If a cerebrovascular accident occurs, this can lead to the development of an ischemic stroke. In this case, blood flow through the cerebral arteries is disrupted. The prognosis for recovery will depend on how much time has passed from the moment of the attack to the start of medical care. It should be noted that people over 60 years of age experience the disease much more severely.
Brain stroke and its features in older people
The disease progresses due to the fact that an obstacle arises in the blood vessels that lead to the brain, preventing blood from flowing to its final destination. The reason lies in the fatty layer lining the vascular walls. This condition is atherosclerosis. The disease mainly affects the senile body, for this reason most strokes occur after the age of 50-60 years.
Important! The formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel can lead to ischemic stroke, a condition called thrombosis. If a blood clot forms elsewhere in the circulatory system, this pathology is called an embolism.
Local circulatory disorder can occur as a result of three independent pathologies: stroke, ischemia and heart attack. Ischemia develops due to lack of blood circulation in a local organ or tissue. A stroke is characterized by a disruption of blood circulation in the brain.
It must be said that ischemic stroke mainly progresses in older people due to wear and tear of the body.
The disease will manifest itself depending on the type of stroke:
- Atherothrombotic attack - atherosclerosis of a large or medium artery occurs. The pathological condition develops gradually, mainly during sleep;
- Lacunar - a violation of blood circulation in small-diameter vessels. This may occur due to progression of diabetes or hypertension;
- Cardioembolic form - partial or complete blockage of the middle artery of the brain occurs with an embolus. The condition develops sharply while a person is awake. Subsequently, emboli occur in other vascular systems;
- Ischemic attack , which developed due to extremely rare reasons - this could be dissection of the arterial walls, excessively thick blood, vascular pathologies;
- Stroke of unknown origin is a condition when it is impossible to determine the specific cause, since a number of factors are present.
Most ischemic strokes in older people occur unexpectedly and over a short period, leading to the destruction of brain tissue. This happens in a few minutes or hours.
Pathology is divided into the following types:
- ischemic stroke in the left or right hemisphere of the brain;
- cerebellar hemorrhage;
- extensive tissue damage.
Description
A major stroke is a serious injury to the brain that affects a large part of the brain.
Its blood supply is disrupted. Due to oxygen starvation, toxic substances accumulate in the brain tissue, and degenerative processes begin. Table 1. Types of pathology
| Stroke form | Peculiarities |
| Major ischemic stroke | It is considered less dangerous. Poor circulation occurs due to short-term blockage of cerebral vessels by cholesterol plaques or a blood clot. Proper treatment helps to maximize recovery after injury. This type of extensive brain stroke leaves more room for survival. It also has an additional classification:
|
| Extensive hemorrhagic stroke | The prognosis is less encouraging. The chances of survival are very low. Death occurs in 89% of cases. Blood circulation is disrupted due to the fact that the vessel ruptures and biological fluid flows into the brain tissue. Next, swelling of the organ begins, due to which all vital human functions cannot be performed as before. Basically, the patient goes into a vegetative form of existence. Hemorrhagic stroke of the brain can be intracerebral and subarachnoid. |
| Stem | It affects only the base of the organ. However, this is where the vital centers are located. Such a defeat leads to the immediate death of a person. |
In addition, the disease can be classified according to its location:
- Stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain. It leads to paralysis of the right side of the human body. Speech is also impaired, problems with hearing and vision appear, and persistent mental pathologies are observed. The patient is not able to create logical chains of thinking or analyze the information he receives. He loses the ability to remember dates, names, and the ability to build a time sequence of events is impaired. Math skills suffer.
Differences in the effects of stroke on the right and left side
- Stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain. Due to extensive hemorrhage, sensitivity is lost on the left side. Memory and vision also suffer. Speech may be preserved, but the ability to nonverbally process information is impaired. Imagination, spatial orientation, figurative memory, and emotions suffer (the victim’s condition can hardly be called adequate).
The human brain consists of highly specific tissue that has a constant need for large amounts of oxygen, the lack of which causes negative changes.
Cerebral infarction (or ischemic stroke) is an ischemic lesion of areas of the brain that occurs as a result of circulatory disorders. There is also a hemorrhagic cerebral infarction, but we will talk about it in another article.
Gray matter is the most sensitive to oxygen starvation; the cells of the cerebral cortex that it forms die off within a few minutes after the onset of hypoxia.
Consequences of a brain stroke for older people
For the most part, the consequences of ischemic stroke are not so rosy. If a person manages to survive, it will take months, or even years, to recover.
And even in this case, no one guarantees complete or even partial restoration of the body. The patient suffers both physically and intellectually.
The prognosis is made based on many factors, such as the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the time of providing medical care in a short time after the attack.
Thus, the consequences of ischemic stroke in the elderly can be the following manifestations of the body:
- Mental disorders . Often, due to his helplessness, a person develops depression, he becomes aggressive or, on the contrary, indifferent, and mood swings are not uncommon.
- The sensitivity of the face and limbs is impaired
- Movement functions are impaired . Sometimes, after an ischemic stroke, people have to use a cane; their hands can no longer cope with simple movements - washing dishes, changing clothes, etc.
- Cognitive impairment - this manifests itself in forgetfulness of simple things. An elderly person becomes like a child, confuses the date and time, forgets the address and telephone number, etc.
- Swallowing reflex disorder.
- Coordination is impaired .
- In 10% of cases, epilepsy develops after an ischemic stroke, especially in elderly patients.
Stages
Official medicine distinguishes 4 stages of the disease.
The first stage is the acute course of the disease. The acute phase of a stroke lasts three weeks from the moment of impact. Fresh necrotic changes in the brain form the first five days after the attack.
The first stage is the most acute of all existing ones. During this period, the cytoplasm and karyoplasm shrink, and symptoms of perifocal edema are noted.
The second stage is the period of early recovery. The duration of this phase is up to six months, during which pannecrosis changes occur in the cells.
A recurrent process of neurological deficiency often occurs. Near the location of the affected lesion, blood circulation begins to improve.
The third stage is the period of late recovery. Lasts from six months to a year after a cerebral infarction. During this time, glial scars or various types of cystic defects develop in the patient’s brain.
The fourth stage is the period of residual manifestations of the infarction. It begins 12 months after the stroke and can continue until the end of the patient’s life.
Features of treatment and rehabilitation
To restore blood circulation in the brain and remove blood clots in the vessels, surgical treatment is required. There is hope for a full recovery only in rare cases when there is minor death of brain cells.
Drug therapy can provide positive changes if treatment is started within 2-3 hours after the stroke. Medicines include:
- anticoagulants;
- thrombolytic drugs;
- disaggregants;
- vasoactive antihypertensive neotropic drugs for pressure above 180/105 mm. rt. Art.
Attention! The main cause of ischemic stroke in old age is atherosclerosis, which appears between the ages of 65 and 70 years.
Rehabilitation will proceed in the following areas:
- neurology;
- neurorehabilitation;
- Spa treatment;
- outpatient and dispensary observation.
Rehabilitation has the following objectives:
- Restoration of lost functions;
- Adaptation in mental and social terms;
- Preventive measures for post-stroke complications.
Since the disease is extremely severe, when taking recovery measures it is necessary to adhere to the appropriate recommendations and regimens.
The diet of an elderly person is of particular importance. It will be harder for him to recover than younger ones, so you need to strictly monitor his diet.
Basically, the menu consists of liquid lean dishes, cereals, salads, fruits and vegetables.
It is advisable to gradually begin to restore joint mobility.
This is achieved through physical education and training on simulators strictly under the supervision of doctors. Physiotherapy also plays an important role.
It is worth remembering that the body of an elderly person is not so strong, and rehabilitation will take a long period. Life after an ischemic stroke can change dramatically for people over 60 years of age. From now on, a person will live according to a special routine, which he needs to get used to.
How to treat
Timely and well-chosen treatment for any form of ischemic cerebral stroke helps not only protect the patient from complications, but also speeds up rehabilitation. It must be prescribed by the attending physician. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
First aid
Treatment of a cerebral heart attack or stroke begins with first aid. The course of action depends on where the injured person is located. If he is on the street, you need to act something like this:
- Call an ambulance immediately.
- Before the doctor arrives, lay the person down, unbutton his clothes, remove his tie and loosen his belt.
- At low air temperatures, cover with something warm. Rub and massage your arms and legs.
If possible, you should inform the victim’s relatives or friends about the incident.
If a stroke occurs at home or in any other room, you need to ensure a flow of fresh air. To do this, you can open windows or doors. Unbutton your clothes. If there is a tonometer nearby, measure the patient's blood pressure. If its readings exceed 150/90 mmHg. Art., lightly press on the solar plexus area or closed eyes. With low blood pressure, slightly raise your legs without lowering your head and massage the carotid artery.
Don't underestimate the effectiveness of first aid. According to medical statistics, it saves the lives of 60% of patients in an acute or severe period of stroke, and makes it possible for those who are faced with a mild form of the pathology to fully recover. In addition, timely assistance improves the process of restoration of brain cells and tissue by 60-70%.
Conservative therapy
Treatment has several goals:
- normalize breathing,
- adjust blood pressure,
- normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system,
- maintain body temperature at the proper level (no more than 37.5°C).
- reduce swelling of the brain,
- reduce the severity of symptoms,
- protect the patient from complications, for example, pneumonia, infections, thrombosis, bedsores, etc.
Medications will help cure the victim. Most often, the doctor prescribes several types:
- to thin the blood,
- antiplatelet drugs,
- anticoagulants,
- vasoactive drugs,
- neurotrophics,
- angioprotectors,
- diuretics,
- antioxidants.
The dosage and duration of the course of taking the drugs is calculated individually for each patient.
Surgery
Ischemic stroke can also be cured through surgery. The main indication for them is the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy. There are several types of surgical intervention:
- Carotid endarterectomy. This is the removal of that part of the carotid artery that is blocked by cholesterol plaque. During the operation, local anesthesia is given. It has a quick recovery and virtually no complications.
- Carotid stenting. It is carried out when the previous operation is contraindicated, or has already been done before. Prescribed for vasoconstriction up to 60%.
This also includes narrowing the arteries and removing blood clots without incisions. A special stent is inserted into the vessels to help improve blood flow. Blood clots are removed by introducing substances that dissolve them.
Prognosis after a brain stroke
The prognosis for life and recovery for older people will depend on many factors. The following circumstances can make it worse:
- Extensive heart attack with paralysis of the entire body. When numbness of the arms and legs occurs, coordination of movement is severely impaired, the swallowing reflex suffers and speech ability is impaired;
- Poor restoration of blood circulation in damaged areas;
- Damage in two vascular areas of the brain;
- Old age of the patient.
The prognosis will be more favorable if the following circumstances are present:
- Damage to brain cells is not as extensive. Formed hematoma of small size;
- Cardiac and vascular parameters are normal.
Important! The prognosis for a positive outcome of ischemic stroke in the elderly will depend on how damaged the brain is, and on the timeliness and systematicity of therapeutic actions on the part of doctors.
It is also worth noting that the prognosis for survival in elderly patients can be aggravated by concomitant diseases, such as myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation preceding a stroke, and congestive heart failure. In 30% of cases, a recurrent ischemic stroke is possible over the next 5 years.
Preventive measures
To prevent the recurrence of the disease, it is necessary not only to undergo a course of rehabilitation, but also to follow all measures in the future to prevent the occurrence of this disease.
Rehabilitation course
Rehabilitation in this case plays a very important role. Sometimes eliminating the consequences is even more important than simply stopping the main symptoms and prescribing priority treatment. While the main treatment usually takes about a month, rehabilitation can take years. Everything will depend on how serious the consequences are. This can be said for sure only after the main acute period has passed - then it is possible to assess how badly the brain has been damaged and which functions are impaired.
Rehabilitation always requires sufficient patience and endurance both from the patient himself and from his relatives and close people. The moral aspect here means no less than medical treatment, sometimes even more. You need to try in every possible way to convince a person how important and dear he is to everyone. But at the same time, you should not show excessive pity - this can humiliate a person. Especially if this is not an old person yet. In this case, this may cause a backlash - he will begin to feel inferior and become even more depressed, as he will begin to consider himself a burden.
You need to try to communicate as much as possible with such a person and try to understand him as much as possible, even if the speech is very unclear.
Key points that rehabilitation should include:
- drug treatment (taking medications to strengthen blood vessels, thin the blood, normalize blood pressure, strengthen the heart);
- restoration of the ability to move independently;
- restorative therapy (massages, swimming and other moderate physical activity);
- walks in the open air;
- normalization of speech functions and vision.
Unfortunately, sometimes treatment does not completely eliminate the consequences. Impaired coordination of movements, memory, and general state of mind may persist. But still, in most cases, the condition of the blood vessels gradually normalizes and the person manages to return to normal life.
Disease prevention
Every person should understand that the symptoms of this disease almost never arise out of nowhere. Most often, this is triggered by a number of factors, and the more they affect the human body in combination, the higher the chances of developing such a disease. In this case, you should follow the basic recommendations in order to initially reduce the risk of this disease to a minimum:
- promptly begin treatment for diabetes, hypertension and atherosclerosis. Yes, it is unlikely that it will be possible to cure them completely, but it is still quite possible to avoid pressure surges and increased blood sugar levels;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- if a person is at risk or experiences the first symptoms - precursors, then it is better to start taking blood thinners in advance;
- lead an active lifestyle, but at the same time avoid excessive stress and extreme fatigue;
- minimize the use of hormonal drugs;
- try not to be nervous and avoid stressful situations;
- monitor the level of cholesterol in the blood, do not eat foods that provoke its increase (sour cream, eggs, butter);
- control your weight, avoid obesity (limit the consumption of fatty, floury, fried, smoked, salty, bitter foods).
Moreover, the important point is that absolutely all of these recommendations are important not only for healthy people, but also for those who have already suffered from this disease. Alas, if you do not follow all the basic recommendations, you can fully expect a relapse. There have been cases when people suffered 3-4 heart attacks in their lives. No one is immune from this. And therefore, even if you managed to return to normal life as much as possible, it is still very important to adhere to the basic recommendations in order to avoid a recurrence of such a disease. This is very important, since each time the situation worsens and the prognosis becomes less favorable.
It becomes increasingly difficult for a weakened body to cope with such problems. This is why it is so important to take care of yourself even after full recovery.
1 Characteristics of cerebral infarction
Cerebral infarction is also called ischemic stroke. The central nervous system is well supplied with blood and reacts sharply to insufficient supply of oxygen, glucose and other food products.
For various reasons, there may be a disruption in the flow of blood to certain areas of the brain, and this leads to the appearance of typical symptoms of the disease.
Ischemic stroke is often a complication of one or another pathology of the cardiovascular system. The classification of the disease includes the etiological factor of the disease, and depending on it, the following types of cerebral infarction are distinguished:
- Atherothrombotic stroke. Occurs as a result of atherosclerotic damage to the blood vessels of the brain.
- Cardioembolic stroke. It develops against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the heart - arrhythmias, valve defects, myocardial infarction.
- Lacunar stroke. Develops as a result of damage to a small-caliber vessel.
- Cerebral infarction caused by other causes. Among them are: vasculitis, hypercoagulable states of the blood, stratification of the vascular wall.
- Idiopathic (unknown origin) ischemic stroke. In this case, it is not possible to establish the cause of the acute circulatory disorder.
A separate type is a transient state, or small stroke. It is characterized by the appearance of characteristic symptoms of cerebral infarction, but they disappear within a few hours or days.
Classification
Depending on the etiology and localization, the following forms are distinguished:
- Atherothrombotic. The main cause of such damage is atherosclerosis. Atherothrombotic cerebral infarction occurs more often than others (about 70% of all cases of pathology), affecting mainly elderly women.
- Cardioembolic. Cerebral infarction caused by thrombosis of cerebral arteries. This form of cerebral circulatory disorder develops against the background of cardiac lesions accompanied by parietal thrombi.
- Hemodynamic. Develops due to a sharp decrease in blood pressure. An attack of hemodynamic infarction can develop abruptly, against the background of a person’s good health.
- Lacunarnaya. Accounts for approximately 20% of all cases of pathology. It is characterized by the development of a small (up to 2 cm) necrotic focus in the deep tissues of the cerebral hemispheres or in the brain stem. The cause of this lesion is blockage of small cerebral arteries. Often, a cyst with fluid forms at the site of necrosis, which does not have a negative effect on the functioning of the brain.
- Hemorheological. This form of heart attack is a consequence of a malfunction of the blood coagulation system. It often affects several arteries at once, causing an extensive focus of necrosis. Requires immediate complex therapy with thrombolytics and anticoagulants.
Depending on the pathogenetic features, the following types of cerebral infarction are distinguished:
- thromboembolic - a heart attack caused by thrombosis of the cerebral arteries, i.e. associated with occlusion of an intracranial vessel by a thrombotic mass or atherosclerotic formation;
- rheological – caused by changes in the blood coagulation system. Blockage of blood vessels by blood clots in this case is due to an increase in viscosity and increased blood clotting due to polycythemia or erythrocytosis;
- lacunar - formed when small intracranial arteries are blocked, usually resulting from arterial hypertension. The development of small foci of infarction is characteristic.
Thromboembolic infarction includes atherothrombotic and cardioembolic. In atherothrombotic infarction, thrombosis or embolism of an arterial vessel arises from foci of atherosclerosis in the intracerebral arteries. Cardioembolic cerebral infarction develops as a result of cardiocerebral embolism in heart disease. In this case, emboli formed in the cavities of the heart are introduced into the arterial system of the brain with the blood flow.
The thromboembolic type also includes hemodynamic cerebral infarction, which occurs when there is a sharp drop in blood pressure against the background of severe stenosis of blood vessels in the brain or neck.
By etiopathogenetic subtypes:
- Atherothrombotic cerebral infarction. The cause of a stroke is a blood clot that forms and blocks a blood vessel. This type of lesion is most often observed after sleep in the morning. The pathological condition appears suddenly, and brain damage can be extensive.
- Cardioembolic. Symptoms of pathology are expressed at the very beginning of its development. The disease can be triggered by an artificial heart valve, atrial fibrillation, emotional or physical stress.
- Lacunar stroke. In this case, small blood vessels going into the deep structures of the brain are susceptible to pathological changes. Over time, cysts form at the site of the lesions. A characteristic sign of pathology is increased pressure. Higher nervous activity is practically not disturbed, there are no general cerebral symptoms. This form of the disease lasts no more than 21 days. Its diagnosis is very difficult, since it is not always detected even with CT scans. This type of pathology is provoked by diabetes mellitus, chronic lung disease, and changes in the blood vessels of the fundus.
- Hemodynamic. This type of cerebral infarction is typical for older people who are diagnosed with atherosclerosis and low blood pressure. The onset of an attack can be gradual or sudden.
- Hemorrhagic. The cause of the development of pathology is a violation of blood flow. Impaired brain function may be accompanied by complete loss of mobility, problems with breathing and swallowing. The risk of death of the patient in this case is very high. A heart attack can happen at any time and anywhere. The rehabilitation period here begins in 2-4 weeks.
According to the vascular basin that is affected:
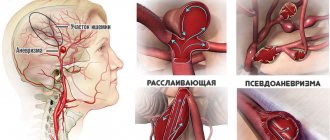
- Internal carotid artery. The most common disease that affects it is atherosclerosis. However, complete blockage may not cause a cerebral infarction, since replacement blood circulation will occur.
- Anterior cerebral artery. This pathological condition is characterized by paresis of the arms and legs. It is characterized by urinary incontinence, spontaneous flexion or extension reflexes, and mental disorders.
- Middle cerebral artery. This type of disease occurs more often than others. If there is a blockage of the main trunk of the presented vessel, then an extensive infarction occurs.
The figure shows the main arteries of the neck and head
Depending on the affected area:
- Infarction of watershed zones. The lesion is located at the junction of the blood supply territories.
- Lacunar. Blood circulation is impaired in the area of the base of the pons. It is usually multiple, and the diameter of the lesions is 1.5 cm.
- Territorial. In this case, the main arteries of the brain are affected.
What factors influence the prognosis
| Factors influencing quality of life | Explanations |
| Volume and localization of the necrotic focus | The larger the area of brain tissue necrosis, the more serious and irreversible the manifestations of the stroke. The likelihood of death is higher if the focus of brain necrosis is located in the area of important centers of the brain |
| The severity of neurological disorders and their reversibility (severity of stroke) | The more severe the stroke, the more serious and severe its symptoms. For example, the likelihood of restoration of sensitivity and motor activity of the paralyzed half of the body is much less than paresis of the arm |
| Patient age | In elderly and elderly people, the disease is more severe. They have a high risk of disability and death |
| Cause of cerebral infarction | The most unfavorable prognosis is for a stroke that occurs against the background of atherosclerosis (as a result of an artery being blocked by a cholesterol plaque) and when a blood clot breaks off and blocks a vessel. |
| Presence of concomitant serious diseases of the heart, blood vessels, and endocrine system | The situation is complicated by existing diseases: diabetes mellitus, heart disease, atrial fibrillation and others |
| Development of complications | In the first 7 days, there is a high probability of death due to cerebral edema, secondary ischemia of the brain stem, damage to the respiratory or cardiovascular centers, transformation of an ischemic infarction into a hemorrhagic one, etc. |
| Timely and competent provision of specialized medical care | The shorter the time interval between the stroke and the start of resuscitation measures, the more favorable the prognosis for life |
Symptoms and signs
In the vast majority of cases, a stroke immediately makes itself felt: a person suddenly begins to experience unbearable headaches, which most often affect only one side, the skin of the face during an attack acquires a pronounced red tint, convulsions and vomiting begin, breathing becomes hoarse.
It is noteworthy that the seizures affect the same side of the body as the side of the brain that was affected by the stroke. That is, if the location of the lesion is on the right side, then the cramps will be more pronounced on the right side of the body and vice versa.
If the left side is affected, the patient will suffer from mental disorders; if the right side is affected, the speech apparatus will suffer.
However, there are cases when the attack as such is completely absent, and only some time after the stroke, which the patient might not even suspect, numbness is felt in the cheeks or hands (one of them), the quality of speech changes, and visual acuity decreases.
Then the person begins to complain of muscle weakness, nausea, and migraines. In this case, a stroke can be suspected if there is a stiff neck, as well as excessive muscle tension in the legs.
Patient survival statistics
Between 15 and 25% of patients die in the first 7–30 days. Mortality in half of the cases occurs due to cerebral edema, in the rest - due to pneumonia, blockage of the pulmonary artery, blood poisoning, kidney or respiratory failure.
Up to 40% of deaths occur in the first 1–3 days; patients die as a result of extensive damage and cerebral edema. Of those who survive, 60–70% have neurological disorders that make them incapacitated and disabled. After six months, these disorders remain in 40% of patients, and by the end of the first year in approximately 25–30%.
An important criterion for prognosis is the restoration of impaired motor functions in the first 3 months. after ischemic stroke. Moreover, the functioning of the lower extremities is restored better than the upper ones. A poor prognostic sign is the absence of any motor activity of the hand by the end of 1 month. The most favorable prognosis is after a lacunar stroke, which occurs due to narrowing of the small arteries of the brain.
Cerebral infarction is a clinical syndrome that is expressed in acute disruption of local brain functions. It lasts more than 24 hours, or leads to the death of a person during this time. An acute circulatory disorder during a cerebral infarction occurs due to blockage of its arteries, which provokes the death of neurons in the area that is fed by these arteries.
Cerebral infarction is also called ischemic stroke. This problem is very relevant in the modern world, since a huge number of people die every year due to cerebral infarction. The mortality rate for ischemic stroke is 25%, another 20% of patients die within a year, and 25% of the surviving people remain disabled.
Encouraging Cases
Separately, doctors diagnose a “minor” ischemic stroke, which is considered to be a mild form of cerebral infarction. With the development of this pathology, the occurrence of severe disorders and disorders is not observed.
But if such an attack of ischemia occurs, you need to think about changing your lifestyle, because a “small” ischemic stroke is almost always a harbinger of something larger and dangerous.
Some people experience a so-called “micro-stroke”, which cannot be hemorrhagic. This pathological phenomenon is characterized by ischemic transient attacks, as well as certain circulatory disorders in the structures of the brain.
The symptoms of a micro-stroke are fully consistent with transient attacks and circulatory disorders: a state of stupor, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, difficulties with orientation in space. This type of pathology is not fatal (you don’t die from it), but it can also be considered a harbinger of a major stroke.
Symptoms of cerebral infarction
Symptoms of a cerebral infarction depend on where the lesion is located.
However, general symptoms of this pathological process can be identified, including:
Loss of consciousness, sometimes coma may develop;
Disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs;
Pain in the eyeballs;
Nausea and vomiting accompanied by severe headache;
Convulsions (not always present).
If the focus of a cerebral infarction is localized in the right hemisphere, then the following clinical picture is characteristic:
Complete immobility (hemiparesis) or significant decrease in strength (hemiplegia) of the left limbs;
Sensitivity in the left half of the body and face disappears or sharply decreases;
Speech impairment will be observed in left-handed people. In right-handed people, speech disorders develop exclusively when the left hemisphere is damaged. The patient cannot reproduce words, but conscious gestures and facial expressions are preserved;
The face becomes asymmetrical: the left corner of the mouth goes down, the nasolabial fold is smoothed out.
Depending on which half of the brain is damaged, symptoms of a cerebral infarction will be observed on the opposite side. That is, if the lesion is located in the left hemisphere, then the right half of the body will suffer.
If a cerebral infarction develops in the vertebrobasilar vascular system, then the patient’s symptoms are as follows:
Dizziness that increases when you tilt your head back;
Coordination suffers, static disorders are observed;
There are disturbances in the movement of the eyeballs, vision deteriorates;
A person pronounces individual letters with difficulty;
Problems with swallowing food appear;
Speech becomes quiet, hoarseness appears in the voice;
Paralysis, paresis, and loss of sensation in the limbs will be observed on the side opposite to the lesion.
It is worth considering separately the symptoms of cerebral infarction depending on which cerebral artery is damaged:
Anterior cerebral artery – incomplete paralysis of the legs, the occurrence of grasping reflexes, impaired eye movements, motor aphasia;
Middle cerebral artery – incomplete paralysis and sensitivity disorder of the hands, as well as the lower half of the face, sensory and motor aphasia, laterofixation of the head;
Posterior cerebral artery – visual disturbances, the patient understands the speech of another person, can speak himself, but he forgets most words.
In severe cases, consciousness is depressed and the person falls into a coma, which can occur when any part of the brain is damaged.
Developing complications
During a cerebral infarction, a large number of cells and tissues are affected, so the likelihood of developing serious complications in the first days and hours is quite high. If edema occurs, the risk of death increases significantly in the first 5-7 days.
The most dangerous and common complications also include:
- Congestive pneumonia. It develops against the background of the patient’s constant bed rest, so it is often diagnosed only 30-45 days after the stroke.
- Acute heart failure, pulmonary embolism (the development of these pathologies is noted in the first month).
- Bedsores. Lying down in patients should only occur on dry and clean beds. Patients must be systematically turned, placed as comfortably as possible, and all necessary hygiene products must be used.
Lack of treatment or incorrectly prescribed therapy can affect the occurrence of various complications. Treatment of cerebral infarction should begin with establishing the root cause of the pathology, as well as its elimination.
Patients who have a severe form of ischemic stroke are extremely vulnerable, so during therapy, doctors monitor the functioning of all organs and systems. This is due to the fact that in a short time after a heart attack, almost the entire body is drawn into the developing pathological process.
Particular attention should be paid to the patient's diet. Nutrition should be balanced: proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are important. Patients are prescribed a special regimen of fluid intake (depending on the presence or absence of edema).
In some cases, a person cannot feed on his own (unconsciousness, numbness or loss of sensation in the limbs, difficulty swallowing), so they resort to tube feeding with special mixtures.
Causes of cerebral infarction
The following causes of cerebral infarction are distinguished:
Atherosclerosis. It develops in men earlier than in women, since at a young age female blood vessels are protected from atherosclerotic lesions by sex hormones. The coronary arteries are the first to be affected, then the carotid ones, and subsequently the cerebral blood supply system;
Hypertension. Mild hypertension (pressure up to 150/100 mm Hg), which is the most dangerous, enhances atherosclerosis and disrupts the adaptive reactions of the arteries;
Heart diseases. Thus, people who have had a myocardial infarction have a high risk of developing a cerebral infarction. In 8% of patients after myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke will develop within the first month, and in 25% of patients - within six months. Coronary heart disease and heart failure are also dangerous;
High blood viscosity;
Atrial fibrillation. They cause blood clots to form in the left atrial appendage, which are subsequently transported to the brain;
Disorders of the endocrine system, primarily diabetes mellitus;
Vascular diseases (pathologies of their development, Takayasu's disease, anemia, leukemia, malignant tumors).
In addition, do not forget about risk factors that increase the likelihood of a cerebral infarction, including:
Age (every ten years of life increases the risk of developing cerebral infarction by 5-8 times);
Smoking (if this bad habit is supplemented by taking oral contraceptives, then smoking becomes a leading risk factor for the development of cerebral infarction);
Acute stress or prolonged psycho-emotional stress.
Prevention
Considering the danger of a heart attack, it is much wiser to try to prevent its development. To do this, you will have to significantly change your lifestyle, but the result will affect not only the blood vessels, but also your health in general.
- Diet . Must be balanced. Less fried, less fatty, more vegetables and fruits. A good idea would be to eat citrus fruits and garlic, a bad idea would be to overeat on sweets and fast food.
- Mode . You should go to bed and get up at the same time, and spend at least eight hours sleeping so that your body has time to rest. It is also better to eat by the hour, at least five times a day, in small portions.
- Exercise stress . Should be uniform and moderate. Walks in the park are great.
You should also give up bad habits, visit a doctor once a year (it will be useful for older people to measure cholesterol and blood pressure levels) and protect yourself from stress.
Of course, prevention is not a panacea for everything, but it can significantly reduce the chances of a cerebral infarction. The main thing is not to lose your optimistic attitude and love for life.
The video talks about possible problems with the blood vessels of the brain, explains how to diagnose and avoid them.
What is the difference between a cerebral infarction and a stroke?
When a cerebral infarction occurs, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, as a result of which the tissues of the affected area begin to die. Insufficient blood flow to the brain occurs due to atherosclerotic plaques that prevent its normal flow, due to heart rhythm disturbances, or due to problems with the blood coagulation system.
With a hemorrhagic stroke of the brain, on the contrary, the blood flow to it increases, which causes an artery rupture. The cause is vascular pathologies or hypertensive crisis.
There are differences in the course of the disease. Thus, cerebral infarction develops gradually, over several hours or even days, and hemorrhagic stroke occurs almost instantly.
Diagnostics
A cerebral infarction causes symptoms that help to quickly determine the presence of the disease. Thanks to knowledge of the signs of a stroke, it is possible to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and provide emergency assistance in the first hours after the onset of the disease, making it possible to prevent complex consequences and even death.
To confirm the diagnosis, doctors collect a complete medical history, clinical and biochemical blood tests, and an ECG. And to identify lesions, computer and magnetic resonance imaging are used. The most informative and important method in diagnosing cerebral infarction is MRI, as it allows you to accurately identify the affected area and the condition of the blood vessels that feed it. A CT scan helps determine the consequences of a stroke.
Definition of Stroke
A heart attack is the necrosis of organ tissue caused by insufficient or absent blood supply. Most people immediately think of heart disease when the term is mentioned. However, myocardial infarction is a special case of ischemic necrosis. Cell death due to lack of blood supply can affect almost any organ: lungs, kidneys, liver, brain, intestines. In this case, they talk about a heart attack of the lung, kidney, liver, brain or intestine.
A stroke is an acute disruption of the blood supply to the brain, accompanied by the appearance of neurological symptoms: fainting, loss of coordination, paralysis, numbness of the extremities. Types of stroke are cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke), hemorrhage in the brain or subarachnoid space (hemorrhagic stroke). They all have similar symptoms, but a different prognosis.