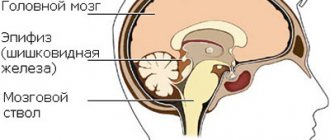
Senile degeneration of the brain is also known as senile insanity or dementia. The first prerequisites for the development of brain dystrophy can occur in a person after 60 years of age, although the weakening of memory over time is not a normal phenomenon.
The concept of degeneration means the weakening or loss of special functions of an organ. Dementia (dementia) is a chronic mental disorder in which behavioral disorders and loss of basic self-care skills are possible.
Thus, there is a violation of higher cortical functions. Senile (senile) brain degeneration is most often diagnosed in people over 65 years of age.
Types and stages of violation
In medical practice, there are three degrees of degenerative disorders in the brain:
- Mild degree . It is characterized by a loss of professional skills and apathy to what is happening around. The patient is not interested in subjects that were previously considered his hobby. In this degree of illness, orientation and consciousness are preserved.
- Average degree . The patient copes with personal hygiene skills, but may forget the rules for using household appliances. Such people often need help; leaving them unattended is dangerous.
- Severe degree . Patients lose orientation in space and are unable to serve their own needs.
Degenerative diseases of the brain can be expressed in a total or lacunar form.
- The total form of the disorder is characterized by poor emotionality and apathy. Personality degradation occurs.
- The lacunar (partial) form is characterized by impairment in short-term memory. But the “core of personality” remains.
The course of the disease occurs in stages:
- Predementia is a stage of the disease characterized by memory loss, absent-mindedness and apathy. The ability to think abstractly decreases. Thus, disturbances affect fresh layers of memory.
- Early degeneration (the second stage of the disease) is characterized by more pronounced disorders. The progressive disease is expressed in impaired motor activity and incoherent speech. The patient cannot always express his thoughts, his movements are absurd, but at the same time remnants of memory and sanity are preserved.
- Moderate dementia (third stage) manifests itself in the fact that a person begins to confuse words, does not recognize his loved ones, and partially loses reading and writing skills. There may be elements of delusion. An elderly person is able to leave home, but it is not possible for him to return back due to impaired consciousness. In addition to these symptoms, patients cease to control the natural needs of the body.
- After these stages, severe dementia . The person practically does not speak, does not get out of bed and loses the ability to perform the most basic movements. In this case, exhaustion of the body occurs. Death occurs as a result of pneumonia or bedsores that arise in such conditions.
Symptoms of brain atrophy and senile degeneration
Symptoms of brain atrophy
Many diseases that cause cerebral atrophy are accompanied primarily by the development of dementia.
The main symptoms are:
- dementia;
- convulsions;
- speech disorders or aphasia;
- memory impairment;
- deterioration of intellectual abilities;
- inability to accurately plan (absent-mindedness);
- disorientation in space;
- repetitive movements;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions.
Symptoms of senile degeneration
Early stage symptoms:
- forgetfulness about recent events;
- difficulties in carrying out simple calculations;
- poor orientation in time, location and direction of movement;
- passivity;
- apathy.
Symptoms of the middle stage:
- impairment of cognitive abilities (learning, calculations, calculations, logic, thinking, memory);
- emotional instability;
- excessive agitation or passivity;
- inability to perform normal daily activities (patients need help with household chores - cleaning, cooking, shopping, etc.);
- disturbance of sleep rhythms;
- disorientation regarding the time of day.
Late stage symptoms:
- loss of all cognitive abilities;
Is it possible for cancer patients to have X-rays done? Find out more information in articles by doctors at the European Clinic.
Sooner or later, all people grow old, and the body ages along with them. It primarily affects the heart, brain and spinal cord. If the heart ceases to properly cope with its task - pumping blood - then over time this will affect the condition of the brain, the cells of which will not receive enough nutrients to maintain vital functions.
Causes and clinic of dystrophic processes
The causes of weakening of brain functions in old age may be:
- In the case of vascular dementia , a history of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and stroke is noted. Thus, the cause of this pathology is impaired blood supply to parts of the brain. For this reason, massive death of neurons occurs. In this case, the pathology is considered incurable. Cells have a low ability to regenerate in old age.
- In the atrophic type of dementia, a history of Pick's disease, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's disease should be noted. There is cerebrovascular insufficiency here. Alzheimer's disease more often affects older women. Prerequisites for its occurrence are genetic predisposition, alcohol and smoking, severe stress, thyroid pathologies or traumatic brain injuries.
- The mixed type is characterized by a combination of vascular pathologies with atrophic changes.
Among the causes of the disease are also brain tumors, chronic alcoholism, and severe viral infections.
Vascular etiology of dystrophy
Vascular dementia accounts for 25% of cases. It develops with chronic oxygen starvation of brain cells due to vascular disorders in the organ. The cause may be congenital vascular defects, diabetic angiopathy and stroke.
At risk are people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, have an unhealthy diet and are addicted to alcohol. Patients with obesity, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis are susceptible to vascular degeneration.
With this pathology, the patient’s thinking process is disrupted and he is unable to identify the logical connection of events. A person loses his things that are in plain sight. The appearance loses its neatness. In this state, tearfulness, apathy, and unpredictable mood swings are often observed. Due to decreased physical activity, a person sleeps a lot.
Alzheimer's type dementia
Despite the fact that this type of disease is the most common, it is very difficult to distinguish it from vascular dementia.
Often the correct diagnosis is determined after the death of the patient. At risk are women over 70 years of age, patients with atherosclerosis and diseases of the endocrine system, and people with unfavorable heredity.
At the beginning of the development of Alzheimer's brain degradation, there is a decrease and partial loss of short-term memory, and later long-term memory.
In patients, an aggressive state may predominate. They behave rudely and lack the attention of loved ones.
Progressive pathology further causes delusions of persecution, delusions of grandeur and other similar deviations.
The tendency to wander is manifested by frequent leaving home. The patient's appearance is sloppy.
Alcohol-type brain dystrophy
This condition develops in people with alcohol dependence over 10-20 years. It is characterized by aggressive behavior, impaired intellectual qualities and apathy.
But in rare cases, when you give up a harmful addiction, the pathological process regresses.
Senility
Elderly people become absent-minded, grumpy, and intractable. Forgetfulness and behavior changes occur due to aging and death of brain cells.
Patients may suffer from insomnia at night and tend to sleep during the day. Mental disorders, touchiness and tearfulness are typical for them. Apathy and even hallucinations may occur.
The cause of these disorders may be surges in blood pressure and hyperglycemia.
Epileptic dementia
This is a secondary disease secondary to epilepsy. It is also called functional dementia.
This condition is caused by oxygen deprivation and the consequences of traumatic brain injury and brain tumors. There is a decrease in memory and impaired thinking abilities, accompanied by an indifferent attitude to what is happening.
Patients become rude, selfish and vindictive. A characteristic feature is the use of most words from a poor vocabulary in a diminutive form. With this form of the disease, therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause.
Symptoms of dystrophy of the brain substance
It is better to prevent any disease than to treat it later, and for this you need to know its external manifestations (signs) and symptoms.
The exact changes in the brain substance can be determined using MRI.
Without treatment, diseases such as:
- Alzheimer's disease. The most common form of nervous system degeneration.
- Pick's disease. A rare progressive disease of the nervous system, manifesting itself from 50-60 years of age.
- Huntington's disease. Genetic disease of the nervous system. developing from 30-50 years.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Cardiocerebral syndrome (impairment of basic brain functions due to cardiac pathology).
What modern medicine has to offer
Treatment of brain dystrophy of any origin and maintaining a stable state of health of the patient consists of two main methods:
- drug therapy;
- care.
Senile brain degeneration is treated taking into account concomitant diseases, of which the patient may have many by this age. These include hypertension, pneumonia, heart attacks and strokes and many others. Patients are treated with herbal and synthetic drugs.
The first group of drugs includes psychostimulants. Their action is aimed at increasing the ability of the nervous system to adapt to stress. The second group of drugs are nootropics, the action of which is aimed at restoring memory and improving cognitive functions. This group is able to reduce the brain's need for oxygen.
Treatment of senile dementia involves the use of medications that can restore nutrition to the nervous tissue of the brain. Their effect is somewhat weakened by combinatorial treatment with drugs that improve blood supply to the organ. But the results of treatment still have positive dynamics.
Feelings of unreasonable fear, anxiety, and insomnia are treated with the use of tranquilizers. Patients may need psychotherapeutic methods of influence that can return a person to normal behavior.
Features of care
Drug therapy will not give the expected effect without proper care. The patient’s relatives should know that it is almost impossible to create the necessary conditions at home.
This is explained by the fact that at home there are a large number of objects dangerous to the patient (cutting, piercing, electrical and fire hazardous). In addition, due to the patient's possible aggression, it is very difficult to remain calm in the house. The diet of patients should be monotonous.
Their cognitive abilities are impaired, and the variety of dishes can cause unpredictable confusion. Older people need help going to the toilet. You may need to use special hygiene items (diapers).
From all this it follows that the best option is to place the patient in a specialized medical facility or care for a professional nurse.
The patient should be treated with respect. His behavior is a manifestation of a serious illness, not a character trait. With a positive attitude, good, patient care, there is a significant improvement in the condition.
What is brain atrophy and senile degeneration, diagnosis
As people age, their brains lose a certain number of cells, but such loss is physiological and acceptable. However, when the number of neurons lost exceeds a certain limit and the brain shrinks in size, a condition called cerebral atrophy occurs.
The brain gradually decreases in size with each decade of life, but until the age of 60, the rate of such loss is very slow and almost imperceptible. From 0.5 to 1% of brain tissue is lost per year from the initial volume.
At age 75, the brain is on average 15% smaller than at age 25.
The areas of the brain responsible for short-term memory are usually more susceptible to degenerative processes, and in men, neuronal loss occurs more actively than in women, which means that degenerative processes occur more intensely.
To identify anomalies, the following diagnostic procedures are used:
- MRI;
- CT;
- PET (positron emission tomography);
- SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography).
The loss of brain neurons is an extremely undesirable process, since it inevitably entails behavioral and cognitive disorders. When the brain tends to lose neurons, patients are required to undergo diagnostic testing every six months to monitor the process and monitor or prevent symptoms caused by this condition.
Senile brain degeneration is a condition that is synonymous with senile dementia. Senile dementia is a disease caused by the degeneration of brain cells. This disease is different from the usual marasmus that develops in older people. In the case of senile degeneration, the patient's brain function gradually declines, leading to progressive memory loss and mental retardation, as well as noticeable personality changes.
Treatment
Individual changes in the white matter, which are clearly visible on MRI, may mean that the patient has abnormalities in the blood circulation of the brain of vascular origin. Based on these data, the doctor will prescribe an examination that will more clearly show the causes of this situation and allow you to prescribe the correct treatment.
To select treatment for focal changes in the brain substance of a dyscirculatory nature, the doctor first prescribes therapy for the disease that led to this situation. Drugs are prescribed that improve blood circulation between brain structures, oxygen exchange, reduce blood viscosity, have a sedative and analgesic effect, as well as complexes of vitamins and essential elements.
Establishing diagnosis
To make an accurate diagnosis, an anamnesis is collected. On its basis, symptoms are differentiated from depression, severe asthenia and iatrogenic mental disorders (delirium, malingering, and others).
When examining a patient, a neurologist identifies focal symptoms, extrapyramidal disorders and disturbances in walking.
The final diagnosis is made based on the results of magnetic resonance imaging and laboratory tests of the patient.
Article on the topic: Lyoton analogues - a list of drugs similar in action and composition