Meningioma makes up ¼ of brain tumors. In terms of prevalence, it ranks second after glioma. The tumor develops between 40 and 70 years of age, and more often in women.
Let's find out what post-traumatic meningioma of the brain is. Let's look at the signs and diagnosis of brain tumors.
Traumatic brain injury can trigger the growth of so-called post-traumatic meningioma
What is meningioma?
A tumor that develops from the hard, soft or arachnoid membrane of the brain is a meningioma. Most tumors are benign, but malignant forms also occur. Most often, the tumor is located in the upper part of the brain, but often affects deep structures. Superficial benign meningioma becomes dangerous because it affects the brain centers and disrupts their functions.
There are several suspected causes of meningiomas, and one of them is traumatic brain injury.
Damage to the meninges causes increased growth of their cells. As a result, a tumor forms. It is often discovered many years after the injury. This type of brain meningioma is characterized by slow growth and may not manifest itself for many years. By the time it is detected, the tumor has already reached a large size and requires surgical intervention. The signs of meningioma that develops after injury are no different from other types. Externally, it looks like a node fused to the membranes of the brain.
How is it formed?
How does a brain contusion form (the consequences of the injury can be so serious that the injured person may remain disabled for life)? At the point where the mechanical force is applied, an impact zone appears where the pressure increases. It is in this area that primary damage to the structures of nerve cells, as well as blood vessels, occurs. In this case, an anti-impact zone appears in the opposite side, which is characterized by low pressure. By the way, in this area the damage may be more extensive than at the site of application of force.
After a bruise, processes of swelling of brain tissue and its edema develop in the brain, and blood supply processes are also disrupted. This significantly worsens the patient’s condition and requires immediate attention to a specialist.
Classification and causes of neoplasms
According to WHO, brain meningioma is divided into 3 types:
- The benign form accounts for 90% of all types of meningiomas. It is characterized by slow growth.
- The atypical form differs from the benign form by the presence of atypical cells that are prone to division. At this stage, the tumor begins to increase in size, but does not invade the brain structure.
- A malignant type of neoplasm grows into brain tissue, often recurs and metastasizes.
The causes of brain tumors are not fully understood. However, genetic predisposition and exposure, including those associated with professional activities, are considered to be generally recognized risk factors. Meningioma often develops after a traumatic brain injury.
Medical criteria for determining the severity of harm caused to human health
Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on August 13, 2008
Registration No. 12118
In accordance with paragraph 3 of the Rules for determining the severity of harm caused to human health, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 17, 2007 N 522 (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2007, N 35, Art. 4308), I order:
Approve Medical criteria for determining the severity of harm caused to human health, in accordance with the appendix.
Minister T. Golikova
Appendix to the order
Medical criteria for determining the severity of harm caused to human health
I. General provisions
1. These Medical criteria for determining the severity of harm caused to human health (hereinafter referred to as the Medical Criteria) were developed in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated August 17, 2007 N 522 “On approval of the Rules for determining the severity of harm caused to human health” ( hereinafter referred to as the Rules).
2. Medical criteria are a medical characteristic of qualifying characteristics that are used to determine the severity of harm caused to human health during a forensic medical examination in civil, administrative and criminal proceedings on the basis of a court ruling, a decision of a judge, the person conducting the inquiry, or an investigator.
3. Medical criteria are used to assess injuries discovered during a forensic medical examination of a living person, examination of a corpse and its parts, as well as during forensic medical examinations based on case materials and medical documents.
4.
The degree of severity of harm caused to human health is determined in medical institutions of the state health care system by a doctor - a forensic medical expert, and in his absence - by a doctor of another specialty (hereinafter referred to as the expert) brought in to carry out the examination, in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, and in accordance with the Rules and Medical Criteria.
5. Harm caused to human health is understood as a violation of the anatomical integrity and physiological function of human organs and tissues as a result of exposure to physical, chemical, biological and psychogenic environmental factors1.
II. Medical criteria for qualifying signs of severity of harm to health
6. Medical criteria for qualifying signs in relation to grievous bodily harm are:
6.1. Harm to health that is dangerous to human life, which by its nature directly poses a threat to life, as well as harm to health that has caused the development of a life-threatening condition (hereinafter referred to as harm to health that is dangerous to human life).
Harm to health, dangerous to human life, creating a direct threat to life:
6.1.1. wound of the head (scalp, eyelid and periorbital region, nose, ear, cheek and temporomandibular region, other areas of the head), penetrating into the cranial cavity, including without damage to the brain;
6.1.2.
fracture of the vault (frontal, parietal bones) and (or) base of the skull: cranial fossa (anterior, middle or posterior) or occipital bone, or upper wall of the orbit, or ethmoid bone, or sphenoid bone, or temporal bone, with the exception of an isolated external crack bone plate of the cranial vault and fractures of the facial bones: nose, lower wall of the orbit, lacrimal ossicle, zygomatic bone, upper jaw, alveolar process, palatine bone, lower jaw;
6.1.3.
intracranial injury: crushing of the brain substance; diffuse axonal brain damage; severe brain contusion; traumatic intracerebral or intraventricular hemorrhage; moderate cerebral contusion or traumatic epidural, or subdural, or subarachnoid hemorrhage in the presence of cerebral, focal and brain stem symptoms;
6.1.4. a neck wound penetrating into the lumen of the pharynx or larynx, or the cervical trachea, or the cervical esophagus; injury to the thyroid gland;
6.1.5. fracture of the cartilages of the larynx: thyroid or cricoid, or arytenoid, or epiglottis, or corniculate, or tracheal cartilages;
6.1.6. fracture of the cervical spine: fracture of the body or bilateral fracture of the arch of the cervical vertebra, or fracture of the tooth of the II cervical vertebra, or unilateral fracture of the arch of the I or II cervical vertebrae, or multiple fractures of the cervical vertebrae, including without dysfunction of the spinal cord;
6.1.7. dislocation of one or more cervical vertebrae; traumatic rupture of the intervertebral disc at the level of the cervical spine with compression of the spinal cord;
6.1.8. contusion of the cervical spinal cord with impairment of its function;
6.1.9. a chest wound penetrating into the pleural cavity or into the pericardial cavity, or into the mediastinal tissue, including without damage to internal organs;
6.1.10. closed damage (crushing, tearing, rupture) of the thoracic cavity organs: heart or lung, or bronchi, or thoracic trachea; traumatic hemopericardium or pneumothorax, or hemothorax, or hemopneumothorax; diaphragm or lymphatic thoracic duct, or thymus gland;
Source: https://rg.ru/2008/09/05/medicina-dok.html
Brain tumor after head injury
Neurosurgeons at the Brain Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg published a clinical case of brain meningioma that arose after trauma.
Patient M., 66 years old, was hospitalized in 2007 in the neurosurgical department due to a tumor formation in the right frontotemporal lobe of the head. He considers himself sick for 20 years after a blunt head injury, when a protruding tumor formed in the temple area. The patient notes that over the past 10 years the tumor has noticeably increased. Upon admission, the patient's condition was satisfactory. Neurological status without features.
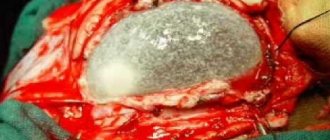
Objectively, in the temple area, a bone density tumor measuring 52 x 45 x 20 mm is detected, not fused to the skin, painless on palpation.
A computed tomography scan of the head and skull did not reveal a brain tumor. Hyperostosis (overgrowth of bone tissue) is noted. Positron emission tomography (PET) revealed a bone tumor with signs of growth in the upper layers of the cranial vault. The patient underwent surgery to remove a periosteal (bone) meningioma of the temporal region. The postoperative period passed without complications. In the long-term period, the patient had no complaints.
In this case, the tumor, growing into the periosteum, caused active growth of the calvarial bone in the area of injury. The meningioma had spread to the outer soft tissues of the head. As a result of the operation, the outcome of the disease after an injury 20 years ago ended without consequences.
Moderate bruise
This injury is characterized by more severe damage to brain tissue. It is almost always combined with a skull fracture, resulting in subarachnoid hemorrhage. The main symptoms of brain contusion of this degree are:
- Underestimation of the severity of one’s own condition, loss of consciousness for 1-3 hours, episodes of psychomotor agitation.
- Amnesia (retrograde, congrade, anterograde).
- Severe headaches, severe dizziness.
- Repeated vomiting, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, increased breathing, nausea, increased temperature.
- Severe focal neurological symptoms (changes in muscle tone, paresis, loss of sensation in the extremities, pathological hand and foot symptoms, strabismus, facial distortion, spontaneous nystagmus, epileptic seizures, speech impairment).
- Meningeal symptoms.
Symptoms of such a bruise last from several weeks to two months. Over time, neurological symptoms gradually disappear. However, a number of changes that occur immediately after injury may be irreversible.
Signs of brain tumors
Headache is a general cerebral symptom
Manifestations of tumors are divided into general cerebral and focal. Brain symptoms as the tumor grows cause an increase in intracranial pressure. Focal signs are associated with a brain area that is compressed by a growing tumor.
Symptoms of brain meningioma:
- nausea and vomiting;
- severe headaches at night or after leaving a horizontal position;
- decreased visual acuity and double vision;
- drooping upper eyelid on one side;
- impairment of memory and thinking ability;
- epileptic seizures;
- visual hallucinations;
- weakness in the legs and arms on one side;
- paralysis of legs and arms;
- decreased or loss of hearing;
- feeling of pressure inside the eyes;
- psychical deviations.
Even one such sign should alert you to the possibility of a brain tumor and requires examination.
The complex of signs of neoplasms varies depending on the affected area. Superficially located tumors manifest themselves as headaches when lying down and seizures. Orbital meningioma occurs when one eye on the affected side protrudes outward. When the temporal lobe is damaged, hearing and speech impairment occurs.
Meningioma of the left orbit
The neoplasm of the frontal lobe is manifested by behavioral abnormalities. The patient ceases to realistically evaluate himself and the environment. He is prone to unjustified aggressive actions. When the tumor grows into the parietal lobe, hearing and speech are impaired. Further progression of the process is accompanied by paresis and paralysis.
Localization of the tumor in the cerebellum is manifested by impaired coordination of movements - the patient’s gait becomes unsteady. He loses his balance when walking. An enlarged cerebellar tumor can cause compression of the respiratory center, which is located in the medulla oblongata under the cerebellum. The first signs appear in the form of difficulty swallowing. In this case, the patient experiences difficulty swallowing not only solid food, but also water.
Symptoms of meningioma after a traumatic brain injury develop gradually and unnoticed by the patient. When the headache intensifies and new symptoms appear, the patient remembers the head injury. The doctor clarifies the situation after an instrumental examination.
What harm to health
Closed craniocerebral injury occurs due to a rough impact on the skull (a blow to or against the head). Intentional bruising of the skull with any blunt object is a criminal offense. The punishment for this bodily injury is determined by the relevant article of the Criminal Code.
If there is doubt as to whether the brain contusion was accidental as a result of a careless fall, or whether it was caused by violent acts, an examination is ordered. Concussion occurs when there is an axial load that is transmitted through the spine. Such conditions arise from a fall on the lower limbs, buttocks, an accident, or a broken nose.
In these situations, there is a strong shaking of the skull. The brain is subject to severe hydrodynamic shock because it is located in the spinal fluid. With enormous destructive force, bruising of brain tissue on the cranial bone is possible.
The manifestations of TBI are based on a disruption of normal communication between the brain stem and its hemispheres. Mechanical action on tissue is a factor in changing the state of brain tissue. It is possible that brain dysfunction is associated with metabolic disorders in neurons.
Depending on the severity, the health damage from a concussion varies. Let's find out the main differences between the manifestations of mild, moderate and severe concussion.
Mild degree
It is characterized by a short loss of consciousness (sometimes it is completely preserved), and a satisfactory state afterwards. Within 7 days all complaints are resolved. No residual effects are observed.
With a mild form, pallor and decreased muscle tone of the limb are noticeable (sometimes it disappears completely). There may be no vomiting. A distinctive feature of this degree is the absence of amnesia, that is, the person remembers the events preceding the concussion.
Mild closed TBI requires bed rest for at least 2 days. Improvement in health occurs quite quickly.
Average degree
With a moderate concussion, a short loss of consciousness is always recorded. Pathological neurological symptoms are largely present - dizziness, prolonged lethargy, disorientation, severe nausea. Vomiting almost always occurs. The victim has a low-grade fever for some time. Short-term amnesia develops.
Moderate concussions always require bed rest for at least a week. This category of patients is indicated for prophylactic use of nootropic drugs.
Zchmt and sgm what article of the criminal code
However, it is quite difficult to correctly diagnose a concussion, because most often it does not leave behind any visual consequences on the brain, which can be detected using computed tomography, neurosonography, MRI, etc. With this injury, the substance of the brain itself is not disrupted, but the functioning of neurons in the brain is disrupted.
With the help of CT, MRI, neurosonography and other modern methods of studying the brain, it is possible to exclude a brain contusion, and even then not always.
The fact is that completely identical symptoms can be subjectively assessed by different forensic experts as a concussion or a brain contusion.
A concussion is a blunt head injury that entails a number of functional disorders in the brain. These changes, according to most scientists, do not entail irreversible consequences.
What to do when contacting the police:
- How to stop beatings and bring the offender to justice? Write a statement with a detailed description of the crime, the characters involved, the methods of inflicting pain and the locations of the blows.
- Examination by an expert in the direction of the police, followed by a conclusion on the severity level.
If you decide to identify harm yourself, then you should adhere to the following algorithm:
- Visiting a clinic, hospital, or emergency room. There, a certificate is issued with the diagnosis upon application, the nature of the injuries and the time of admission to the medical facility.
- With all the documents, go to the police to write a statement.
- Repeated examination with the participation of forensic doctors.
The last point is not always fulfilled, since the investigation may only need documents from the hospital.
Common signs of injury
The general symptoms of the disease in question are:
- transient confusion;
- syncope, observed at rest and intensifying when changing the position of the body or head;
- pulsating pain;
- extraneous sounds in the ears;
- general weakness;
- nausea or occasional vomiting;
- retardation of movements;
- slowing down the rate of speech;
- feeling of double objects;
- overreaction to sounds;
- photophobia;
- violation of the coherence of movements.
During diagnosis, the following symptoms are observed that are among the most important.
- The patient complains of pain in the eyes, he experiences difficulty moving them to the sides.
- Immediately after the injury, a change in the diameter of the pupils is noticeable.
- There is a difference in reflexes from different sides.
- Uncontrolled eye movements may occur.
- In the Romberg pose (legs should be together, arms straightened, positioned horizontally and extended forward, with eyes closed), unsteadiness and instability are determined.
- Spasms of the neck muscles.
Algorithm for assessing the severity of harm to health in cases of traumatic brain injury
Which automatically equates the act to Articles 111 and 112.
- Torture is characterized by the infliction of suffering, both physical and psychological, but the main thing is the systematic infliction of damage to a person.
Light harm to health is the duration of treatment for a patient up to 21 days inclusive and temporary loss of ability to work is less than 10%, and moderate harm to health is the duration of treatment of a patient for more than 21 days and loss of ability to work is less than 30%.
Practice shows that most often a concussion, from the point of view of a forensic expert, causes slight harm to the health of the victim, but if pathologies subsequently develop that are caused by the concussion, and the duration of treatment is more than 21 days, then the harm to the health of the victim is determined by the forensic expert as average degree of severity.
First aid for a brain injury
In any case, it is necessary to call for medical help, especially if the patient is unconscious. The person must be placed on a hard surface, with joints bent. The face should be tilted towards the ground. If the wound is bleeding, a bandage should be applied to stop the bleeding.
If there is no fainting, the patient is placed horizontally with his head slightly raised. All people with such an injury should go to a trauma center.
Treatment of concussion
During treatment you need to rest. The victim needs to lie down and avoid any mental or physical stress that could adversely affect brain function. If a person follows all the necessary recommendations on time, then the treatment ends with recovery.
Patients are prescribed medications to relieve unpleasant symptoms: headache, syncope, nausea. At the same time, medications are used, the action of which is aimed at improving physiological processes in the brain. The use of sleeping pills and sedatives is indicated: they help compensate for brain function.
It is prohibited to do any physical work for 30 days after the incident. Mental work and watching videos should be limited. There is no need to use headphones when listening to music.
A severe brain injury is an indication for a deferment from the army.
Complications of severe head injury
Severe brain contusion can cause encephalopathy. The motor skills of the legs are impaired, manifested in some dissociation of coordinated movements. If the disease is not treated, patients experience such phenomena.
- Confusion and retardation, poor speech, changes in behavior.
- There are episodes of mental imbalance and aggressive behavior (patients later regret them).
- Increased sensitivity to alcohol and infectious pathologies. Moreover, as a result of drinking alcohol, patients develop delirium.
- Convulsive attacks.
- Sharp headache.
- Psychoses and hallucinations rarely occur.
- In rare cases, patients develop dementia, lack of orientation and impaired judgment.
In 1 case out of 10, a serious brain contusion contributes to post-concussion syndrome. It manifests itself in severe pain, insomnia, and attention disorders. This syndrome is difficult to treat.
A concussion is a serious injury that causes temporary disruption of brain function. If you do not adhere to bed rest, the patient may develop impairments in the ability to remember and maintain attention. A decrease in intelligence is also possible. Early diagnosis and early therapy helps to get rid of the dangerous consequences of the disease.
Source: https://mega-garden.ru/dieta/zchmt-kakoy-vred-zdorovyu/