of the cavity are sent for histological examination. This is necessary in order to exclude malignant neoplasms. The fact is that malignancy (transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant one) of a cyst can occur extremely rarely.
If cancer cells are detected, the patient is transferred to oncologists and radiologists for further examination, as well as chemotherapy and radiation treatment.
Treatment of epiphysis cyst
In most cases, this pathology does not reveal itself in any way and does not affect the functioning of the brain and the entire body as a whole. Therefore, even by chance and having discovered it, doctors do not prescribe any treatment. It is necessary to regularly undergo an MRI examination approximately once a year.
Symptoms may only appear if the cyst is quite large. Then a biopsy is performed and laboratory tests determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant. The decision to undergo surgery is made when symptoms interfere with the normal functioning of the body, and also if the cyst is formed as a result of infection with echinococcus. Surgery is resorted to only when the risk to the life of a patient with a cyst is greater than the danger of the operation itself.
The location of the pineal gland is very difficult to reach. Neurosurgeons undertake such operations with caution, as there is a danger of affecting functionally significant areas of the brain.
In modern neurosurgery, the following types of treatment for pineal cysts are used:
- endoscopy – fluid is removed from the cavity through punctures. This method is the safest; with the help of an endoscope, the neurosurgeon sees the smallest blood vessels and nerves, so it does not damage them. He brings the instruments strictly to the desired section, without injuring other areas of the brain;
- bypass of the cyst cavity - a special hose made of silicone is installed, through which fluid is removed into the abdominal cavity or the atrium cavity. This type of surgery is effective for hydrocephalus. With this intervention there is a high risk of infection;
- Craniotomy is the most effective, but also the most dangerous type of neurosurgical intervention, since there is a threat of damaging brain tissue. During this operation, the skull is opened where it is necessary to remove the cyst. This occurs using two methods: resection or osteoplastic. The first is used for urgent intervention, since it involves biting off the required hole with forceps. It leaves a defect on the skull. With the osteoplastic method, flaps of tissue and bone are cut out with a special wire saw or pneumatic turbotrepan at an angle of 45 degrees, so that during the postoperative period the bone flap does not fall inward. To prevent a hematoma from occurring as a result of such an intervention, rubber tubes are inserted under the flaps, through which blood fluid flows and, in case of leakage, cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid. As a result, infection of the brain, namely meningitis and encephalitis, can occur. The consequences of trepanation are very serious: impairment of vision, memory, speech, and can cause paralysis and convulsions. Therefore, it is carried out only when it is the only way to save the patient’s life.
Drug treatment of a pineal cyst helps eliminate the causes of its growth, but not the tumor itself. If it does not increase, then there is no need to use drugs. But in the case of pronounced symptoms, conservative treatment is prescribed to relieve one or another pain syndrome that most worries the patient. For severe headaches, analgesics are prescribed; for sleep disorders - adaptogens, medications that normalize sleep; for epilepsy - antiepileptics; for hydrocephalus - diuretics to drain fluid and relieve pressure on certain areas of the brain; for hormonal imbalances - tablets containing melatonin.
Traditional medicine will also be effective in relieving symptoms. So, to reduce intracranial pressure and to resolve the cyst, you need to take an oil tincture of spotted hemlock, decoctions of black elderberry, violet, and horsetail. Chamomile and rosehip teas will help relieve headaches and dizziness. To cleanse the blood vessels of the brain, you should take an alcohol tincture of the root of the Caucasian dioscorea.
Possible complications
Serious complications of this disease can occur only in cases where the cyst reaches a serious size. If left untreated, it can lead to the formation of hydrocephalus. Compression of the brain tissue occurs. This increases the level of intracerebral pressure. This condition is dangerous due to the formation of general cerebral symptoms. Over time, this disease will lead to a decrease in memory, level of intelligence, as well as hearing and visual acuity.
Regardless of the symptoms of cystic neoplasms of the pineal gland, the patient should adhere to all recommendations of specialists, since the further quality of his life will depend on this.