No one is insured against an unfortunate fall, an accidental blow, a sports injury or a traffic accident. The hyperactivity and insatiable curiosity of modern children also often lead to traumatic brain injuries, the annual number of which reaches 1 million worldwide. One type of these injuries is a concussion.
Main symptoms and severity of injury
The main symptoms of a concussion: loss of consciousness, dizziness, nausea, poor coordination of movements, sweating, pale skin.
The severity of the injury allows us to distinguish several degrees of its manifestation. Although in our country cases of using such a classification are not so frequent. The first degree is characterized by a short-term loss of consciousness for several minutes. There are cases when fainting does not occur at all. Within 15-20 minutes, the injured person feels better, but experiences nausea. The pulse is unstable, breathing is rapid. But these manifestations are not caused by the resulting brain damage, but by a state of stress.
The second degree is characterized by loss of consciousness for a longer period (10-20 minutes). If you look at the victim's pupils, you will notice a difference in their sizes. This phenomenon is called anisocoria in medicine. A person also experiences a headache, difficulty focusing attention on an object, a disturbance in temporal orientation, and sometimes convulsions. If you ask a question, you can hear incoherent speech and answers that are inadequate to the situation.
The third degree is the most severe and severe concussion in terms of consequences. Fainting can last for an hour, sometimes a coma occurs. Some victims experience memory loss - they do not remember the events that preceded the injury. In addition to the symptoms inherent in the second degree, heavy bleeding from the nose and ears, tinnitus, and severe headache appear. Photosensitivity and painful reaction to noise are also noted.
Symptoms manifest themselves in different ways, much depending on the person’s age. In children under one year of age, there may be no loss of consciousness, but drowsiness and increased sweating will appear. Increased heart rate and pale skin are a clear sign.
Teenagers and adults are more likely than children to lose consciousness, even if it is a mild or moderate concussion. In cases of severe trauma, this age group experiences long-term memory lapses regarding previous events. Fainting due to head trauma is less common in people aged 60 years or older. But disturbances in spatial and temporal orientation make themselves felt.
An important prognostic criterion is the intensity of clinical manifestations of the lesion. It directly correlates with the severity of damage to nerve tissue. In this regard, it is customary to differentiate several degrees of severity of concussion, for each of which characteristic clinical signs are described:
- A slight bruise of nerve tissue may not manifest itself in any way. In many cases, patients complain only of a headache and short-term disorientation in space. This degree of concussion is also characterized by unpleasant sensations in the neck, since this part of the spine often absorbs the blow received. In most cases, victims remain conscious. They also complain of visual hallucinations, ringing in the ears and confusion. All of these concussion symptoms subside within a few hours of the injury. In some cases, unpleasant sensations persist for 2–3 days.
- More severe contusion is observed with moderate severity of injury. Patients complain of nausea and vomiting. The headache is of a strong bursting nature. Often victims are unable to move, fall and lose consciousness. A specific sign of a concussion is the appearance of seizures. They are not observed in all cases, but are considered grounds for urgent hospitalization. Changes in the nature of pulse and breathing are also recorded. If the victim for some reason does not seek medical help, cognitive impairment develops, which can persist for the rest of his life.
- A severe concussion is associated with a high risk of complications. A distinctive feature of this problem is prolonged loss of consciousness. In the absence of adequate care, the patient may die from damage to the centers responsible for breathing and blood circulation. Severe convulsions and differences in the size of the pupils of the right and left eyes are often noted. Subsequently, patients suffer from amnesia, speech and coordination problems. A severe concussion requires long-term rehabilitation, which does not always allow one to get rid of all complications after the injury.
Forecast
Patients who have suffered a concussion are recommended to undergo clinical observation by a neurologist for a year.
Mortality with this pathology is not recorded, active symptoms are safely resolved within 2-3 weeks, after which the patient returns to the usual mode of work and social activity.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
A concussion is damage to the structure of the brain, its functions and characteristics. Only a few can correctly explain what a “concussion” is and how to correctly diagnose and prescribe rehabilitation for the victim?
We will try to answer this question in this not very long article!
There are few people in the world who have not heard anything about concussions. Most, both men and women, can talk about situations in which they have been and received various types of injuries. In some cases there were concussions, and maybe someone was on the verge of it. But no one can give a clear answer. They usually say that there was a severe headache and dizziness, but “I” did not turn anywhere.
Let's get creative! Imagine a decent-sized egg - it will be a human head, where the skull replaces the shell, the brain is the yolk inside, and the white is cerebrospinal fluid. Introduced? Now let’s shake the egg or hit it. The yolk floating inside collides with the shell, and each touch leaves marks on the yolk.
The same thing happens with the human brain (usually everyone has one!). He is very gentle and fragile. Any contact of the brain with the skull leads to a change in the shape of brain cells or a so-called concussion. The condition of a concussion is not a pleasant one. There are cockroaches rushing somewhere in my head all the time! But this is much better than if, upon impact, the integrity of the skull was not preserved.
The consequences of such injuries can be different. For example, loss of connection. This can occur selectively between any brain cells, and maybe between entire departments. There is poor interaction between the trunk and its identical opposite hemispheres.
Some symptoms of a concussion
Such symptoms include an increase in the size of the eye pupils, vomiting, even slight memory loss, partial or complete loss of taste and impaired sense of smell. But a head concussion does not always cause these symptoms, and if something bad happened to you, after which you have been dizzy for several days or have signs of a headache, contact the clinic. See a neurologist to examine your skull.
Concussion
Most concussions occur due to some kind of blow. And blows reach our heads in different ways and usually cause swelling and minor hemorrhages. These can, of course, include reckless fights, serious falls with injuries and, of course, accidents. A concussion occurs only due to a strong blow (the direction does not matter) to the head, because the brain must be displaced in such a way that a collision with the skull occurs. A weak impact does not cause a concussion.
After such a strong blow, damage occurs and sometimes even destroys some of the nerve cells that are responsible in the body for the passage of impulses to the brain. There comes disorder in their work, you can call it a neural storm in the brain. It is cellular rabies that leads to significant loss of vision and loss of memory (full or partial), vomiting and nausea, headaches, etc.
The brain heals us!
It's good that our amazing brain itself is engaged in our treatment. He voluntarily begins the process of pacifying rebellious neurons by increasing glucose production. After all, with the help of glucose, blood vessels contract, and this means the work of the brain slows down. And the restoration process will end only when everything returns to its normal appearance.
Self-medication usually takes several weeks. The only requirement: do not receive new concussions or negative impacts during this period. Otherwise, new damage may not be reversible and will lead you to dementia. The main medicine in this situation is peace and only peace!
Lie down and rest in silence, preferably without TV. So as not to disturb the nerve cells. If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor, as rest alone may not be enough! You may need treatment with medications, because the head is not to be trifled with! Take care of your health!
Pathogenesis
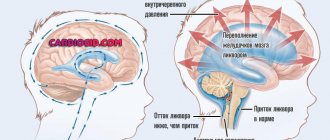
The following mechanical factors influence most of all - fixation of the head at the time of the concussion or it was in motion, the second moment is associated with an increase in intracranial pressure, which causes transient ischemia (oxygen starvation) of the brain.
All this causes various biochemical and biophysical changes in cells, which are often reversible. There are also symptoms that are combined into post-concussion syndrome - dizziness, headaches and various manifestations of apathy and depression.
For various brain injuries, transcranial micropolarization of the brain is very effective.
Every third person in the world has signs of pituitary adenoma, but do not despair. It is better to familiarize yourself with the methods of treating the disease.
Actions before the doctor arrives
Calling an ambulance is the first thing to do for a person who has suffered a traumatic brain injury. To avoid dirt, wounds and abrasions on the head must be treated. Any antiseptics will do - Miramistin (regular or in the form of a spray), Septomirin. It is advisable to treat the edges of wounds with iodine solution.
If there is one hundred percent certainty that there is no spinal injury, the victim must be placed on his right side. The head should be slightly raised, and the left arm and leg should be bent at an angle of 90 degrees. This position of the body will ensure immobility and prevent rolling over onto your back.
If drowsiness occurs, you should try to prevent the patient from falling asleep until the ambulance arrives. Otherwise, there is a chance of falling into a coma. But there is no sufficient evidence for this assumption in practice.
If loss of consciousness occurs, first aid for a concussion consists of giving the body a special position. The head should be slightly thrown back and the face should be directed towards the ground or floor. This will allow air access and prevent tongue retraction and suffocation in case of vomiting.
You can apply dry ice to the damaged area if you have it on hand. Any item that can provide cooling to the damaged area will do. If waiting for doctors is not possible, the patient must be taken independently to the nearest trauma department. During transportation, it is advisable to reduce the number of shaking of the victim.
What are the signs of a concussion?
What are the symptoms of a concussion?
The main signs of a concussion in adults:
- Almost always, during SGM, a person loses consciousness. The stronger the damage, the longer the period of fainting; in extreme cases, coma occurs.
- The manifestation of disorientation, memory is also impaired. The duration of the period of memory loss can also be used to judge the damage received.
- Nausea, vomiting, pallor, dizziness and headache, ringing in the ears, blurred vision, increased breathing - all these are also signs of a concussion. The condition of the eyes can also tell a lot - constricted or, conversely, dilated pupils are a sign of a concussion, as the nerve pathways responsible for vision are disrupted. Also, by the reaction of the pupils to light, one can judge the degree of concussion - they react sluggishly - a weak concussion, they do not react - a severe concussion. If only one icon reacts to light, one of the cerebral hemispheres is damaged.
Loss of consciousness, nausea and vomiting are always the first and main signs and symptoms of a concussion.
Based on the duration of symptoms, three degrees of SHM are distinguished:
- Mild - the patient is unconscious for no more than 5 minutes. Signs and symptoms of a mild concussion: pale skin, decreased or absent muscle tone in the arms and legs. The heart rate may either increase or decrease. Some people vomit.
- Average - loss of consciousness from 5 to 15 minutes. Disintegration of consciousness, retrograde amnesia, nystagmus (shifting eyes), nausea and vomiting, headaches and dizziness, adynamia and asthenia are observed.
- In case of loss of consciousness for a period of more than 15 minutes or falling into a coma, a severe degree of SHM is stated.
Delayed symptoms are symptoms that appear weeks or even months after the injury. These include:
- compressive headache, which usually appears a week and a half after the injury, less often after a month;
- causeless dizziness;
- fatigue developing into asthenia;
- irritability;
- increasing memory and attention disorders;
- causeless feeling of anxiety, aggressiveness, tearfulness;
- loss of hearing, vision, appearance of extraneous noise;
- stress resistance decreases, a craving for alcoholism appears;
- disorder of sexual functions.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a concussion is difficult due to the paucity of objective data, the lack of specific signs and is based mainly on the patient’s complaints.
One of the main diagnostic criteria for the disease is regression of symptoms within 3–7 days.
In the structure of neurotrauma, concussion accounts for 70 to 90% of all cases.
In order to differentiate a possible brain contusion, the following instrumental studies are carried out:
- radiography of the skull bones (no fractures);
- electroencephalography (diffuse cerebral changes in bioelectrical activity);
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (no changes in the density of gray and white matter of the brain and the structure of the cerebrospinal fluid containing intracranial spaces).
Carrying out a lumbar puncture in cases of suspected brain injury is contraindicated due to lack of information and a threat to the patient’s health due to possible dislocation of the brain stem; the only indication for it is the suspicion of the development of post-traumatic meningitis.
Diagnostic procedures
Only a thorough diagnosis and collection of the patient’s medical history will allow the attending physician to choose the right tactics for managing the patient. Despite the satisfactory condition and minor deviations from the norm, it is not advisable to cancel the medical examination. A concussion creates a risk of complications if the injury is not fully understood.
The patient is interviewed using the Glasgow scale. If the test result is from 13 to 15 points, then the doctor was able to determine a concussion. In this case, the following studies may additionally be prescribed:
- EEG;
- Vascular ultrasound;
- X-ray of the head and cervical spine;
- MRI or CT.
An EEG helps measure electrical activity in the brain. Examination of the fundus will help you indirectly find out about the presence of increased intracranial pressure.
Since some symptoms appear 12-15 hours after injury, patients are not recommended to leave the hospital. If the patient's condition worsens, the treatment period increases.
Consequences of trauma in children
Although the symptoms of a concussion disappear quickly, recovery can take a long time for teenagers and children. The pathological condition in patients in this category can worsen even due to fluent reading.
Doctors say that severe TBI can affect a child's brain activity and development. The patient's condition and symptoms of the disease may become more complicated with subsequent skull injuries several years after the concussion. Changes in the neurophysiology of the brain center are observed most often after the third episode.
Infants are characterized by more frequent regurgitation, and loss of consciousness is not observed at all. Increased excitability may be observed, sleep may be disturbed, and increased pallor is characteristic in the first minutes after the impact.
After an injury, preschoolers are more likely to experience adult-like symptoms such as loss of consciousness, nausea, and vomiting.
The child has a headache, the pulse may become faster or slower, there are jumps in blood pressure, sweating and pallor.
Sleep disturbances, tearfulness and moodiness may also occur.
Some children experience post-traumatic blindness - immediately after the injury or later, loss of vision occurs from a couple of minutes to several hours - then it goes away on its own. The nature of this disorder is not clear.
It is worth remembering that in children the body’s compensatory capabilities can suppress the manifestation of symptoms for a long time, but then the picture worsens sharply. The child may fall during the day and only in the evening the symptoms will begin to increase.
Read more about the symptoms of concussions in children in our article.
The first signs and symptoms of a concussion in children that parents should know As we all know, the child’s body is very mobile.
Rarely do children develop without receiving blows and bruises and abrasions.
Among all types of injuries, the first...
Features of treatment and prescribed medications
After determining the severity of the injury, the doctor determines the specifics of further therapy. In case of minor injury, the patient can be treated at home. It is important to strictly follow the instructions. If the injury is severe or moderate, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
Nootropic drugs are prescribed - Nootropil, Piracetam, Picamilon, etc. Vasotropic drugs help prevent complications at the vascular level - Oksibral, Teonicol, Vasotropin. Pantogam, Cogitum and Vasobral will help reduce fatigue and increased irritability.
Diuretic medications will help eliminate brain swelling. B vitamins and folic acid will speed up the recovery of damaged nerve cells. For severe headaches, treatment is symptomatic - doctors prescribe Pentalgin, Maxilgan. Sometimes it is necessary to take tranquilizers, for example, Phenazepam.
The severity of the injury affects the recovery time. In the most severe forms, hospital stay lasts for several months. A mild concussion can be treated within a couple of weeks. In any case, a gentle regimen is indicated for the patient.
What drugs are prescribed
Magnesia is the most commonly prescribed medication; rest and sleep play an important role in treatment. Medicines are needed to relieve headaches, dizziness, anxiety, insomnia and other symptoms.
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
Therefore, the patient is recommended to take painkillers, sedatives and sleeping pills (preferably in tablet form).
As a pain reliever, the following are prescribed: Analgin, Sedalgin, Pentalgin. Sedatives are: Valerian, Corvalol, Valocordin, Motherwort. The most commonly used tranquilizers are: Sibazon, Afobazol. Donormil and Relaxon will help you get rid of insomnia.
To quickly and completely restore the functioning of the brain, it is necessary to undergo a full course of metabolic and vascular therapy. In this case, it is best to combine vascular drugs with nootropic drugs (Cavinton, Glycine, Noopept).
In order to prevent the development of possible complications in time, you should undergo clinical observation for one year by a neurologist at your place of residence.
First aid
The reaction and composure of people who are close to the victim determine his further condition and the likelihood of any consequences occurring after a concussion or brain damage. When the first symptoms of a pathological condition occur, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance team. While waiting for medical workers, the victim needs to provide first aid:
- Place the patient on a horizontal surface if he is conscious. Raise your head with a pillow or cushion (folded clothing), cover with a warm blanket. if the victim has lost consciousness, then he cannot be carried or moved;
- protect the injured person from sharp sounds and light. Find out about his well-being, sensations, details about what happened and the nature of the TBI;
- track heart rate and blood pressure. It is necessary to talk to the victim only in a whisper, preventing him from falling asleep.
If a person is unconscious, he must be revived with the help of medical ammonia.
When providing first aid, you should not perform the following actions:
- Transport or move a patient if his condition is constantly deteriorating and his life is in danger.
- Give the victim drink and food, as such manipulations can complicate symptoms and provoke vomiting.
- Apply lotions and compresses to the injured area.
- Give the person pain medications.
- Make the victim nervous.
- Try to bring the person to his senses by making noise, shaking or slapping him.
Upon arrival of the emergency room, medical workers need to talk about their observations, conclusions and what is known about the event that occurred, the first signs of a concussion. This will enable doctors to determine the severity of the TBI, make a diagnosis, and prescribe the correct treatment.
The victim needs to radically change his diet, the intensity of mental and physical activity, leisure time and psychological attitude. In the absence of adequate treatment, complications from a concussion can be quite serious and manifest themselves many years later.
First, be sure to consult a doctor who will select the most suitable course of treatment for you.
For at least the first 2-3 days, bed rest.
The best cure for SHM is sleep; if you have problems with it, you can take sedatives based on valerian and motherwort.
You also need to reduce the load on the brain - you should stop reading, working on the computer and watching TV for a few days.
You should also avoid bright lighting - curtains on the windows and a night light in the evening will help you with this.
A common consequence of SHM is cerebral edema - to prevent it, it is recommended to drink less, leave mineral water in the drink, and exclude coffee and tea. In your diet, you should stick to fermented milk and vegetables; citrus fruits, bananas, and walnuts are useful.
Avoid household chores, physical activity and driving for two weeks.
Features of the mode
While at home during the recovery period, the patient should remain in bed. Its duration depends on the severity of the concussion. It is important to remember that on these days the following are contraindicated:
- watching TV;
- reading books, newspapers, magazines;
- working or playing on a computer;
- long conversations.
The patient’s nervous condition is stabilized with the help of sedatives: Motherwort or Valerian tablets, Corvalol drops. The room where the person who has suffered an injury is located must be well ventilated, and the temperature must be maintained at 18-20 degrees.
Sleep is also part of successful recovery, as long as it lasts at least 10 hours a night. If photophobia is observed, then it is better to close the curtains in the room. Extraneous noise should be excluded, but pleasant relaxing music (not with headphones!) will be beneficial.
The patient may be under the supervision of an on-duty therapist if we are talking about home recovery. At the hospital, observation is carried out by a surgeon and a neurologist. In extreme cases, consultation with a neurosurgeon is required.
Treatment
Therapy in case of diagnosing a concussion should be comprehensive. Its intensity directly depends on the degree of damage.
So, with a mild concussion, treatment at home is allowed, but only with the permission of a doctor. Basic recommendations:
- Bed rest, long sleep.
- While you are awake, you are allowed to listen to music (but not through headphones).
- It is necessary to adhere to a dairy-vegetable diet with minimal inclusion of table salt.
- Herbal soothing teas and infusions are used as therapeutic agents.
More serious injuries cannot be avoided without drug treatment and hospitalization of the patient. After three days, the doctor makes a conclusion about the possibility of transferring the patient to outpatient treatment. What drugs are used to treat concussions?
- Painkillers – Baralgin, Ketorol, Sedalgin.
- Neuroleptics (to improve blood circulation in brain structures, speed up metabolism) - Piracetam.
- Medicines to improve metabolism in tissues, antioxidants - Mexidol, Mexiprim.
- Means for preventing and reducing cerebral swelling - Cavinton, Eufillin, Sermion, Trental.
- Calming and sleeping pills, the prescription of which is justified for concussion - Finlepsin, Phenobarbital, Glycine.
- Anticonvulsants – Nozepam, tincture of hawthorn, motherwort, Phenibut.
The patient is prescribed plenty of fluids - up to 3 liters of water per day, vitamins B and C, magnesium, Omega - 3. If, after the completed course of treatment, symptoms such as dizziness, decreased performance, memory impairment, increased irritability persist, an additional course of B vitamins is prescribed , Betaserks, Westinorm, motherwort tincture.
After diagnosing and establishing the extent of the injury, the specialist determines how to treat the concussion. Moderate and severe conditions are treated in a hospital setting. If a patient is diagnosed with a mild concussion, it is possible to undergo therapeutic treatment at home.
Medicines
To restore normal brain function, the patient is prescribed medications with different directions; they should be taken according to the doctor’s recommended regimen:
- Piracetam, Aminalon, Nootropil, Picamilon are nootropic neuroprotectors for restoring the functioning of the nerve nodes of the brain.
- Cavinton, Gliatilin, Teonicol are vasotropic drugs to stabilize the functioning of blood vessels and prevent the development of complications.
- Pantogam, Cogitum, Vasobral - to eliminate increased fatigue, impotence, increased irritability.
- Diuretics - to prevent swelling of brain tissue.
- Vitamin complexes with folic acid, phosphorus, group B drugs - to accelerate the regeneration of damaged gray matter cells.
Treatment for even a mild concussion can take anywhere from two weeks to 30 days. The more severe the injury, the longer it is necessary to adhere to a gentle regimen. Sometimes you have to stay in the hospital for 2-3 months.
Features of the mode
Has the person been diagnosed with a concussion? At home, bed rest is observed for three days or more, depending on the patient’s condition. When treating a concussion, it is strictly prohibited:
- Watch TV.
- Read.
- Play games on your tablet or phone.
- Work on computer.
- Talk for a long time.
- Be nervous and worry.
To normalize the nervous state, the doctor may recommend taking sedatives: Valerian tablets, Corvalol drops, Motherwort.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to frequently ventilate the room and maintain the air temperature in the room at 18-20 degrees. The patient should sleep a lot, at least 10 hours a day. You should not strain the patient's eyes with bright light; during the day it is better to keep the curtains drawn. It is not recommended to be exposed to loud noise. You can listen to soft music, but not with headphones.
If a patient is diagnosed with a moderate or severe concussion, treatment is possible only in hospitalization. The patient is observed by a neurologist, surgeon, and therapist. If necessary, to treat a concussion after severe injuries, consultation with neurosurgeons is carried out.
Medicinal herbs
A concussion is one of the most common types of traumatic brain injury. There are many reasons for the occurrence, most often these are sports, household and impacts received as a result of an accident. The signs of a mild concussion in children and adults have some differences. In case of injury, it is important to provide first aid to the person, as the condition may worsen.
Important! If left untreated, a concussion can cause serious consequences.
Treatment of mild concussion is carried out on an outpatient basis if there is no threat to the patient’s life. The patient is first prescribed bed rest for 3 weeks. If an injury is diagnosed in a child, rest should be observed for a month.
The patient needs to create the most comfortable conditions, eliminate all possible overexertion and anxiety, limit watching TV and time spent at the computer.
Important! With a mild concussion, symptoms may include photophobia and increased sensitivity to sounds. They should also be taken into account and all conditions should be provided to the patient.
Your doctor will tell you how to treat a mild concussion. All medications should be taken only as prescribed by a traumatologist or neurologist, who, based on the patient’s condition, determines the required dosage. It is strictly prohibited to exceed it.
The list of medications for a mild concussion may include antidepressants and sedatives. They are prescribed in cases of sleep disturbances, apathy and irritability. Many patients are interested in what to drink for a mild concussion. In case of injury in adults and children, the following medications are prescribed:
- "Nicotinate" based on nicotinic acid.
- Dihydrates in tablet form. The most effective is Diakarb.
- "Quintol" in order to normalize the functioning of blood vessels.
- "Somarin" or "Cerebrolysin" intravenously.
- Neuroleptics. They are the basis of treatment. Piracetam and its analogues are often prescribed.
- For a mild concussion, it is necessary to take vitamin complexes and amino acids, such as ascorbic and folic acids, phosphorus to restore brain cells.
To normalize sleep and relieve nervous disorders, taking sedatives is indicated. The most effective are Adaptol, Noopept and Dormiplant. They help not only get rid of unpleasant symptoms, but also avoid the negative consequences of injury.
Treatment of mild concussion with these means is carried out both in a hospital setting and at home. The course of therapy is about two months, depending on the severity of the lesion.
Physiotherapy
After the patient’s condition has been alleviated, a course of physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed. They help restore brain function and nervous system function. Patients are prescribed:
- Electrophoresis using drugs to constrict blood vessels.
- Acid baths.
- Laser therapy.
- Galvanization of the brain.
- Aerotherapy.
- Massage.
- Reflexology.
Physiotherapeutic methods help speed up the healing process and avoid the development of serious consequences.
Mild concussion is the leader in number among closed craniocerebral injuries. The signs of a mild concussion are very similar to those of a stroke or oxygen deprivation, but a head injury is a prerequisite.
With a mild concussion, loss of consciousness may not occur or its duration does not exceed 5 minutes. At first glance, the condition of the injured person seems quite satisfactory. External damage may be completely absent, however, there remains the possibility of an intracranial hematoma, the symptoms of which will appear over time.
It is believed that a mild concussion is the safest form of traumatic brain injury and, sometimes, it is quite possible to recover from it at home.
But you can still identify a number of typical unpleasant symptoms:
- Rumble in my head. Severe throbbing pain that is difficult to eliminate with conventional means.
- Dizziness. Loss of coordination. Difficulty maintaining an upright body position.
- Nausea, which is sometimes accompanied by vomiting.
- Visual impairment: difficulty focusing on one object, double vision, feeling of a white veil before the eyes.
- Hearing impairment.
- General weakness.
- Tachycardia or bradycardia, thready pulse.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Hyperhidrosis.
- Emotional instability.
- Impaired diction.
- Lethargy.
At the first suspicion of a concussion, you should:
- Call an ambulance or take the victim yourself to the nearest emergency room.
- The patient should be examined by a traumatologist, neurologist and surgeon. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to take an x-ray of the skull, and if possible, a CT or MRI of the brain.
- If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient should be hospitalized for further observation and treatment.
If the patient's loss of consciousness was short-term, then with the return of consciousness it is necessary to provide him with a comfortable lying position, raising his head slightly.
In case of prolonged loss of consciousness, you need to put the victim in a saving position:
- body position – on the right side;
- the head is slightly thrown back;
- face turned to the ground;
- the left arm and leg are bent at a right angle.
Consequences of trauma in adults
Despite the extensive list of the main manifestations of a concussion, sometimes such an injury remains underestimated. After all, it happens that several hours or even days pass from the time of receiving a blow to the appearance of true signs. Therefore, immediately after an injury you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- tinnitus;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache in the occipital area, increasing with sudden movements;
- pupils of different sizes;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- fainting.
Since a concussion is a mild, but still traumatic brain injury, the victim should not self-medicate, and at the first signs of a disorder in his functioning, he should seek qualified medical help.
Early symptoms of a concussion most often disappear within 2-3 days or weeks, but can persist for a long period of time, accompanied by various complications. In 10-20% of cases, signs of TBI may be present for 2-3 months. Patients over 55 years of age take longer to recover than younger victims.
Factors that can complicate the course of the pathology:
- psychological disorders;
- abuse of smoking, alcohol-containing drinks;
- prolonged depression;
- state of stress;
- associated diseases.
In the future, a concussion can cause decreased mental and physical activity, including loss of temporary memory. This condition, if left untreated, can persist for up to 3 years or more after TBI.
A concussion and its consequences can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Repeated injuries cause a disorder that is characteristic of boxers and patients who are periodically exposed to TBI due to their professional activities (athletes, rock climbers, rescuers).
Encephalopathy (post-traumatic) is manifested by a slight lag in the movements of one lower limb, staggering, and loss of balance. Some patients experience lethargy, confusion, mental abnormalities, tremors of the legs, arms and head.
The outcome of the disease is determined, first of all, by the degree of its severity. The timeliness of assistance is also important. Even with the formation of extensive hematomas and damage to the skull bones, doctors are able to prevent fatal consequences. The prognosis for the pathology ranges from favorable to cautious.
Modern medicine is successfully treating concussions. This made it possible to significantly reduce the incidence of complications after such injuries. However, the asymptomatic course of mild damage remains an unresolved problem. In such cases, patients often do not go to the doctor, but prefer to be treated at home on their own.
Available studies provide information on the identification of post-concussion syndrome in these patients. This problem, which develops after an injury, most often occurs in the absence of timely and adequate treatment. Such people suffer from both mental disorders and cognitive impairment.
The main complaints remain pain and dizziness. Doctors are often faced with the absence of objective reasons for such symptoms. Patients have somatoform disorders, that is, the presence of a clinical picture when it is impossible to identify the organic basis of their formation. Such patients require a thorough examination and a long period of rehabilitation.
First aid and further treatment for a concussion From the point of view of human physiology and anatomy, a concussion is a disruption of the functional connections between the nerve cells of the cerebral cortex...
It is worth noting the following consequences:
- Some patients experience clouding of consciousness when drinking alcohol or getting infected (for example, with the flu).
- Headaches that worsen with physical exertion or certain bends of the body. There may be a rush of blood to the head followed by paleness, accompanied by sweating.
- Loss of ability to concentrate and very easy fatigue.
- Uncontrollable outbursts of aggression, after which the patient experiences awareness and remorse for what he has done.
- Convulsions similar to an epileptic seizure may appear.
- The appearance of paranoid qualities - constant anxiety, fear, worries about any reason. This leads to insomnia and general personality degradation.
Read more about the consequences in our article.
Consequences and complications after a concussion - psychosis, parkinsonism and others. A concussion is a violation of the integrity of the bones of the skull or soft tissues.
An accident can happen to a person in which...
Concussion: causes of injury and risk factors
It is logical to assume that such an injury can be caused by physical impact on a person’s head. However, it is important to know what exactly can cause a concussion , and which people are at risk.
- Our brain is located inside the skull, it is surrounded by 3 meninges, between which cerebrospinal fluid circulates. It is this liquid that plays the role of a kind of shock absorber and protects the brain in the event of an impact.
- If the blow is not very strong, the brain does not hit the hard shells, but if the blow is strong enough, the cerebrospinal fluid will not cope and the brain will be injured.
- A concussion can be caused by a blow to the head and upper neck, a fall, hitting the head on a hard object, or sudden shaking of the head.
Comes from a blow
- The most susceptible to concussions are young children who are learning to walk, since their coordination of movements is not yet adequately developed, and older people, who, due to their age, can also stumble or fall due to dizziness or loss of consciousness. Also at risk are people who have previously had any head injuries, since they are usually accompanied by dizziness even after a long time.
Prevention
You need to remember that:
- When playing contact games or rollerblading, cycling, skating, skiing, or skateboarding, wear a helmet.
- If you like to engage in martial arts, pay due attention to head protection.
- When driving a car, buckle up.
- At home, think over the situation so that you do not trip over interior elements or these elements do not fall on you. Do not block passages in rooms and corridors along which you move in the dark.
- Use caution in situations where there is a risk of traumatic brain injury.
Remember! If you, or someone close to you, has an unfortunate fall or hit your head hard, do not let the incident take its course - consult a doctor. If everything is fine, then you can sleep peacefully; if not, then you can avoid all the consequences described above.
And do not pay attention to the thoughtful statements of the learned neighbors - you got a concussion, now you will suffer from headaches to death - with timely treatment, after a year, headaches are observed in only 1% of patients.
Concussion prevention includes head protection at work and during sports. Working on a construction site requires wearing a helmet; some sports (skateboarding, hockey, baseball, cycling or motorcycle riding, roller skating) require wearing special helmets. When traveling in a car, you must wear seat belts. In domestic conditions, it is necessary to ensure that the corridors are free for passage, and that liquid accidentally spilled on the floor is immediately wiped up.
Reviews from our patients
In 2020, I had an appointment with Dr. Alexei Anatolyevich Zhivotov. I have different degrees of flat feet, and the orthopedic insoles I bought at the pharmacy no longer gave the desired effect. Alexey Anatolyevich diagnosed all the defects, made custom insoles, and also gave a lot of advice.
I have known the author of the defanotherapy method, A.I. Bobyr, since 1995. and didn’t think that I would have to resort to his help myself. But in 2003. after carrying heavy loads, he was so skewed from left to right that he moved 20 cm, and treatment in the clinic did not give the expected results. In December I remembered.
I came to the Bobyr clinic with back pain and headaches. Being a medical worker myself, I was examined more than once, and I was prescribed treatment. But there were no results! At the “bobyr” clinic, I was re-examined by Mikhail Anatolyevich, he prescribed treatment. The back went away, and so did the head.
I am undergoing treatment at the clinic. Hernia in the cervical spine. During treatment, a protrusion in the lumbar region was also discovered. Periodic pain throughout the year. After the 5th procedure there is no pain, I lead an active lifestyle. Attending physician, Babiy Alexander Sergeevich. Thank you very much for your golden hands and professionalism.
| Performing spontaneous movements on command | 6 | ||||
| Purposeful pushing away in response to pain | 5 | ||||
| Withdrawal of a limb in response to pain | 4 | ||||
| Pathological flexion in response to pain (decortication) | 3 | ||||
| Abnormal extension in response to pain (decerebration) | 2 | ||||
| No motor response | 1 | ||||
Speech (R) | Orientation in space and time | 5 | |||
| Confused speech, disorientation | 4 | ||||
| Says incomprehensible words | 3 | ||||
| Makes strange sounds | 2 | ||||
| No voice response | 1 | ||||
Eye opening (D) | Spontaneous | 4 | |||
| To the command, addressed speech | 3 | ||||
| To the pain | 2 | ||||
| Doesn't open his eyes | 1 | ||||
General valueNote: Coma points = D + R + G. Patients scoring 3 or 4 on the Glasgow Coma Scale have an 85% chance of dying or entering a residual vegetative state. Patients scoring >11 on the Glasgow Coma Scale have only a 5–10% chance of dying or entering a residual vegetative state and an 85% chance of moderate disability or full recovery. Mean Glasgow Coma Scale scores correlate with the proportional odds of recovery. The classification of traumatic brain injury is based on many factors. An alternative traumatic brain injury severity scale. | |||||
| Severity | Structural changes (MRI, CT) | Loss of consciousness | Confusion | Post-traumatic (retrograde) amnesia | Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), points |
| Light | Norm | 0–30 min ( 30 min, but 24 h | 1–7 days | 9–12 | |
| Heavy | Norm or pathology | >24 h | >24 h | >7 days | 3–8 |
Nuances of rehabilitation
After completing bed rest and stabilizing the patient’s condition, doctors recommend undergoing a recovery course. Massage, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises will help return the circulatory system to normal. It will be useful to follow a diet. Among dairy products, the emphasis should be on cheeses and cottage cheese. Plant foods should be represented by an abundance of fruits and vegetables.
Despite the possible difficulties, it is better for smokers and alcohol drinkers to give up bad habits. It is recommended to limit the consumption of coffee, sweets, carbonated drinks, and reduce the amount of fatty and salty foods.
The restriction on performing heavy physical work should be at least a month; excessive mental stress is extremely undesirable. Compliance with simple rules will form the basis of a gentle regime and will allow you to quickly restore your performance.