What is throat neurosis?
Pharyngeal neurosis is a violation of the sensitivity of the mucous membrane of a small canal (10-12 cm) connecting the nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus.
The development of pathological changes is associated with a violation of the integrity of the nerve plexuses in the throat or a disorder of the nervous system. To identify pathology, it is necessary to undergo examination by a neurologist and otolaryngologist. Specialists will be able to accurately determine the nature of the disease: whether the cause of the development of the disease was actually a disruption of the nervous system or whether the pathology arose as a result of diseases of the pharynx.
The disease manifests itself in the following forms.
- anesthesia;
- hypoesthesia;
- hyperesthesia;
- paresthesia.
Anesthesia of the pharynx
Anesthesia of the throat is expressed in a decrease or complete absence of sensitivity of the larynx, while the patient experiences difficulty swallowing. Most often, similar symptoms are observed during hysteria. In addition, this may be evidence of a blockage of the signal sent by brain cells to the pharynx. Often, anesthesia of the throat is a sign of the development of multiple sclerosis, paralysis, infection, or a malignant tumor in the brain.
Hypesthesia
This form of the disease has similar symptoms to anesthesia, however, it manifests itself to a milder degree. Although the pharyngeal reflex is present, the sensitivity of the mucous membrane is very weak. Pathology can develop against the background of influenza or other viral diseases. As a rule, after some time the sensitivity of the pharynx is restored. If the symptoms do not go away, or even worse - they get worse, you should definitely consult a doctor.
In some cases, neglect of the treatment of the disease can even lead to death, because with loss of sensitivity in the pharynx, the risk of choking on water or food increases.
Hyperesthesia
This form of pathology, on the contrary, is characterized by increased sensitivity of the pharyngeal mucosa. The patient complains of difficulties arising when eating food. Hyperesthesia is characterized by symptoms such as itching, tingling, and pain in the throat. This form of pharyngoneurosis can develop against the background of previous pharyngitis, tonsillitis or tonsillitis.
Paresthesia
The symptoms of this form of pharyngoneurosis are almost the same as with hyperesthesia. The clinical picture is complemented by the following signs:
- sensation of a lump in the throat;
- feeling of numbness;
- severe itching.
There are also constant headaches that get worse when swallowing and eating.
Most often, people who are emotionally unstable and irritable suffer from paresthesia. Women often complain about a lump in their throat during menopause.
Causes of the disease
The most common cause of any form of pharyngoneurosis is hysteria. This mental disorder causes changes in the fields of consciousness, which is accompanied by disturbances in motor skills and sensory function.
Neurosis of the pharynx and larynx can also manifest itself as other neuropsychic abnormalities. Organic lesions can provoke changes in the sensitivity of the mucous membrane of the throat towards decrease or increase. For example, the reasons for laryngeal anesthesia may be the following:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- a brain tumor;
- past infections (diphtheria, measles, typhoid, influenza, etc.);
- syphilis;
- multiple sclerosis.
Increased sensitivity of the pharynx can be caused by the following factors:
- chronic laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis;
- work in hazardous production;
- acute inflammatory processes in the pharynx, trachea, larynx;
- alcoholism and smoking abuse.
In addition, paresthesia can develop against the background of VSD, chronic insomnia, after a nervous shock, severe stress, etc.
Once discomfort in the throat occurs, it forces a person to concentrate his attention on this problem, resulting in a feeling of anxiety, excitement, as well as a desire to find out the cause of an incomprehensible phenomenon. Against this background, the signs of pathology can only intensify.
Each form of the disease is characterized by certain symptoms. Thus, with hypoesthesia, there is a pathological change in the pharyngeal reflex towards a decrease or its complete absence. Conversely, hyperesthesia is characterized by an increase in the swallowing reflex, as well as the following symptoms:
- the presence of itching, soreness;
- sensation of a lump or film in the throat;
- attempts to cough, causing nausea and vomiting.
With paresthesia, patients most often complain of itching, pressure in the throat, goose bumps in the throat, numbness, and tingling. Moreover, the severity of these symptoms during the day can vary from almost imperceptible to annoying and very strong.
Paresthesia that lasts for a long time can cause the patient to feel like there is a constant presence of a lump in the throat. In some cases, there is pain that can radiate to the tongue or ear.
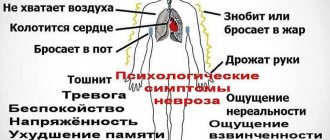
All forms of pharyngoneurosis are characterized by the following symptoms:
- tearfulness;
- irritability;
- tachycardia;
- sweating;
- insomnia.
Signs such as excessive excitability, decreased attention and memory, appetite disturbances, and headache are often observed. Sometimes pharyngoneurosis is accompanied by a painful reaction to light and sounds, as well as migraines.
Complications of the pathology most often occur against the background of such a form of laryngeal neurosis as anesthesia. Neurosis, which has a pronounced form, can cause the effect of suction of food and saliva, which causes asphyxia and can cause serious consequences for the lungs.
Diagnostics
If you experience a sore throat or difficulty swallowing, you should definitely visit a doctor, since such symptoms may be the first signs of any serious illness. With timely treatment, treatment will go much faster. The specialist will carry out the necessary diagnostic measures, namely the following:
- Tomography of the spine. Medical practice shows that pharyngoneurosis often occurs due to problems with the spine.
- X-ray of the neck. Such a study will help determine the cause of the violation.
Diagnostics
As in the case of diagnosing all psychosomatic diseases, the doctor first prescribes a series of examinations to exclude organic pathologies. If there are no abnormalities in the body in which symptoms of throat neurosis would be included in the clinical picture, the patient receives a referral to a psychotherapist.
The list of diagnostic measures includes:
- general blood test to determine inflammatory processes in the body;
- blood test for syphilis;
- X-ray of the brain and neck to exclude a tumor;
- if multiple sclerosis is suspected, MRI of the brain;
- examination by an otolaryngologist, throat swab.
Why does neurosis cause a lump in the throat and how to deal with it?
If a lump in the throat occurs during neurosis, this means that the problem that caused this condition has not been solved for a long time and the body informs the person about it.
Ordinary pain is a signal that action needs to be taken, and pharyngeal neurosis signals that further ignoring the problem can lead to serious consequences.
In other words, pharyngeal neurosis in most cases is a psychosomatic phenomenon that has nothing to do with the physical state of the body, and accordingly, it can be cured without medication. With pharyngeal neurosis, symptoms and treatment are interrelated, that is, the chosen method of therapy depends on the intensity and causes of the first appearance.
Laryngeal neurosis can be caused by both psychosomatic causes and physiological abnormalities. In order to understand them, you need to know that throat neurosis is conventionally divided into 3 types - anesthesia, hyperesthesia and paresthesia:
- Anesthesia is the phenomenon when the pharynx loses sensitivity. A person's throat, neck and even shoulders become numb. Such sensations occur against the background of a tumor in the brain, with syphilis or influenza. Also, numbness in the throat occurs as a result of hysteria.
- Hyperesthesia is felt as a strong spasm of the head, causing suffocation. As a rule, this phenomenon occurs during infectious diseases. In the same way, neurosis manifests itself against the background of severe nervous shock.
- Paresthesia is a spasm of the throat during neurosis. Typically, this symptom is described by people with an unstable psyche. They describe it as a “lump in the throat.” Paresthesia mainly occurs in people with mental disorders.
In any case, a patient with complaints of laryngeal spasm undergoes a standard examination for the presence of infectious and other throat diseases. To do this, a blood sample is taken from him: from it, the doctor determines the presence of infectious agents in the body.
A test for syphilis is required. In order to exclude or confirm the presence of a tumor in the brain or neck, the patient is given an X-ray of the head.
To determine multiple sclerosis, the patient undergoes a magnetic resonance imaging examination.
In addition, a biochemical analysis of the smear and an external examination of the pharynx by an otolaryngologist are performed. And only after eliminating any possibility of throat diseases, the patient is sent for examination to a psychiatrist. He determines what is the motivating cause of the spasm, and, based on this knowledge, chooses therapy designed to remove the lump in the throat.
If pharyngeal neurosis arose as a manifestation of neurasthenia or some other mental disease, it is impossible to do without the help of a psychotherapist. Phenomena such as hysterics, a state of imbalance and constant irritability are exactly what need to be treated only by a specialist.
First of all, the psychotherapist determines the reason that caused the emotional conflict. The patient is then trained to ignore these causes or replace them with positive stimuli. In each individual case, an individual method of relaxing the psyche in a stressful situation is selected.
In most cases, pharyngeal neurosis quickly passes if the patient begins to lead a correct lifestyle, namely, follows a sleep-wake schedule, eats on time and gives up smoking and drinking alcohol. That is, the treatment of pharyngeal neurosis consists of returning to a normal lifestyle.
Unfortunately, the modern pace of life often does not allow a person to undergo a full course of treatment for neurasthenia from a specialist. And the question arises, what to do if throat neurosis finds a person in a situation where quick medical help is impossible.
1) First you need to suppress the sign of panic.
In ancient times, this condition saved a person’s life, as it causes muscle activity that can help one very quickly climb a tall tree, rock, or simply run away.
Since in the modern world it is impossible to relieve muscle tension caused by panic, you need to learn to ignore panic in principle so that your muscles do not cramp.
2) You need to relax, there are several ways to do this. For example, breathing exercises: on the count of “one,” a strong inhalation is taken, and the exhalation should be done long, on the count of “one, two, three.”
If a panicked state leads to hyperventilation due to rapid breathing, the person may lose consciousness.
In order to avoid this, some doctors recommend breathing into a paper bag, pressing it tightly to the skin around the lips, thus inflating it as you exhale and drawing air out of it as you inhale.
3) You can relax the muscles step by step, that is, first the legs, then the muscles of the abdomen, back, chest, shoulders, arms and then the neck.
4) Another method of relaxation is called the distraction method. It is necessary to distract from your inner state to contemplate the world around you - the flight of birds or clouds, the rustle of the wind in the foliage of trees, the murmur of water in a stream, and so on. The main thing is not to think about the reason that caused the stressful state.
5) Signs of stress and impending laryngeal spasm can be relieved by light physical activity, such as a light jog or walk.
But if a person, having driven far from home, discovers that he forgot to take the medicine, then a panic attack will quickly cause a throat spasm. That is, the medicine is always in a person’s head, he can always calm himself down, as well as vice versa - he can turn his psyche into a fit.
All this once again suggests that a psychiatrist should treat pharyngeal neurosis.
In severe cases, the patient is prescribed a course of drug therapy. This includes taking tranquilizers and antidepressants.
Since neurosis needs to be treated only under the supervision of a doctor, it is the psychotherapist who prescribes a specific drug, its dosage and regimen. In addition, tranquilizers and antidepressants are not available in pharmacies without a doctor's prescription.
But there are drugs that can be purchased without a prescription. They have a therapeutic effect for chronic stress and neuropathy; they should also be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor:
- A spasm in the throat due to neurosis is well relieved by tincture of valerian or motherwort. The drugs are freely sold in pharmacies and are used, among other things, to stabilize the functioning of the heart and lungs.
- The drug Nervo-Vit has a sedative effect. Very good for people suffering from sleep disorders. This drug helps get rid of anxiety and chronic fear. In addition, it contains vitamin C, which has a beneficial effect on the human immune system.
- For reactive or clinical depression, a drug containing St. John's wort helps, St. John's wort P, which is a high-quality antioxidant.
- To lift your mood and restore high tone to your muscles, you can take the vitamin complex Apitonus P. This drug contains more than 20 different amino acids necessary for the proper functioning of the body.
Treatment with this drug increases brain activity.
Conclusion and conclusions
How to get rid of a spasm in the throat due to neurosis is best determined by a doctor. But anyone can help themselves, the main thing is to have a firm goal to heal and confidence that everything will work out. After all, as Eastern healers said, if you know the cause of your illness, then you are already half healthy.
Sessions with a psychotherapist
All provocateurs of the “lump in the throat” phenomenon, regardless of the type of neurosis, in any case require treatment from a psychotherapist or psychologist:
That is, treatment of the symptom of pharyngeal neurosis should begin with stabilization of the nervous system . The psyche of a healthy person has a good reserve of strength, that is, a rare factor can cause such vivid and strong negative emotions in a person, accompanied by physical sensations. Moreover, if we are not talking about an exceptional case, but about an ordinary everyday problem.
Therefore, the psychotherapy plan should include the following points:
In addition, psychological health is positively influenced by a healthy lifestyle, proper sleep and rest patterns, a healthy balanced diet, and the absence of bad habits.
Taken together, all this will strengthen the nervous system in such a way that the question of how to get rid of a lump in the throat during neurosis will no longer be relevant, since there will be no neurosis itself, and the stressful situation will be perceived calmly due to the accumulated reserves of the nervous system.
Types and symptoms
Depending on what contributes to the course of pharyngoneurosis, the pathology is classified into 4 types:
- Anesthesia and hypoesthesia. The pharyngeal reflex is either completely absent or significantly reduced. In some cases, the pathology extends to the entrance to the larynx. This often results in aspiration of food or saliva and serious pulmonary complications. Among the causes are hysteria, multiple sclerosis, brain tumor, syphilis, and viral diseases.
- Hyperesthesia. The pharyngeal reflex is strengthened, the sensitivity of the pharyngeal mucosa is excessively increased. Symptoms include sensations of a lump and sore throat. Frequent cough, sometimes triggering gag reflexes. Hyperesthesia occurs against the background of chronic tonsillitis, granulosa pharyngitis and other inflammatory ENT diseases. It is considered the main symptom of neurasthenia.
- Paresthesia. The sensations are vague. Patients simultaneously complain of spasms, numbness, tingling, burning, and a feeling of a foreign body in the larynx. The ability to concentrate and memory decreases. This form of neurosis is most often found in women prone to hysteria during menopause.
Symptoms common to all forms:
- Feeling of a lump in the throat. The most common symptom.
- Paroxysmal suffocation.
- Problems with the vocal cords: hoarseness, sudden changes in timbre, aphonia (complete loss of voice).
- Imaginary aphonia: full voice appears only during laughter or coughing. At other times it’s a whisper.
- Dry paroxysmal cough or systematic debilitating coughing.
- Sensation of a “hair” in the throat.
- Referring pain to the ear or tongue.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Increased sweating.
- Tachycardia.
- Emotional instability.
- Frequent headaches.
There are 3 forms of pharyngeal neurosis:
- Anesthesia;
- Hyperesthesia;
- Paresthesia.
Anesthesia of the pharynx is manifested by a decrease or absence of throat sensitivity and impaired swallowing. The disease develops in patients suffering from brain tumors, syphilis, and hysterical neurosis. The patient may aspirate food or saliva into the airway and develop aspiration pneumonia.
Pharyngeal hyperesthesia is accompanied by an increase in the pharyngeal and gag reflex. The patient has a cough and tries to cough up non-existent phlegm. This type of throat neurosis can develop after severe stress or a chronic disease of the pharynx or larynx. Patients experience a spasm, a sore throat, and a sore throat. He may feel a “scratching” sensation on the surface of the larynx.
Pharyngeal paresthesia occurs under stress. Patients feel soreness, itching and a “lump” in the throat. Women who are in menopause, impressionable and irritable people are susceptible to the disease.
How to treat pharyngeal neurosis with folk remedies
Neuroses are a group of diseases that are psychosomatic in nature.
This means that certain psycho-emotional disorders (stress, depression, psychological trauma, feelings of dissatisfaction, hysteria) are manifested by somatic disorders, that is, dysfunction of certain organs. One of these diseases is pharyngoneurosis.
This condition occurs due to disruption of the conductivity of nerve fibers innervating the larynx. The reasons for this may be psychological, but organic disorders of the nervous tissue and brain damage can also lead to neurosis.
Symptoms of the pathology: impaired swallowing reflex, increased sensitivity of the pharynx, spasm, discomfort in the throat not associated with organic damage to the laryngeal tissue.
- Laryngeal neurosis - what is it?
- Causes of pharyngeal neurosis
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of pathology
Treatment depends on the causes of the disease. If the reasons are psychological, it is necessary to change your lifestyle and eliminate the irritating factor. There are folk recipes that are used for neuroses. They have a calming effect and normalize sleep.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition
For any painful symptoms that appear in the throat, people most often turn to a therapist or otolaryngologist. Based on the results of anamnesis and initial examination, the doctor can determine the main causes of the pathological condition, analyze them and prescribe additional studies. After passing them, the specialist selects the appropriate effective treatment.
Often, after drug control of some signs of the disease, most of them continue to bother the person. This is a direct sign that problems arise due to the patient’s mental state.
And therefore, additional consultation may be required not only from a psychologist or psychiatrist, but also from a neurologist, as well as an endocrinologist.
Diagnosis of such a pathological condition as a lump in the throat may be associated with the following studies:
An additional diagnostic test for a lump in the throat of a nervous nature is a procedure to exclude the pathological condition of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Differential diagnosis is based on the location of the coma itself, the patient’s described feelings and the presence or absence of accompanying symptoms.
How to treat pharyngeal neurosis with folk remedies
Therapy with folk remedies as a treatment outside the complex is allowed only in cases where pharyngeal neurosis is caused exclusively by a psychogenic factor, and its cause is inorganic in nature.
In the treatment of any neurosis, the primary task is to relieve tension. Mint, lemon balm, oregano, valerian, hop cones, sweet clover, willow bark, European rosemary, and thyme are widely known for their sedative effects. Decoctions and infusions of these herbs normalize sleep, relax and soothe.