Behavior and personality disorder
Often people who have suffered a concussion complain of irritability and aggressiveness appearing in their behavior. Even minor troubles make them angry and nervous. They become either whiny or rude, their mood constantly changes - from menacingly quiet to brightly hostile. They do not notice the joyful moments of life, see only the negative, are offended by the people around them, consider themselves misunderstood and deprived of attention. If similar symptoms were observed before the injury, then in the post-traumatic period they noticeably worsen.
Scientists have noticed that if a person has an injury to the frontal part, then he is more likely to experience a state of euphoria, a decrease in critical attitude towards himself and his actions. This is perceived by others as arrogance or pride.
Healing time
This process depends on many related factors:
- the nature of the injury and the extent of damage;
- state of the body as a whole;
- the patient's wishes for recovery;
- course of prescribed therapy;
- compliance with rehabilitation treatment.
The process of restoring brain functionality takes from 6 to 12 months. Therefore, only compliance with all rehabilitation rules can lead to a quick and complete recovery, and, of course, repeated head injuries must be avoided.
Psychotic symptoms
After a concussion, psychotic symptoms are not observed very often, but there are still precedents. In these cases, they talk about damage to the areas of the brain responsible for vision, smell, hearing and speech. The affected person is haunted by hallucinations, i.e. he hears voices, sees some images. Sometimes he becomes obsessed with delusional ideas (for example, about domination over the world or global surveillance of him by intelligence services, etc.). This happens especially often to those who hit the back of their head.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to predict and prevent the occurrence of a concussion, but if you follow some recommendations, you can reduce the likelihood of injury. It should be remembered that playing hazardous sports (boxing, hockey, football, etc.) increases the likelihood of getting a head injury.
When roller skating, skateboarding, or horse riding, you must use head protection - a helmet with a special pad. You need to choose the size and use the helmet correctly. While driving a car, all passengers in the car must wear a seat belt.
The number of people seeking medical treatment for traumatic brain injuries increases sharply in the winter, when the likelihood of falls on slippery streets is high. It is recommended to use special anti-slip devices for shoes, and for older people to use a cane with a sharp tip.
Post-traumatic epilepsy
There is an opinion that post-traumatic epilepsy can occur only with a severe head injury with memory loss or deep fainting. However, analysts talk about the possibility of persistent, repeated epileptic seizures even with minor external influences. Or, doctors emphasize, there is an activation of hidden foci that did not make themselves known before. This type of epilepsy occurs more often when the injury occurs in the temporal regions or crown.
Initial attacks may occur with mild symptoms, little attention is paid to them, and the person remains without treatment for a long time. Meanwhile, this directly affects cognitive abilities and the patient’s state of mind.
First aid
It is important to know how to provide first aid to a victim in order to avoid unwanted consequences.
So, a short reminder of what to do when providing first aid before the doctors arrive:
- Calm the victim if he is conscious.
- Place his body in a horizontal position on a flat surface.
- Apply a cold compress to your head (an ice pack, a towel soaked in cold water, or any frozen product). If the incident happened on the street, you can soak any thing in water and apply it to your head.
- In case of fainting, the victim must be turned on his side to prevent clogging of the airways with vomit.
- In case of mild fainting, try to bring the person to his senses (patting the cheeks, using a cotton swab with ammonia).
- The most important thing is that the victim cannot drink water; you can only lightly moisten your lips with a wet cloth.
Neuroses and psychoses
A fairly common consequence of a concussion is neurosis. Feelings of intense anxiety, fear, horror that constantly haunt a sick person, an absolute inability to concentrate, engage in educational or work activities - these and other manifestations of neuroses prevent a person from living fully in society. Neuroses, if left untreated, can progress to the stage of psychosis. And these are already cardinal violations in the perception of the surrounding world. Without professional treatment, psychoses threaten the development of dementia and other serious disorders of brain function.
- 4 minutes to read
A concussion occurs as a result of injury to the bones, tissues, vessels of the back of the head or the frontal part of the skull with a blunt object and can disrupt the functions of this organ. They are usually restored if treatment is started in a timely manner and the regime recommended by the doctor is not ignored.
Content
Basically, pathology does not pose a mortal danger to humans. But even after a few years, consequences can unexpectedly manifest themselves.
Diagnostics
Signs of a concussion in an adult allow the doctor to make a diagnosis based on the clinical picture. It is being clarified whether there was a blow to the head or to the head and loss of consciousness.
The following features are also taken into account:
- during the first hours, there may be a slight change in the width of the pupils towards decreasing or increasing, and their sensitivity to light remains normal;
- painful sensations when moving your gaze;
- when you try to move your eyes to extreme positions, involuntary trembling begins;
- instability in the Romberg position;
- slight tension in the muscles of the back of the head (usually disappears after 3 days);
- the presence of asymmetry of skin and tendon reflexes (variable sign).
A concussion is diagnosed based on the patient’s complaints, collected information about the incident and the period during which there was no consciousness, examination by a neurologist and tests prescribed by him.
Long-term observation of the victim is of great importance, since more serious pathologies can manifest very similar symptoms. If the diagnosis was made correctly, then the deviations that were initially identified completely disappear after 3-7 days.
If a traumatic brain injury has been sustained, an X-ray examination is required, through which skull fractures can be detected. Hidden brain injuries can be excluded by examining the condition of the fundus, echoencephalography and electroencephalography.
MRI and CT do not reveal any abnormalities that may occur in the tissue structure, therefore neuroimaging is considered the best modern diagnostic method. It allows you to detect swelling or hemorrhage, in which case it is a bruise, not a concussion, that should be treated.
Diagnosis and treatment of the condition is carried out by a neurologist (neurologist). Initially, the doctor assesses the patient’s vital signs (breathing, pulse) and checks the integrity of the skull and spine. CT screening is required to exclude intracranial hemorrhage in the presence of such signs as:
- progressive headache;
- constant vomiting;
- worsening confusion or deterioration in level of consciousness;
- different pupil sizes.
In addition to the physical examination, the neurologist will certainly ask several simple questions or tests to test thinking, memory, attention and concentration, and will also assess the ability to make the right decisions in a reasonable time.
Complications
There are several consequences.
Manifestation of short-term disorder
Even after discharge from the hospital, where a person was treated for a head injury that caused a concussion, the pathological symptoms do not immediately go away. They appear as:
- severe dizziness;
- frequent migraines;
- difficulty concentrating ;
- problems that arise in the process of reading or writing.
The person continues to suffer from nausea and fatigue. Becomes weak and absent-minded. Drowsiness is constantly present.
If these signs do not stop within a month after receiving a traumatic brain injury, you should consider visiting your doctor again. Because if the disorders that have arisen that do not allow the brain to function normally are not treated, the consequences can be dangerous.
Postconcussion syndrome
The consequence of a concussion in the absence of timely treatment sometimes becomes post-concussion syndrome. Symptoms of the pathology can manifest themselves in the form of migraine attacks, sleep disturbances, and the presence of anxiety.
A person is unable to work normally because he cannot concentrate, concentrate on something that previously did not cause any problems. Even a slight load leads to severe fatigue. It is often accompanied by causeless anxiety and dizziness.
The syndrome often develops months later and can appear years after the concussion.
Post-traumatic encephalopathy
Repeated shock to the organ sometimes leads to complications in the form of post-traumatic encephalopathy. Athletes who practice boxing and participate in fist fights often suffer from this phenomenon. Development goes through several stages, during which:
- circulation is disrupted ;
- cerebrospinal fluid stagnates;
- nerve die ;
- connective tissues grow
- scars form adhesions form;
- activity decreases .
On this topic
Everything you need to know about concussions
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2020
Post-traumatic encephalopathy leads to the fact that a person becomes lethargic, arms or legs often tremble, consciousness is confused, problems arise with balance, convulsions appear, and changes in character are noticeable.
Asthenic syndrome causes anger, anxiety, and frequent outbursts of emotions. Mental abilities noticeably decrease; learning simple topics becomes quite difficult for a person.
The occurrence of autonomic disorders
A concussion can lead to problems with the supply of oxygen to tissues and organs, which causes autonomic disorders. They are accompanied by:
- headache attacks ;
- groundless worries;
- surges ;
- tachycardia;
- numbness of the limbs.
The person becomes lethargic, sometimes faints, gets tired quickly, and sweats a lot. He may have problems in his sex life.
Video: what is a concussion and how to recognize it?
A concussion is the mildest form of brain damage, usually accompanied by loss of consciousness for a short period.
It is caused by the brain hitting the inside of the skull without damaging the blood vessels. The integrity of the tissues is not compromised and the structure of the main organ of the central nervous system does not undergo changes. Cells retain their viability, but lose the ability to fully perform their intended functions. Doctors do not agree on what causes the central nervous system to fail at the moment of impact. Experts put forward several assumptions:
- disruption of strong connections between neurons;
- vasospasm. At the same time, brain cells do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients;
- a sharp increase in intracranial pressure;
- molecular changes.
However, during computed tomography, no visible damage or tissue changes are observed. In most cases, this disorder of normal brain functioning is short-term and passes quickly.
According to various medical studies, concussions are diagnosed in 60-70% of patients who have suffered a head injury. It is often observed in people whose skull was not directly affected, for example, by an unexpected fall on the buttocks or sudden braking in a car.
In the article “Concussion in a child,” you will learn how to behave if a child is injured, how to provide assistance, diagnose and how to treat a concussion.
To avoid the above consequences, if there is the slightest suspicion of a concussion, you should immediately consult a doctor. Modern research methods make it possible to accurately diagnose and promptly prescribe appropriate treatment. And strict adherence to medical recommendations guarantees a complete and rapid recovery.
Features of the consequences
A concussion can go away without leaving a trace, but sometimes the result of the injury lasts almost a lifetime and manifests itself with various symptoms, including changes in character. A person gets irritated over trifles, becomes touchy and vulnerable. Depression often occurs. They may be haunted by fears in the form of a fear of enclosed spaces.
- intolerance to heat and cold;
- increased sensitivity to infection;
- nervous disorders;
- emotional outbursts.
Worsening mood can lead to aggressive behavior. Unreasonable anxiety, headaches will become constant companions for a person, and psychosis will begin to develop. As a result, perception of reality is lost and hallucinations appear.
A concussion cannot be ignored. Even a mild degree of damage can result in serious complications, leading to consequences that are impossible to get rid of.
Psychotherapy in this case is powerless; constant use of drugs can lead to dependence on them. Only comprehensive treatment started on time will help avoid problems.
A concussion is considered a mild closed traumatic brain injury (CTBI), which is diagnosed more often than others. A concussion itself does not pose a threat to human life and health, provided proper treatment and adherence to the recommended regimen, but sometimes after an injury undesirable consequences develop in the form of various unpleasant symptoms.
The consequences of a concussion can appear after several years, significantly complicating normal life. The hardest thing is for those who, for one reason or another, did not seek medical help in time for a timely diagnosis of the problems that arose.
SGM degrees
Doctors distinguish 3 degrees of concussion depending on the severity of the manifestation and symptoms:
- light. It is characterized by a short loss of consciousness (up to 5 minutes); in some cases, memory loss is not observed at all. The general condition of the victim is noted as satisfactory, there are no changes in the sensory organs, motor and speech apparatus. In some cases, severe headache and vomiting were diagnosed.
- the average degree is characterized by loss of consciousness for 5–15 minutes. The general condition is assessed as moderate, nausea, vomiting, severe headache, nystagmus - involuntary eye movement.
- severe degree is characterized by loss of consciousness for a period of several seconds to 6 hours. In this case, there is a dysfunction of some organs, the victim’s condition is serious.
Short-term disorders
In most cases, after a concussion, a person is bothered by certain symptoms, which most often disappear within a month after a head injury, subject to adequate treatment and compliance with the recommended regimen. Such consequences that occur in the near future after injury include:
- Intense headaches of a migraine or liquorodynamic nature. In most cases, cephalalgia persists during the first two weeks after injury, in case of severe injuries - a little longer.
- Difficulty concentrating, absent-mindedness, memory impairment.
- Attacks of dizziness, often interfering with the patient’s normal movement.
- Nausea; sometimes – vomiting, which does not bring relief.
- Difficulty with reading and writing.
- Drowsiness, general weakness, fatigue.
All of these symptoms are characteristic of the recovery period and are associated with pathological changes resulting from the blow - swelling of brain tissue, destruction of neural connections and asthenia.
If unpleasant symptoms have not disappeared after 3 weeks, you should re-visit a neurologist to determine the cause of this disorder, since it is possible that long-term consequences of a concussion have developed that require special treatment.
How to help at home
In case of severe concussion, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
The mild form can be treated at home only if all procedures prescribed by the doctor are strictly followed:
- The patient should be provided with complete rest.
- Minimize communication with the patient.
- If necessary, dim the light in the room with the patient.
- Taking sedatives and antidepressants prescribed by a doctor is carried out in the dosage indicated in the prescription.
- Reduce mental activity to a minimum.
- Eliminate irritating factors from the victim’s life for a time: computer and TV.
- Provide a diet based on a dairy-vegetable diet.
- Dream.
↑
Other consequences
In addition to those listed, other unpleasant long-term consequences of a concussion are possible, but they develop much less frequently than others. It can be:
- Psychoses, neuroses, paranoid states.
- Inadequate perception by the body of alcoholic beverages, in which poisoning, intoxication and alcoholic delirium more often occur after previously habitual doses.
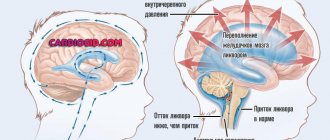
- Increased production of cerebrospinal fluid, which entails an increase in the level of intracranial pressure and the occurrence of corresponding unpleasant symptoms.
- Reduced cerebrospinal fluid production - in this case, on the contrary, cerebrospinal fluid is produced in insufficient quantities, which entails the development of chronic fatigue, dizziness, apathy and headaches.
To summarize, we can conclude that concussion should not be neglected. Even a mild degree of the disease requires compliance with a special regime, since it is possible that unpleasant symptoms will develop, which are very difficult to get rid of in the future. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment will help avoid consequences and allow the patient to get back on his feet faster.
Light damage
Concussions are divided into:
There is no point in deciphering them, since the name interprets its decoding. The question is how to diagnose and help a person with a mild concussion.
For a mild concussion:
- The patient must be provided with bed rest.
- The room in which the patient is located must be well ventilated.
- Provide sedative medications based on valerian root.
- Limit your intake of hard foods. It is best to drink low-fat broths and eat pureed cereals.
- As soon as the victim’s condition improves, he must be shown to a doctor to undergo diagnostics and rule out more serious injuries.
Drugs for treatment
Drug treatment for concussion includes drugs from the following groups:
- Painkillers.
- Nootropic drugs.
- Vasotropic agents.
- Diuretics.
- Sedatives.
- Tranquilizers.
- Vitamins.
The medications that are usually chosen are drugs that reduce pain in the skull area, improve blood circulation in the brain, and relieve nausea and dizziness.
At the same time, medications with neuroprotective properties that can improve brain function can be used. In some situations, sleeping pills and sedatives are indicated. During the rehabilitation process, the doctor may prescribe nootropics and restoratives.
For dizziness, doctors usually prescribe plant extracts of ginkgo biloba or belladonna, ergotoxin. Motherwort or valerian can be used as sedatives.
Insomnia, if indicated, is treated with Phenozepam, Medazepam or Oxazepam. A grade 3 concussion requires vascular neurometabolic therapy with the use of magnesium and antioxidants.
For 1 month after a concussion, it is recommended to avoid heavy physical labor and limit any sports activities. Violation of sleep and rest patterns is strictly contraindicated. You should minimize your time at the PC monitor and watching television programs. Listening to calm music without using headphones is helpful.