Multiple Sclerosis Research Archive
This study plans to examine the effects of yoga on symptoms and quality of life compared with regular exercise and no exercise in patients with multiple sclerosis.
This study is an observational study, meaning that participation in the study does not affect your treatment and no additional treatment is prescribed.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that affects the brain and spinal cord due to a malfunctioning immune system. Weakness, increased fatigue, and impaired mobility are the most common symptoms of MS. It is known that properly selected physical activity can have a beneficial effect on the manifestations of the disease. In addition to standard gymnastics (physical therapy, exercise therapy), other rehabilitation methods are also used. One of them is classical hatha yoga. Yoga classes are suitable for patients with MS because they have a gentle effect on the musculoskeletal system and muscles of the internal organs, and do not cause an excessive increase in body temperature, which is important for patients with MS.
Various studies, including foreign ones, have shown that yoga has a positive effect on the condition of patients with MS (for example, it improves exercise tolerance, emotional background and quality of life). However, yoga did not cause serious side effects.
In Russia, yoga is gradually becoming part of the practice of patients with MS. So, in , for patients with MS, yoga classes are held with the support of a subsidy from the Moscow Public Relations Committee. However, there is not yet enough scientific research to study the effect of yoga on patients with MS, which is why this project is being organized.
If you voluntarily decide to participate in the study, your research physician will discuss the information below with you and ask you to sign an informed consent form.
Your participation in the study will last just over 3 months (up to 14 weeks) and will include a pre-assessment (up to 1 week), a session period (12 weeks) and a final assessment of your condition (up to 1 week after the last session).
After signing the informed consent form, the doctor-researcher will collect your data to the extent necessary for the study: gender, age, information about MS and other diseases, medications taken, lifestyle, bad habits.
If you meet the study eligibility criteria, you will be randomly assigned to one of three groups:
- Group 1 (25 people). Patients will do yoga 2 times a week for 12 weeks, for a total of 24 sessions.
- Group 2 (25 people). Patients will engage in exercise therapy, also 2 times a week for 12 weeks, for a total of 24 sessions.
- Group 3 (25 people). Patients will be asked to refrain from any physical activity (yoga, exercise therapy, fitness, swimming) and continue to lead their usual lifestyle without changes for 12 weeks.
Which group you fall into does not depend on your doctor or anyone else, but is determined by a random draw. You will have an equal chance of getting into one group or another. The study coordinator will tell you which group you are in and what you will need to do.
Regardless of the group, you will undergo a medical examination , including:
- doctor's assessment using the EDSS (Expanded Disability Status Scale),
- filling out questionnaires about your health and quality of life,
- Berg balance scale (exercise test),
- 6-minute walk test.
This assessment will take approximately 1 hour and will be carried out twice during the study - before the start of participation and 12 weeks after the end of the study.
Medical examination will be performed at the research center. The research physician will schedule a day and time for your examination.
Yoga classes will be held at. The duration of one lesson is approximately 60 minutes. The study coordinator will tell you the time and location of the classes. Exercise therapy classes will be held at the research center. The duration of one lesson is approximately 45 minutes. The study coordinator will tell you the time and location of the classes. If for some reason you cannot come to a yoga or exercise class, you can do it at home (just like in the center); in this case, you will be asked to fill out a special exercise record form and bring it to the instructor at your next visit.
If you successfully complete the study, you will be offered free access to yoga classes for 6 months in order to improve your quality of life and further monitor your condition. Successful completion of the study is considered to be attendance at at least 20 classes and attendance at medical examinations (in groups 1 and 2); or compliance with the requirement not to engage in regular other physical activity for 12 weeks and to attend medical examinations (in group 3).
Causes
The following causes cause multiple sclerosis:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- spinal injuries;
- stress;
- overwork;
- smoking;
- infectious diseases;
- hepatitis B vaccine;
- intoxication.
Researchers have noted the negative impact of metabolic disorders due to poor diet and place of residence.
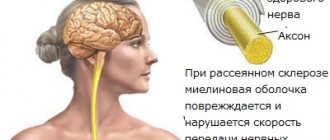
The pathology is based on a viral infection (measles, mumps, rubella, herpes). These viruses destroy the cell and myelin, which is the protein sheath of nerve fibers. In their place, a foreign protein is formed - a prion. In response to the appearance of these unfamiliar elements, lymphocytes begin to produce antibodies. The fight begins with the body’s own cells, and not with the virus.
The immune system begins to malfunction. This leads to an autoimmune reaction. In this condition, the nervous system is suppressed by its own defenses. Inflammatory foci of myelin destruction form in the brain and spinal cord. The location of these foci is scattered, and they may have different ages of formation.
There are three stages.
- acute stage, which has recently arisen;
- lesions that arose a long time ago, and they may be in an inactive form;
- chronic foci lead to both a latent course of the disease and an active form. During any phase, white matter is destroyed.
In multiple sclerosis, not only the white matter, but also the gray matter (the body of nerve cells), as well as nerve fibers, are destroyed. The process of decay occurs gradually. Slow wear and tear continues not only during the acute stage, but also during the subsidence of symptoms, when apparent calm is created.
Among the factors that provoke this disease, several can be identified.
- There are more young people who developed the disease;
- female;
- various diseases of the human psyche and emotional sphere;
- infectious pathologies of viral or bacterial origin;
- problems in the functioning of blood vessels;
- hereditary factor;
- radiation.
Autoimmune diseases can also be a trigger. The list of such diseases is very long. One organ or an entire system may suffer. Systemic diseases include, for example, lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Damage to individual organs can also affect the functioning of the body as a whole. These diseases include, for example, liver cirrhosis and myocarditis. Endocrine diseases: diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies.
Characteristic diagnostic signs
The occurrence of multiple sclerosis can be suspected by disruption of the functions performed by the spinal cord and brain. Loss of myelin in various structures of the nervous system leads to the manifestation of one or several nonspecific symptoms. The signs of multiple sclerosis are fickle, periodically disappear, leaving a feeling of imaginary recovery, but later they reappear with greater force.
Cerebral, bulbar and spinal forms of multiple sclerosis are determined by the predominance of symptoms from the structure that has undergone the greatest destruction of myelin. Multiple sclerosis is self-diagnosed based on the following symptoms:
- Loss of certain areas of visibility and blurred vision (in most patients this is the first diagnostic symptom of multiple sclerosis).
- Lack of movement in the arms and legs and sensitivity in various segments of the skin.
- Violation of the nervous regulation of the pelvic organs. Incontinence or retention of urine and feces.
- In women, the menstrual cycle is distorted, and in men, impotence appears.
- An unsteady gait appears, trembling in the hands, and falls out of the blue are possible.
- Paresis of facial muscles, strabismus, impaired swallowing, speech.
- Euphoria or persistent depression, cognitive impairment and progressive dementia. The appearance of symptoms of chronic fatigue, epileptic seizures rarely occur.
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis rarely appear alone; more often they are a combination of functional disorders. You should seek help from the hospital in the early stages after the above symptoms appear. Multiple sclerosis progresses every day and without timely treatment leads to death.
Why does the disease occur?
The reason why multiple sclerosis occurs is still not clear. But in recent years, scientists have associated the development of this pathology with disturbances in the functioning of genetics and the immune system.
In a normal state, our “body defense” reacts sharply to the penetration of an unknown object into the body, which can be any virus or microorganism. She first attacks the “invader” and then removes him. The speed of this process is influenced by the speed of connection between the links of immunity, as well as the production of cells designed to eliminate danger.
What happens with multiple sclerosis? Scientists believe that the immune system is altered by the virus. She begins to perceive myelin as a dangerous object and attacks the cells of this fatty tissue. This phenomenon is called “autoimmunity”.
4. Mental and emotional disorders. The reason for contacting a doctor may be a feeling of fatigue after a long rest. This is an early sign of multiple sclerosis. The disease also manifests itself in cases where it is difficult for a person to remember or retell information. Signs of pathology are also constant irritability and dissatisfaction, lack of former ambitions and depression, as well as excessive “playing to the public.”
5. Feeling constantly tired. Of course, it is familiar to workaholics, young mothers and students. However, if it persists, you should consult a doctor. A feeling of constant fatigue overtakes patients with multiple sclerosis already in the morning hours. While still lying in bed, they have a feeling of heaviness, like after working a triple shift. Sometimes a similar feeling comes over the patient right on the street.
6. Failure of the menstrual cycle in women. The presence of foci of pathology on nerve fibers leads to hormonal imbalance and general disorder of the reproductive system.
7. Intestinal dysfunction. A person’s digestive system can tell them about the first signs of multiple sclerosis. If, despite eating little flour products, he rarely goes to the toilet for a long time and constipation has become more frequent, then this should be a cause for concern. Of course, such symptoms often occur during sudden weight gain, when changing a diet to lose weight, or during pregnancy. And here it is necessary to analyze whether you have any other signs of multiple sclerosis.
8. Hand trembling. If a person notices that he has difficulty fastening buttons or threading a needle, this may be the first sign of multiple sclerosis. After all, one of the symptoms of pathology is hand trembling.
Multiple sclerosis is an insidious disease due to the variability of symptoms.
Today a person may have a sore eye, but tomorrow he will feel only dizziness and weakness. Then everything may stop, and the patient will begin to feel quite normal.
Specialist treating multiple sclerosis, rules for collecting anamnesis
Multiple sclerosis is diagnosed at an early stage by a neurologist. The doctor begins the conversation by asking about complaints and collecting anamnesis. The doctor can collect the necessary information on the disease using questions that need to be answered clearly and in detailed form:
- In what chronological order did the symptoms of the current disease develop, whether the person was treated by other specialists, and what diagnosis was made.
- Did you take medications in the early stages of multiple sclerosis? If medications were used independently or as prescribed by a doctor, then the names of the medications must be clearly stated.
- What diseases have you suffered before? Particular emphasis is placed on viral infections, which, according to popular theory, can lead to MS.
- Did your parents and immediate relatives have similar health problems?
- Is the person dependent on alcoholic beverages, smoking, or drugs?
Pathogenetic therapy
During an exacerbation of the disease, several methods of combating the disease are distinguished.
- The main one is hormonal therapy, which is carried out in short courses, but the dose is maximum. The earlier treatment is started, the more effective the anti-inflammatory effect will be. Together with similar drugs, they give medications that protect the gastric mucosa, a vitamin complex, and drugs containing potassium and magnesium.
- Plasmapheresis. The essence of the procedure is to safely cleanse the blood at the cellular level using special devices.
- Cytostatics. They inhibit pathological cell reproduction or completely eliminate it.
- B-interferons are immunomodulators that help fight viruses and slow down the progression of the disease.
Objective neurological examination for MS
In order to know how to diagnose multiple sclerosis, doctors of any specialty study neurology and learn to use a special hammer. For the diagnosis to be reliable, the doctor must detect at least 2 areas of damage to the white matter of the central nervous system, which occurred at different times. Screening for multiple sclerosis includes:
- Assessment of movements in the limbs, determination of muscle tone and strength.
- Identifying enhanced and unnatural reflexes.
- Checking superficial and deep sensitivity. The sensations of pain, temperature, and touch on symmetrical areas of the body are compared.
- Assessing the correct functioning of the cranial nerves. The presence of strabismus, double vision, total or partial loss of visual fields is objectively established. Paresis of the muscles of the face, palate, tongue, pharynx and neck is determined.
- Detecting unsteadiness in Romberg's static posture, hand tremors and handwriting distortion.
The patient is monitored for several days. It is important to conduct a topical diagnosis to determine the most damaged structure of the nervous system. During this time, transient functional changes can be noticed. A typical example of clinical manifestations in multiple sclerosis is the loss of abdominal reflexes on the first day of examination and their recovery on the next day.
Symptoms
After the destruction of the myelin sheath, the transmission of nerve impulses is disrupted. Demyelination can form anywhere, resulting in neurological disorders. During the illness, stages of exacerbation alternate with stages of remission. If the disease is discovered for the first time, then neurological problems may not be visible.
During the next exacerbation, neurological signs may intensify or be supplemented by new disorders. What pathologies will arise depends on the place where demyelination occurred, as well as on the importance of the nerve segment in the functioning of the body as a whole. The locations of destruction are in a chaotic order throughout the nervous system. There can be many of them.
Some people may have mild symptoms. A comprehensive examination by all doctors will help identify this disease.
The person himself may also notice behavioral disturbances.
- impaired coordination of the body, and coordination suffers not only during movement, but in a static position;
- tremor of the limbs;
- sensory disturbances (a person may feel tingling or numbness in certain parts of the body).
It happens that a person does not experience symptoms of the disease for several years after the first exacerbation. But that doesn't mean it disappeared. The active stage will still occur. This stage is characterized by more severe symptoms.
- Pathologies of motor functions are most often observed: paresis, paralysis, paresis of the muscles of the limbs, a feeling of tension in the muscles of the arms and legs;
- hyperkinesis – involuntary movement in various muscle groups: tremor, dystonia;
- optic neuritis, visual acuity is impaired, sometimes complete blindness is observed, a film may appear before the eyes;
- brainstem and cerebellar symptoms, double vision, dizziness with nausea, staggering during movement, clumsiness of the hands;
- some reflexes disappear;
- sphincter symptoms, any urinary disorders;
- mental disorders (asthenia, euphoria, depression, neurosis);
- dysarthria - a speech disorder consisting of difficulty reproducing individual words and sounds; distortion of taste;
- weakness of the facial muscles: skewed cheeks, eyelids do not close.
These disturbances may periodically disappear and then return again.
Symptom complexes
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by a number of symptom complexes.
- The “clinical discrepancy” syndrome is when a person does not perceive objective symptoms of the pathways. For example, an examination revealed a violation of muscle tone in the legs, but the patient can move well over long distances.
- Syndrome of “inconsistency of clinical symptoms.” The patient’s existing symptoms can change not only over many years, but even during the day. The severity of one symptom may decrease or increase.
- Feelings of heat in the body, “hot bath syndrome.” The patient begins to feel worse when the ambient temperature rises. For example, even after hot dishes.
Laboratory and hardware diagnostics
Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis at an early stage using modern technologies is due to the ability to detect the smallest pathological foci. Tests for MS also help determine the true nature of the disease. To carry them out, biological fluids of the human body are taken. The use of advanced research methods is necessary to confirm the current diagnosis and exclude other diseases.
General blood analysis
A nonspecific study performed on all admitted patients includes a general blood test. In case of multiple sclerosis, this method is not very informative, however, it allows one to exclude infectious, oncological and other pathologies that are similar in the nature of symptomatic development.
Lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid diagnostics
The study is certainly performed if multiple sclerosis is suspected. The analysis should be preceded by psychological preparation of the patient, since many are afraid that the spinal cord will be damaged during the manipulation. During a lumbar puncture, a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid is removed from the spinal canal. Already at the sampling stage, the doctor can carry out differential diagnostics by determining the pressure in the spinal cord.
During the period of exacerbation, the number of lymphocytes in the analysis may increase, the protein may increase, but this is not enough for diagnosis. When multiple sclerosis is not active, they disappear. It is much more informative to isolate class G oligoclonal immunoglobulins by electrophoresis. The detection of this protein fraction indicates an autoallergic process and aggression of one’s own immune cells towards myelin. The analysis helps both diagnose multiple sclerosis and exclude other diseases.
Highly accurate method for detecting multiple sclerosis
MRI is superior to other tests for multiple sclerosis in terms of information content, being the “gold” standard for diagnosis. When conducting a hardware study, it is possible to determine the expansion of the cavity of the cerebral ventricles and atrophy of the cortex.
To obtain a high-quality image, paramagnetic contrast fluid is used during MRI. In areas that have undergone myelin destruction, the accumulation of a special substance occurs more actively. The highly accurate method allows you to see the smallest defects in the white matter of the nervous tissue. An MRI diagnosis is made when at least 4 areas of demyelination larger than 3 mm are detected, at least one of which must be located near the cerebral ventricles (periventricular).
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
The value of PMRS lies in its ability to determine the metabolic activity of tissue in real time. In a patient with MS, the concentration of the marker N-acetylaspartate in the affected area is reduced by 60-80%. When combining the method with MRI, it is possible to study the functional and morphological state of the nervous substance and the development of multiple sclerosis.
Superposition electromagnetic scanning
The latest diagnostic device makes it possible to objectively calculate the activity of enzymes in nervous tissue. In multiple sclerosis, total and focal myelin loss can be assessed. SPEMS also allows one to determine the state of ion exchange in tissues and the activity of neurotransmitters. The method is very valuable for determining the functionality of the affected tissue and determining the severity of demyelination, however, it is not enough for a final diagnosis.
Determination of electrical activity of the brain
The method is based on the study of signals of different modalities from central nervous structures using an electroencephalograph. In multiple sclerosis, the following evoked potentials are determined:
The study allows us to determine the condition of the nerve fibers and the degree of their damage. Using the method, you can monitor the patient’s recovery during treatment and evaluate the effectiveness of prescribed medications.
How was the disease previously diagnosed?
So, the main question: how to identify multiple sclerosis? After all manifestations have been analyzed and similar diseases have been eliminated, the doctor must move on to a more accurate analysis, which with almost 100% probability confirms or refutes the diagnosis of MS.
The first step is a neurological examination. Thanks to the examination, the doctor has the opportunity to determine the level of sensitivity impairment and determine whether the patient is disabled.
After a neurological examination, the patient is prescribed an MRI. This study is considered the most effective method of diagnosis. Thanks to the results of an MRI, medical personnel are able to determine the presence of focal inflammation in the brain, characteristic of this disease, causing disturbances in the transmission of nerve impulses.
At the onset of MS, magnetic resonance imaging is performed exclusively with the use of a contrast agent. The injected contrast accumulates in areas of inflammation, or areas of demyelination. Thus, the doctor is able to establish an accurate diagnosis and record the current level of damage to the fibers of the nerve endings. These data are subsequently used to study the dynamics of the disease.
Immunological testing is also used as one of the methods for determining the disease.
Remember that this disease is a very serious autoimmune disease that has an extremely high rate of progression without appropriate treatment. If you experience even minor symptoms, consult your doctor.
Be healthy, spend enough time on your body and don’t ignore the symptoms that bother you.
Timely diagnosis will ensure the patient many years of active life
How was multiple sclerosis diagnosed before and what has changed to date?
In the absence of additional diagnostic methods that reliably confirm the diagnosis, the doctor was guided by the presence in the anamnesis of typical symptoms of “dispersion”, which either arose or disappeared - thus, the undulating course of the disease manifested itself. Only in the 80s of the last century, the study of brain potentials was added to the clinical signs, confirming damage to areas of the nervous system.
In the late 80s, MRI was used for the first time in diagnostics. During the procedure, a contrast agent was injected. In patients, foci of damaged nervous tissue with the absence of myelin substance were detected. However, at the beginning of the introduction of this method, there were repeated errors in diagnosis. Detecting the disease using MRI diagnostics became possible after the method was improved in 2005.
Database
In collaboration with practicing neurologists, a constantly updated database has been created to collate, track and evaluate a huge amount of data, including demographic information, data on relapse rates, changes in neurological status (EDSS score), the effectiveness of immunomodulatory treatments, etc. .
Unfortunately, this registry does not yet contain information about patients from post-Soviet states:
Unlike most clinical research protocols, the creators of MS Base placed an emphasis on long-term assessments: annually, a neurologist enters data on the number of relapses in a particular patient, the results of basic diagnostic tests and procedures (MRI, evoked potentials, etc.), disease progression (changes in EDSS scores), treatment received. There are no exclusion criteria in the MS Base: information about any patient with multiple sclerosis can be included in the database on an anonymous basis, regardless of the type of course, accumulated neurological deficit, or duration of the disease.
For specialists, MS Base is a unique platform for conducting global observational research, collaboration and exchange of experience. Partial access to information is also open to patients, which allows them to make another attempt to assess possible prospects, compare their level of accumulation of neurological deficits, duration of the disease, frequency of exacerbations with information about other patients living with MS (MS severity calculator, see below).
Open information contains the following data:
Gender statistics of multiple sclerosis incidence
Age structure of multiple sclerosis incidence Duration of MS disease
Disability Score (EDSS)
Frequency of relapses (exacerbations) of multiple sclerosis
Another tool contained on the MS Base website is a calculator that allows you to get a general idea of the current severity of multiple sclerosis and compare it with information about other patients with a similar duration of the disease.
Important! The majority of patients in the database are receiving preventive therapy, which obviously influences the EDSS values.
EDSS Calculator
Because The site is in English, I will provide a brief “User Guide” that allows you to correctly enter the necessary data and interpret the results:
Information taken from https://www.msbase.org
- We select the type of multiple sclerosis: CIS - CIS (clinically isolated syndrome) / RRMS - relapsing-remitting MS / SPMS - secondary progressive MS; or PPMS - primary progressive MS/ PRMS - progressive relapsing MS;
- Opposite each period (in years) of the duration of the disease, we select the corresponding value of the EDSS score;
- Click Calculate.
Provoking factors
– lack of vitamin D in the body; – severe stress; – genetic predisposition, which is expressed in the presence of altered genes; – bacterial and viral diseases.
Some scientists believe that the development of multiple sclerosis is promoted by vaccination against hepatitis B. However, this theory has not been confirmed to date.
There is also an opinion that the pathology can be caused by a virus. For example, it could be a mutated measles pathogen. This theory is confirmed by the fact that in practice the condition of patients improves after the administration of antiviral interferons.
Multiple sclerosis and modern methods of diagnosing multiple sclerosis
Publication date
: 20.12.2015 2015-12-20
Article viewed:
3113 times
Bibliographic description:
Plaksina S.V., Kutashov V.A. Multiple sclerosis and modern methods of diagnosing multiple sclerosis // Young scientist. - 2020. - No. 24. - pp. 273-275. — URL https://moluch.ru/archive/104/24587/ (access date: 02.24.2020).
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a severe disease of the central nervous system, most often occurring among young active people, accompanied by a variety of neurological symptoms, leading to disability over several years. In recent years, there has been an increase in the incidence of MS, as well as a rejuvenation of the patient population.
The reasons that lead to the occurrence of this disease have not yet been fully established. There are many hypotheses. Thus, some scientists associate the occurrence of multiple sclerosis with a genetic defect or viral infection (some researchers classify this disease as a group of so-called “slow infections”). In addition, disorders of the body's immune system have been identified in multiple sclerosis, which does not exclude an autoimmune process as the cause of MS.
During autoimmune processes, antibodies are produced to the tissues of one’s own body, in particular to the myelin sheath in multiple sclerosis. Antibodies, which normally do not attack the cells of one’s own body, but perform a protective role (fighting microorganisms in infectious diseases), in patients with multiple sclerosis begin to destroy their own cells, which are no longer recognized by the body as “its own”, but are rejected as foreign. In MS, these target cells for antibodies are Schwann cells, which produce an insulating substance for nerve conductors - myelin. Recently, data have emerged on specific metabolic disorders of certain substances in patients with multiple sclerosis, which cause the death of Schwann cells (metabolic theory).
Multiple sclerosis is a multifactorial disease. Modern neurology, together with such sciences as biochemistry, immunology, genetics, has achieved great success in the study of this disease and the scientific search does not stop for a minute.
The diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis are:
Age of onset of the disease is from 20 to 50 years.
The presence of symptoms indicating a disease of the brain or spinal cord.
MRI signs of two or more foci of demyelination.
Objective signs of a disease of the brain or spinal cord, identified during a medical examination.
Two or more episodes of exacerbations lasting at least 24 hours, separated by at least one month.
Lack of alternative explanation for presenting symptoms
Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is a very difficult task due to the lack of specific clinical, radiological, electrophysiological and laboratory signs in the early stages of the disease, which would confirm the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis with absolute certainty. Nevertheless, the integrated use of these methods for multiple sclerosis makes it possible to confirm the diagnosis, assess the nature of the course of the disease, the severity and stage of the process, as well as the effectiveness of the treatment. In multiple sclerosis, early diagnosis is important, as timely treatment can slow the progression of the disease.
Methods for diagnosing multiple sclerosis:
Electromyography, evoked potentials (EMG EP)
The method is based on the fact that in MS, due to demyelination, i.e. destruction of the insulator of nerve conductors, the conduction of nerve impulses slows down. The speed of their implementation is recorded by special equipment and subjected to computer processing. Based on the data obtained, the percentage of decrease in the speed of nerve impulses is established, which only indirectly indicates demyelinating pathology.
Computed tomography (CT)
This is a method in which large foci of demyelination can be detected, as well as other signs that occur in patients with multiple sclerosis. Inferior in sensitivity and resolution to magnetic resonance imaging.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
It is a very sensitive method that allows clear visualization of areas of demyelination. However, MRI findings are also not specific because areas of increased intensity described as “areas of demyelination” may occur in other diseases.
Cerebrospinal fluid examination (Lumbar puncture)
The only diagnostic method with high information content. This is a diagnostic procedure during which a needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space between the vertebrae to collect a small volume of cerebrospinal fluid for subsequent laboratory analysis of its composition. Positive results on these tests indicate the presence of an abnormal immune response and are found in 90% of MS patients. However, it should be noted that these tests are not specific for multiple sclerosis (pathological autoimmune reactions are also found in other diseases).
Immunological methods
An innovative technique based on determining the content in blood, taken in a small amount from a vein, of specific markers that are present in patients with multiple sclerosis. This technique provides valuable results in terms of diagnosis and allows you to either confirm or refute the diagnosis of MS.
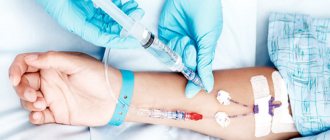
blood test
This method is one of the most innovative in modern medicine, and at the moment is not yet as widespread as previous diagnostic methods. This method was developed and patented by Perm State Medical University named after. E. A. Wagner. Using special reagents, the presence in the blood of certain substances that are found in patients with multiple sclerosis is determined.
Despite the large number of new research methods, at the moment the dominant role is occupied by the clinical diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. An ophthalmological examination has not lost its value. An ophthalmologist detects changes in the fundus that are characteristic of patients with multiple sclerosis. In addition, he examines the visual fields (with multiple sclerosis, the phenomenon of loss of visual fields often occurs).
Thus, it should be remembered that the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is made by a neurologist on the basis of clinical data and additional examination methods described above, and it is impossible to make a final diagnosis based on the data of any one method (I had to meet with a patient who was mistakenly diagnosed with MS based on data from EMG with EP and MRI only).
- Bisaga G. N., Pozdnyakov A. V. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy // Multiple sclerosis / ed. I. A. Zavalishin, V. I. Golovkin. M., 2000. pp. 244–249.
- Internal medicine according to Tinsley R. Harrison. Ed. E. Fauci, Y. Braunwald, K. Isselbacher, J. Wilson, J. Martin, D. Kasper, S. Hauser and D. Longo. In two volumes. Per. from English - M., Practice - McGraw - Hill (joint publication), 2002.
- New technologies for prediction of therapy for multiple sclerosis / Golovkin V.I., Pozdnyakov A.V., Kamynin Yu.F., Martens // Bulletin of Siberian Medicine. - 2010, No. 4. - S. - 138–144.
- Pozdnyakov A.V. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in the diagnosis of remission and exacerbation of the disease // Immune-mediated relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis / ed. V. I. Golovkin, N. M. Kalinina. St. Petersburg: “Rose of the World”, 2003. pp. 35–50.
- Pozdnyakov A.V. The role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the diagnosis of brain diseases: abstract. dis. ...Dr. med. Sci. St. Petersburg, 2001. 32 p.
- Multiple sclerosis: a guide for doctors / T. E. Schmidt, N. N. Yakhno. -2nd ed. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2010. - 272 p.
Types of studies of biological fluids
When taking tests, it is important to follow all prescribed measures regarding:
- physical activity;
- smoking;
- psycho-emotional state.
Let's look at what types of tests are taken and what their results show.
Examination of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to determine the extent of damage to this part. A puncture is made with a needle at the lumbar level, the analysis is carried out immediately (no later than half an hour) in four stages:
- biochemical research - study of the qualitative and quantitative composition of cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of tumors;
- microscopic – counting elements at the cellular level;
- macroscopic – by color (normally transparent), red indicates the presence of red blood cells (inflammation), green or yellow indicates the presence of meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, fibrinous film (normally absent);
- bacterioscopic and bacteriological - allows you to determine the presence of bacteria (tuberculosis bacilli, meningococci, streptococci and staphylococci), determine immune reactions (Kahn, Wasserman, RIBT, Wright, etc.).
In multiple sclerosis, oligoclonal immunoglobulin G is detected in the cerebrospinal fluid, which indicates the influence of the immune system on the brain (infection). Cerebrospinal fluid and venous blood (serum and cerebrospinal fluid) are taken for analysis.
IMPORTANT! The results are obtained within half an hour after collection and the answer is positive in the presence of IgG.
Quantitative IgG
It is done when collecting venous blood to check for the presence of infections, rubella or its history in the past, to count the number of antibodies (oligoclonal immunoglobulin G indicates the presence of MS at any of its stages), the execution period is about ten days.
IgG value:
- Reference values are the polyclonal type of IgG synthesis.
- Positive result – MS, pathologies and damage to the nervous system, vascular inflammation.
- A negative result is normal.
The analysis takes serum from venous blood (peripheral vein) or cerebrospinal fluid, and the analysis takes nine days.
Its increased concentration indicates the presence of destruction and inflammation. Used to predict and monitor the development of MS.
Study results – negative (normal), positive (RS)
Albumin index
Sampling of venous blood and CSF to assess nutritional status and protein-synthetic liver function. It is done immediately after sampling using the calculation of the index - the amount of albumin in the blood plasma is divided by the amount of albumin in the esophageal fluid. Its low rate indicates the presence of pathologies and diseases.
Total protein in cerebrospinal fluid
REFERENCE! CSF is used immediately after collection for the assessment and diagnosis of infectious and inflammatory diseases, oncological changes, and diseases of the central nervous system.
If the analysis results increase, they indicate a disease:
- bacterial (0.4-4.4 g/l);
- cryptococcal (0.3-3.1 g/l);
- tuberculous (0.2-1.5 g/l) meningitis and neuroborreliosis.
Gamma globulin
A venous blood test is performed to assess the amount of immunoglobin antibodies or immune gamma globulins. A certain amount indicates the presence of various infections and inflammations.
- The norm is IgA (0.4–2.5 g/l), IgG (7–16 g/l).
- IgM in women over 10 years of age (0.7–2.8 g/l).
- In men over 10 years of age (0.6–2.5 g/l), IgD (0.008 g/l or lower), IgE (20–100 kU/l).
Comparing the concentration of gamma globulin in the blood and CSF helps to assess the stage of development of MS, as well as the nature of its manifestation, the execution period is 11 working days.
The norm for a healthy person is from 7 to 16 g/l. An increase in the norm indicates the presence of diseases (MS, infections).
IgG ratio
Normally, IgG in blood serum is 70-80/about all immunoglobulins. The content of the main part of the antibodies indicates resistance to a number of viruses and bacteria. Oligoclonal accumulations in the cerebrospinal fluid are found in 98% of MS patients. The CD4/CD8 ratio is 2:1.
When sclerosis is not “sclerosis”
Multiple sclerosis is a completely different disease than age-related memory problems, popularly called “sclerosis.”
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease in which the myelin sheath of fibers in the brain and spinal cord is spontaneously damaged and replaced by connective tissue.
In the world there are about two million such patients, in Russia – 150 thousand. It is believed that multiple sclerosis will not significantly reduce life expectancy, but its quality can greatly worsen.
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis:
Loss of sensitivity in certain areas of the body (numbness),
sudden significant decrease in vision, double vision,
motor disorders (impaired balance, changes in gait).
Differential diagnosis
The specificity of the disease is manifested in the general nature of symptoms and diagnostic methods. Only based on the totality of the results of the studies, a specialist makes an accurate diagnosis.
Mandatory criteria confirming multiple sclerosis:
- Anamnesis that revealed at least 2 lesions located separately from each other.
- Slow progression of sclerosis.
CNS disorders are not explained by other pathologies:
- The patient has impaired sensitivity and pelvic disorders.
- Remissions occur in patients under 40 years of age
- A brain tumor has been ruled out .
On this topic
- Multiple sclerosis
Let's find out what multiple sclerosis is in young people
- Editorial office of Neuralgia.ru
- March 26, 2020
The composition of the spinal cord fluid is significantly changed.
Multiple sclerosis is a severe disorder that is often the cause of disability. Timely diagnosis is the key to proper treatment. It is designed to protect a person from severe complications of sclerosis: bladder problems, pneumonia, bedsores, leg paralysis, changes in mental performance.
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by:
The onset of the disease is at the age of 15-50 years;
alternation of exacerbation and remission (situation “doctor, I had these sensations, but then they passed”);
thermosensitivity (even if the patient has undergone a course of treatment, and it was effective, the discomfort resumes when heated - hot bath, solarium, beach);
a feeling of “current running along the spine”;
How to “catch” a disease
A specialist who may suspect a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is a neurologist . But very often the patient first goes to other doctors - for example, to an ophthalmologist. If, with complaints of sharply decreased vision, the ophthalmologist does not see changes in the eyes, you need to ask him to refer the patient to a neurologist. Perhaps the problem is optic neuritis, a damage to the sheath of the nerves that carry signals from the eye to the brain.
The diagnosis of “multiple sclerosis” is very difficult to make, since its main criterion is the prevalence (“dispersal”) of symptoms in space and time.
“Widespread in space” in this case means different complaints - when describing his condition, the patient mentions problems with vision, coordination, and weakness in the legs that happened at different times. At the same time, lesions corresponding to the complaints are recorded on MRI.
“Prevalence over time” means that the patient describes various manifestations of the disease in development (the appearance and disappearance of symptoms, periods of exacerbation and remission), and MRI shows the presence of foci at different times - active and no longer active.
Multiple sclerosis may manifest itself in the form of a clinically isolated syndrome – a one-time manifestation of the disease. But, since in domestic practice the diagnosis of “multiple sclerosis” is usually made only after making sure of the chronic nature of the disease (when the symptoms that fit into its picture are repeated over the course of a year), in case of an isolated attack the diagnosis of “multiple sclerosis” is usually not made, but systematic treatment - not prescribed.
Integral treatment
The goal of this therapy is to restore nerve cells in the period between exacerbations. At the same time, medications prescribed by a doctor protect the spinal cord and brain from attacks by the immune system.
During this period and when multiple sclerosis is in remission, treatment is carried out using drugs such as Cyclosporin A, Azathioprine, Mitoxatron and others.
Sometimes the patient is offered surgical treatment. In order to reduce the immune attack, his spleen may be removed or sometimes such patients undergo a bone marrow transplant.
1. Garlic oil. To prepare it, the chopped head of the vegetable is infused in sunflower oil. Consume with lemon juice. 2. Honey with onions. This remedy strengthens the blood vessels of the extremities and resolves blood clots. To prepare it, squeezed onion juice is mixed with honey.3. Alcohol tincture of garlic. This remedy fights sclerotic formations and helps relieve vascular spasms.
In addition, traditional medicine recommends that all patients with multiple sclerosis not include sweets in their daily diet. The menu should include foods with low cholesterol levels, as well as those that do not cause high blood pressure. In this case, it is advisable to season the dishes with vegetable oils. Frequent drinking of green tea and natural juices is also recommended.
What tests detect MS?
The following methods are effective for identifying multiple sclerosis:
Spinal cord puncture with analysis for oligoclonal antibodies. The accuracy of diagnosis is 85-95%.
In terms of the degree of danger, the procedure is comparable to a regular injection (there may be a headache after the procedure; stories about when legs were lost after a spinal puncture are MYTH).
MRI – 70-90% when repeating the procedure every 3-6 months for a year. Once the diagnosis is established, there is no need to repeat the MRI.
Visual evoked potential – diagnostic accuracy is 50-90%. The method involves placing electrodes on the surface of the head to trace the path of the signal from the retina to the visual cortex. Effective if the patient has complaints to the ophthalmologist.
At the same time, multiple sclerosis must be distinguished from inflammatory diseases, hereditary and infectious diseases, which have a similar analysis pattern.
If the patient has been ill for a long time and the symptoms are clear, a diagnosis can be made without special tests based on a conversation with a neurologist.
In difficult cases, the patient may be prescribed additional studies (for example, genetic). In particularly difficult situations, diagnosis can take up to several years.
The scientific literature describes cases where patients with an incorrect diagnosis of MS were observed by doctors for more than ten years and even participated in clinical studies.
The “insidiousness” of MS is that over time, the foci of the disease are restored and look healthy on MRI. Thus, it is difficult to assess the course of the disease from each individual image.
Blood analysis
Laboratory tests for MS play a supporting role. Imaging methods are used for diagnosis. Only the presence of foci of demyelination allows a diagnosis to be made and treatment to begin. But MRI is a complex and expensive procedure. And it needs to be done every six months.
Therefore, scientists around the world are developing an effective test to detect MS in the early stages. There is a search for markers that increase during the autoimmune process. And the first results have already been received. We will talk about this in detail below.
Complete blood count (CBC)
How to submit?
Blood is taken from a finger or from a vein. The first method is preferable. The test is performed on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours must pass after the last meal.
What is UAC used for?
The test shows any changes in the body. It's non-specific. During the inflammatory process, there is an increase in leukocytes, lymphocytes and ESR. In patients with MS during remission, the analysis does not show any changes.
Preparing for the study
No special preparation is required. It is better to donate blood on an empty stomach.
Side effects
Blood is taken from a finger using a special instrument. The laboratory technician uses individual gloves for each patient. Use a sterile scarifier or lancet. If sanitary standards are observed, there are no complications.
| Indicators | Norm | For MS |
| Leukocytes | 4-9 at 109 | Possible increase during exacerbations |
| Red blood cells | 3.7-5.1 per 1012 | Without changes |
| Platelets | 180-400 at 109 | Without changes |
| Hemoglobin | 120-160 g/l | Without changes |
| Hematocrit | 34-46% | Without changes |
| Formula: rod | 1-6% | Without changes |
| Segmented | 47-72% | Possible decrease in performance |
| Eosinophils | 0-5% | Without changes |
| Basophils | 0-1% | Without changes |
| Lymphocytes | 20-40% | Possible promotion |
| Monocytes | 2-9% | Without changes |
Biochemical blood test (BAC)
How to submit?
Blood is drawn from a vein. The cubital vessel in the cubital fossa is used. If it is impossible to carry out analysis here, any accessible place is punctured (femoral vein, veins of the forearm or hand).
What is BAK used for?
The test reflects the work and function of organs. It is nonspecific for MS. During illness, changes in the ratio of blood proteins are formed. Globulin fractions increase.
Preparing for the study
Blood is donated on an empty stomach. You must not smoke before the examination. The day before you should avoid eating fatty foods.
Side effects
Hematomas at the puncture site are possible if the sampling technique is violated or if the vessel becomes fragile. In rare cases, phlebitis and thrombophlebitis of the cubital veins form.
| Indicators | Norm | For MS |
| Total protein (fractions) | 65-83 g/l | Possible increase during exacerbations due to the globulin fraction |
| Bilirubin (total, free and bound) | 3.4-17.1 µmol/l 1-7.9 µmol/l 1-19 µmol/l | Promotion due to common and free faction |
| ALAT/ASAT | up to 45/up to 37 units | Without changes |
| Urea | 2.8-7.2 mmol/l | Possible promotion |
| Creatinine | 53-115 µmol/l | Possible promotion |
| GGTP | Up to 55 units | Without changes |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 30-120 U/l | Without changes |
| Uric acid | 150-420 µmol/l | Without changes |
| Potassium/Sodium | 3,5-5,5/135-145 | Without changes |
| Chlorine | 98-107 | Without changes |
| CRP (c-reactive protein) | 0-5 mg/l | Possible increase during exacerbation |
Routine biochemical testing is not used to diagnose multiple sclerosis. Changes in tests are nonspecific and depend on the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Other tests
The role of vitamin D deficiency in the development of multiple sclerosis is now being actively discussed. It is known that residents of northern latitudes are more likely to suffer from the disease, while patients who received the supplement responded better to treatment. Therefore, once the diagnosis is established, it is recommended to undergo a calciferol 25-OH test.
How is it surrendered?
The test is performed on an empty stomach. Blood is donated from a vein. Avoid taking vitamin D supplements or medications the day before.
Why is it used in diagnostics?
A correlation has been found between vitamin deficiency and the progression of disease symptoms.
Side effects
Blood is drawn from a vein. After manipulation, hematoma, phlebitis and thrombophlebitis of the cubital vessel may appear.
Normal European values for total vitamin D:
- 60 – 100 ng/ml;
- 150-250 nmol/l.
Standards of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists:
| Norm | 30-100 ng/ml |
| Failure | 20-30 ng/ml |
| Shortage | Less than 20 ng/ml |
Signs of exacerbation
This is the return of symptoms that were already noticed, without fever or fever (that is, it is not an accompanying cold or infection), and the appearance of new symptoms.
It should be kept in mind that approximately one out of ten new MS lesions manifests symptoms; the patient simply does not feel the appearance of the remaining nine.
The main task of a patient in an exacerbation is to see a doctor as quickly as possible to receive treatment.
The patient’s goal is to go from an exacerbation into a remission phase, if possible, completely eliminate all symptoms during remission and remain in remission for as long as possible.
In remission, the patient needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, exercise, quit smoking and undergo regular examinations to assess walking pace, balance, and depression. MRI is used only to evaluate the effectiveness of prescribed medications.
The goal is to maintain functionality for as long as possible.
Medicines
Medicines for multiple sclerosis are prescribed by a doctor . Drugs may include corticosteroids, plasmapheresis, symptomatic drugs that relieve individual symptoms, drugs that control the immune system, and sometimes painkillers. The risk of developing multiple sclerosis is a low level of vitamin D, which is maintained taking into account the recommendations of an endocrinologist.
It is important for the patient to follow the treatment regimen not only during exacerbations, but also during periods of remission, since the body needs support even when the course of the disease does not appear outwardly.
Worse and worse
Around the world, 2.3 million people are diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. In Russia, according to experts, there are at least 150 thousand such patients. Most of them suffer from relapsing multiple sclerosis (RRS), which progresses with periods of a relapsing form of the disease, characterized by exacerbations followed by remissions - that is, quiet periods when the condition of patients improves.
But over time, disorders still accumulate, and the disease steadily progresses, new symptoms appear or existing symptoms worsen. Nevertheless, thanks to timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment, doctors manage to curb the development of pathology.