Myelitis is a dangerous disease characterized by inflammatory processes within the substance of the spinal cord. The disease is relatively rare, but is difficult to treat and often leads to subsequent complications. In some cases, this disease can be either focal or cover the entire spinal cord.
As a rule, when the diagnosis of “spinal cord myelitis” is confirmed, the prognosis for the development of this disease largely depends on the location and severity of the disease.
Reasons for the development of myelitis
No age or gender patterns in the incidence of myelitis have been identified, although a number of experts consider young people from 10 to 20 years of age, as well as the elderly, to be at risk.
The reason for the development of myelitis lies in the penetration of infectious agents and toxins into the spinal cord through lymphatic and blood vessels , which leads to inflammatory processes and degenerative changes in the nerve trunks, membrane and roots of the spinal cord. Often the disease develops against the background of vertebral osteomyelitis - purulent inflammation of the vertebral bodies, leading to the destruction of bone tissue.
The starting point for the initiation of the pathological process can be considered swelling of the spinal cord, which occurs due to infection or soft tissue injury. The subsequent disturbance of blood circulation and the occurrence of vascular blood clots, which in turn increase swelling, form a kind of vicious circle.
Do you know: How to treat juvenile osteochondrosis?
As a result, circulatory problems lead to softening and necrosis of the spinal cord tissue, and after recovery, the site of necrosis is replaced by connective scar tissue.
Features of transverse myelitis
Transverse myelitis develops rapidly, with symptoms occurring within hours or days. Such myelitis may be characterized by pain in the neck and back, after which pain in the pelvis and lower extremities begins to appear.
In most cases, such myelitis occurs due to influenza, measles, and various infectious diseases. In addition, vaccination can cause the development of transverse myelitis. Often the disease manifests itself during the period of recovery of the body after an infectious disease. In this case, it is not possible to detect the pathogen in the nervous system. This indicates that transverse myelitis arose in the body as a reaction to an infectious disease.
Types of disease
There are several types of classification of the disease, based on different parameters (duration, localization of the pathological process, factors contributing to the onset of the disease).
Depending on the duration of the disease, there are:
- acute transverse myelitis (symptoms are very pronounced, the course of the disease is severe, there is a high probability of complications),
- subacute (symptoms progress gradually),
- chronic (more often affects older people, or young people with impaired immune system function).
According to the localization of the pathological process, they are distinguished:
- limited (presence of one focus of the disease),
- disseminated (presence of two or more affected areas),
- widespread (the entire spinal cord is affected),
- transverse myelitis of the spinal cord (damage to several segments adjacent to each other).
Depending on the root cause:
- infectious (viral, bacterial),
- traumatic,
- post-vaccination,
- idiopathic,
- ray,
- toxic.
According to the method of development:
- primary (occurs independently, under the influence of unfavorable factors),
- secondary (develops against the background of a disease, most often chronic).
How does the disease manifest itself?
With the development of spinal cord myelitis, the patient usually experiences the following symptoms:
- decreased sensitivity in the lower and upper extremities;
Levels of spinal cord damage - loss of pain and temperature sensitivity of the skin of the entire body;
- general weakness of the body (the patient is sometimes unable to walk around the room without anyone’s help);
- problems with bowel movements or urination (retention or incontinence occurs);
- impaired muscle tone in the limbs (hypertonicity);
- signs of the development of an inflammatory process in the body, which include increased sweating, high body temperature, lethargy and depression.
Symptoms of myelitis
On a note! Signs of myelitis can appear immediately, literally in 1-2 hours, or gradually over several months. Features of the manifestation of pathology depend on the location of the source of inflammation. But in order to quickly cure the disease, you need to respond to its first manifestations, so you should immediately consult a doctor if you suspect you have spinal cord myelitis.
Symptoms
The first signs of the disease are not much different from the manifestations of ordinary infectious diseases. If spinal cord inflammation is suspected, the symptoms may initially resemble a common cold:
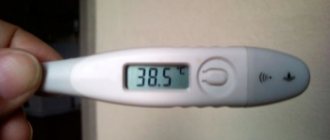
- malaise,
- chills,
- temperature rise to 39 degrees.
Further, the disease acquires pronounced neurological features , characterized by pain in the back, often spreading to neighboring areas of the body.
Manifestations of paresis are also possible, followed by an increase in motor and sensory disorders. There are frequent cases of disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs , manifested in the form of fecal and urinary incontinence.
Inflammation in the lumbar region manifests itself in the form of leg paresis, accompanied by atrophy and degeneration reactions. When myelitis appears in the thoracic region , spastic paralysis of the legs, impaired abdominal reflexes and pelvic disorders are observed.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing myelitis, it is important not only to confirm the fact of the disease itself, but also to establish the cause of the disease.
Typically, history, symptoms and cerebrospinal fluid analysis are sufficient to establish a preliminary diagnosis.
If it is necessary to obtain more complete information, a lumbar puncture and myelography are performed, and a CT or MRI of the spine is prescribed.
In the process of making a final diagnosis, it is necessary to differentiate myelitis from diseases such as poliomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, spinal stroke, and spinal cord injuries.
Diagnostic procedures
Having understood the question of what myelitis is, you should understand how it is detected. The initial examination and patient complaints are usually not enough to make a diagnosis, so specialists almost always prescribe laboratory and hardware tests. Diagnostics consists of the following stages:
- Neurological examination. During the process, the doctor carefully examines the patient, conducts a series of simple tests to determine violations of the body’s natural reactions and reflexes, loss of sensitivity and muscle tone.
- Blood and urine tests. The results obtained show ESR and leukocyte levels, which indicate the extent of inflammation, the presence of antibodies and other data.
- Electroneuromyography. With its help, the conductivity of nerve impulses, the degree of disturbance and the location of the lesion are determined.
- MRI. One of the most informative research methods, which allows you to obtain images of the spinal cord in layers. The results help determine the boundaries of the infectious focus and choose the most effective treatment tactics.
MRI is often replaced by CT, which does not affect the quality of the study. Additionally, some patients are prescribed the use of contrast to increase the accuracy of the procedure. And it is also important to carry out tests to identify the pathogen if the cause of the lesion is infectious or viral. After its determination, the general antibiotic is changed to a highly specialized one that suppresses the growth and reproduction of specific pathogenic microflora.
MRI is the most informative way to determine the cause and extent of the lesion
In the process of making a diagnosis, it is extremely important not to confuse myelitis with epiduritis, which requires immediate surgical intervention. Their clinical pictures are very similar, but in addition to general tests, an additional explorative laminectomy will also be required. Affected tissues are examined for the presence of radicular disease or a purulent focus, which distinguishes the disease from myelitis.
Treatment
As a rule, a full course of treatment during an exacerbation is possible only in a hospital setting under the supervision of a specialist.
Subsequent treatment procedures, mostly aimed at restoring full body functions and stopping possible relapses, are possible outside the medical institution.
Drug therapy
broad-spectrum antibiotics are primarily At the same time, the maximum dosage of drugs is prescribed in order to eliminate inflammation and prevent the destruction of the spinal cord.
Glucocorticoids, a number of analgesics, and antipyretics can also be used together with antibiotics.
Vitamin preparations of group B (in injection form) are also used, whose task is to regenerate nerve cells.
In some cases, based on the patient’s condition, muscle relaxants and uroseptics are prescribed, and in case of urinary retention, anticholinesterase drugs. In the latter case, if the use of these drugs does not have the desired effect, the bladder is washed with an antiseptic solution by catheterization.
Therapeutic techniques
They include a number of the following procedures:
- detoxification,
- dehydration,
- measures aimed at preventing bedsores,
- control over regular bladder emptying,
- artificial ventilation (in case of paralysis of the respiratory muscles),
- orthopedic styling.
Upon completion of the acute stage, for full rehabilitation, combating possible complications and relapses, the following methods are used:
- vitamin therapy,
- physiotherapy,
- massage treatments,
- physiotherapy,
- rehabilitation treatment at resorts and sanatoriums.
Surgery
Neurosurgical intervention in the treatment of this disease is due to clearly pronounced disturbances in motor activity at the final stage of the disease.
Also, indications for surgical intervention are the presence of foci of pus, or serious manifestations caused by compression of the spinal cord.
An illustrative example is vertebral osteomyelitis, the symptoms of which do not always make it possible to accurately diagnose it in the early stages.
At the same time, processes of active formation of pus and inflammation take place inside the vertebrae, which makes the treatment process long and labor-intensive. Such inflammation of the bone marrow of the spine is extremely dangerous for the patient’s life and requires immediate action.
Unconventional methods of treating myelitis
Folk remedies for the treatment of myelitis are aimed primarily at eliminating spasmodic pain and combating the inflammatory process.
For these purposes, it is recommended to use a compress of potatoes and honey, which is placed on the cervical spine. Another type of compress based on mustard, aloe, propolis and vodka acts as a pain reliever.
Also, non-traditional methods of treating myelitis include sessions of hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches).
Features of the fight against the disease
Spinal cord tumor symptoms
- Increased body temperature above 38 degrees.
- Chills and feeling of weakness.
- Acute back pain.
- Feeling of tightness or stiffness.
- Swelling at the site of injury.
- Impaired mobility.
- Weakness in the lower extremities.
- The appearance of numbness or “pins and needles”.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs, inability to control excretory processes.
Symptoms of inflammation of the spinal cord are especially pronounced in the acute course of the disease; in subacute and chronic forms, the signs are vague. With lumbar lesions, there is often paralysis of the legs, poor circulation or the risk of developing bedsores.
When an infection or injury occurs, the disease develops almost immediately; with the radiation nature of the process, manifestations may appear only 6–12 months or even several years after strong radiation.
A treatment regimen for spinal cord inflammation is determined depending on the results of the tests obtained, the location of the lesion and the age of the patient. In the acute form, patients often require immediate surgical intervention. Assistance is provided in a hospital setting, since the person requires rest, constant care and supervision of medical staff. Tactics to combat pathology usually involve an integrated approach, including several types of influences.
Neurology deals with the study and treatment of pathology, so first of all, for consultation, you need to consult a doctor with this profile. The medication regimen is prescribed individually based on the symptoms of the disease and the cause of the pathology.
Typically these are the following groups of medications:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics (Amoxicillin). Aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and suppressing the progression of infection through brain structures. They are prescribed by a doctor in any case, not only if the cause of the development of pathology is the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the body, but also in case of injury or an autoimmune reaction.
- Antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Zovirax, Valtrex). If the causative agent was a herpes virus, then a long course of these medications cannot be avoided. Only when the active substance accumulates is it possible to stably suppress its spread.
- Glucocorticosteroids (Diprospan, Kenalog, Trimcinolone). Drugs in this group have excellent anti-inflammatory properties, relieve inflammation, and improve well-being. If myelitis was caused by an allergen, then these substances help eliminate swelling. They are prescribed to each patient individually.
- Analgesics (Trimecaine, Lidocaine). When the pain syndrome is too severe, drugs are prescribed to block it. Usually these are drugs from the NSAID group or novocaine blockade for especially severe cases. The feasibility of this is decided individually for each patient.
- Immunostimulants (“Viferon”, “Immunal”). Aimed at activating the body's defenses and increasing resistance to infectious processes. They are selected individually if the patient has no contraindications.
- Muscle relaxants (Baclofen, Sirdalud, Mydocalm). Active substances are aimed at reducing muscle tone and relaxing the smooth structure, allowing you to relieve tension and stiffness, and reduce the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
- Diuretics (“Diacarb”, “Lasix”, “Oxodolin”). Often the inflammatory process in the vertebrae is accompanied by disruption of the pelvic organs, so the use of diuretics can eliminate congestion in the bladder and relieve the inflammatory process in the internal organs in the coccyx area.
If myelitis is diagnosed in children, then drug therapy is selected taking into account age and the presence of contraindications. The dosage is selected with care so as not to provoke an allergic reaction or complication.
Bed rest is a basic requirement in the successful treatment of myelitis
Consequences of the disease
According to studies, the death rate in cases of myelitis is about 30%.
In a favorable scenario, after an illness, it takes a considerable period of time to restore the patient’s health. At the same time, sensitivity first returns, and then the breathing function (if it was previously lost). Paresis and paralysis of the limbs, as well as disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs, can often persist until the end of life.
Thus, the only way out in this situation for those suffering from myelitis is to register for disability.
Rehabilitation period
Disseminated myelitis or any other form of it is treated in a hospital setting, since it is important for the patient to provide adequate care. It is he who plays a particularly important role in the first months for the gradual restoration of health.
The main features are:
- Providing adequate bed rest. The patient must be constantly turned over and treated with every part of the body that bears the maximum load with antiseptic agents in order to avoid bedsores.
- Bed linen must be properly straightened to avoid wrinkles. Even they can cause unpleasant consequences.
- Any traditional medicine recipes must be strictly coordinated with the attending physician; their use without control can negatively affect the general well-being of the patient.
- Medicines are taken only against the background of physiotherapy or exercise therapy, if there is a doctor’s prescription. During the acute period, any exercise is strictly prohibited.
Myelitis, unlike osteoporosis, can easily lead to death if treated incorrectly or without proper treatment. In some patients, motor function was permanently lost due to delay in seeking help. That is why in many cases outpatient treatment is unacceptable.
Acupuncture is performed using special needles with rounded edges
Restoration of damage and normal well-being occurs after relief of the acute stage, the most dangerous of all. To do this, the doctor prescribes the following courses:
- Massage. It perfectly helps to avoid the formation of bedsores on the body and gradually restore sensitivity to the lower extremities. It is carried out by medical specialists, since any incorrect actions or excessive pressure are dangerous for the patient.
- Physiotherapy. At first, it is carried out with medical personnel and for this the patient does not even need to leave the bed. The classes are very simple and are aimed at eliminating stagnant processes, gradually returning to physical activity, improving blood circulation in all tissues, and normalizing metabolism.
- Acupuncture. Impact on certain active points can affect the general condition, reduce pain and swelling, relieve inflammation, and get rid of dysfunction of the pelvic organs. As in other cases, only experienced specialists with a high level of qualifications are allowed to conduct sessions to obtain the desired result.
- Catheterization of the bladder or epicystostomy.
Myelitis is diagnosed in both men and women, but in the fair sex it appears more often due to more unstable hormonal levels and constant exposure to stress. The treatment complex is compiled for each patient individually based on the cause and extent of the lesion.
Prevention
Taking into account the specific causes of myelitis, there is no universal recommendation for prevention. Vaccination can partially prevent the disease, as well as prompt elimination of chronic infectious foci in the body, such as caries or sinusitis.
As a rule, preventive actions are prescribed to patients after their recovery in order to prevent possible relapses. For these purposes, physical therapy, vitamin therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as sanatorium treatment are used.
Warnings and prognoses regarding myelitis
The prognosis for myelitis is based on the degree of development and location of the lesion. An advanced form of inflammation in the upper neck sometimes causes the death of the patient, and swelling in the lumbar or thoracic spine leads to disability in the absence of proper and timely treatment. If it is present, the clinical signs soften after about two to three months, and complete recovery will occur in one to two, sometimes three, years.
If the disease is “advanced”, the prognosis can be extremely unfavorable
Myelitis has many causes, so there is no absolute concept of “prevention of myelitis.” However, incomplete prevention of this disease can be called vaccination, as well as timely elimination of chronic infections in your body (sinusitis, caries, and others).
For prevention, from the first day of the onset of the disease, it is necessary to carry out passive therapeutic physical training, which will be prescribed by a specialist in this matter. After the acute period, you should move on to other recovery procedures:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture.