Cephalgia is simply a headache. Depending on the density of nerve receptors in tissues, they can be sensitive or insensitive to pain. The head is literally permeated with nerve receptors everywhere - they are in the skin, muscles, tendons, in the vessels of the skin of the head, the meninges, the periosteum of the skull, intracranial veins and arteries.
Cephalgia, according to experts, comes in five types:
- vascular;
- tension;
- liquorodynamic;
- infectious-toxic;
- neuralgic.
Each type has its own clinical manifestations and mechanism of pain. Often the mechanisms are determined by the primary disease - meningitis, swelling of the meninges, obstructed outflow of venous blood, intracranial pressure, etc. In this case, the approach to the treatment of such cephalgia should be combined.
Cephalgia of the brain - what is it?
Cephalgia is a headache, a pathological condition that occurs under the influence of external factors or develops as a symptom or sign of a disease.
A person may be genetically predisposed to headaches due to the structure of the vascular system or the characteristics of the brain. The patient’s living conditions can also provoke pain: constant emissions of harmful substances from chemical and industrial enterprises, gas pollution in large cities.
Cephalgia can be local - affecting only one area of the head or diffuse - spreading over its entire surface, even affecting the face and neck.
The opinion that pain in the head is caused by nerve cells in the brain is erroneous. The brain is actually made up of neurons, but has no nerve receptors. Cephalgia of the brain is pain in blood vessels, bone tissue, facial, neck muscles and other structures located in the head.
Reasons for the development of cephalgia
The occurrence of headaches can be triggered by external factors and features of a person’s lifestyle. Leads to cephalgia:
- Constant nervous tension, stress, depression.
- Improperly organized sleeping place: soft pillow, uncomfortable mattress.
- Not getting enough sleep.
- Failure of the daily routine - sleep during the day, wakefulness at night.
- Work in stuffy, smoky, poorly ventilated rooms.
- Smoking, taking drugs, drinking too much alcohol.
- Sedentary work, lack of at least minimal physical activity.
- Poor nutrition, fasting, insufficient fluid intake, foods with synthetic additives.
- Sudden change in weather.
- Heatstroke, sunstroke.
- Poisoning from medicines, food, gas.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Trauma to the face, neck, head.
Most often, pain syndrome acts as a sign of the development of some pathology in the human body. This may be a general chronic disease or a one-time infection. Cephalgia of the brain is observed when:
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Migraine, cluster syndrome.
- Arterial hypertension or hypotension.
- Osteochondrosis, myogelosis, cervical spondylosis.
- Arteritis of the temporal arteries.
- Diseases of the ENT organs: sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, otitis media.
- Infectious diseases: meningitis, encephalitis.
- Colds, flu, sore throat.
- Damage to the ocular apparatus.
- Neuralgia of the facial, occipital, trigeminal nerve.
- Arthritis, arthrosis of the jaw joints, upper spine.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Cancerous tumors.
- Hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke.
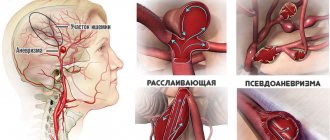
- Aneurysm rupture.
Headache rarely acts as the only symptom of the disease. Most often, cephalalgia appears in combination with other signs of pathology.
Symptoms of pathology
Cephalgia manifests itself individually in each person. Moderate cephalgic syndrome is accompanied only by headache and general malaise. The localization of pain depends on the affected organ:
- With neuritis of the facial nerve, the facial area is affected; in severe cases, visual and hearing impairment occurs.
- Temporary pain is typical for cephalgia, which appears against the background of hormonal imbalances or nervous overstrain.
- If there are problems with blood vessels, the pain becomes chronic and hypertension appears.
- With VSD, pain affects not only the head, but also the vestibular apparatus, dizziness, surges in blood pressure and unsteadiness of gait appear.
The most dangerous symptoms, which should definitely serve as a reason to contact a specialist, include:
- Unbearable pain that occurs along with nausea;
- Frequent mood swings and mental disorders;
- Increased pain during sneezing, coughing;
- Temperature increase;
- The appearance of muscle tension;
- Pronounced pulsation in the temples and eyes.
Cephalgic syndrome (Cephalgia) is severe, prolonged and regular headaches. This serious disorder of brain functioning occurs in both adults and children.
The occurrence of pain is caused by excessive fatigue and lack of sleep, so the symptoms of cephalgia may disappear after the person has had a good rest and sleep. However, other reasons that provoke the appearance of unbearable pain cannot be excluded.
Cephalgic syndrome (ICD-10 code – R51) can become one of the serious symptoms of another chronic disease.
The simplest answer to the question: “What is cephalgic syndrome?” – constant headaches. This is a pathological condition of the body.
This phenomenon not only reduces the comfort of life and ability to work, but can also be a symptom of serious, terrible diseases. Cephalgia is a pathology that is increasingly occurring in adults and children.
It is difficult to diagnose and treat the acute form of the disease, so it is better to prevent its occurrence.
Causes
According to doctors, cephalgia (ICD code 10 R51 - headache) is currently almost the most common secondary syndrome. Most diseases are accompanied by headaches. Some pathologies can lead to the development of an acute form.
Recently, in our society, due to numerous lifestyle disorders, cephalgic syndrome is actively gaining momentum.
These include:
- infections;
- inflammation;
- oncological diseases;
- metabolic problems;
- incorrect way of life and non-compliance with the daily routine;
- smoking and alcohol.
Migraine, or as it is also called - classic headache, can appear due to:
- burdened heredity;
- blood vessel diseases;
- neuralgic diseases;
- wrong way of life.
The development of this pathology is especially clearly manifested in childhood. Also, the child’s body reacts sharply to low activity, a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition and lack of oxygen.
These factors, in combination with burdened heredity, lead to the rapid development of cephalgia. This disease must be treated. In extreme cases, it can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Doctors talk about the difficulty in diagnosing cephalalgia of the brain due to the large number of causes of the disease and inaccurate and vague symptoms. It is quite difficult for a specialist to find out reliable symptoms in a patient, which is associated with the patient’s subjective perception.
Headache has the following characteristics of conditions and symptoms: short- and long-term fluctuations in the intensity of cephalalgia
It can be caused by diseases such as:
- glaucoma;
- hypertonic disease;
- pre-stroke condition.
Causes
Classification of cephalgia
According to experts, five types of cephalalgia of the brain are distinguished depending on how it manifests itself, the characteristics of localization and the nature of pain.
Vascular
If the cerebral vessels suffer from excessive expansion and are constantly subject to spasms, it is believed that the patient develops vascular cephalgia. The arteries of the head and neck are stretched under the uneven flow of blood, overflowing, and painful tension occurs.
Patients compare vascular headaches to rhythmic hammer blows in the head, appearing in one place. Discomfort is characterized as pulsation, synchronous compression. This type of cephalgia is observed when:
- Migraine.
- Physical fatigue.
- Emotional stress.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Due to increased tone of the vascular bed, the supply of oxygen to brain tissue is disrupted, and hypoxia develops. The patient complains of a pressing, bursting headache, severe dizziness, the appearance of spots before the eyes, sparkling circles, and stars. There is a rhythmic pulsating noise in the ears, the skin of the face and neck is paler.
Vasomotor
The feeling of compression in the head, tightness of the neck muscles, tightness of the back of the head, squeezing of the frontal part is provoked by physical or nervous fatigue. Vasomotor cephalalgia of the brain is usually associated with muscle tension. The pain can be of mild or moderate intensity, and it does not go away for a long time; patients characterize it as monotonous, aching.
Typically, vasomotor cephalgia appears on both sides of the head and has no pulsation. What causes this type of pain syndrome? Leads to headaches:
- Stress, both negative and positive.
- Neurotic conditions.
- Depression.
Headaches are often accompanied by muscle stiffness, poor coordination, decreased concentration, and memory impairment.
Liquorodynamic
This type of pain syndrome directly depends on the level of cerebral fluid in the human skull. Both an increase and a decrease in intracranial pressure lead to headaches. They have a pressing, bursting character. Patients complain that when their eyes are closed, they experience a feeling of painful pressure on the eyes. Liquorodynamic cephalalgia of the brain occurs when:
- Hydrocephalus of any kind.
- The growth of a cystic formation in the cranial cavity.
- Development of a cancerous tumor in brain tissue.
- Violation of the integrity of the meninges.
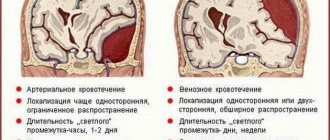
- Failure of venous outflow.
Unpleasant sensations worsen if the patient coughs, sneezes, tilts his head, stands up suddenly or turns his head to the side.
Infectious-toxic
This type of headache is characterized by increasing intensity. At first it can be localized at one point, gradually spreading throughout the head. Patients note a feeling of heat, pressure, fullness in the head, pulsation, similar to blows on a cast-iron helmet placed on the head. Infectious-toxic cephalalgia develops when:
- Food, drug, alcohol poisoning.
- Development of an infectious disease.
- The course of the inflammatory process in the tissues of the head and ENT organs.
- Colds.
Patients with this type of pathology complain of a general loss of strength, a strong increase in temperature, a feeling of fatigue, and confusion.
Neuralgic
Neuralgic cephalgia is a response of inflamed nerves to irritation. Patients complain of cutting, intense pain felt in one place. In addition, there is the appearance of lumbago in the ear, under the eye socket, and jaw when moving, sneezing, chewing food, and in an absolutely static position.
Diagnostics and first aid
Determining the cause of cephalgia begins with collecting anamnesis and questioning the patient about complaints. Treatment can be started only after the underlying disease has been determined.
The diagnosis is made based on the results of laboratory tests and examination. Only after this is appropriate therapy prescribed.
Most often, headaches are a consequence of pathologies of the cervical spine. Therefore, first the doctor examines the neck and determines the presence of injury. To exclude the presence of acute diseases, internal organs are examined.
In most cases, with such problems, the patient must undergo:
- radiography;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography;
- electroencephalography;
- lumbar puncture;
- general blood and urine analysis.
You may need to consult an ophthalmologist, psychotherapist and other highly specialized specialists, depending on the accompanying symptoms.
First aid can be provided to a patient only if the type of pain can be determined. If unpleasant sensations arise as a result of nervous tension, fatigue or stress, then you should try to avoid the influence of these factors on the body. To effectively eliminate cephalalgia syndrome, healthy sleep is best.
You can also improve your well-being with a neck massage and a contrast shower. If it is not possible to take a shower, then you need to wash your face first with warm water, then with cold water.
You should seek help from medications only in extreme cases, when the pain cannot be tolerated. To eliminate this symptom, you can take No-shpu, Combispasm, Spasmalgon and similar drugs.
If relief does not occur within 24 hours, and the pain does not go away, but only intensifies, and is accompanied by nausea and irritation from bright light, you should consult a doctor.
Clinical manifestations of cephalalgia in newborns
Even newborn children experience headache attacks. Since the child cannot directly say what hurts, the mother should focus on the external manifestations of pathology. With cephalalgia, a newborn:
- Refuses breastfeeding.
- Cries a lot and starts screaming.
- Cries out during sleep, jumps up.
- Throws his head back.
- Burps like a fountain.
The baby's muscle tone is noticeably impaired, the fontanel pulsates strongly and bulges. The focus of the eyes may be impaired, the child may develop squint and drooping pupils.
Diagnostic methods
There are a lot of diseases accompanied by headaches. In order to determine what cephalalgia of the brain is and how to treat it, the patient needs to undergo an examination. To establish a diagnosis, a neurologist may recommend:
- Make an encephalogram of the brain.
- Get an MRI and CT scan of the head and neck.
- Check whether the blood flow in the head is normal using a rheoencephalogram.
- Perform angiography of cerebral vessels.
- Undergo an ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
The final diagnosis is made based on the symptoms that the patient complains about, examination data and general tests.
Stress disease
Tension cephalalgia is accompanied by aching, dull, monotonous, squeezing, squeezing sensations. The syndrome is mainly localized in both halves of the head, but unilateral occurrence is often observed. The areas of the head where cephalgia is localized are frontal and parietal. The syndrome can also affect the cervical and shoulder regions.
An intensification of the symptom is observed when touching the head with hands, when putting on a headdress, or combing hair. The syndrome almost never occurs at night. It can also be noted that this type of pathology occurs without accompanying nausea or vomiting. If such symptoms occur, this indicates a different type of syndrome. The most common symptom that can occur in conjunction with tension cephalgia is decreased appetite.
Considering the duration of this type of disease, two types can be distinguished:
- Episodic. Occurs mostly infrequently.
- Chronic. Such chronic headaches can occur if episodic pathology is not treated.
Features of the treatment of cephalalgia
There are many different ways to treat headaches. We can highlight:
- Traditional drug treatment.
- Physiotherapy.
- Manual therapy.
- Surgical intervention.
- Aromatherapy.
- Traditional methods of treatment.
The choice of therapy depends on how the headache manifests itself, how often the person is bothered, and whether the disease causing the pain is amenable to traditional treatment.
Some patients decide not to see a doctor and simply take painkillers. But this does not always have a positive effect. For example, tension cephalgia cannot be treated with analgesics, to get rid of pain, you should take sedatives, sedatives, and undergo treatment with a psychotherapist. Therefore, it is advisable not to self-medicate, aggravating your condition, but to receive qualified medical care.
Prevention
Human health directly depends on lifestyle. That is why, in order to prevent headaches, you need to follow some rules:
- Walk more often in the evenings;
- Avoid stress;
- Do yoga, which will help you relax and put your thoughts in order;
- In your free time, do breathing exercises;
- Do gymnastics and exercises in the morning;
- Take a course of acupuncture and phototherapy;
- Watch your posture;
- Sleep 6-8 hours a day;
- Replace a regular mattress with an orthopedic one;
- Eat more fruits and vegetables that are rich in vitamins, minerals and trace elements;
- To refuse from bad habits.
Persistent remission and relief of pain is ensured by a correct lifestyle, giving up bad habits and stabilizing the emotional background. It is worth paying attention to the child’s health status if he complains of discomfort in the head area. It is always easier to prevent a disease than to completely cure it.
Unfortunately, people often self-medicate and think that taking analgesics will relieve unpleasant symptoms. This is certainly true. But this will not affect the underlying disease, but will only worsen the current situation. In some cases, analgesics have a beneficial effect on human health, this applies to people suffering from hypotension. However, frequent use of medications can lead to abuse, and the pathological circle will close.
WE RECOMMEND:
- Psychosomatic causes of hemorrhoids
- How to cure schizophrenia: medications and traditional methods of treatment
- I'm terribly afraid of hair and beard - what should I do?
- How to overcome fear of driving and fear of cars