It is quite difficult to identify signs of a concussion in a child; the difficulties of identification are associated with the structural features of the nervous system of children. A concussion is clearly defined and is diagnosed when, after an injury, there are symptoms of brain dysfunction, but no physical damage is found in the brain.
In children, signs of a concussion directly depend on the child's age.
Damage occurs at the level of neuron synapses, and changes in the chemical and colloidal composition of cells cannot be ruled out. This is expressed by a disruption of connections between parts of the brain and irritation of certain structures. To determine the signs of a concussion, you need to find out what level of development of the child's nervous system is, and what disorders he may have.
Causes of concussion in childhood
Immediate causes
Starting from birth, a child has a number of causes of the disease:
- falling from a changing table, bed, sofa, stroller;
- at an older age, falling from scooters, bicycles, trees;
- road accidents;
- shaken baby syndrome.
The last reason should be discussed in more detail, since it is becoming more and more common nowadays. Shaken baby syndrome is a manifestation of child abuse. This cause of concussion occurs as a result of shaking a child from front to back by the shoulders.
The unfixed head makes sudden movements in the direction of movement of the shoulders. The presence of a large fontanelle, cranial sutures, a large amount of fluid, weakness of the head and neck muscles, and a large area of the subarchnoid space contribute to trauma to the child’s brain, as well as rupture of the vessels of the central nervous system, which leads to intracranial hemorrhages.
Children in the first two years of life suffer.
Risk group
Who is more susceptible? Who is at risk? Boys, infants who require constant attention, children in the period of colic and teething, premature babies, children with physical and mental disorders, as well as intrauterine growth retardation are more often exposed to violence.
Who is more likely to be involved in such situations that could harm their own child? These are young parents, men, people without education, those in difficult life situations, parents suffering from alcohol and nicotine addiction, people with unstable psycho-emotional behavior.
When and how does a concussion occur in children? It happens that parents do not notice the serious consequences of a child’s injury: he ran, slipped, fell - yes, it’s dangerous, but in most cases, adults rely on the injury. Meanwhile, it has been proven that concussion is one of the most “popular” diagnoses in the traumatology department for a child.
Contents: 1. Signs 2. Symptoms 3. Diagnosis 4. Treatment 5. Consequences 6. First aid
Children constantly receive various injuries, including head injuries. Impacts to the head that cause injury or concussion can occur from a fall or as a result of a car accident.
A concussion is not the most dangerous thing that can happen to your head, since it is the simplest level of head injury, and then there will be a bruise, various hematomas - injuries that require urgent intervention by a surgeon. That is why you need to figure out what kind of injury the child received, whether the intervention of medical personnel is necessary or whether home treatment can be done. But still, a consultation with a neurologist will not be superfluous.
Traditional childhood symptoms of a concussion include loss of consciousness for a short period of time, perhaps even a few moments. There may be disorientation in the child's environment, followed by severe headache, dizziness, loss of strength and weakness in the child, as well as possible loss of vision and pain in the eyes when viewing literature. Therefore, if you were far away at the moment when something happened to the child, try to ask the people watching it how it all happened and how exactly he fell, since the child himself may lose sight of important points after the fall. This condition is called retrograde amnesia.
Age has a big impact on the types of concussion symptoms in children. For example, a baby with this type of injury may not lose consciousness, but will simply spit up more often than always, which is very typical for children of this age and parents may not notice the difference. Symptoms may also include disturbed sleep, an increased state of excitability, and paleness on the baby’s face, but all this is only in the first few minutes after the injury itself. Symptoms of concussion in schoolchildren last about three days. There are also not so important symptoms with such trauma in children. This may be the release of a large amount of sweat, a rush of blood to the face, or discomfort. It may be the other way around: a sharp improvement in the child’s well-being. But we must remember that visible and invisible disorders of the body have already been set in motion, which in the future will affect health in a negative aspect, in the form of complications.
Knowing that the first symptoms of a childhood concussion are very false, deceptive, or the victim’s well-being is improving rapidly, you should immediately visit a specialized doctor, that is, a neurologist. Only such a doctor can determine whether your baby is experiencing a concussion based on head and eye signs. After undergoing examinations and not finding various complications or pathologies, the attending physician may allow treatment at home. How long it should take for treatment can be determined only by the severity of the injury, but it cannot be less than three calendar days, and in some cases it can last a whole month.
You should always remember that the signs of a concussion in a child are not very dangerous for his life, but it is the consequences of such an injury, if not treated, that are very dangerous not only for the health, but also for the life of the child. And if you know that a child has suffered such an injury, do not wait another minute. First, ask him about it himself, then you can look at the site of the impact to feel for a tumor or even a dent. If there is nothing like that, then let the child just be a little quiet and relax. And if you notice obvious changes in behavior or health, consult a doctor immediately. This is necessary to prevent complications.
Find out how to identify the symptoms of a concussion in this article. Find out what side effects of radiation therapy are here.
Rehabilitation after traumatic brain injury
Signs
First, you need to find out the cause and circumstances of the child’s injury and determine the severity. In any case, consultation with specialists is necessary.
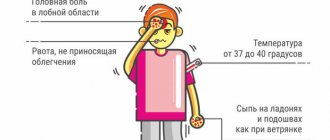
The main signs of a concussion in a child are short-term loss of consciousness for a short period of time. Poor orientation in a familiar space, headache, weakness, dizziness are noticed, and in some cases vision deteriorates.
Symptoms of a concussion also depend on the age of the child: infants with such an injury do not lose consciousness, but only often burp (this fact may go unnoticed by parents), sleep poorly, are agitated or pale in the first minutes after the blow.
In school-age children, the initial symptoms of a concussion stop on the 3rd day. There are a number of other signs that are insignificant at first glance: sweating, blood flow to the face, general discomfort. It happens that the child’s condition rapidly improves. However, we should not forget that the process of disturbances in the body has begun and can lead to further serious complications.
Obvious signs are frequent vomiting, pale skin, anxiety, moodiness, poor appetite, and less commonly, increased lethargy or poor sleep. Preschool children are more likely to lose consciousness, experience nausea and vomiting, their pulse and blood pressure jump, and they may complain of headaches. Whims, mood swings, appetite and sleep disturbances are observed.
Symptoms
The usual symptoms of a concussion in a child are loss of consciousness, but for a short period, perhaps even for seconds. Disorientation in the previously familiar environment will also noticeably manifest itself, followed by headache, dizziness, weakness and sometimes blurred vision, and pain in the eyes when reading. Therefore, if you were not around when the child fell, it will be important to ask possible eyewitnesses how and where exactly the child fell. After all, having lost consciousness, he may lose sight of important points. This process is called retrograde amnesia.
Symptoms of concussion in children also depend on the age of the child. For example, with such an injury, a baby often does not lose consciousness at all, but only a frequent regurgitation reflex appears (to which parents may not pay due attention). They also have disturbed sleep, increased excitability, or noticeable pallor, but this is the first time after the injury. In addition, the first signs of a concussion in school-age children disappear within three days.
There may also be symptoms of concussion in children that are less important at first glance. Such symptoms may include sweating, flushing of the face, and a general feeling of discomfort. Or vice versa: the child’s well-being improves dramatically. But we must not forget that certain disorders in the body have already begun to take effect, which leads to more serious complications in the future.
We must remember that the symptoms of a concussion in a child are not so dangerous to health, but the consequences of this injury, and even more so if it is not treated, are dangerous not only for health in general, but also for life. Therefore, if you find out about a head injury that your child has received, do not delay. First, ask the baby exactly how this happened (the location and nature of the blow), then you can examine the head to see if you can feel any bumps or even dents in the skull. If there are no physiological changes, let the victim simply rest. But if you notice a sharp change in the baby’s behavior or he himself complains of nausea, dizziness or pain in the eyes, you should immediately seek help from a neurologist. In order not to miss such important days when a concussion can simply be treated with calmness and light medications with virtually no complications.
Diagnostics
In case of severe injuries, hospitalization in the neurosurgery department is mandatory.
To exclude skull fractures, an x-ray is required. An ultrasound examination can determine the state of the brain.
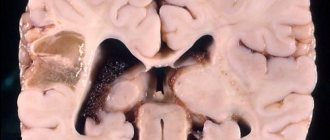
Young children undergo neurosonography. The images clearly show the brain. If there are disorders: swelling, hemorrhages, hematomas, they are easily diagnosed. This method is effective up to two years of age.
Later, the skull bones in children thicken and another ultrasound method is used - echo-encephalography. It reveals displacements of the brain, which indirectly indicates space-occupying formations (hematomas and tumors). This method is simple, but has low reliability.
The most effective way to detect brain damage is computed tomography. With this examination, a complete picture of the condition of the skull and brain is obtained.
Treatment
After the baby has fallen, before the doctor examines him, helping the child is to create a calm environment. You need to put the baby to bed and provide him with peace. If there is bleeding from the wound, treat it and bandage it if possible.
In addition to diagnostic procedures, the hospital’s emergency room treats injuries to the soft tissues of the head (bruises, abrasions, wounds). Children, especially young children, with a confirmed traumatic brain injury, including a concussion, are subject to mandatory hospitalization.
Hospitalization has several purposes.
Firstly, for several days the child is under the supervision of doctors in a hospital setting for early detection and prevention of complications of injury - cerebral edema, the appearance of intracranial hematomas, epileptic (convulsive) attacks. The likelihood of these complications is low, but their consequences are extremely serious and can lead to a catastrophically rapid deterioration of the child’s condition. Therefore, for a concussion, the standard hospitalization period is a week. With good technical equipment of the hospital (computed tomography, neurosonography), which makes it possible to exclude more severe brain damage, the length of stay in the hospital can be reduced to 3-4 days.
Secondly, during hospitalization the patient is provided with the creation of psycho-emotional peace. This is achieved by limiting the child’s motor and social activity. Of course, it is difficult to achieve complete bed rest for children, but still, hospital conditions do not allow running around, noisy games, watching TV for a long time, or sitting at the computer. After discharge, the home regimen is maintained for another 1.5-2 weeks, and sports activities are limited for several weeks.
Drug therapy for concussion has several goals. First of all, the child is prescribed diuretic drugs (most often DIACARB, less often FUROSEMIDE) in mandatory combination with potassium drugs (ASPARKAM, PANANGIN). This is done to prevent swelling of the brain. Calming therapy is carried out (PHENOSEPAM, VALERIAN ROOT INDUSTRY) and antihistamines are prescribed (SUPRASTIN, DIAZOLIN, DIMEDROL). For headaches, analgesics (BARALGIN, SEDALGIN) are prescribed, and for severe nausea - CERUKAL. At a later date, nootropic drugs that improve metabolic processes in the brain and vitamins may be prescribed.
Monitoring of the children's condition is carried out by the attending and duty doctors, as well as by guard nurses. In case of any deterioration, the child is re-examined and additional diagnostic tests (neurosonography, computed tomography, EEG) are prescribed.
When suggesting going to the hospital, the doctor first of all takes care not to miss a more severe injury than a concussion, and this is only possible with qualified supervision of the child.
If the baby’s condition is satisfactory, after a few days the parents can take him home with a signature. However, at home it is also necessary to observe a therapeutic and protective regime, limit watching TV, playing on the computer, walking, visiting friends, and continue drug therapy. If there is any suspicion of a deterioration in the child’s condition (the appearance of nausea and vomiting, headaches, unmotivated drowsiness, convulsive attacks, the appearance of weakness in the limbs, frequent regurgitation in babies), you should immediately consult a doctor again for further examination and possible hospitalization.
As a rule, after 2-3 weeks the child’s condition completely returns to normal. A concussion usually resolves without consequences or complications. The child can again attend nursery and kindergarten and play sports.
In conclusion, it is once again necessary to emphasize the importance of promptly visiting a specialized children's hospital, which will eliminate more severe forms of traumatic brain injury.
Consequences
If a concussion is not treated, it is fraught with consequences. Meteorological dependence may develop, and headaches may become constant companions. The most severe consequence of a concussion can be epilepsy and other irreversible disorders.
After a child suffers a concussion, after a certain period of time, this can be weeks, months or even years, the so-called repetition effect may occur. He begins to experience the same symptoms as with a traumatic brain injury. These are headaches, irritability, insomnia. In such cases, it is advisable to visit a doctor and undergo additional examinations to make sure that there are no new or untreated pathological processes in the brain. During these days, it is advisable to provide the child with rest and bed rest. If the symptoms become more intense, it is advisable to call an ambulance.
In our overly active world, the risk of traumatic brain injury in children is very high. They themselves are active, and if we also take into account the total employment of parents, and sometimes the negligent attitude of nannies and grandmothers, then the risk increases. Therefore, mothers need to understand that they and only they are responsible for their children, for their health in the future.
First aid
If there is no obvious damage to the bones of the skull, a cloth moistened with cold water or ice in a rag should be applied to the site of impact. This will reduce pain and stop tissue swelling and bleeding. Bleeding can be stopped in this way - by applying a thick piece of dry cloth (tampon) to the wound. If it becomes saturated with blood, place a second one on top of the first tampon. Attention! If bleeding continues after 15 minutes, call a doctor immediately.
After any head injury, the child needs rest, but do not let him fall asleep for an hour, otherwise you will not understand how serious his condition is. Wake up your baby at night too. If he does not answer simple questions, or has poor coordination of movements, or vomiting repeatedly, call a doctor immediately. Pay attention to the pupils: their unequal size indicates severe brain damage. If you suspect a serious injury, and the baby has fallen asleep, do not wait until he wakes up: call a doctor. If a child has lost consciousness after hitting his head and you have already called an ambulance, lay the baby on his side so that vomit does not enter the respiratory tract. If you suspect that, in addition to the brain, the spine has been damaged (from a fall from a height onto the head or back), the child must be turned extremely carefully and so that the body and head are on the same axis: this will help avoid additional injury.
But still, the most important thing that is required of you if a child is injured is to remain calm. Too much depends on the adequacy of your reactions - the health of the little person.
Clinical symptoms of concussion
The clinical picture is quite different from the manifestations of the disease in adults. Since it is not always possible to clearly trace the connection with the disease, and the symptoms are often nonspecific.
Clinical picture in young children
- vomit;
- regurgitation during feeding;
- cardiopalmus;
- there may be a decrease in blood pressure;
- anxiety gives way to lethargy and drowsiness;
- sleep disturbance;
- pallor of the skin is noted immediately after the injury;
- the disease occurs without impairment of consciousness;
- causeless crying.
Symptoms of concussion in older children
- it is possible to establish the fact of loss of consciousness of the child;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- pain when moving the eyeballs;
- noise in ears;
- sleep disturbance;
- sweating;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- Some children experience post-traumatic blindness, the cause of which cannot be determined. Duration ranges from several minutes to several hours.
Children may experience a period of “imaginary well-being,” that is, when after an injury the child does not complain, but after some time the symptoms increase and the condition worsens.
Possible complications
Complications of a concussion can only occur with combined organ damage:
- intracranial (subdural, subarachnoid) hematomas;
- decreased visual acuity, up to blindness;
- paralysis and paresis;
- decreased mental capacity of the brain;
- epilepsy.
First aid
For any head impact, a child, regardless of age, needs to consult a doctor. Until the doctors arrive, you need to do everything to keep the child awake, since very often the baby becomes drowsy after an injury. In this case you should:
- Place the baby on a hard surface and cover.
- If the child is unconscious, he should be placed on his right side, and his left limbs (arm and leg) should be bent at an angle of 90 degrees. This will ensure a stable position for the victim and conditions for normal breathing.
- Having noticed a disturbance in the pulse and breathing, the victim needs to be given artificial respiration and possibly a cardiac massage.
- Examine the child carefully. If you notice bruises, fractures, or other injuries or wounds on his body, they need to be treated with an antiseptic.
Before the ambulance arrives, the baby should be in a horizontal position.
At this time, adults should ask him about his well-being and certain symptoms that may be characteristic of this type of injury. Even if a child does not have significant symptoms of a concussion, this does not mean that it did not occur.
Often, even with hemorrhages, the victim may not complain of pain or show signs of concern for some time (up to 2 days). But, such a condition can suddenly develop into malaise.
The first aid algorithm is told and demonstrated by Honored Doctor of Russia, military surgeon Leonid Borisenko:
Diagnosis of concussion
In most cases, diagnosis can be made based on medical history and clinical findings. But in young children, due to the presence of only nonspecific symptoms, additional methods of examining the patient may be required:
- A general blood and urine test is used to rule out inflammatory changes in the child’s body.
- X-ray of the skull in 2 projections: direct and lateral - the method allows you to determine the integrity of the bones of the skull and see the fracture. In infants, linear fractures are often identified that are not clinically apparent.
- Neurosonography - ultrasound examination of the brain is relevant only for children of the 1st year of life, since the device’s sensor is installed on the large fontanel, which closes by the age of one year. In older children, dense bone structures do not allow ultrasonic beams to penetrate into the brain. Neurosonography makes it possible to visualize the ventricles and the structure of the brain. In this way, it is possible to determine cerebral edema, the presence of hematomas, and also identify intracranial hypertension. Today, this method is the most effective and widespread, due to its non-invasiveness and information content.
- Computed tomography is also one of the best methods for diagnosing a concussion, as this study allows you to assess the extent and level of brain damage. Computed tomography scans the child’s brain layer by layer, which means that the location of the lesion can be easily determined. In children it is performed under general anesthesia.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is highly informative for concussion, but has a number of disadvantages: the method is expensive, not available in every hospital, does not determine damage to the bone structures of the marrow, and the child must be given anesthesia in order to lie quietly for 20 minutes.
- An electroencephalogram is a method that is used to determine the presence of lesions in the cerebral cortex, which are potential sources of epilepsy. For concussion, this method is prescribed according to indications when there is a suspicion of a complication.
- Lumbar puncture with collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for analysis. Changes in the cerebrospinal fluid indicate traumatic brain injury, hemorrhages, and inflammatory processes in the membranes of the brain. Lumbar puncture is performed if the patient has strict indications.
- Consultation with a neurologist or neurosurgeon to assess the severity of brain damage.
- Consultation with an ophthalmologist with a fundus examination. Optic disc congestion may indicate intracranial hypertension.
- Consultation with an otorhinolaryngologist with audiometry to determine the child’s hearing acuity.
Features of injury in infants
If you compare a concussion in an adult and a child, you can see that the same injury manifests itself differently in them. This difference is due to the structural features of the brain in children.
Signs of a concussion in a newborn and infant
The main symptoms that indicate that a newborn or infant has a concussion:
- loss of consciousness;
- refusal to eat;
- frequent regurgitation after feeding;
- increased body temperature;
- vomit;
- lethargy and drowsiness or, conversely, overexcitation and anxiety;
- sleep disturbance;
- muscle twitching in the limbs;
- paleness of the face or covering it with red spots.
Any of the signs may appear only the next day after the injury. In addition, the child may begin to cry some time after the injury. This picture is explained by a short-term loss of consciousness, which lasts a fraction of a second, which is why it goes unnoticed.
It is worth remembering that even a mild head injury is a good reason to take your child to the doctor.
Symptoms in children from 1 to 3 years old
During this period, not all children can speak, which means they will not be able to talk about their feelings. Despite this, attentive parents can immediately notice uncharacteristic behavior of the child. The main signs that a child under 3 years of age has a concussion are as follows:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- frequent vomiting;
- change in facial skin color;
- unstable pulse and blood pressure readings;
- disorientation in space;
- refusal to eat;
- pain in the navel area;
- temperature increase;
- poor sleep;
- capriciousness.
TBI can make itself felt through one symptom or a whole complex of them. To do this, parents need to observe the child for a certain time.
Signs of a concussion in older adults
It is much easier to identify a TBI in a child who is already 4, 5 or more years old than in a one-year-old or newborn, since he is already able to tell what hurts and where. Head injuries at this age manifest themselves as follows:
- temporary loss of consciousness;
- partial memory loss (the baby does not remember what happened before the head injury);
- headaches and dizziness;
- the appearance of a gag reflex;
- constant nausea;
- pallor;
- slow reaction of the baby to the people around him;
- severe weakness in the body;
- hypotension;
- heartbeat disturbances.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor decides what to do next with the baby: hospitalize him or allow treatment at home. As a rule, children under 6 years of age are treated as inpatients. This is due to the fact that there is a risk of developing complications such as swelling, hematomas, and convulsions. If this happens at home, parents will not be able to provide the child with the necessary help.
Therapy in hospital using medications
In a hospital setting, a child who has suffered a concussion is given medication treatment using the following groups of drugs:
- diuretics;
- painkillers;
- nootropic;
- sedatives;
- antiallergic;
- potassium-containing;
- from attacks of nausea;
- vitamins.
- Diuretics help prevent brain swelling. These include Furosemide and Diacarb.
- In parallel with drugs of this group, potassium-containing drugs are prescribed - Panangin, Asparkam.
- Nootropic drugs - Piracetam, Cavinton - activate the supply of nutrients to the brain and also help improve blood circulation in it.
- An infusion of valerian or Phenozepam is usually used as a sedative.
- To alleviate the child's condition and eliminate his painful sensations, analgesics such as Baralgin or Sedalgin are used.
- To get rid of attacks of nausea, Cerucal is used.
- Vitamins and antiallergic drugs - Fenistil, Diazolin, Suprastin - are prescribed for a speedy recovery.
Treatment at home
If hospital treatment brings positive results and the child begins to feel better, he may be discharged home, but on the condition that the parents follow the following recommendations:
- the baby should not watch TV or play computer games;
- bright and sunlight should not affect the patient;
- the child must move as little as possible;
- it is required to remain in bed for at least 7 days after discharge from the hospital;
- it is necessary to exclude situations that provoke hysterics in the child;
- It is important to strictly adhere to medications.
Indeed, babies fall often. But it is rare for a fall to result in a concussion. It seems that nature itself took care of the baby, rewarding him with soft and pliable skull bones and fontanelles.
During the first year of life, the fontanelles remain open. At the same time, the volume of intracerebral fluid in children at this age is slightly increased.
It turns out that the brain seems to float in it and does not hit the walls of the skull. Therefore, during a fall, cerebral fluid, which is also called cerebrospinal fluid, plays a shock-absorbing function. This happens in a newborn, in a child of 6 months, and in older children.
Therefore, even a fall such as falling upside down from a crib or changing table does not always result in a traumatic brain injury. The baby gets more scared and starts crying because of this, and not because of the pain associated with the injury, as parents think.
You should know that the height from which the baby falls plays a big role here. If it is a low sofa or your own height, then you can get a concussion here only in the rarest cases.
Falls from a changing table or high chair are more traumatic. This means you can get a concussion with such an injury. But not always, and the consequences of such flights can be unpredictable.
Therefore, the main task of parents is to protect the baby from injuries in the first year of life and prevent all possible falls.
If the baby does fall, mom and dad must know the symptoms and manifestations of a traumatic brain injury.
You should know that during a fall and a concussion, the baby’s brain hits the bones of the skull from the inside. Although this injury is considered the mildest, it has three degrees of severity. In this case, a short-term disruption of the child’s brain function is possible. however, everything recovers quickly and after a couple of weeks there is no trace left of this injury.
You should definitely visit a traumatologist, since this disease is considered an injury. It would not be a bad idea to show the newborn to a neurologist. Only under this condition can one accurately understand whether the child had a concussion or not.
If the baby hurts his head, the first thing parents should do is take the baby to the hospital or call an ambulance. It is important to remember that failure to contact a specialist in a timely manner can threaten the child’s health and even his life.
So, how to treat a concussion in a child? It is prohibited for adults to prescribe or give children any medications on their own, without examination and consultation with a doctor, especially for newborns.
After falls and head injuries, the baby should definitely be shown to a doctor, who, after examination, makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. If necessary, the treatment process can take place in a hospital, where complete and thorough monitoring of the little patient’s condition is ensured.
Almost all children, especially young ones, are hospitalized if a concussion is suspected. First of all, this is due to the fact that in the first 24 hours after a head injury, the baby needs careful monitoring in order to identify signs of more serious traumatic brain injuries in the early stages.
Plus, in the hospital it is easier to limit the child’s physical activity and provide him with complete psycho-emotional peace. .
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe drug therapy. Read on to find out what medications are prescribed for concussions in children.
After discharge, you need to provide the child with a quiet home environment for about 2 weeks. Play quiet games with your baby: less running, noise, and pampering. Limit TV viewing to a minimum.
What is prescribed for children with a concussion? After a diagnosis has been made, the doctor may prescribe medication to treat a traumatic brain injury. We will talk about the medications that are most often prescribed, among them the following:
- diuretics in combination with potassium supplements. Prescribed to prevent or eliminate swelling of the scalp tissue (Diacarb, Furosemide, Panangin and others);
- painkillers are used for prolonged and severe headaches (Analgin, Sedalgin);
- antihistamines promote calm and help normalize the sleep of a young patient (Suprastin, Diazolin);
- antiemetic medications are prescribed for severe nausea, prolonged and profuse vomiting (Cerucal);
- nootropic drugs are intended to stimulate metabolic processes in the brain, as well as to normalize its functioning (Glycine, Cavinton, Pantogam);
- sedatives are prescribed to normalize sleep and reduce the baby’s excitability. These can be either tablets (Phenazepam) or various infusions (valerian root);
- general vitamins are intended to strengthen and restore the child’s body.
This damage to brain function is considered a fairly harmless type of injury, after which a small mark from the blow may remain on the head in the form of a bruise, wound or bump, but the skull remains intact.
The very definition of injury - a concussion - means that a kind of “shaking of the head” occurs, in which no special changes in the structure are observed.
Moreover, if during diagnosis it was possible to look inside the skull, no specialist would notice anything specific, since changes in this injury occur at the smallest cellular level.
If a child hits his head or falls, then in any case you should seek qualified help from a specialist. If it is impossible to provide medical assistance, the following actions can be taken:
- if the child is conscious, place him on a hard surface and cover him with a blanket;
- if the child has lost consciousness, then he should be laid on his right side, while for a stable position and to create conditions for proper breathing, the left leg and arm should be bent at an angle of 90 degrees;
- in case of uneven breathing and slow pulsation, artificial respiration and cardiac massage can be performed if possible;
- thoroughly examine the child for fractures or bruises; if there are bleeding wounds, they should be treated.
The most important thing is to ensure complete rest in a horizontal position; before the doctor arrives, if possible, try to interview the child about all the symptoms that are currently bothering him in order to pass on all the information to specialists.
- A concussion is a medical condition that has specific symptoms in the form of a short-term loss of consciousness and does not require specialized treatment.
- A sufficient condition for recovery after injury is rest and rest in a horizontal position with an absolute limitation on jumping and walking.
- In children, metabolic processes occur at such a high intensity that additional stimulation, even after injury, is not required.
- The risk of complications from a concussion cannot be prevented by medication.
Differential diagnosis
Differentiate a concussion in a child from other diseases of closed craniocerebral injury (brain contusion, brain compression).
A brain contusion is characterized by injury to brain tissue. Among the symptoms, loss of consciousness comes first, as well as amnesia, which can be either retrograde (the patient does not remember events that occurred before the injury) or antegrade (memory impairment after the moment of injury). Also characteristic cerebral symptoms (headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness). In severe cases, focal symptoms may appear (nystagmus, disturbance of the respiratory, vasomotor center).
Compression of the brain is a more severe injury, which can be complicated by herniation of the brain into the foramen magnum: severe focal symptoms, lack of pupillary response to light, coma.
Consequences and complications
Despite the fact that this type of injury is a mild pathology, it does occur. The consequences of a concussion include:
- constant intense headaches of a prolonged nature;
- inhibition in performing usual daily activities;
- periodic bouts of vomiting for no apparent reason;
- irritability from games and activities that brought joy before the injury;
- weather dependence - any change in weather has a depressing effect on the child, manifesting itself in headaches and malaise;
- sleep disturbance, rarely insomnia.
Most often, the negative symptoms of a concussion disappear over time without treatment, but if they persist, you should definitely visit a specialist to rule out irreversible damage.
The main lines of treatment for concussion in childhood
If a child falls from a bed or changing table at home, you must call an ambulance!
- Hospitalization: all children with a concussion are subject to hospitalization, as well as if there is a need for a correct diagnosis when the clinical picture of the disease is unclear.
- Bed rest is established for 2 - 3 days.
- Painkillers: Baralgin, Ibuprofen, Sedalgin, Pentalgin.
- Calming therapy is prescribed according to indications for children with psycho-emotional behavior disorders: tincture of valerian, motherwort. It is also possible to use tranquilizers: Phenazepam, Sibazon, Elenium.
- If there are disturbances in liquorodynamics, the following is prescribed: Diacarb in combination with Asparkam.
- Vascular therapy: Cavinton, Stoucheron.
- Nootropic therapy: Nootropil, Aminalon.
- For repeated vomiting: Cerucal.
- Drugs that improve brain nutrition: Pantogam, Vasobral.
If positive dynamics are observed (disappearance of symptoms), the child is discharged home for outpatient treatment. Within a year after the injury, monitoring by a neurologist is necessary.
Treatment
To avoid complications, a child injured before the age of 6 is in the hospital under the supervision of doctors. After examination and diagnosis, treatment is carried out. If abrasions or wounds are observed, treatment and dressing are performed. Therapy for concussions includes:
- bed rest;
- applying cold to the injury site;
- psycho-emotional peace;
- hyperbaric oxygenation (saturation of tissues with oxygen).
The goal of drug treatment is to improve metabolic and energy processes in the brain, prevent the appearance of edema, and normalize the relationship between excitation and inhibition. For this, doctors use drugs:
- nootropic;
- potassium-containing;
- sedatives;
- antiallergic;
- painkillers;
- diuretics;
- stopping vomiting;
- vitamin complexes.
Treatment continues after discharge from the hospital , when the threat of complications has passed. At home, two weeks of bed rest is mandatory. The treatment regimen involves :
- continuing to take prescribed medications;
- limited mobility;
- organization of a calm environment;
- excluding exposure to bright sunlight;
- refusal to watch TV;
- stopping computer games.
Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
Concussion (MC) is the main clinical form of mild traumatic brain injury (TBI), in particular, diffuse damage to the brain parenchyma. It ranks first among all childhood injuries requiring inpatient treatment.
According to epidemiological studies, TBI in children and adolescents in many countries reaches 200 cases per 100 thousand people. Moreover, TBI is more common in males (up to 70% of all cases). [7]
There are two age groups with a high risk of traumatic brain injury:
- children under 5 years old;
- patients from 15 to 25 years old.
From the first year of life, children begin to have high physical activity, they have a desire to learn everything, try, and get to different places. This occurs against the background of imperfect motor skills and coordination of movements, a reduced sense of danger and overestimation of physical capabilities, which leads to injury.
The main causes of concussion in childhood are:
- trauma during birth;
- falling of infants and children under three years old from beds, changing tables, from the hands of parents, strollers, etc.;
- lack of coordination as a result of disproportionate physical development of the body in children under three years of age (heavy head weight) and falling head down during sudden acceleration or braking (at this age children have not yet learned to protect themselves with their hands during a fall);
- impacts when children 4-7 years old fall from a height (children's slides, swings, window sills or trees);
- violation of traffic rules and car accidents with an unsecured child in a special car child seat;
- violation of safety regulations and lack/malfunction of sports equipment during outdoor games and sports competitions.
Specifics of concussion in children
It can be very difficult to determine that a child received not just a bruise after a blow, but a real concussion. This is due to the fact that younger children cannot tell what is bothering them, and absent-mindedness, forgetfulness, inability to concentrate for long periods of time and unclear speech in a young child are normal age-related characteristics.
Older children, especially those who enjoy dangerous sports and extreme games, often skillfully hide the effects of a concussion in order not to be suspended from training or competitions, or so that their parents do not prohibit them from riding a skateboard or bicycle.
Sometimes doctors and parents have to deal with the complete opposite, when the child deliberately exaggerates the symptoms: he claims that he is dizzy, that he has fog before his eyes. This causes a lot of trouble for adults, because such signs can mean that the concussion is really dangerous. In such cases, it is better to play it safe and take complaints seriously. Moreover, if there is pretense, the child quickly gets tired of following the treatment regimen, and the little pretender is healed.